Deck 17: Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/280
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Monetary Policy
1
The top policy goal for Paul Volcker when he became chairman of the Federal Reserve's Board of Governors in 1979 was
A) fighting inflation.
B) increasing employment.
C) increasing economic growth.
D) increasing regulation of commercial banks.
E) a low current account deficit.
A) fighting inflation.
B) increasing employment.
C) increasing economic growth.
D) increasing regulation of commercial banks.
E) a low current account deficit.
fighting inflation.
2
During the turmoil in the market for subprime mortgages in 2007 and 2008,the Fed increased the volume of discount loans.The goal of the Fed was to
A) reduce the rate of inflation.
B) stimulate economic growth.
C) reduce unemployment.
D) reassure financial markets and promote financial stability.
E) reduce the current account deficit.
A) reduce the rate of inflation.
B) stimulate economic growth.
C) reduce unemployment.
D) reassure financial markets and promote financial stability.
E) reduce the current account deficit.
reassure financial markets and promote financial stability.
3
Maintaining a strong dollar in international currency markets is not one of the four monetary policy goals of the Fed listed in the textbook.
True
4
Rising prices erode the value of money as a ________ and as a ________.
A) unit of barter; unit of account
B) store of value; unit of liquidity
C) medium of exchange; store of value
D) store of value; unit of barter
A) unit of barter; unit of account
B) store of value; unit of liquidity
C) medium of exchange; store of value
D) store of value; unit of barter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following are goals of monetary policy?
A) maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, economic growth, and high employment
B) price stability, maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, and high employment
C) price stability, economic growth, and high employment
D) price stability, economic growth, and maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies
A) maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, economic growth, and high employment
B) price stability, maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, and high employment
C) price stability, economic growth, and high employment
D) price stability, economic growth, and maximizing the value of the dollar relative to other currencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In 2017,some banks in Europe had to make interest payments to borrowers rather than receive interest payments from borrowers.Which of the following statements describes this situation?
A) For these banks, the loans increased required reserves.
B) These banks were receiving negative nominal interest rates on these loans.
C) For these banks, the loans were liabilities instead of assets.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) For these banks, the loans increased required reserves.
B) These banks were receiving negative nominal interest rates on these loans.
C) For these banks, the loans were liabilities instead of assets.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Since World War II,the Federal Reserve has not been involved in carrying out monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Federal Reserve System's four monetary policy goals are
A) low government budget deficits, low current account deficits, high employment, and a high foreign exchange value of the dollar.
B) a low rate of bank failures, high reserve ratios, price stability, and economic growth.
C) price stability, high employment, economic growth, and stability of financial markets and institutions.
D) price stability, low government budget deficits, low current account deficits, and a low rate of bank failures.
A) low government budget deficits, low current account deficits, high employment, and a high foreign exchange value of the dollar.
B) a low rate of bank failures, high reserve ratios, price stability, and economic growth.
C) price stability, high employment, economic growth, and stability of financial markets and institutions.
D) price stability, low government budget deficits, low current account deficits, and a low rate of bank failures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Inflation rates during the years 1979-1981 were the highest the United States has ever experienced during peacetime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the probability of losing your job remains ________,a recession would be a good time to purchase a home because the Fed usually ________ interest rates during this time.
A) low; lowers
B) low; raises
C) high; lowers
D) high; raises
E) low; does not change
A) low; lowers
B) low; raises
C) high; lowers
D) high; raises
E) low; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When the Federal Reserve System was established in 1913,its main policy goal was
A) encouraging strong economic growth.
B) promoting price stability.
C) preventing bank panics.
D) keeping employment high.
A) encouraging strong economic growth.
B) promoting price stability.
C) preventing bank panics.
D) keeping employment high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The goals of monetary policy tend to be interrelated.For example,when the Fed pursues the goal of ________,it also can achieve the goal of ________ simultaneously.
