Deck 12: Marine Life and the Marine Environment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Marine Life and the Marine Environment
1
Match the description of the marine organism's lifestyle with the correct term. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
lives in benthic sediments
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
lives in benthic sediments
D
2
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
mesopelagic
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
mesopelagic
D
3
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
subtidal
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
subtidal
B
4
The lowest and most specific level in Linnaeus' classification scheme is the family.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
hadal
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
hadal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The majority of marine species are associated with the pelagic environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Match the description of the marine organism's lifestyle with the correct term. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
lives on top of benthic sediments
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
lives on top of benthic sediments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
epipelagic
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
epipelagic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Meroplankton are organisms that spend the larval phase of their life cycle associated with the ocean bottom (benthos)and the adult phase of the life cycle as plankton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Match the description of the marine organism's lifestyle with the correct term. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
floats for a portion of its life
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
floats for a portion of its life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Plankton includes all organisms such as bacteria, algae, and animals that actively swim independently of ocean currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
littoral
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
littoral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Match the description of the marine organism's lifestyle with the correct term. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
swims for its entire life
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
swims for its entire life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
abyssal
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
abyssal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
abyssopelagic
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
abyssopelagic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match the description of the marine organism's lifestyle with the correct term. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
can never swim against a current
A)meroplankton
B)picoplankton
C)nekton
D)infauna
E)holoplankton
F)nanoplankton
G)epifauna
can never swim against a current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Phytoplankton are small in size as a result of predation pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The science of classifying and naming organisms is called taxonomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Epifaunal organisms live deep within benthic sediments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Match the marine zone with its correct location. Use each choice once, more than once, or not at all.
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
bathyal
A)neritic
B)benthic
C)pelagic, neritic
D)pelagic
bathyal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following word pairs correctly link a descriptor with the way in which the organism lives in the ocean?
A)benthos-drift
B)benthos-swim
C)nekton-bottom-dwelling
D)nekton-swim
E)plankton-bottom-dwelling
A)benthos-drift
B)benthos-swim
C)nekton-bottom-dwelling
D)nekton-swim
E)plankton-bottom-dwelling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Species diversity and total biomass are greater in warm-water marine environments in comparison to cold-water marine environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Tropical marine organisms tend to grow more slowly, live longer, and are smaller in general than their cold-water counterparts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A euryhaline organism would be poorly adapted to living in coastal environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Cold, high-viscosity water benefits floating organisms more than warmer, low-viscosity water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following associations is incorrect?
A)Kingdom Animalia-dolphins
B)Kingdom Fungi-mushrooms
C)Kingdom Monera-bacteria in hydrothermal vents
D)Kingdom Plantae-algae
E)Kingdom Protista-phytoplankton
A)Kingdom Animalia-dolphins
B)Kingdom Fungi-mushrooms
C)Kingdom Monera-bacteria in hydrothermal vents
D)Kingdom Plantae-algae
E)Kingdom Protista-phytoplankton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The deep scattering layer is produced by masses of migrating phytoplankton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Stenothermal organisms are likely to be found in deep open-ocean water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The oxygen minimum layer is found in the bathypelagic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Nekton are restricted to particular ocean areas by:
A)availability of food.
B)differences in water pressure with depth.
C)changes in salinity.
D)temperature variations with latitude and depth.
E)All of the above conditions may restrict the distribution of nekton.
A)availability of food.
B)differences in water pressure with depth.
C)changes in salinity.
D)temperature variations with latitude and depth.
E)All of the above conditions may restrict the distribution of nekton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The euphotic zone is contained entirely in the mesopelagic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
One reason that polar climates support a higher biomass is that colder water can hold more dissolved oxygen than warmer water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The hadal zone is associated with deep-ocean trenches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that range in complexity from simple sponges to complex vertebrates belong to the kingdom:
A)Animalia.
B)Fungi.
C)Monera.
D)Plantae.
E)Protoctista.
A)Animalia.
B)Fungi.
C)Monera.
D)Plantae.
E)Protoctista.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Planktonic organisms that spend part of their life in planktonic form, and the rest of their life as either benthos or nekton are called:
A)bacterioplankton.
B)holoplankton.
C)macroplankton.
D)meroplankton.
