Deck 4: Phylogeny and Evolutionary History
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Phylogeny and Evolutionary History
1
The study of phylogeny predominantly aims to
A)understand the branching relationships of populations as they give rise to descendant populations over time.
B)uncover evidence for natural selection.
C)provide a theoretical basis for Darwin's idea of a branching pattern of descent with modification.
D)All of the above
A)understand the branching relationships of populations as they give rise to descendant populations over time.
B)uncover evidence for natural selection.
C)provide a theoretical basis for Darwin's idea of a branching pattern of descent with modification.
D)All of the above
A
2
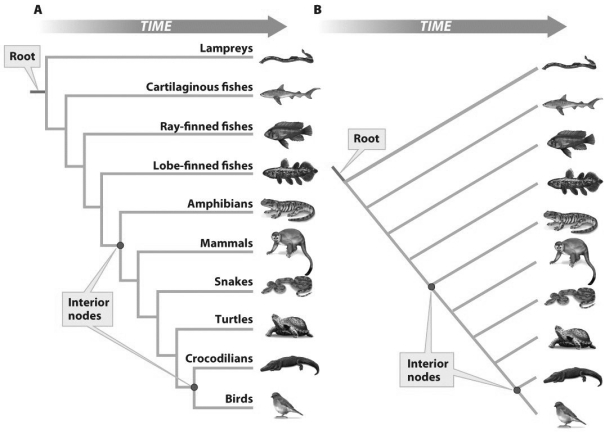 Based on the figure above,what does the upper dot in each figure represent?
Based on the figure above,what does the upper dot in each figure represent?A)An ancestral population
B)The most recent common ancestor of birds and crocodilians
C)The most recent common ancestor to all tetrapods
D)A and C
D
3
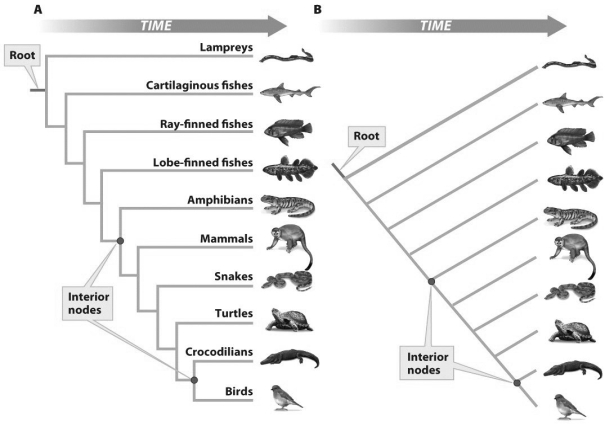 Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?
Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?A)Fish is not a monophyletic group.
B)Fish is a monophyletic group.
C)Tetrapod vertebrates is a monophyletic group.
D)A and C
D
4
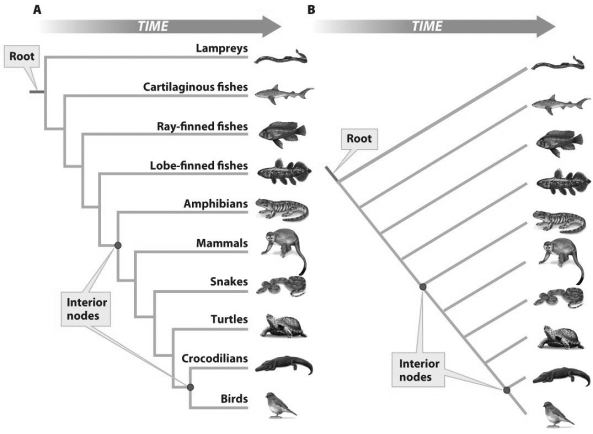 Based on the figure above,the two roots (labeled)represent which of the following?
Based on the figure above,the two roots (labeled)represent which of the following?1)Ancestral populations
2)A common ancestor of birds and crocodilians
3)A common ancestor to all tetrapods
4)The ancestral lineage from which all other lineages on the tree are derived
A)1 and 2
C)3 and 4
B)1 and 3
D)1,2,3,and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Linnaean taxonomy and the resulting system of scientific nomenclature (naming system)
A)was derived from evolutionary thinking.
B)was not derived from evolutionary thinking.
C)has been used by biologists for nearly three centuries.
D)A and C
E)B and C
A)was derived from evolutionary thinking.
B)was not derived from evolutionary thinking.
C)has been used by biologists for nearly three centuries.
