Deck 42: Animal Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/261
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 42: Animal Reproduction
1
Suppose three female sharks are housed without males in a large tank for many years.One morning the caretakers find a single pup swimming with one of the females.They test the pup's DNA and find that it is the same as that of the adult female.The pup likely resulted from
A) parthenogenesis.
B) budding.
C) regeneration.
D) sexual reproduction.
E) sexual reproduction with delayed fertilization.
A) parthenogenesis.
B) budding.
C) regeneration.
D) sexual reproduction.
E) sexual reproduction with delayed fertilization.
A
2
While examining histological sections derived from the ovaries of human females at various life stages, you come across a slide from the prenatal period.Which stages in egg development would you see on this slide?
A) Oogonia only
B) Oogonia and primary oocytes
C) Secondary oocytes
D) Primary oocytes only
E) Ova
A) Oogonia only
B) Oogonia and primary oocytes
C) Secondary oocytes
D) Primary oocytes only
E) Ova
B
3
Which statement about reproduction is true?
A) Asexual reproduction involves an inefficient use of resources.
B) Sexually reproducing species are found almost exclusively in relatively constant environments where genetic diversity is relatively unimportant.
C) Because it is produced by meiosis, a bud is genetically different from the parent.
D) Only lost limbs can be replaced by regeneration.
E) In some species, parthenogenesis requires all the sexual behaviors of courtship and mating.
A) Asexual reproduction involves an inefficient use of resources.
B) Sexually reproducing species are found almost exclusively in relatively constant environments where genetic diversity is relatively unimportant.
C) Because it is produced by meiosis, a bud is genetically different from the parent.
D) Only lost limbs can be replaced by regeneration.
E) In some species, parthenogenesis requires all the sexual behaviors of courtship and mating.
E
4
Which statement about asexual reproduction is true?
A) It occurs in some invertebrates but is not found in any vertebrate species.
B) Asexually reproducing species tend to live in variable environments.
C) Asexually reproducing species can adapt more quickly to environmental change than sexually reproducing species.
D) Asexual reproduction is more energy efficient than sexual reproduction.
E) Female tammar wallabies use a form of asexual reproduction when they become pregnant immediately after giving birth.
A) It occurs in some invertebrates but is not found in any vertebrate species.
B) Asexually reproducing species tend to live in variable environments.
C) Asexually reproducing species can adapt more quickly to environmental change than sexually reproducing species.
D) Asexual reproduction is more energy efficient than sexual reproduction.
E) Female tammar wallabies use a form of asexual reproduction when they become pregnant immediately after giving birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about asexual reproduction is true?
A) It must involve meiosis but not fertilization.
B) Males of an asexually reproducing population are necessarily diploid.
C) It allows single individuals to produce offspring.
D) It allows for the generation of genetic diversity in changing environments.
E) Offspring are always diploid.
A) It must involve meiosis but not fertilization.
B) Males of an asexually reproducing population are necessarily diploid.
C) It allows single individuals to produce offspring.
D) It allows for the generation of genetic diversity in changing environments.
E) Offspring are always diploid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sexual reproduction has an evolutionary advantage over asexual reproduction because it
A) results in both males and females of a species.
B) is a more lengthy process.
C) promotes genetic variability that potentially enables a population to adapt to a change in the environment.
D) is controlled by many hormonal mechanisms.
E) protects and nurtures the embryo.
A) results in both males and females of a species.
B) is a more lengthy process.
C) promotes genetic variability that potentially enables a population to adapt to a change in the environment.
D) is controlled by many hormonal mechanisms.
E) protects and nurtures the embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
While examining histological sections derived from the testes of human males at various life stages, you come across a slide from the prenatal period.Which cells would you see on this slide?
A) Spermatogonia
B) Spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes
C) Secondary spermatocytes
D) Spermatids
E) Sperm
A) Spermatogonia
B) Spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes
C) Secondary spermatocytes
D) Spermatids
E) Sperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Parthenogenesis
A) is theoretically possible but has never been confirmed in nature.
B) occurs only in fish.
C) is the development of offspring from unfertilized eggs.
D) allows some species to produce only males.
E) occurs in tammar wallabies.
A) is theoretically possible but has never been confirmed in nature.
B) occurs only in fish.
C) is the development of offspring from unfertilized eggs.
D) allows some species to produce only males.
E) occurs in tammar wallabies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which feature is usually associated with asexual reproduction?
A) Identical genetic makeup of parent and progeny
B) Fertilization
C) Spawning
D) Genetic diversity among the offspring
E) An inability to reproduce sexually
A) Identical genetic makeup of parent and progeny
B) Fertilization
C) Spawning
D) Genetic diversity among the offspring
E) An inability to reproduce sexually

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone.Removal of the ovaries in the parthenogenetic whiptail lizard Cnemidophorus uniparens would result in
A) the absence of male sexual behavior.
B) the presence of female sexual behavior.
C) repeated ovulations.
D) a switch to sexual reproduction.
E) the growth of testes.
A) the absence of male sexual behavior.
B) the presence of female sexual behavior.
C) repeated ovulations.
D) a switch to sexual reproduction.
E) the growth of testes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Reproduction in Cnemidophorus uniparens, a parthenogenetic species of whiptail lizard, requires sexual behavior, but all members of the species are female.How do these lizards reproduce?
A) Females hybridize with males of a related species, but accept only some of the chromosomes in the sperm.
B) Females that are the most fit temporarily become males, produce and transfer sperm to other females, and then revert to being females.
C) The least fit females temporarily become males, produce and transfer sperm to other females, and then revert to being female.
D) Females with high progesterone levels act like males, but they do not produce any sperm.