A) high employment; economic growth
B) high employment; lowering government spending
C) economic growth; a low current account deficit
D) stability of financial markets; a low current account deficit
A) high employment; economic growth
B) high employment; lowering government spending
C) economic growth; a low current account deficit
D) stability of financial markets; a low current account deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Monetary policy refers to the actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage
A) the money supply and income tax rates to pursue its economic objectives.
B) the money supply and interest rates to pursue its economic objectives.
C) income tax rates and interest rates to pursue its economic objectives.
D) government spending and income tax rates to pursue its economic objectives.
A) the money supply and income tax rates to pursue its economic objectives.
B) the money supply and interest rates to pursue its economic objectives.
C) income tax rates and interest rates to pursue its economic objectives.
D) government spending and income tax rates to pursue its economic objectives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Federal Reserve Board Chairmen Paul Volcker,as well as later Fed chairs,focused on which of the following as their main goal of monetary policy?
A) high employment
B) price stability
C) economic growth
D) stability of financial markets
A) high employment
B) price stability
C) economic growth
D) stability of financial markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The main goal of monetary policy for recent Fed Chairmen has been to maintain high employment in labor markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One of the monetary policy goals of the Federal Reserve is price stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Fed seeks to promote stability of financial markets because
A) they want to lift the self-esteem of workers.
B) Congress directed them to do so by the Employment Act of 1946.
C) lower output occurs over time when there is not an efficient matching of savers and borrowers.
D) unstable markets result in increased efficiency.
A) they want to lift the self-esteem of workers.
B) Congress directed them to do so by the Employment Act of 1946.
C) lower output occurs over time when there is not an efficient matching of savers and borrowers.
D) unstable markets result in increased efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
List the Fed's four main monetary policy goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Monetary policy refers to the actions the
A) President and Congress take to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue their economic objectives.
B) Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue its macroeconomic policy objectives.
C) President and Congress take to manage government spending and taxes to pursue their economic objectives.
D) Federal Reserve takes to manage government spending and taxes to pursue its economic objectives.
A) President and Congress take to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue their economic objectives.
B) Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue its macroeconomic policy objectives.
C) President and Congress take to manage government spending and taxes to pursue their economic objectives.
D) Federal Reserve takes to manage government spending and taxes to pursue its economic objectives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Monetary policy is conducted by the U.S.Treasury Department.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The money demand curve has a
A) negative slope because an increase in the interest rate decreases the quantity of money demanded.
B) positive slope because an increase in the interest rate increases the quantity of money demanded.
C) negative slope because an increase in the price level decreases the quantity of money demanded.
D) positive slope because an increase in the price level increases the quantity of money demanded.
A) negative slope because an increase in the interest rate decreases the quantity of money demanded.
B) positive slope because an increase in the interest rate increases the quantity of money demanded.
C) negative slope because an increase in the price level decreases the quantity of money demanded.
D) positive slope because an increase in the price level increases the quantity of money demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 17-1
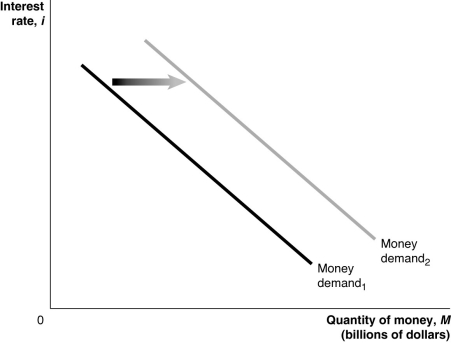
Refer to Figure 17-1.In the figure,the money demand curve would move from Money demand₁ to Money demand₂ if
A) real GDP increased.
B) the price level decreased.
C) the interest rate increased.
D) the Federal Reserve sold Treasury securities.

Refer to Figure 17-1.In the figure,the money demand curve would move from Money demand₁ to Money demand₂ if
A) real GDP increased.
B) the price level decreased.
C) the interest rate increased.
D) the Federal Reserve sold Treasury securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that households became mistrustful of the banking system and decide to decrease their checking account balances and increase their holdings of currency.Using the money demand and money supply model and assuming everything else is held constant,the equilibrium interest rate should
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) increase, then decrease.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) increase, then decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When the Federal Reserve increases the money supply,at the previous equilibrium interest rate households and firms will now have
A) more money than they want to hold.