D)A and C
E)B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Based on the phylogenetic tree above,which of the following groups is most closely related to mammals?
Based on the phylogenetic tree above,which of the following groups is most closely related to mammals?A)Snakes
B)Amphibians
C)Amphibians and all reptiles
D)All reptiles and birds
E)All reptiles but not birds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The study of phylogeny rests on our observation of traits,which may include
A)anatomical features.
C)genetics sequences.
B)embryological processes.
D)All of the above
A)anatomical features.
C)genetics sequences.
B)embryological processes.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
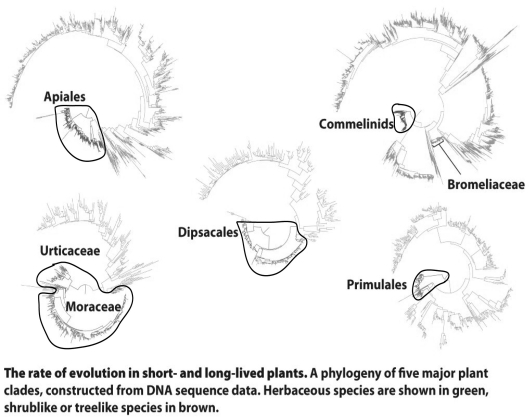 In the figure above,the shrublike or treelike species are circled in black.Based on the figure,which of the following statements is true?
In the figure above,the shrublike or treelike species are circled in black.Based on the figure,which of the following statements is true?A)For the herbaceous species, the branch lengths tend to be shorter, and the rates of sequence change more slowly.
B)For the herbaceous species, the branch lengths tend to be longer, and the rates of sequence change more slowly.
C)For the herbaceous species, the branch lengths tend to be longer, and the rates of sequence change faster.
D)For the herbaceous species, the branch lengths tend to be shorter, and the rates of sequence change faster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
German biologist Willi Hennig (1913-1976)
A)established the modern approach to classification.
B)documented evolutionary history in his book Phylogenetic Systematics.
C)noted that phylogenetic trees can help us to classify organisms according to their evolutionary history.
D)All of the above
A)established the modern approach to classification.
B)documented evolutionary history in his book Phylogenetic Systematics.
C)noted that phylogenetic trees can help us to classify organisms according to their evolutionary history.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
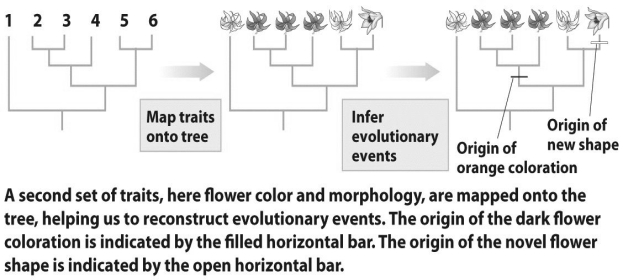 Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?
Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?A)Flower shape was used to infer this phylogenetic tree.
B)The origin of a new flower shape evolved after the origin of dark coloration.
C)The origin of a new flower shape evolved before the origin of dark coloration.
D)A and B
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements about pedigrees and phylogenies is true?
A)Both show the splitting and the recombining of branches or lineages over time.
B)A pedigree tells us about the ancestry of individuals, whereas most phylogenies tell us about the ancestry of populations.
C)Both expand as one looks backward in time.
D)All of the above
A)Both show the splitting and the recombining of branches or lineages over time.
B)A pedigree tells us about the ancestry of individuals, whereas most phylogenies tell us about the ancestry of populations.
C)Both expand as one looks backward in time.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Traits are critical in the study of phylogeny because
A)a phylogenetic tree is a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships.
B)we use observations of traits to infer patterns of ancestry and descent among populations.
C)by mapping individual traits onto a phylogeny we have already created, we can study the sequence and timing of evolutionary events.
D)A and C
E)B and C
A)a phylogenetic tree is a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships.
B)we use observations of traits to infer patterns of ancestry and descent among populations.
C)by mapping individual traits onto a phylogeny we have already created, we can study the sequence and timing of evolutionary events.
D)A and C
E)B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The study of phylogeny allows us to understand the
A)major events in evolutionary history.
C)relationships among taxa of organisms.
B)history of descent.
D)All of the above
A)major events in evolutionary history.
C)relationships among taxa of organisms.