E) Females with high estrogen levels act like males, but they do not produce any sperm.
A) Females hybridize with males of a related species, but accept only some of the chromosomes in the sperm.
B) Females that are the most fit temporarily become males, produce and transfer sperm to other females, and then revert to being females.
C) The least fit females temporarily become males, produce and transfer sperm to other females, and then revert to being female.
D) Females with high progesterone levels act like males, but they do not produce any sperm.
E) Females with high estrogen levels act like males, but they do not produce any sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The sexual role assumed during courtship by an individual of the parthenogenetic whiptail lizard species Cnemidophorus uniparens
A) depends on its testosterone levels.
B) determines whether it will produce sperm.
C) depends on its current stage in the ovarian cycle.
D) determines whether it will fertilize its mate's eggs.
E) is determined at birth.
A) depends on its testosterone levels.
B) determines whether it will produce sperm.
C) depends on its current stage in the ovarian cycle.
D) determines whether it will fertilize its mate's eggs.
E) is determined at birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which cells result from the second meiotic division of spermatogenesis?
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which cell types differentiate into sperm cells at the end of spermatogenesis?
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which feature characterizes both spermatogenesis and oogenesis in humans?
A) A period of developmental arrest in prophase I of meiosis
B) Reproductive stem cells that arrive in the gonad during development and proliferate by mitosis
C) The production of four haploid gametes
D) The completion of a second meiotic division at fertilization
E) A period of developmental arrest after the first meiotic division
A) A period of developmental arrest in prophase I of meiosis
B) Reproductive stem cells that arrive in the gonad during development and proliferate by mitosis
C) The production of four haploid gametes
D) The completion of a second meiotic division at fertilization
E) A period of developmental arrest after the first meiotic division

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which are the initial products of germ cells that arrive in the male gonad?
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which cells are produced from mitotic divisions of spermatogonia but are no longer mitotic themselves?
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which are the first haploid germ cells produced in spermatogenesis?
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes
A) Sperm
B) Spermatogonia
C) Spermatids
D) Primary spermatocytes
E) Secondary spermatocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Budding and regeneration both
A) can lead to the production of a new individual through mitotic growth.
B) use meiosis to replace lost tissue.
C) can lead to the production of a new individual through meiotic growth.
D) serve as a trigger for the sexual phase of reproduction.
E) are restricted to simple multicellular animals.
A) can lead to the production of a new individual through mitotic growth.
B) use meiosis to replace lost tissue.
C) can lead to the production of a new individual through meiotic growth.
D) serve as a trigger for the sexual phase of reproduction.
E) are restricted to simple multicellular animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the early 1900s, oyster fishermen cut sea stars (starfish), which are predators of oysters, into pieces and threw them back into the sea.This practice led to an explosion in the sea star population because
A) other sea stars ate the pieces and were able to increase their reproductive output.
B) each arm with a portion of the central disc regenerated into a new individual.
C) competition was removed from the stronger sea stars that were not caught, allowing them to increase their reproductive output.
D) the oyster population grew in response to this new supply of food, allowing the population of their predators to increase as well.
E) each arm could form a new individual through budding.
A) other sea stars ate the pieces and were able to increase their reproductive output.
B) each arm with a portion of the central disc regenerated into a new individual.
C) competition was removed from the stronger sea stars that were not caught, allowing them to increase their reproductive output.
D) the oyster population grew in response to this new supply of food, allowing the population of their predators to increase as well.
E) each arm could form a new individual through budding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which event occurs during the process of fertilization in sea urchins?
A) Activation of spermatids
B) Species-specific binding of sperm to egg
C) Contribution by sperm of nutrients, mitochondria, and mitochondrial genes
D) Fusion of egg and sperm diploid nuclei
E) Fusion of sperm with cortical granules of the egg
A) Activation of spermatids
B) Species-specific binding of sperm to egg
C) Contribution by sperm of nutrients, mitochondria, and mitochondrial genes
D) Fusion of egg and sperm diploid nuclei
E) Fusion of sperm with cortical granules of the egg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In which animals is external fertilization relatively common?
A) Mammals
B) Birds
C) Fishes
D) Lizards
E) Snakes
A) Mammals
B) Birds
C) Fishes
D) Lizards
E) Snakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During oogenesis, the first haploid cell with abundant cytoplasm that is produced is the
A) second polar body.
B) primary oocyte.
C) secondary oocyte.
D) first polar body.
E) ootid.
A) second polar body.
B) primary oocyte.
C) secondary oocyte.
D) first polar body.
E) ootid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In humans, a primary oocyte is _______ and arrested in _______ of meiosis.
A) haploid; prophase I
B) diploid; prophase I
C) haploid; prophase II
D) diploid; prophase II
E) haploid; metaphase
A) haploid; prophase I
B) diploid; prophase I
C) haploid; prophase II
D) diploid; prophase II
E) haploid; metaphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
At which stage does the secondary oocyte resume meiosis in humans?
A) During prenatal development
B) At birth
C) When it is fertilized
D) At menopause
E) At puberty
A) During prenatal development
B) At birth
C) When it is fertilized
D) At menopause
E) At puberty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which statement about blocks to polyspermy in sea urchins is true?
A) The slow block creates a physical barrier that sperm cannot penetrate.
B) Blocks to polyspermy prevent more than one sperm from approaching an egg.
C) The fast block causes release of the acrosomal enzymes.
D) The fast block results from a change in the electrical charge difference across the plasma membrane of the sperm.
E) The slow block results from a sequestration of calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum of the egg.
A) The slow block creates a physical barrier that sperm cannot penetrate.
B) Blocks to polyspermy prevent more than one sperm from approaching an egg.
