Deck 5: Water and Seawater
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Water and Seawater
1
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
high temperature
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
high temperature
B
2
The overall electrical charge of most atoms is balanced because each atom contains an equal number of protons and neutrons.
False
3
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
charged atoms due to the gain or loss of one or more electrons
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
charged atoms due to the gain or loss of one or more electrons
G
4
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
river input
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
river input

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
precipitation
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
change in state from solid to gas
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
change in state from solid to gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
bonds that hold adjacent water molecules together
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
bonds that hold adjacent water molecules together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Water molecules exhibit strong cohesion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
area of rapid change in density with slight change in depth
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
area of rapid change in density with slight change in depth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
sea ice formation
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
sea ice formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit an atomic nucleus
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit an atomic nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Water is a polar molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
change in state from gas to liquid
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
change in state from gas to liquid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
evaporation
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
evaporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
bonds that involve the sharing of electrons between atoms
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
bonds that involve the sharing of electrons between atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
change in state from liquid to gas
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
change in state from liquid to gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Water can pile up higher than the edge of a container due to its low surface tension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
area of rapid change in salinity with slight change in depth
A)evaporation
B)halocline
C)isocline
D)sublimation
E)thermocline
F)deposition
G)pycnocline
H)condensation
area of rapid change in salinity with slight change in depth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules are responsible for the unique chemical and physical properties of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all.
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
basic building blocks of all matter
A)protons
B)hydrogen bonds
C)neutrons
D)atoms
E)polarity
F)covalent bonds
G)ions
H)electrons
basic building blocks of all matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The density of seawater is affected by salinity and temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Water is the only naturally occurring substance on Earth that readily exists in all three states of matter simultaneously (ice, water, and water vapor).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The covalent bonds form between hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a water molecule form as a result of the:
A)polarity of water molecules.
B)sharing of electrons between the atoms.
C)surface tension of water.
D)transfer of electrons between the atoms.
E)viscosity of water.
A)polarity of water molecules.
B)sharing of electrons between the atoms.
C)surface tension of water.
D)transfer of electrons between the atoms.
E)viscosity of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At high latitudes, abundant precipitation and runoff from melting of freshwater icebergs both increase salinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The latent heat of vaporization of water is larger than the latent heat of melting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Greater temperature fluctuations are seen in coastal areas due to the marine effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Independent of the actual salinity, the ratios or proportions of the major dissolved constituents of seawater such as chloride, sodium, and magnesium are relatively constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The heat capacity of liquid water is 1 calorie per gram per degree C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The density of seawater is slightly lower than the density pure water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Any solution with a pH of greater than 7.0 is acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Processes that decrease seawater salinity include evaporation and sea ice formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In distillation, saltwater is highly pressurized to drive water molecules through a membrane to remove salts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Salinity refers to all of the solid materials in seawater including dissolved and suspended substances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Deep-ocean water contains more carbon dioxide than surface water because deep water is colder and has the ability to dissolve more gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Precipitation, runoff, melting icebergs, and sea ice formation all decrease salinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Except for the water itself, the chloride ion is the most abundant constituent in seawater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Evaporation causes cooling in the liquid left behind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Chlorinity, which is the weight of the chloride ion, of a water sample can be used to calculate salinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
As a whole, the pH of the ocean is slightly alkaline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Hydrogen bonds form between neighboring water molecules because of:
A)electron sharing.
B)electron transfer.
C)the polarity of water molecules.
D)surface tension.
E)the viscosity of water.
A)electron sharing.
B)electron transfer.
C)the polarity of water molecules.
D)surface tension.
E)the viscosity of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Water can pile up a short distance above a container's rim due to:
A)strong covalent bonds.
B)high surface tension.
C)high viscosity.
D)low surface tension.
E)low viscosity.
A)strong covalent bonds.
B)high surface tension.
C)high viscosity.
D)low surface tension.
E)low viscosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
All of the following statements regarding pH are true except:
A)A pH of 3.0 is acidic and a pH of 10.0 is alkaline.
B)As a whole, the pH of the ocean is slightly acidic.
C)Buffers prevent large changes in the pH of a solution.
D)pH will be buffered in deeper water where organisms with calcite shells sink.
E)pH relates to relative acid-base ion balance in a solution.
A)A pH of 3.0 is acidic and a pH of 10.0 is alkaline.
B)As a whole, the pH of the ocean is slightly acidic.
C)Buffers prevent large changes in the pH of a solution.