B)history of descent.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
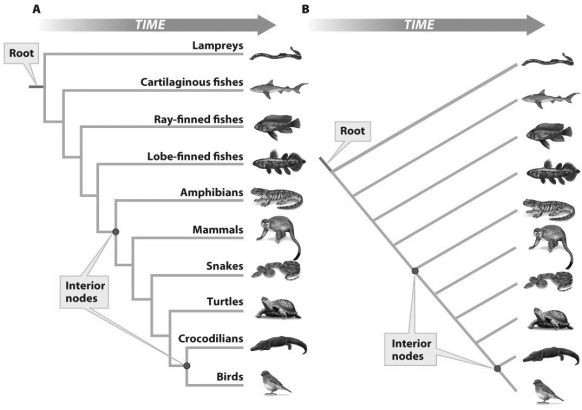
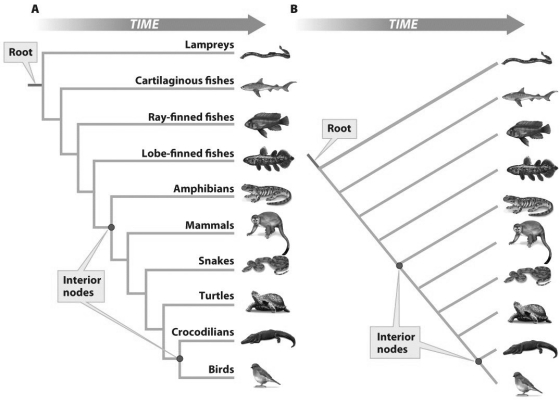 Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?
Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?A)The two phylogenies of the vertebrates shown illustrate exactly the same information.
B)The figure on the left (A) is sometimes referred to as a ladder representation.
C)The figure on the right (B) is sometimes referred to as a tree representation.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following pairs correctly matches the phylogenetic tree type (1,2,or 3)with the information it represents (i,ii,or iii).
1)Cladograms
2)Phylograms
3)Chronograms
I)A tree with aligned branch tips that indicates only the evolutionary relationships among the taxa shown
Ii)A tree in which branch lengths represent actual time rather than the amount of evolutionary change
Iii)A tree in which branch lengths represent the relative amount of evolutionary change
A)(1-i),(2-ii),and (3-iii)
C)(1-ii),(2-i),and (3-iii)
B)(1-i),(2-iii),and (3-ii)
D)(1-ii),(2-iii),and (3-i)
1)Cladograms
2)Phylograms
3)Chronograms
I)A tree with aligned branch tips that indicates only the evolutionary relationships among the taxa shown
Ii)A tree in which branch lengths represent actual time rather than the amount of evolutionary change
Iii)A tree in which branch lengths represent the relative amount of evolutionary change
A)(1-i),(2-ii),and (3-iii)
C)(1-ii),(2-i),and (3-iii)
B)(1-i),(2-iii),and (3-ii)
D)(1-ii),(2-iii),and (3-i)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778)
A)was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, and physician.
B)wrote Systema Naturae.
C)had the insight that organisms can be organized into a system hierarchical classification without having a theoretical explanation for why these patterns should exist.
D)All of the above
A)was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, and physician.
B)wrote Systema Naturae.
C)had the insight that organisms can be organized into a system hierarchical classification without having a theoretical explanation for why these patterns should exist.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
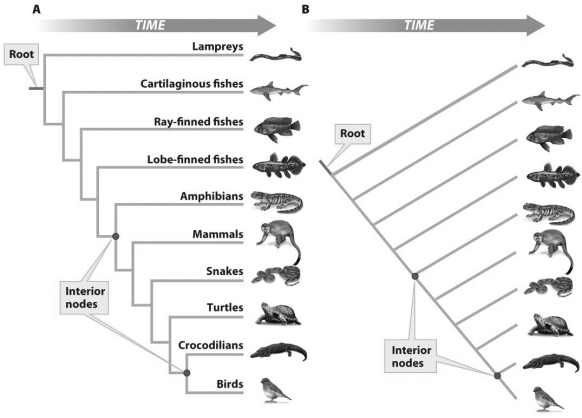 Based on the figure above,what does the lower interior node in each figure represent?
Based on the figure above,what does the lower interior node in each figure represent?A)An ancestral population
B)The common ancestor of birds and crocodilians
C)The common ancestor to all tetrapods
D)A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Charles Darwin
A)inferred the patterns of common ancestry without a mechanistic understanding of genes and heredity.
B)developed a hypothesis about past events that later became testable.
C)argued that humans descended from another primate species.
D)All of the above
A)inferred the patterns of common ancestry without a mechanistic understanding of genes and heredity.