C) The fast block causes release of the acrosomal enzymes.
D) The fast block results from a change in the electrical charge difference across the plasma membrane of the sperm.
E) The slow block results from a sequestration of calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum of the egg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which product of oogenesis acquires the energy, raw materials, and RNA needed for the first cell divisions after fertilization?
A) Second polar body
B) Primary oocyte
C) Secondary oocyte
D) First polar body
E) Ootid
A) Second polar body
B) Primary oocyte
C) Secondary oocyte
D) First polar body
E) Ootid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You observe two species of amphibians mating in a stream.Species A is engaging in external fertilization and species B is engaging in internal fertilization.In which species would recognition molecules on gametes be more critical?
A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Recognition molecules would be equally critical in both species A and species B.
D) Neither, because vertebrates do not need recognition molecules on their gametes.
E) There is insufficient information to make a determination.
A) Species A
B) Species B
C) Recognition molecules would be equally critical in both species A and species B.
D) Neither, because vertebrates do not need recognition molecules on their gametes.
E) There is insufficient information to make a determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A simultaneous hermaphrodite
A) has primary sex organs of both sexes at the same time.
B) functions as a male at one time in its life and as a female at another.
C) develops from unfertilized eggs.
D) usually self-fertilizes.
E) has gonads that alternate between being ovaries and testes.
A) has primary sex organs of both sexes at the same time.
B) functions as a male at one time in its life and as a female at another.
C) develops from unfertilized eggs.
D) usually self-fertilizes.
E) has gonads that alternate between being ovaries and testes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which group of vertebrates includes some species that display internal fertilization without copulation?
A) Bony fishes
B) Cartilaginous fishes
C) Frogs
D) Salamanders
E) Birds
A) Bony fishes
B) Cartilaginous fishes
C) Frogs
D) Salamanders
E) Birds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Of the various stages of human life, the earliest time that an arrested primary oocyte would resume meiosis would be
A) during prenatal development.
B) at birth.
C) when it is fertilized.
D) at menopause.
E) at puberty.
A) during prenatal development.
B) at birth.
C) when it is fertilized.
D) at menopause.
E) at puberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In many species of birds, males lack a penis.Which statement about the reproductive process of these birds is true?
A) They cannot engage in internal fertilization.
B) They deposit sperm packets in the environment, where they are retrieved by a female and used to fertilize her eggs.
C) They engage in internal fertilization but without an accessory sex organ.
D) They engage in indirect sperm transfer.
E) Their offspring develop via parthenogenesis.
A) They cannot engage in internal fertilization.
B) They deposit sperm packets in the environment, where they are retrieved by a female and used to fertilize her eggs.
C) They engage in internal fertilization but without an accessory sex organ.
D) They engage in indirect sperm transfer.
E) Their offspring develop via parthenogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which feature is characteristic of animals with amniote eggs?
A) Production of an egg surrounded by a protective layer of jelly
B) External fertilization
C) Spawning
D) Primary sex organs in the absence of accessory sex organs
E) Reproduction in terrestrial environments
A) Production of an egg surrounded by a protective layer of jelly
B) External fertilization
C) Spawning
D) Primary sex organs in the absence of accessory sex organs
E) Reproduction in terrestrial environments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
While examining histological sections derived from the ovaries of human females at various life stages, you come across a slide labeled "Section of an ovary from a mature female." You would expect to find all of these cells on the slide except for a(n)
A) second polar body.
B) arrested primary oocyte.
C) secondary oocyte.
D) first polar body.
E) primary oocyte resuming meiosis.
A) second polar body.
B) arrested primary oocyte.
C) secondary oocyte.
D) first polar body.
E) primary oocyte resuming meiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When examining histological sections derived from the testes of male mammals, you come across cells that are near the lumen of the seminiferous tubules and connected by cytoplasmic bridges.Which cells have you found?
A) Leydig cells
B) Spermatogonia
C) Secondary spermatocytes and/or spermatids
D) Sertoli cells
E) Mature sperm
A) Leydig cells
B) Spermatogonia
C) Secondary spermatocytes and/or spermatids
D) Sertoli cells
E) Mature sperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which statement about sea urchin fertilization is true?
A) The bindin in the egg jelly causes the acrosome reaction.
B) Bindin attaches to receptors on the egg's cell membrane.
C) The acrosomal reaction helps sperm penetrate protective layers around the egg.
D) Activation of the sperm is species-specific but triggering the acrosomal reaction is not species-specific.
E) Enzymes from the egg's cortical granules trigger the fast block to polyspermy.
A) The bindin in the egg jelly causes the acrosome reaction.
B) Bindin attaches to receptors on the egg's cell membrane.
C) The acrosomal reaction helps sperm penetrate protective layers around the egg.
D) Activation of the sperm is species-specific but triggering the acrosomal reaction is not species-specific.
E) Enzymes from the egg's cortical granules trigger the fast block to polyspermy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Fertilization in mammals and sea urchins is similar in which way?
A) The first structure surrounding the egg with which the sperm comes in contact triggers the acrosomal reaction.
B) It occurs in the external environment.
C) Sperm recognition molecules occur on the egg plasma membrane.
D) Rises in calcium in the cytoplasm prevent entry by additional sperm.
E) The fast block to polyspermy occurs when there is a change in the electrical charge difference across the egg plasma membrane.
A) The first structure surrounding the egg with which the sperm comes in contact triggers the acrosomal reaction.
B) It occurs in the external environment.
C) Sperm recognition molecules occur on the egg plasma membrane.
D) Rises in calcium in the cytoplasm prevent entry by additional sperm.