D)pH will be buffered in deeper water where organisms with calcite shells sink.
E)pH relates to relative acid-base ion balance in a solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The surface tension of water:
A)increases as density decreases.
B)is related to salinity.
C)is relatively high.
D)is relatively low.
E)is very similar in other liquids.
A)increases as density decreases.
B)is related to salinity.
C)is relatively high.
D)is relatively low.
E)is very similar in other liquids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
As the salinity of seawater increases, its:
A)density decreases.
B)density increases.
C)residence time increases.
D)residence time decreases.
E)residence time changes.
A)density decreases.
B)density increases.
C)residence time increases.
D)residence time decreases.
E)residence time changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
All of the following processes decrease the salinity of water except:
A)precipitation.
B)runoff.
C)icebergs melting.
D)evaporation.
E)sea ice melting.
A)precipitation.
B)runoff.
C)icebergs melting.
D)evaporation.
E)sea ice melting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In comparison to most other liquids, the heat capacity of liquid water is:
A)a function of salinity.
B)about the same as other liquids.
C)higher than other liquids.
D)lower than other liquids.
E)related to solvent concentration.
A)a function of salinity.
B)about the same as other liquids.
C)higher than other liquids.
D)lower than other liquids.
E)related to solvent concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Principle of Constant Proportions states that:
A)ocean salinity varies as a function of season.
B)ocean salinity varies with geographical location.
C)the percentage of chloride varies with geographical location.
D)the percentage of sodium varies with ocean depth.
E)the relative concentrations of the major ions in seawater does not change.
A)ocean salinity varies as a function of season.
B)ocean salinity varies with geographical location.
C)the percentage of chloride varies with geographical location.
D)the percentage of sodium varies with ocean depth.
E)the relative concentrations of the major ions in seawater does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A beaker contains a mixture of ice and pure liquid water at 0ᵒC. What happens to the temperature of the liquid water as heat is added?
A)It immediately begins to rise slowly.
B)It remains constant until the ice melts, and then it begins to rise.
C)It rises rapidly as the ice melts.
D)It rises slowly until it reaches 32ᵒC, and then it remains constant as the ice melts.
E)The temperature pattern cannot be predicted.
A)It immediately begins to rise slowly.
B)It remains constant until the ice melts, and then it begins to rise.
C)It rises rapidly as the ice melts.
D)It rises slowly until it reaches 32ᵒC, and then it remains constant as the ice melts.
E)The temperature pattern cannot be predicted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The transfer of water between the atmosphere, the oceans, and the continents is known as the:
A)closed cycle.
B)geologic cycle.
C)hydrobiological cycle.
D)hydrologic cycle.
E)meteorological cycle.
A)closed cycle.
B)geologic cycle.
C)hydrobiological cycle.
D)hydrologic cycle.
E)meteorological cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An area of the ocean where rapid change in ocean density occurs with a change in depth is the:
A)barocline.
B)halocline.
C)isocline.
D)pycnocline.
E)thermocline.
A)barocline.
B)halocline.
C)isocline.
D)pycnocline.
E)thermocline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The average salinity of typical seawater is:
A)0)35%.
B)2)0%.
C)3)5%.
D)10%.
E)25%.
A)0)35%.
B)2)0%.
C)3)5%.
D)10%.
E)25%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which property of water causes coastal communities to have only moderate differences in daily highs and lows when compared to inland communities?
A)high heat capacity
B)high salinity
C)high viscosity
D)low heat capacity
E)low viscosity
A)high heat capacity
B)high salinity
C)high viscosity
D)low heat capacity
E)low viscosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Many of the unique properties of water are attributed to the fact that water:
A)contains ionic bonds.
B)exists in three states of matter on Earth's surface.
C)is a polar molecule.
D)is a universal solvent.
E)requires heat to condense.
A)contains ionic bonds.
B)exists in three states of matter on Earth's surface.
C)is a polar molecule.
D)is a universal solvent.
E)requires heat to condense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The amount of energy that is necessary to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree C is the definition of:
A)boiling point elevation.
B)calorie.
C)latent heat of condensation.
D)latent heat of evaporation.
E)thermal capacity.
A)boiling point elevation.
B)calorie.
C)latent heat of condensation.
D)latent heat of evaporation.
E)thermal capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
All of the following processes decrease seawater salinity except:
A)evaporation.
B)iceberg melting.
C)precipitation.
D)river runoff.
E)sea ice melting.
A)evaporation.