B)developed a hypothesis about past events that later became testable.
C)argued that humans descended from another primate species.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
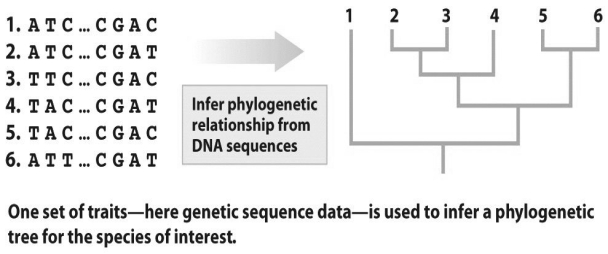 Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?
Based on the figure above,which of the following statements is true?A)There is a one base change between the analyzed sequences of lineages 1 and 2.
B)There is a one base change between the analyzed sequences of lineages 2 and 3.
C)The analyzed sequences of lineages 5 and 6 are the most similar.
D)A and B
E)B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
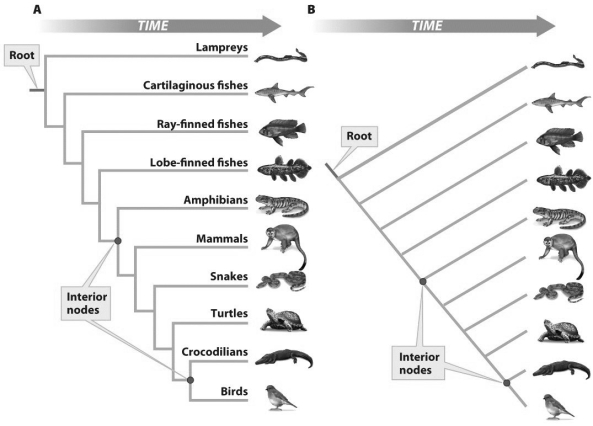 Based on the phylogenetic tree above,which of the following two groups are most closely related?
Based on the phylogenetic tree above,which of the following two groups are most closely related?A)Turtles and snakes
C)Birds and crocodilians
B)Ray-finned fishes and lobe-finned fishes
D)Mammals and snakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In what ways do the processes of reconstructing phylogenetic trees and mapping evolutionary events onto trees generate hypotheses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
 Considering the figure above,what are the sister taxa,outgroups,and polytomies in each of the trees?
Considering the figure above,what are the sister taxa,outgroups,and polytomies in each of the trees?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Give an example of two groups of closely related organisms that have developed divergent traits because natural selection has worked differently on them,and then contrast this with an example of two groups of organisms that share one or more similar traits from being exposed to similar selective conditions.Explain the selective processes that worked on the groups of organisms in both examples,and be sure to use the scientific term for each set of conditions.Try to use examples other than those presented in your text.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Homologous traits are found in two or more species because
A)some evolutionary process (usually natural selection) has independently fashioned similar traits in each species.
B)those traits are from a common ancestor.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above
A)some evolutionary process (usually natural selection) has independently fashioned similar traits in each species.
B)those traits are from a common ancestor.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
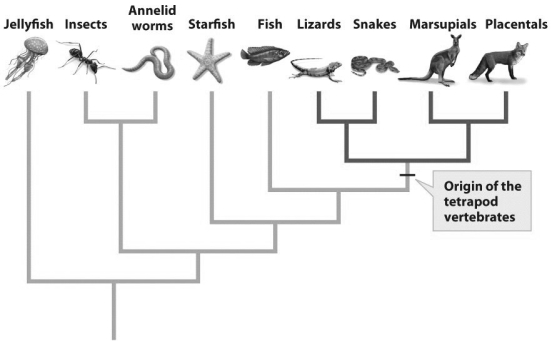 Vestigial traits serve as a strong test of Darwin's theory of evolution by common ancestry.Based on the figure above,in which limbless organisms would you expect to find vestigial limbs?
Vestigial traits serve as a strong test of Darwin's theory of evolution by common ancestry.Based on the figure above,in which limbless organisms would you expect to find vestigial limbs?A)Jellyfish
C)Fish
B)Annelid worms
D)Snakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What are the differences between rooted and unrooted phylogenetic trees?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider a set of populations in which,over evolutionary time,the coat color of one or more populations of organisms changes from light to dark.Using this example of light and dark coat coloration,describe what might occur to produce each of the following evolutionary conditions:
A.A derived trait
B.A synapomorphy
C.A homoplasy
D.A symplesiomorphy
A.A derived trait
B.A synapomorphy
C.A homoplasy
D.A symplesiomorphy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Give an example of two groups of organisms that share one or more similarities due to shared ancestry,and contrast this with an example of two groups of organisms that share one or more similarities because natural selection independently fashioned similar traits.Explain the shared ancestry and the selective processes that resulted in the similarities in each example.Be sure to use the scientific term for each set of similarities.Try to use examples other than those presented in your text.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following terms is used for a situation in which the derived trait has arisen recently and appears in only one of the two most related species or populations,while the two most distantly related groups share the same trait?