B) less money than they want to hold.
C) the amount of money that they want to hold.
D) to sell Treasury bills.
A) more money than they want to hold.
B) less money than they want to hold.
C) the amount of money that they want to hold.
D) to sell Treasury bills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An increase in the interest rate causes
A) a movement up along the money demand curve.
B) a movement down along the money demand curve.
C) the money demand curve to shift to the left.
D) the money demand curve to shift to the right.
A) a movement up along the money demand curve.
B) a movement down along the money demand curve.
C) the money demand curve to shift to the left.
D) the money demand curve to shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is a banking panic,and what role did banking panics play in the decision by Congress to establish the Federal Reserve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An increase in the price level causes
A) the money demand curve to shift to the left.
B) the money demand curve to shift to the right.
C) a movement up along the money demand curve.
D) a movement down along the money demand curve.
A) the money demand curve to shift to the left.
B) the money demand curve to shift to the right.
C) a movement up along the money demand curve.
D) a movement down along the money demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When Congress established the Federal Reserve in 1913,what was its main responsibility? When did Congress broaden the Fed's responsibilities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 17-1

Refer to Figure 17-1.In the figure above,the money demand curve would move from Money demand₁ to Money demand₂ if
A) real GDP decreased.
B) the price level increased.
C) the interest rate decreased.
D) the Federal Reserve sold Treasury securities.

Refer to Figure 17-1.In the figure above,the money demand curve would move from Money demand₁ to Money demand₂ if
A) real GDP decreased.
B) the price level increased.
C) the interest rate decreased.
D) the Federal Reserve sold Treasury securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in the interest rate
A) decreases the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) increases the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) decreases the percentage yield of holding money.
D) increases the percentage yield of holding money.
A) decreases the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) increases the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) decreases the percentage yield of holding money.
D) increases the percentage yield of holding money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following will lead to a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate in the economy?
A) an increase in the price level
B) a sale of government securities by the Fed
C) a decrease in GDP
D) an increase in the discount rate
E) an increase in the reserve requirement
A) an increase in the price level
B) a sale of government securities by the Fed
C) a decrease in GDP
D) an increase in the discount rate
E) an increase in the reserve requirement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Using the money demand and money supply model,an increase in money demand would cause the equilibrium interest rate to
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) not change.
D) increase, then decrease.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) not change.
D) increase, then decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Using the money demand and money supply model,an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve would cause the equilibrium interest rate to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) increase, then decrease.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) increase, then decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Federal Reserve can directly affect its monetary policy ________,which then affect its monetary policy ________.
A) goals; targets
B) goals; tools
C) targets; goals
D) targets; tools
A) goals; targets
B) goals; tools
C) targets; goals
D) targets; tools

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What problems can high inflation rates cause for the economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Federal Reserve's two main ________ are the money supply and the interest rate.
A) monetary policy targets
B) policy tools
C) fiscal policy targets
D) fiscal tools
A) monetary policy targets
B) policy tools
C) fiscal policy targets
D) fiscal tools

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following would cause the money demand curve to shift to the left?
A) an open market purchase of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve
B) an increase in the interest rate
C) an increase in the price level
D) a decrease in real GDP
A) an open market purchase of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve
B) an increase in the interest rate
C) an increase in the price level
D) a decrease in real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply,at the previous equilibrium interest rate households and firms will now want to
A) buy Treasury bills.
B) sell Treasury bills.
C) neither buy nor sell Treasury bills.
D) hold less money.
A) buy Treasury bills.
B) sell Treasury bills.
C) neither buy nor sell Treasury bills.
D) hold less money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using the money demand and money supply model,an open market purchase of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve would cause the equilibrium interest rate to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) increase if the economy is in a recession.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) not change.
D) increase if the economy is in a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An increase in real GDP can shift
A) money demand to the right and decrease the equilibrium interest rate.