B)iceberg melting.
C)precipitation.
D)river runoff.
E)sea ice melting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
All of the following are methods used to desalinate water except:
A)electrolysis.
B)freeze separation.
C)osmosis.
D)reverse osmosis.
E)distillation.
A)electrolysis.
B)freeze separation.
C)osmosis.
D)reverse osmosis.
E)distillation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Latent heat is the quantity of heat gained or lost as a substance undergoes a:
A)change in chemical composition.
B)change in molecular weight.
C)change in state.
D)change in atomic mass.
E)change in subatomic structure.
A)change in chemical composition.
B)change in molecular weight.
C)change in state.
D)change in atomic mass.
E)change in subatomic structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The states of matter in which water exists is primarily determined by:
A)density.
B)salinity.
C)chlorinity.
D)temperature.
E)pH.
A)density.
B)salinity.
C)chlorinity.
D)temperature.
E)pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The ion in sea water that serves as a buffer is:
A)Ca⁺².
B)Cl⁻.
C)CO₂.
D)Na⁺.
E)HCO₃⁻.
A)Ca⁺².
B)Cl⁻.
C)CO₂.
D)Na⁺.
E)HCO₃⁻.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A rapid change in ocean temperature with a change in depth occurs in the:
A)barocline.
B)halocline.
C)isocline.
D)pycnocline.
E)thermocline.
A)barocline.
B)halocline.
C)isocline.
D)pycnocline.
E)thermocline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. boiling point
B) precipitation
C) freezing point
D) heat capacity
E) surface tension
A. boiling point
B) precipitation
C) freezing point
D) heat capacity
E) surface tension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe the various methods used to desalinate seawater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
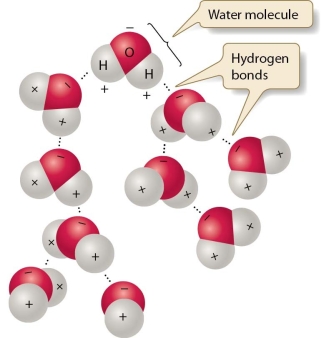
Explain how seawater salinity is affected by surface processes (such as precipitation and evaporation, for example).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
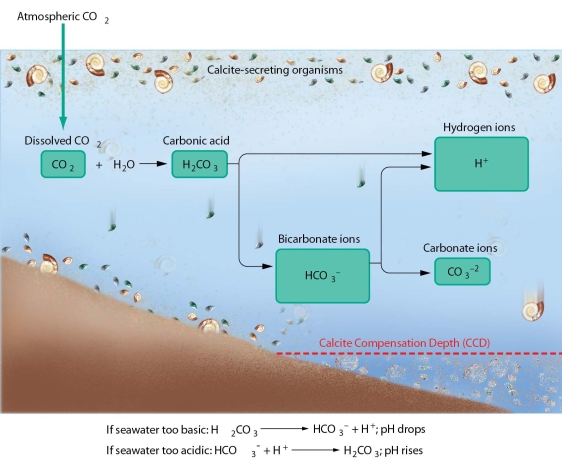