A)Homology
C)Homoplasy
B)Synapomorphy
D)Symplesiomorphy
A)Homology
C)Homoplasy
B)Synapomorphy
D)Symplesiomorphy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Although they serve no current functions,vestigial traits may persist in some organisms because
A)the trait is not costly to the organism.
B)natural selection does not act against the trait.
C)there is some natural selection against the trait, and it is on its way out-eventually will be lost.
D)All of the above
A)the trait is not costly to the organism.
B)natural selection does not act against the trait.
C)there is some natural selection against the trait, and it is on its way out-eventually will be lost.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider a population in which the coat color of a population or species changes from light to dark over evolutionary time.Using this example,draw an evolutionary tree to illustrate each of the following evolutionary conditions:
A.A derived trait
B.A homoplasy
C.A symplesiomorphy
A.A derived trait
B.A homoplasy
C.A symplesiomorphy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
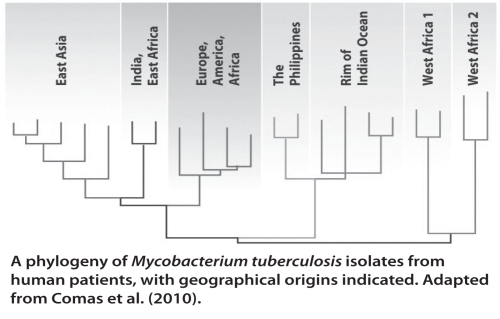 Examine the phylogenetic tree of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the figure above and give a possible explanation for the appearance of a split branch that has tips in both the Philippines and the rim of the Indian Ocean.
Examine the phylogenetic tree of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the figure above and give a possible explanation for the appearance of a split branch that has tips in both the Philippines and the rim of the Indian Ocean.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
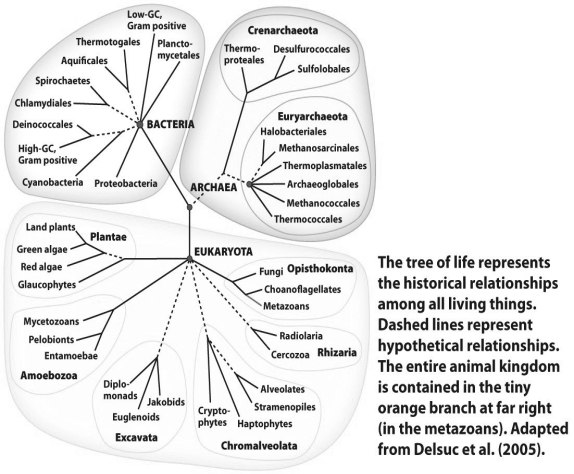 Examine the tree of life of all known living organisms in the figure above.Describe the relationship of the animal kingdom to the rest of life on Earth.
Examine the tree of life of all known living organisms in the figure above.Describe the relationship of the animal kingdom to the rest of life on Earth.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Analogous traits are found in two or more species because
A)some evolutionary process (usually natural selection) has independently fashioned similar traits in each species.
B)those traits are from a common ancestor.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above
A)some evolutionary process (usually natural selection) has independently fashioned similar traits in each species.
B)those traits are from a common ancestor.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
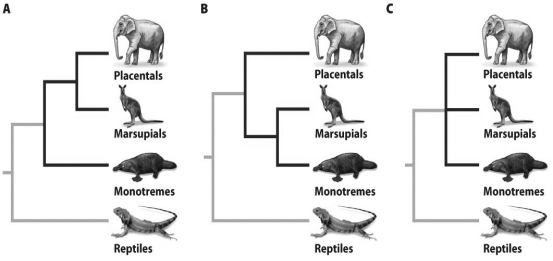
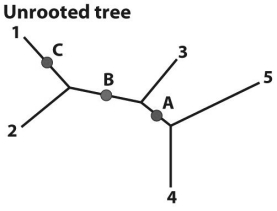 Based on the figure above,draw the three rooted trees that would result from rooting at each of the nodes (A,B,and C)indicated by the labeled dots.