B) money demand to the right and increase the equilibrium interest rate.
C) money demand to the left and decrease the equilibrium interest rate.
D) money demand to the left and increase the equilibrium interest rate.
A) money demand to the right and decrease the equilibrium interest rate.
B) money demand to the right and increase the equilibrium interest rate.
C) money demand to the left and decrease the equilibrium interest rate.
D) money demand to the left and increase the equilibrium interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the Fed raises the interest rate,this will ________ inflation and ________ real GDP in the short run.
A) reduce; raise
B) increase; lower
C) increase; raise
D) reduce; lower
A) reduce; raise
B) increase; lower
C) increase; raise
D) reduce; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is true?
A) The money market model is essentially a model that determines the short-term nominal rate of interest.
B) The money market model is essentially a model that determines the short-term real rate of interest.
C) The loanable funds model is essentially a model that determines the short-term real rate of interest.
D) The loanable funds model is essentially a model that determines the long-term nominal rate of interest.
A) The money market model is essentially a model that determines the short-term nominal rate of interest.
B) The money market model is essentially a model that determines the short-term real rate of interest.
C) The loanable funds model is essentially a model that determines the short-term real rate of interest.
D) The loanable funds model is essentially a model that determines the long-term nominal rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Fed can attempt to increase the federal funds rate by
A) selling Treasury bills, which increases bank reserves.
B) buying Treasury bills, which increases bank reserves.
C) selling Treasury bills, which decreases bank reserves.
D) buying Treasury bills, which decreases bank reserves.
A) selling Treasury bills, which increases bank reserves.
B) buying Treasury bills, which increases bank reserves.
C) selling Treasury bills, which decreases bank reserves.
D) buying Treasury bills, which decreases bank reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For purposes of monetary policy,the Federal Reserve has targeted the interest rate known as the
A) federal funds rate.
B) Treasury bill rate.
C) discount rate.
D) prime rate.
A) federal funds rate.
B) Treasury bill rate.
C) discount rate.
D) prime rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An increase in the demand for Treasury bills will
A) decrease the price of Treasury bills.
B) decrease the interest rate on Treasury bills.
C) increase the opportunity cost of holding money.
D) eventually cause households to hold less money.
A) decrease the price of Treasury bills.
B) decrease the interest rate on Treasury bills.
C) increase the opportunity cost of holding money.
D) eventually cause households to hold less money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose the Fed increases the money supply.Which of the following is true?
A) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is equal to the quantity of money supplied.
B) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is less than the quantity of money supplied.
C) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is greater than the quantity of money supplied.
D) The interest rate must rise for the money market to clear.
A) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is equal to the quantity of money supplied.
B) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is less than the quantity of money supplied.
C) At the original interest rate, the quantity of money demanded is greater than the quantity of money supplied.
D) The interest rate must rise for the money market to clear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Changes in the federal funds rate usually result in
A) changes in both short-term and long-term interest rates with more of an effect on short-term interest rates.
B) changes in both short-term and long-term interest rates with more of an effect on long-term interest rates.
C) changes in both short-term and long-term interest rates with equal effect on both.
D) no change in either short-term or long-term interest rates.
A) changes in both short-term and long-term interest rates with more of an effect on short-term interest rates.
B) changes in both short-term and long-term interest rates with more of an effect on long-term interest rates.
C) changes in both short-term and long-term interest rates with equal effect on both.
D) no change in either short-term or long-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Increases in the price level
A) increase the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) decrease the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) increase the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.
D) decrease the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.
A) increase the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) decrease the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) increase the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.
D) decrease the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When the price of a financial asset ________ its interest rate will ________.
A) rises; rise
B) falls; fall
C) falls; rise
D) rises; remain the same
A) rises; rise
B) falls; fall
C) falls; rise
D) rises; remain the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A monetary policy target is a variable that
A) the Fed can affect directly.
B) equals one of the Fed's main policy goals.
C) the Fed has no ability to change.
D) the Fed cannot affect directly.
A) the Fed can affect directly.
B) equals one of the Fed's main policy goals.