Explain how the pH of seawater remains slightly alkaline AND relatively constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
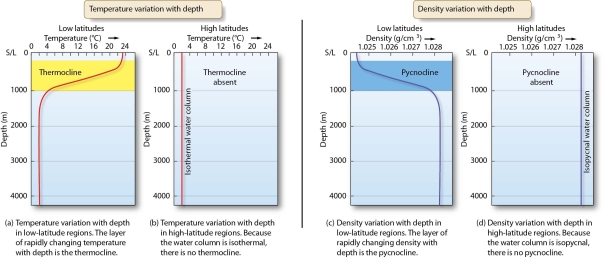
Discuss the relationship between seawater density and water temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
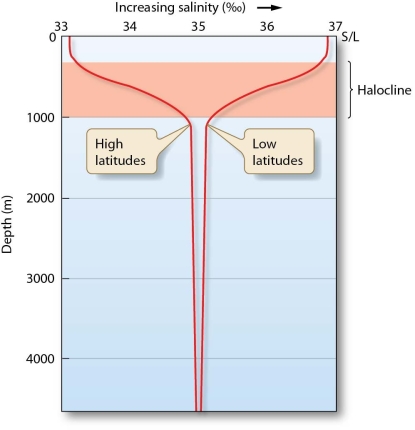
How does the ocean's salinity vary with depth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. sodium ion
B) calcium ion
C) potassium ion
D) hydrogen ion
E) magnesium ion
A. sodium ion
B) calcium ion
C) potassium ion
D) hydrogen ion
E) magnesium ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
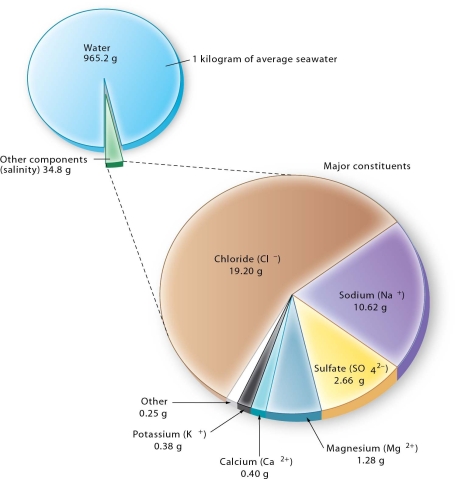
List the major constituents dissolved in seawater in decreasing concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
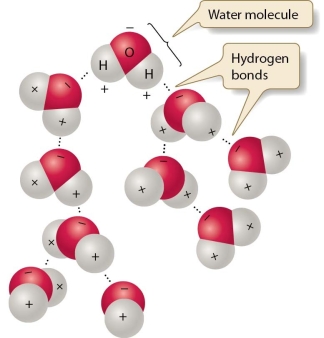
Discuss how hydrogen bonding in water allows water to support life on earth. Include in your answer how hydrogen bonding affects the physical and chemical properties of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. desalination
B) solar distillation
C) pycnocline
D) electrolysis
E) reverse osmosis
A. desalination
B) solar distillation
C) pycnocline
D) electrolysis
E) reverse osmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. temperature
B) salinity
C) thermocline
D) pycnocline
E) distillation
A. temperature
B) salinity
C) thermocline
D) pycnocline
E) distillation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
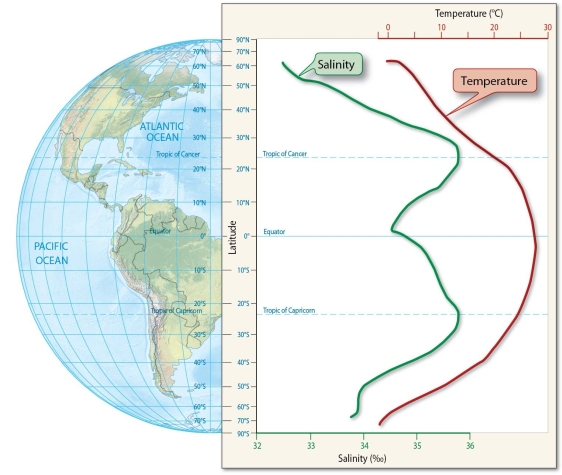
Discuss how latitude and climatological processes affect seawater salinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. pH
B) latitude
C) precipitation
D) salinity
E) temperature
A. pH
B) latitude
C) precipitation
D) salinity
E) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
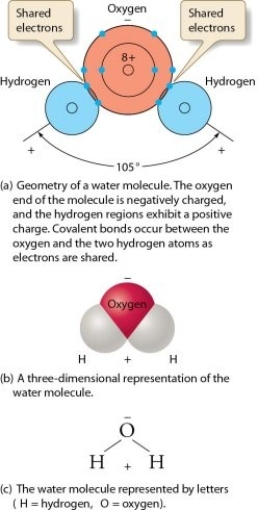
Describe what condition exists in water molecules to make then dipolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
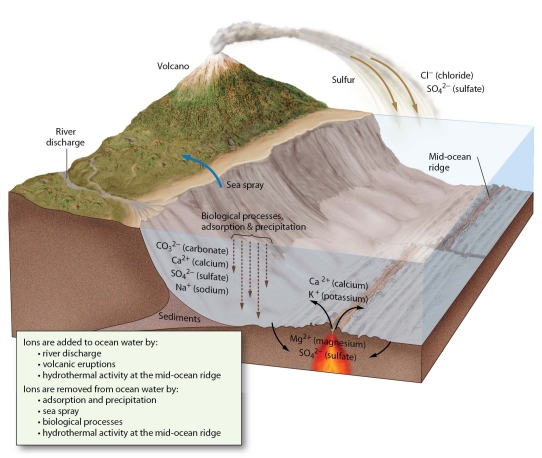
What is the origin of the salt ions in seawater?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