E)zooplankton.
A)bacterioplankton.
B)holoplankton.
C)macroplankton.
D)meroplankton.
E)zooplankton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An example of an organism that might be part of the infauna is a/an:
A)bull kelp.
B)crinoid.
C)lug worm.
D)shark.
E)tuna.
A)bull kelp.
B)crinoid.
C)lug worm.
D)shark.
E)tuna.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements concerning bacteria is false?
A)Bacteria can be found living in extreme environments (heat, salinity, cold, etc.).
B)Bacteria have a cell membrane and a cell wall.
C)Bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles and a distinct nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
D)Bacteria reproduce asexually only.
E)Bacteria were the first type of cells to evolve on earth.
A)Bacteria can be found living in extreme environments (heat, salinity, cold, etc.).
B)Bacteria have a cell membrane and a cell wall.
C)Bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles and a distinct nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
D)Bacteria reproduce asexually only.
E)Bacteria were the first type of cells to evolve on earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The neritic province is associated with the continental shelf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Osmosis occurs when salt ions diffuse through a selectively permeable membrane with a lower ion concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Streamlining in fishes and other nektonic organisms means that the minimum amount of energy is expended to swim through the water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A small size is advantageous for marine organisms because it:
A)increases the ability to absorb nutrients.
B)increases the ability of wastes to diffuse out of the organism.
C)increases the surface area to volume ratio that in turn reduces frictional resistance to sinking.
D)All of the above statements are advantageous to marine organisms.
E)None of the above statements are advantageous to marine organisms.
A)increases the ability to absorb nutrients.
B)increases the ability of wastes to diffuse out of the organism.
C)increases the surface area to volume ratio that in turn reduces frictional resistance to sinking.
D)All of the above statements are advantageous to marine organisms.
E)None of the above statements are advantageous to marine organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Compared to freshwater fishes, marine fishes:
A)drink seawater and produce a large volume of urine.
B)do not drink seawater in an effort to conserve as much water as possible.
C)produce a large volume of dilute urine in an effort to rid their bodies of excess water.
D)tend to gain water by osmosis since their internal salt concentration is higher than that of seawater.
E)tend to lose water by osmosis since their internal salt concentration is lower than that of seawater.
A)drink seawater and produce a large volume of urine.
B)do not drink seawater in an effort to conserve as much water as possible.
C)produce a large volume of dilute urine in an effort to rid their bodies of excess water.
D)tend to gain water by osmosis since their internal salt concentration is higher than that of seawater.
E)tend to lose water by osmosis since their internal salt concentration is lower than that of seawater.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The majority of marine invertebrates are:
A)adapted to life in the pelagic zone.
B)estuarine.
C)found only in benthic environments.
D)hypertonic with respect to their environment.
E)isotonic with respect to their environment.
A)adapted to life in the pelagic zone.
B)estuarine.
C)found only in benthic environments.
D)hypertonic with respect to their environment.
E)isotonic with respect to their environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
All of the following are adaptive solutions employed by marine organisms to prevent sinking except:
A)building a flotation mechanism such as a swim bladder.
B)decreasing density.
C)decreasing cellular fat content.
D)producing extensions that increase drag in the water.
E)increasing the surface area to volume ratio.
A)building a flotation mechanism such as a swim bladder.
B)decreasing density.
C)decreasing cellular fat content.
D)producing extensions that increase drag in the water.
E)increasing the surface area to volume ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45

With respect to their marine environment, these organisms can be referred to as:
A)benthos.
B)heterotrophs.
C)nekton.
D)plankton.
E)predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When compared to their warmer water counterparts, cold-water plankton often:
A)are larger in size.
B)are smaller in size.
C)exhibit countershading.
D)have more spines and ornamentation on the cell wall.
E)reproduce asexually only.
A)are larger in size.
B)are smaller in size.
C)exhibit countershading.
D)have more spines and ornamentation on the cell wall.
E)reproduce asexually only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Most marine species are found in the:
A)bathypelagic environment.
B)benthic environment.
C)mesopelagic environment.
D)oceanic environment.
E)pelagic environment.
A)bathypelagic environment.
B)benthic environment.
C)mesopelagic environment.
D)oceanic environment.