C) the Fed has no ability to change.
D) the Fed cannot affect directly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The monetary policy target the Federal Reserve focuses primarily on today is
A) the unemployment rate.
B) M1.
C) the inflation rate.
D) the interest rate.
E) M2.
A) the unemployment rate.
B) M1.
C) the inflation rate.
D) the interest rate.
E) M2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An increase in real GDP
A) increases the buying and selling of goods and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
B) increases the buying and selling of goods and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
C) decreases the buying and selling of goods and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
D) decreases the buying and selling of goods and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
A) increases the buying and selling of goods and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
B) increases the buying and selling of goods and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
C) decreases the buying and selling of goods and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
D) decreases the buying and selling of goods and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The money demand curve,with the interest rate on the vertical axis,has a
A) positive slope.
B) negative slope.
C) zero slope.
D) positive slope for low levels of money demand, and a negative slope for high levels of money demand.
A) positive slope.
B) negative slope.
C) zero slope.
D) positive slope for low levels of money demand, and a negative slope for high levels of money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure 17-2
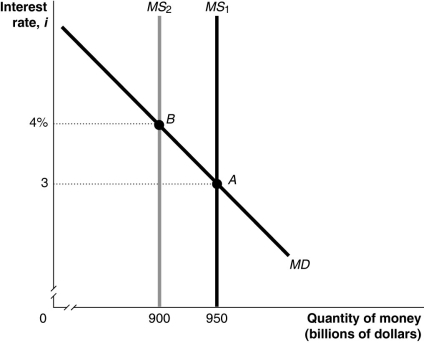
Refer to Figure 17-2.In the figure above,the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in real GDP.
C) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve.
D) a decrease in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve.

Refer to Figure 17-2.In the figure above,the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in real GDP.
C) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve.
D) a decrease in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 17-4
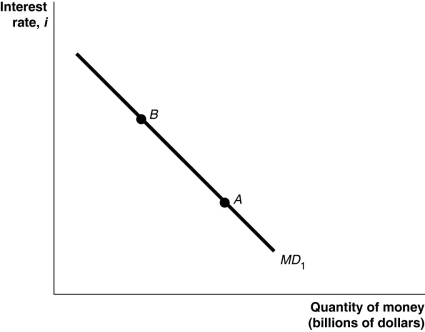
Refer to Figure 17-4.In the figure above,a movement from point A to point B would be caused by
A) a decrease in real GDP.
B) an increase in the price level.
C) a decrease in the price level.
D) an increase in the interest rate.

Refer to Figure 17-4.In the figure above,a movement from point A to point B would be caused by
A) a decrease in real GDP.
B) an increase in the price level.
C) a decrease in the price level.
D) an increase in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The money demand curve has a negative slope because
A) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to financial assets.
B) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from financial assets to money.
C) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to stocks.
D) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to bonds.
A) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to financial assets.
B) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from financial assets to money.
C) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to stocks.
D) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 17-3
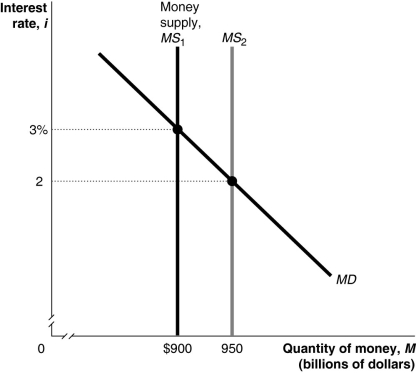
Refer to Figure 17-3.In the figure above,when the money supply shifts from MS₁ to MS₂,at the interest rate of 3 percent households and firms will
A) buy Treasury bills.
B) sell Treasury bills.
C) neither buy nor sell Treasury bills.
D) want to hold more money.

Refer to Figure 17-3.In the figure above,when the money supply shifts from MS₁ to MS₂,at the interest rate of 3 percent households and firms will
A) buy Treasury bills.
B) sell Treasury bills.
C) neither buy nor sell Treasury bills.