E) The fast block to polyspermy occurs when there is a change in the electrical charge difference across the egg plasma membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which part of a mammalian egg is functionally similar to the vitelline envelope of a sea urchin egg?
A) Cumulus
B) Plasma membrane
C) Zona pellucida
D) Cytoplasm
E) Jelly coat
A) Cumulus
B) Plasma membrane
C) Zona pellucida
D) Cytoplasm
E) Jelly coat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which is the most likely advantage of hermaphroditism?
A) For a given species, every organism is a potential mate.
B) Compared to reproduction in dioecious species, simpler behavior patterns are required for mate selection.
C) More rapid reproduction of genetically successful individuals is possible through asexual reproduction compared to sexual reproduction.
D) Complex hormonal control and feedback mechanisms are not required for reproduction.
E) Complex primary sex organs are not required.
A) For a given species, every organism is a potential mate.
B) Compared to reproduction in dioecious species, simpler behavior patterns are required for mate selection.
C) More rapid reproduction of genetically successful individuals is possible through asexual reproduction compared to sexual reproduction.
D) Complex hormonal control and feedback mechanisms are not required for reproduction.
E) Complex primary sex organs are not required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
You observe a zebrafish pair in a tank and notice that first the male chases after the female, then the female releases eggs, and then the male releases sperm on top of the eggs.The most likely adaptive advantage to this behavior is that it
A) creates a bond between the male and female that will be important for raising the fish larvae.
B) ensures that the breeding pair knows where their fertilized eggs are and can thereby care for them through embryonic development.
C) enhances the likelihood that sperm and eggs of the same species will meet.
D) allows sperm to fertilize the amniote eggs before the shells harden.
E) assures that a female breeds with only one male.
A) creates a bond between the male and female that will be important for raising the fish larvae.
B) ensures that the breeding pair knows where their fertilized eggs are and can thereby care for them through embryonic development.
C) enhances the likelihood that sperm and eggs of the same species will meet.
D) allows sperm to fertilize the amniote eggs before the shells harden.
E) assures that a female breeds with only one male.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the mammalian ovary, granulosa cells of the follicle produce inhibin, which makes them similar to
A) thecal cells of the follicle.
B) Leydig cells in the testes of males.
C) endometrial cells.
D) Sertoli cells in the testes of males.
E) cells of the corpus luteum.
A) thecal cells of the follicle.
B) Leydig cells in the testes of males.
C) endometrial cells.
D) Sertoli cells in the testes of males.
E) cells of the corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the figure showing male reproductive hormones. 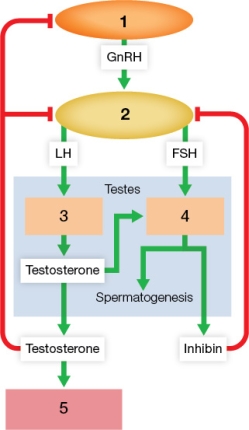 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?
A) Inhibin exerts negative feedback on the structure at point 1.
B) Circulating testosterone inhibits the release of FSH from the structure at point 2.
C) Examples of structures at point 5 are genitals, larynx, and skeletal muscles.
D) The cells at point 3 are located inside seminiferous tubules.
E) Low levels of circulating testosterone inhibit the structure at point 2.
 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?A) Inhibin exerts negative feedback on the structure at point 1.
B) Circulating testosterone inhibits the release of FSH from the structure at point 2.
C) Examples of structures at point 5 are genitals, larynx, and skeletal muscles.
D) The cells at point 3 are located inside seminiferous tubules.
E) Low levels of circulating testosterone inhibit the structure at point 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which is the correct sequence of structures through which a mammalian sperm passes before fertilizing an egg?
A) Uterus, vagina, cervix, oviduct, ovary
B) Vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct
C) Oviduct, uterus, vagina, ovary, body cavity
D) Vagina, cervix, oviduct, uterus
E) Vagina, uterus, oviduct, body cavity
A) Uterus, vagina, cervix, oviduct, ovary
B) Vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct
C) Oviduct, uterus, vagina, ovary, body cavity
D) Vagina, cervix, oviduct, uterus
E) Vagina, uterus, oviduct, body cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the figure showing the human male reproductive system. 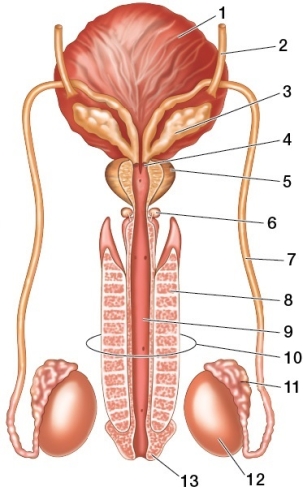 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?
A) The structure at point 7 is cut in a vasectomy.
B) The structure at point 11 is the ejaculatory duct.
C) The structure at point 7 joins the bladder.
D) The structure at point 5 contributes an acidic fluid that makes up about 30 percent of the volume of semen.
E) The structure at point 6 is the seminal vesicle, which contributes fructose to the semen.
 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?A) The structure at point 7 is cut in a vasectomy.
B) The structure at point 11 is the ejaculatory duct.
C) The structure at point 7 joins the bladder.
D) The structure at point 5 contributes an acidic fluid that makes up about 30 percent of the volume of semen.
E) The structure at point 6 is the seminal vesicle, which contributes fructose to the semen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If a woman has scar tissue completely blocking both of her oviducts about halfway down their length, which event would be impossible without medical intervention?
A) Fertilization
B) Ovulation
C) Buildup of the endometrium
D) Menstruation
E) Formation of the corpus luteum
A) Fertilization
B) Ovulation
C) Buildup of the endometrium
D) Menstruation
E) Formation of the corpus luteum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which would be an expected outcome of removal of the prostate gland?