Based on the figure above,draw the three rooted trees that would result from rooting at each of the nodes (A,B,and C)indicated by the labeled dots.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
By placing a given trait on a phylogenetic tree that we have already constructed using other data,we can
A)generate a hypothesis about when and how this trait evolved.
B)generate a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of the species in which those traits appear.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above
A)generate a hypothesis about when and how this trait evolved.
B)generate a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of the species in which those traits appear.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose a population splits into two descendant populations prior to the evolution of dark coloration,then splits again after the evolution of dark coloration.Which of the following terms best describes the dark coloration trait in this situation?
A)Homoplasy
C)Synapomorphy
B)Analogy
D)Symplesiomorphy
A)Homoplasy
C)Synapomorphy
B)Analogy
D)Symplesiomorphy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Convergent evolution occurs when
A)closely related populations or species diverge from one another because natural selection operates differently on each of them.
B)two or more populations or species become more similar to each other because they are exposed to similar selective conditions.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above
A)closely related populations or species diverge from one another because natural selection operates differently on each of them.
B)two or more populations or species become more similar to each other because they are exposed to similar selective conditions.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A trait that is similar in one or more species even though it was not present in their common ancestor is called a
A)homology.
C)homoplasy.
B)synapomorphy.
D)symplesiomorphy.
A)homology.
C)homoplasy.
B)synapomorphy.
D)symplesiomorphy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Divergent evolution occurs when
A)closely related populations or species diverge from one another because natural selection operates differently on each of them.
B)two or more populations or species become more similar to each other because they are exposed to similar selective conditions.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above
A)closely related populations or species diverge from one another because natural selection operates differently on each of them.
B)two or more populations or species become more similar to each other because they are exposed to similar selective conditions.
C)Both of the above
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
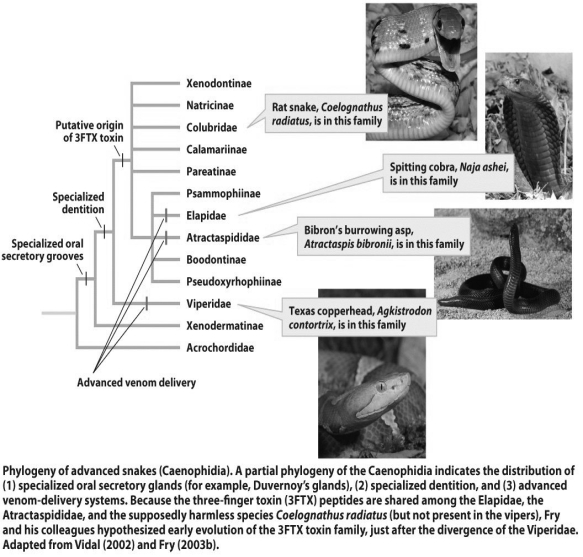 Considering the figure above,could you come up with an alternative hypothesis to the one proposed by Fry and his colleagues? Why or why not? If so,what would your alternative hypothesis be?
Considering the figure above,could you come up with an alternative hypothesis to the one proposed by Fry and his colleagues? Why or why not? If so,what would your alternative hypothesis be?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume you are an evolutionary biologist who is using coat coloration in several closely related species to reconstruct their evolutionary history.If you find that the coat color trait is symplesiomorphic,what can you do to resolve the species' evolutionary relationships?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
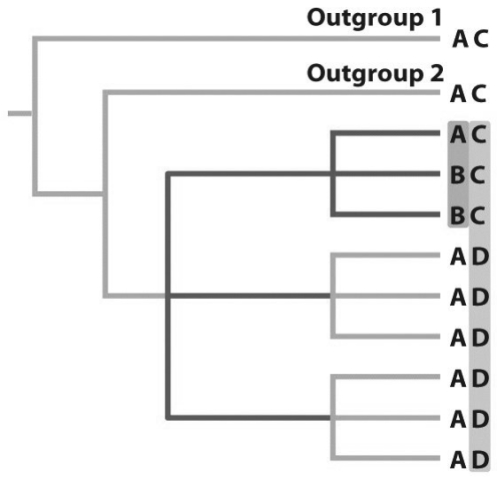 Based on the tree above,draw a tree that resolves two of the four polytomies and explain why you are able to do so using the tree above and your own illustrations.
Based on the tree above,draw a tree that resolves two of the four polytomies and explain why you are able to do so using the tree above and your own illustrations.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