E)pelagic environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The movement of a substance in solution from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration across a selectively permeable membrane in a living organism is called:
A)active transport.
B)Brownian movement.
C)diffusion.
D)osmosis.
E)passive transport.
A)active transport.
B)Brownian movement.
C)diffusion.
D)osmosis.
E)passive transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The seasonal temperature range in the deep ocean is usually:
A)between -2° and 32°C.
B)between 0° and 15°C.
C)between 2° and 8°C.
D)between 8° and 25°C.
E)negligible.
A)between -2° and 32°C.
B)between 0° and 15°C.
C)between 2° and 8°C.
D)between 8° and 25°C.
E)negligible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Planktonic organisms often have needle-like structures that:
A)are used as a defense mechanism.
B)are used as paddles to catch ocean currents.
C)increase density.
D)prevent sinking.
E)serve as a "skeleton" to support the diatom.
A)are used as a defense mechanism.
B)are used as paddles to catch ocean currents.
C)increase density.
D)prevent sinking.
E)serve as a "skeleton" to support the diatom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Neritic marine environments would be found:
A)associated with continental shelves.
B)at mid-ocean ridges.
C)deep in the ocean basin.
D)in subduction zones.
E)within a deep-sea trench.
A)associated with continental shelves.
B)at mid-ocean ridges.
C)deep in the ocean basin.
D)in subduction zones.
E)within a deep-sea trench.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
High-latitude ocean water tends to support large planktonic communities because:
A)there are fewer predators that feed on plankton.
B)of the longer summer day length.
C)of higher dissolved oxygen and nutrient concentrations.
D)there is abundant light.
E)there are abundant nutrients.
A)there are fewer predators that feed on plankton.
B)of the longer summer day length.
C)of higher dissolved oxygen and nutrient concentrations.
D)there is abundant light.
E)there are abundant nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An organism that tolerates a wide range of salinities is referred to as:
A)euryhaline.
B)hypertonic.
C)hypotonic.
D)isotonic.
E)stenohaline.
A)euryhaline.
B)hypertonic.
C)hypotonic.
D)isotonic.
E)stenohaline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Organisms of the mesopelagic zone are characterized by:
A)bioluminescence.
B)large, sensitive eyes.
C)no eyes.
D)A and B are correct.
E)A and C are correct.
A)bioluminescence.
B)large, sensitive eyes.
C)no eyes.
D)A and B are correct.
E)A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A common body shape that streamlines an organism in the marine environment is a flattened body that:
A)has a wide, blunt front end.
B)tapers at the front end.
C)tapers at the top surface.
D)tapers at the back end.
E)tapers at the bottom surface.
A)has a wide, blunt front end.
B)tapers at the front end.
C)tapers at the top surface.
D)tapers at the back end.
E)tapers at the bottom surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Organisms with small bodies, extremely large mouths, and sharp teeth are likely to be found in the:
A)bathypelagic zone.
B)epipelagic zone.
C)intertidal zone.
D)neritic province.
E)photic zone.
A)bathypelagic zone.
B)epipelagic zone.
C)intertidal zone.
D)neritic province.
E)photic zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Osmotic pressure increases as the:
A)difference in salinity decreases.
B)difference in salinity increases.
C)difference in temperature increases.
D)salinity increases.
E)temperature increases.
A)difference in salinity decreases.
B)difference in salinity increases.
C)difference in temperature increases.
D)salinity increases.
E)temperature increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Organisms that cannot withstand large changes in temperature are referred to as:
A)eurythermal.
B)euryhaline.
C)estuarine.
D)isothermal.
E)stenothermal.
A)eurythermal.
B)euryhaline.
C)estuarine.
D)isothermal.
E)stenothermal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The euphotic zone is confined to the:
A)abyssopelagic zone.
B)bathypelagic zone.
C)epipelagic zone.
D)mesopelagic zone.
E)neritic province.
A)abyssopelagic zone.
B)bathypelagic zone.
C)epipelagic zone.
D)mesopelagic zone.
E)neritic province.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The color pattern in which marine organisms are light on the bottom and dark on the top of their bodies camouflaging them against the water-air interface is:
A)countershading.
B)cryptic coloration.
C)defensive coloration.
D)disruptive coloration.