A) Decrease in volume of semen by 60 percent
B) Decrease in the pH of the male reproductive tract
C) Failure of fibrinogen to convert semen into a gelatinous mass
D) Greater survival of sperm once in the female reproductive tract
E) Absence of secretions preceding climax
A) Decrease in volume of semen by 60 percent
B) Decrease in the pH of the male reproductive tract
C) Failure of fibrinogen to convert semen into a gelatinous mass
D) Greater survival of sperm once in the female reproductive tract
E) Absence of secretions preceding climax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In mammals, the egg is propelled through the oviduct by means of
A) cilia on the surface of the egg.
B) the egg's flagellum.
C) uterine contractions.
D) cilia lining the oviduct.
E) amoeboid motion.
A) cilia on the surface of the egg.
B) the egg's flagellum.
C) uterine contractions.
D) cilia lining the oviduct.
E) amoeboid motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Drugs used to treat erectile dysfunction act to
A) block nitric oxide (NO).
B) prolong the effects of nitric oxide (NO).
C) increase testosterone.
D) increase gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
E) prolong the activity of enzymes that break down the second messenger cGMP.
A) block nitric oxide (NO).
B) prolong the effects of nitric oxide (NO).
C) increase testosterone.
D) increase gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
E) prolong the activity of enzymes that break down the second messenger cGMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Testosterone can fuel prostate cancer.Which approach might be included in treatments designed to lower testosterone in a patient with advanced prostate cancer?
A) Blocking luteinizing hormone (LH)
B) Increasing numbers of Leydig cells with growth factors
C) Treating with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
D) Treating with an antagonist to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
E) Cutting and tying off the vas deferens associated with each testis
A) Blocking luteinizing hormone (LH)
B) Increasing numbers of Leydig cells with growth factors
C) Treating with gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
D) Treating with an antagonist to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
E) Cutting and tying off the vas deferens associated with each testis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the hypothalamus in a human male does not produce sufficient GnRH, the
A) man will make functional sperm but is unable to ejaculate.
B) man's sperm will lack functional flagella.
C) fluid that usually lubricates the man's urethra for sperm travel will be defective.
D) man's semen will lack the fructose fuel required for the sperm to swim.
E) man's Leydig cells will not make the testosterone necessary to stimulate spermatogenesis.
A) man will make functional sperm but is unable to ejaculate.
B) man's sperm will lack functional flagella.
C) fluid that usually lubricates the man's urethra for sperm travel will be defective.
D) man's semen will lack the fructose fuel required for the sperm to swim.
E) man's Leydig cells will not make the testosterone necessary to stimulate spermatogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the figure showing the human male reproductive system.  Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?
A) While exiting the male, sperm go from point 11 to point 12 to point 3 to point 5.
B) The structure shown at point 6 produces a neutralizing and lubricating solution.
C) The material shown at point 8 is muscle tissue that contracts to produce an erection.
D) Mature sperm are stored in the structure at point 12.
E) Seminal fluids are produced by the structures at points 3, 5, 6, and 11.
 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?A) While exiting the male, sperm go from point 11 to point 12 to point 3 to point 5.
B) The structure shown at point 6 produces a neutralizing and lubricating solution.
C) The material shown at point 8 is muscle tissue that contracts to produce an erection.
D) Mature sperm are stored in the structure at point 12.
E) Seminal fluids are produced by the structures at points 3, 5, 6, and 11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Mammals differ from other amniotes in that
A) most species are ovoviviparous.
B) they have internal fertilization.
C) most species have a placenta.
D) they have paired ovaries.
E) they protect their offspring internally until birth.
A) most species are ovoviviparous.
B) they have internal fertilization.
C) most species have a placenta.
D) they have paired ovaries.
E) they protect their offspring internally until birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A human female has the most primary oocytes in her ovaries
A) at birth.
B) just before puberty.
C) early in her fertile years.
D) midway through her fertile years.
E) at menopause.
A) at birth.
B) just before puberty.
C) early in her fertile years.
D) midway through her fertile years.
E) at menopause.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the mammalian ovary, granulosa cells of the follicle are stimulated by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to grow and mature.Granulosa cells are therefore similar to
A) thecal cells of the follicle.
B) Leydig cells in the testes of males.
C) endometrial cells.
D) Sertoli cells in the testes of males.
E) cells of the corpus luteum.
A) thecal cells of the follicle.
B) Leydig cells in the testes of males.
C) endometrial cells.
D) Sertoli cells in the testes of males.
E) cells of the corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the mammalian ovary, thecal cells of the follicle are stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) to produce testosterone.Thecal cells are therefore similar to
A) granulosa cells of the follicle.
B) Leydig cells in the testes of males.
C) Sertoli cells in the testes of males.
D) primary oocytes.
E) cells of the corpus luteum.
A) granulosa cells of the follicle.
B) Leydig cells in the testes of males.
C) Sertoli cells in the testes of males.
D) primary oocytes.
E) cells of the corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A tumor in a Leydig cell would most directly affect the
A) production of inhibin.
B) production of testosterone.
C) secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
D) secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
E) secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH).
A) production of inhibin.
B) production of testosterone.
C) secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
D) secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
E) secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Mammalian semen is made up primarily of
A) seminal fluid.
B) Sertoli cells, which provide nutrients for the sperm.
C) alkaline secretions from the prostate gland.
D) sperm.
E) fibrinogen.
A) seminal fluid.
B) Sertoli cells, which provide nutrients for the sperm.
C) alkaline secretions from the prostate gland.