D) want to hold more money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The interest rate that banks charge other banks for overnight loans is the
A) prime rate.
B) discount rate.
C) federal funds rate.
D) Treasury bill rate.
A) prime rate.
B) discount rate.
C) federal funds rate.
D) Treasury bill rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The money supply curve is vertical if
A) banks and the Fed jointly determine the money supply.
B) the Fed is able to completely determine the money supply.
C) banks and households determine the money supply.
D) households and the Fed jointly determine the money supply.
A) banks and the Fed jointly determine the money supply.
B) the Fed is able to completely determine the money supply.
C) banks and households determine the money supply.
D) households and the Fed jointly determine the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Fed's two main monetary policy targets are
A) the money supply and the inflation rate.
B) the money supply and the interest rate.
C) the interest rate and real GDP.
D) the inflation rate and real GDP.
A) the money supply and the inflation rate.
B) the money supply and the interest rate.
C) the interest rate and real GDP.
D) the inflation rate and real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The federal funds rate is
A) the interest rate the Fed charges commercial banks.
B) the interest rate a bank charges its best customers.
C) the interest rate banks charge each other for overnight loans.
D) the interest rate on a Treasury Bill.
A) the interest rate the Fed charges commercial banks.
B) the interest rate a bank charges its best customers.
C) the interest rate banks charge each other for overnight loans.
D) the interest rate on a Treasury Bill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the Fed buys Treasury bills,this will shift the
A) money supply curve to the right.
B) money supply curve to the left.
C) money demand curve to the right.
D) money demand curve to the left.
A) money supply curve to the right.
B) money supply curve to the left.
C) money demand curve to the right.
D) money demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Buying a house during a recession may be a good idea if your job is secure because the Federal Reserve often
A) raises interest rates during recessions.
B) lowers interest rates during recessions.
C) lowers income taxes during recessions.
D) sells Treasury bills to help the housing market.
A) raises interest rates during recessions.
B) lowers interest rates during recessions.
C) lowers income taxes during recessions.
D) sells Treasury bills to help the housing market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The interest rate the Fed pays banks on their reserve holdings
A) guarantees a specific federal funds rate.
B) sets a ceiling for the federal funds rate.
C) sets a floor for the federal funds rate.
D) has no impact on the federal funds rate.
A) guarantees a specific federal funds rate.
B) sets a ceiling for the federal funds rate.
C) sets a floor for the federal funds rate.
D) has no impact on the federal funds rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Following the financial crisis of 2007-2009,banks had a glut of excess reserves.Because of this extraordinary amount of excess reserves being held by banks,the Fed's draining some of them through open market sales of Treasury securities would
A) raise interest rates.
B) have no effect on interest rates.
C) lower interest rates.
D) generate negative interest rates.
A) raise interest rates.
B) have no effect on interest rates.
C) lower interest rates.
D) generate negative interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the Fed sells a security to a financial firm and the Fed agrees to buy back the security the next day,the transaction is known as
A) a repurchase agreement.
B) a reverse repurchase agreement.
C) an open market flip-flop.
D) a federal funds swap.
A) a repurchase agreement.
B) a reverse repurchase agreement.
C) an open market flip-flop.
D) a federal funds swap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Fed can simultaneously reduce the inflation rate and stimulate growth through lowering interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Fed can directly lower the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The rate of interest banks charge other banks for overnight loans of reserves is the
A) discount rate.
B) prime rate.
C) federal funds rate.
D) real rate.
A) discount rate.
B) prime rate.
C) federal funds rate.
D) real rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following correctly describes what the Fed used as monetary targets in the past?
A) The Fed used M1 and M2 as targets after 1993.
B) The Fed focused on M1 as a target after deregulation of the financial markets.
C) The Fed increased its reliance on interest rate targets since the mid-1990s.
D) After 1980 and before the 1990s, the Fed focused on interest rate targets.
A) The Fed used M1 and M2 as targets after 1993.
B) The Fed focused on M1 as a target after deregulation of the financial markets.
C) The Fed increased its reliance on interest rate targets since the mid-1990s.