E)warning coloration.
A)countershading.
B)cryptic coloration.
C)defensive coloration.
D)disruptive coloration.
E)warning coloration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Compare and contrast warm and cold water marine species in terms of life span, body size, and relative abundance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
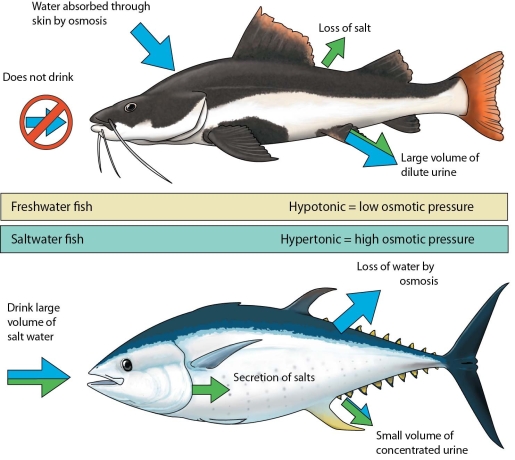
Discuss osmotic balance in freshwater and saltwater fishes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. seagrasses
B) krill
C) jellyfish
D) floating Sargassum
E) zooplankton
A. seagrasses
B) krill
C) jellyfish
D) floating Sargassum
E) zooplankton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Compare and contrast the ways marine organisms are classified including: by mode of nutrition, location in the marine environment where they live, and size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Draw and label a cross-section of the marine environment and include the following biozones: the neritic province (supralittoral, littoral, sublittoral, bathyal, abyssal, and hadal zones)and the oceanic province (epipelagic, mesopelagic, bathypelagic, and abyssopelagic zones).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Explain why the majority of marine organisms are benthic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. holoplankton
B) macroplankton
C) meroplankton
D) nektoplankton
E) picoplankton
A. holoplankton
B) macroplankton
C) meroplankton
D) nektoplankton
E) picoplankton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. Animalia
B) Archaea
C) Fungi
D) Plantae
E) Protoctista
A. Animalia
B) Archaea
C) Fungi
D) Plantae
E) Protoctista

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
List the three major domains of life and the five kingdoms of organisms, along with a brief description of the fundamental criteria used in assigning organisms to these divisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

Discuss why marine phytoplankton are generally smaller and more ornate than their freshwater counterparts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
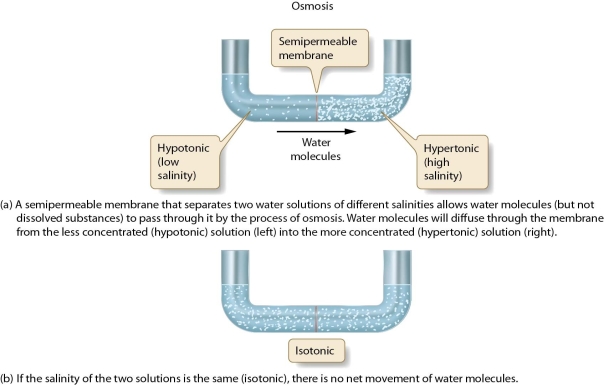
Define the terms hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic and discuss their relationship to osmotic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. littoral
B) sublittoral
C) subneritic
D) suboceanic
E) supralittoral
A. littoral
B) sublittoral
C) subneritic
D) suboceanic
E) supralittoral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The sublittoral (subtidal)zone is the area:
A)above the highest tide.
B)below the intertidal zone on the continental shelf.
C)between the highest high tide and the lowest low tide.
D)beyond the continental shelf.
E)where demersal and pelagic organisms are found.
A)above the highest tide.
B)below the intertidal zone on the continental shelf.
C)between the highest high tide and the lowest low tide.
D)beyond the continental shelf.
E)where demersal and pelagic organisms are found.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Distinguish between plankton, nekton, and benthos and give an example of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Examine the five words and/or phrases and determine the relationship among the majority of words/phrases. Choose the one option that does not fit the pattern.
A. abyssopelagic
B) bathypelagic
C) benthopelagic
D) epipelagic
E) mesopelagic
A. abyssopelagic
B) bathypelagic
C) benthopelagic
D) epipelagic
E) mesopelagic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