D) sperm.
E) fibrinogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which anatomical feature(s) is/are shared by both the reproductive and excretory systems in most male mammals?
A) Prostate gland
B) Seminiferous tubules
C) Vas deferens
D) Urethra
E) Epididymis
A) Prostate gland
B) Seminiferous tubules
C) Vas deferens
D) Urethra
E) Epididymis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A complete blockage in the vas deferens at the end closest to the testis would cause newly matured sperm to remain in the
A) seminiferous tubules.
B) urethra.
C) lumens of the seminiferous tubules.
D) epididymis.
E) vas deferens.
A) seminiferous tubules.
B) urethra.
C) lumens of the seminiferous tubules.
D) epididymis.
E) vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the seminal vesicles in a human male are defective, the
A) man will make functional sperm but be unable to ejaculate.
B) man's sperm will lack functional flagella.
C) fluid needed to lubricate the man's urethra for easier sperm travel will be defective.
D) man's semen will lack the fructose fuel needed for the sperm to swim.
E) man's Leydig cells will not make the testosterone required to stimulate spermatogenesis.
A) man will make functional sperm but be unable to ejaculate.
B) man's sperm will lack functional flagella.
C) fluid needed to lubricate the man's urethra for easier sperm travel will be defective.
D) man's semen will lack the fructose fuel needed for the sperm to swim.
E) man's Leydig cells will not make the testosterone required to stimulate spermatogenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Birth control pills containing synthetic estrogen and progesterone inhibit the ovarian cycle.A similar situation occurs during pregnancy, when levels of estrogen and progesterone are high.During pregnancy, progesterone is produced first by the _______ and then by the _______.
A) placenta; corpus luteum
B) placenta; fetus
C) corpus luteum; follicles remaining in the ovary
D) anterior pituitary; hypothalamus
E) corpus luteum; placenta
A) placenta; corpus luteum
B) placenta; fetus
C) corpus luteum; follicles remaining in the ovary
D) anterior pituitary; hypothalamus
E) corpus luteum; placenta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the graph showing changes in three female reproductive hormones during pregnancy. 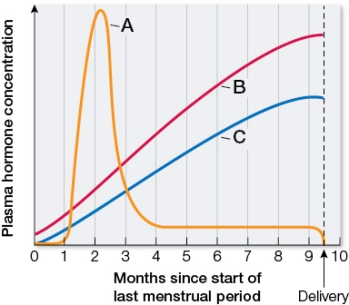 Based on the graph, which statement is true?
Based on the graph, which statement is true?
A) Pregnancy tests detect the presence of the hormone in curve A.
B) The hormone in curve B stimulates ovulation.
C) The hormone in curve C stimulates growth of follicles.
D) The decreasing ratio of the hormone in curve B to the hormone in curve C over the course of pregnancy stimulates uterine contractions.
E) The hormone in curve A stimulates the corpus luteum to degenerate.
 Based on the graph, which statement is true?
Based on the graph, which statement is true?A) Pregnancy tests detect the presence of the hormone in curve A.
B) The hormone in curve B stimulates ovulation.
C) The hormone in curve C stimulates growth of follicles.
D) The decreasing ratio of the hormone in curve B to the hormone in curve C over the course of pregnancy stimulates uterine contractions.
E) The hormone in curve A stimulates the corpus luteum to degenerate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In placental mammals, the blastocyst normally implants within the
A) oviducts.
B) ovary.
C) endometrium of the uterus.
D) myometrium of the vagina.
E) chorion.
A) oviducts.
B) ovary.
C) endometrium of the uterus.
D) myometrium of the vagina.
E) chorion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which hormone would decline immediately after a bilateral oophorectomy (surgical removal of both ovaries)?
A) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
B) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D) Prolactin
E) Estrogen
A) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
B) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
C) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D) Prolactin
E) Estrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the graph showing changes in three female reproductive hormones during pregnancy. 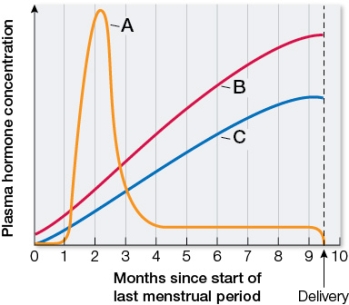 Based on the graph, which statement is true?
Based on the graph, which statement is true?
A) Curve A represents levels of luteinizing hormone (LH).
B) Curve B represents progesterone levels.
C) Curve C represents a hormone responsible for maintaining the endometrium.
D) Curve A represents a hormone secreted by ovaries.
E) Curve B represents a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary.
 Based on the graph, which statement is true?
Based on the graph, which statement is true?A) Curve A represents levels of luteinizing hormone (LH).
B) Curve B represents progesterone levels.
C) Curve C represents a hormone responsible for maintaining the endometrium.
D) Curve A represents a hormone secreted by ovaries.
E) Curve B represents a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Some patients with breast cancer receive aromatase inhibitors as part of their medical treatment.Such an inhibitor causes
A) enhanced growth and maturation of granulosa cells in the ovary.
B) enhanced secretion of inhibin.
C) low progesterone levels.
D) low estrogen levels.
E) maintenance of the corpus luteum.
A) enhanced growth and maturation of granulosa cells in the ovary.
B) enhanced secretion of inhibin.
C) low progesterone levels.
D) low estrogen levels.
E) maintenance of the corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which statement represents the principal difference between the uterine cycle of humans and the cycles of other mammals?
A) The uterine cycles of other mammals occur if fertilization occurs, whereas the uterine cycle of humans occurs if fertilization does not occur.