D) After 1980 and before the 1990s, the Fed focused on interest rate targets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A decrease in real GDP can
A) shift money demand to the right and decrease the interest rate.
B) shift money demand to the right and increase the interest rate.
C) shift money demand to the left and decrease the interest rate.
D) shift money demand to the left and increase the interest rate.
A) shift money demand to the right and decrease the interest rate.
B) shift money demand to the right and increase the interest rate.
C) shift money demand to the left and decrease the interest rate.
D) shift money demand to the left and increase the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The money market model is concerned with ________ and the loanable funds market model is concerned with ________.
A) short-term real interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
B) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
C) short-term real interest rates; long-term real interest rates
D) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term real interest rates
A) short-term real interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
B) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
C) short-term real interest rates; long-term real interest rates
D) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term real interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A monetary policy target is a variable that the Fed can affect directly,which then affects one or more of the Fed's policy goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in the money supply will
A) increase the interest rate.
B) decrease the interest rate.
C) have no affect on the interest rate.
D) decrease the equilibrium quantity of money in the economy.
A) increase the interest rate.
B) decrease the interest rate.
C) have no affect on the interest rate.
D) decrease the equilibrium quantity of money in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The federal funds rate
A) is determined administratively by the Fed.
B) is determined by the supply of and demand for bank reserves.
C) is determined directly by household demand for funds.
D) is determined directly by firm demand for funds.
A) is determined administratively by the Fed.
B) is determined by the supply of and demand for bank reserves.
C) is determined directly by household demand for funds.
D) is determined directly by firm demand for funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In June 2017,the Federal Open Market Committee raised the target for the federal funds rate to a range of 1.00 to 1.25 percent.To keep the federal funds rate in this target band,the Fed set the interest rate it pays on reverse repurchase agreements to
A) 1.00 percent.
B) 1.125 percent, the mid-point of the target range.
C) 1.25 percent.
D) 2.25 percent.
A) 1.00 percent.
B) 1.125 percent, the mid-point of the target range.
C) 1.25 percent.
D) 2.25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 17-5
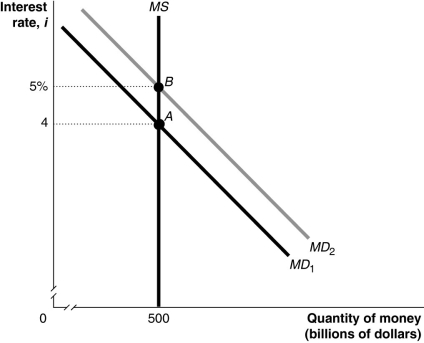
Refer to Figure 17-5.In the figure above,the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in real GDP.
C) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve.
D) an increase in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve.

Refer to Figure 17-5.In the figure above,the movement from point A to point B in the money market would be caused by
A) an increase in the price level.
B) a decrease in real GDP.
C) an open market sale of Treasury securities by the Federal Reserve.
D) an increase in the required reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In June 2017,the Federal Open Market Committee raised the target for the federal funds rate to a range of 1.00 to 1.25 percent.To keep the federal funds rate in this target band,the Fed set the interest rate it pays on bank reserves to
A) 1.00 percent.
B) 1.125 percent, the mid-point of the target range.
C) 1.25 percent.
D) 2.25 percent.
A) 1.00 percent.
B) 1.125 percent, the mid-point of the target range.
C) 1.25 percent.
D) 2.25 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose the Fed decreases the money supply.In response households and firms will ________ short term assets and this will drive ________ interest rates.
A) buy; up
B) buy; down
C) sell; up
D) sell; down
A) buy; up
B) buy; down
C) sell; up
D) sell; down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When the Fed buys a security from a financial firm and the financial firm agrees to buy back the security the next day,the transaction is known as
A) a repurchase agreement.
B) a reverse repurchase agreement.
C) an open market flip-flop.
D) a federal funds swap.
A) a repurchase agreement.
B) a reverse repurchase agreement.
C) an open market flip-flop.
D) a federal funds swap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