B) The uterine cycle of humans occurs if fertilization occurs, whereas the uterine cycles of most mammals occur if fertilization does not occur.
C) The uterine cycles of most other mammals lack menstruation.
D) The uterine cycles of most other mammals do not involve any changes to the uterine lining.
E) Peaks of progesterone in the uterine cycles of most other mammals correspond to periods of enhanced sexual receptivity referred to as estrus or "heat."
A) The uterine cycles of other mammals occur if fertilization occurs, whereas the uterine cycle of humans occurs if fertilization does not occur.
B) The uterine cycle of humans occurs if fertilization occurs, whereas the uterine cycles of most mammals occur if fertilization does not occur.
C) The uterine cycles of most other mammals lack menstruation.
D) The uterine cycles of most other mammals do not involve any changes to the uterine lining.
E) Peaks of progesterone in the uterine cycles of most other mammals correspond to periods of enhanced sexual receptivity referred to as estrus or "heat."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Pregnancy tests that can be done at home detect the presence of
A) luteinizing hormone.
B) follicle-stimulating hormone.
C) human chorionic gonadotropin.
D) estrogen.
E) progesterone.
A) luteinizing hormone.
B) follicle-stimulating hormone.
C) human chorionic gonadotropin.
D) estrogen.
E) progesterone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In women, new follicles do not mature as long as the corpus luteum is maintained because
A) hormones released from the corpus luteum inhibit gonadotropin release.
B) hormones released from the corpus luteum inhibit ovarian secretion.
C) the ovary receives negative feedback from the endometrial lining of the uterus.
D) there is insufficient energy to support both maintenance of the corpus luteum and follicle development.
E) hormones released from the corpus luteum inhibit buildup of the endometrium.
A) hormones released from the corpus luteum inhibit gonadotropin release.
B) hormones released from the corpus luteum inhibit ovarian secretion.
C) the ovary receives negative feedback from the endometrial lining of the uterus.
D) there is insufficient energy to support both maintenance of the corpus luteum and follicle development.
E) hormones released from the corpus luteum inhibit buildup of the endometrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Mifepristone (formerly called RU-486) terminates a pregnancy by blocking the action of progesterone.The termination occurs because progesterone is needed to
A) maintain the endometrium.
B) trigger ovulation.
C) prompt formation of the corpus luteum.
D) promote ovarian development.
E) initiate degeneration of the corpus luteum.
A) maintain the endometrium.
B) trigger ovulation.
C) prompt formation of the corpus luteum.
D) promote ovarian development.
E) initiate degeneration of the corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The _______ cycles of most mammals, other than humans, do not include _______.
A) uterine; buildup of the endometrium
B) uterine; menstruation
C) ovarian; formation of a corpus luteum
D) reproductive; a distinct period of sexual receptivity
E) uterine; a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) before ovulation
A) uterine; buildup of the endometrium
B) uterine; menstruation
C) ovarian; formation of a corpus luteum
D) reproductive; a distinct period of sexual receptivity
E) uterine; a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) before ovulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure depicting the average blood concentrations of four circulating hormones in 100 healthy adult women.Each hormone plays a role in regulating some aspect of the ovarian and/or uterine cycle. 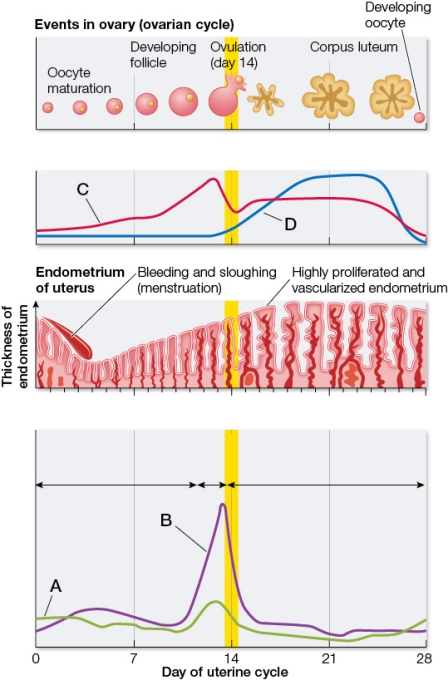 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?
A) Curve A represents luteinizing hormone (LH) levels.
B) Curve B represents progesterone levels.
C) Curve C represents a hormone secreted from the anterior pituitary gland.
D) Curve D represents a hormone produced by the corpus luteum.
E) Curve A represents a hormone secreted by the ovary.
 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?A) Curve A represents luteinizing hormone (LH) levels.
B) Curve B represents progesterone levels.
C) Curve C represents a hormone secreted from the anterior pituitary gland.
D) Curve D represents a hormone produced by the corpus luteum.
E) Curve A represents a hormone secreted by the ovary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
At birth, a female has about one million primary oocytes in each ovary.During a woman's fertile years, about _______ of these oocytes will mature and be released at ovulation.
A) 100
B) 450
C) 900
D) 2,000
E) 4,500
A) 100
B) 450
C) 900
D) 2,000
E) 4,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Women are encouraged to nurse their babies as soon as possible after giving birth because
A) prolactin released in response to a baby's suckling promotes the mother-child bond.
B) oxytocin released in response to a baby's suckling augments uterine contractions, which helps to reduce the size of the uterus and stop bleeding.
C) such contact prompts the release of pain-reducing chemicals by the brain.
D) the absence of a baby's crying stimulates greater release of oxytocin.
E) the infant needs immediate nutrition, since it can no longer rely on the placenta.
A) prolactin released in response to a baby's suckling promotes the mother-child bond.
B) oxytocin released in response to a baby's suckling augments uterine contractions, which helps to reduce the size of the uterus and stop bleeding.
C) such contact prompts the release of pain-reducing chemicals by the brain.
D) the absence of a baby's crying stimulates greater release of oxytocin.
E) the infant needs immediate nutrition, since it can no longer rely on the placenta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the figure showing the human female reproductive system. 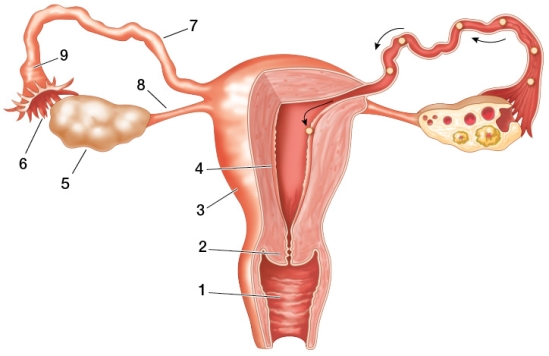 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?
A) The structure at point 1 is covered by a diaphragm, placed immediately below it, as a form of birth control.
B) The structure at point 8 is tied off during female sterilization.
C) Progesterone receptors in the structure at point 4 are blocked by Mifepristone (RU-486).
D) Spermicidal jelly is applied to the structure at point 4.
E) The cycle of the structure at point 3 is stopped by combination estrogen and progesterone birth control pills.
 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?A) The structure at point 1 is covered by a diaphragm, placed immediately below it, as a form of birth control.
B) The structure at point 8 is tied off during female sterilization.
C) Progesterone receptors in the structure at point 4 are blocked by Mifepristone (RU-486).
D) Spermicidal jelly is applied to the structure at point 4.
E) The cycle of the structure at point 3 is stopped by combination estrogen and progesterone birth control pills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Refer to the figure depicting the average blood concentrations of four circulating hormones in 100 healthy adult women.Each hormone plays a role in regulating some aspect of the ovarian and/or uterine cycle. 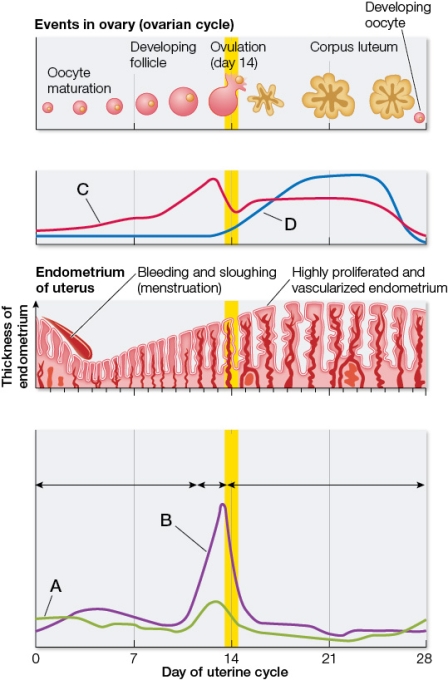 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?
A) The hormone represented by curve A is released by the anterior pituitary in response to GnRH.
B) The hormone represented by curve B is secreted by the developing follicle.
C) The hormone represented by curve C stimulates growth of the follicle.
D) The hormone represented by curve D stimulates ovulation.
E) The hormone represented by curve A is produced by the hypothalamus.
 Based on the figure, which statement is true?
Based on the figure, which statement is true?A) The hormone represented by curve A is released by the anterior pituitary in response to GnRH.
B) The hormone represented by curve B is secreted by the developing follicle.
C) The hormone represented by curve C stimulates growth of the follicle.
D) The hormone represented by curve D stimulates ovulation.
E) The hormone represented by curve A is produced by the hypothalamus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In human males and females, a tumor on the anterior pituitary would most immediately affect secretion of _______ and _______.
A) follicle-stimulating hormone; estrogen
B) estrogen; progesterone
C) follicle-stimulating hormone; progesterone
D) luteinizing hormone; progesterone
E) luteinizing hormone; follicle-stimulating hormone
A) follicle-stimulating hormone; estrogen
B) estrogen; progesterone
C) follicle-stimulating hormone; progesterone
D) luteinizing hormone; progesterone
E) luteinizing hormone; follicle-stimulating hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which hormone might be given to a woman who has experienced recurrent miscarriages?
A) Progesterone
B) Oxytocin
C) Prolactin
D) Inhibin
E) Human chorionic gonadotropin
A) Progesterone
B) Oxytocin
C) Prolactin
D) Inhibin
E) Human chorionic gonadotropin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In women, a drug that blocks the LH surge would most immediately prevent
A) a peak in estrogen.
B) ovulation.
C) a peak in progesterone.
D) implantation of a fertilized egg.
E) degeneration of the corpus luteum.
A) a peak in estrogen.
B) ovulation.
C) a peak in progesterone.
D) implantation of a fertilized egg.
E) degeneration of the corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A woman develops a somatic mutation that prevents the thecal cells in one of her ovaries from producing testosterone.The most likely result of this mutation is that the
A) granulosa cells in the affected ovary will cause multiple follicles to mature simultaneously.
B) follicles in the affected ovary will be incapable of maturing and releasing oocytes.
C) granulosa cells in the affected ovary will produce a greater amount of estrogen than normal.
D) woman will ovulate multiple eggs during each ovarian cycle.
E) woman will have only anovulatory (non-ovulatory) cycles and will therefore be infertile.
A) granulosa cells in the affected ovary will cause multiple follicles to mature simultaneously.
B) follicles in the affected ovary will be incapable of maturing and releasing oocytes.
C) granulosa cells in the affected ovary will produce a greater amount of estrogen than normal.
D) woman will ovulate multiple eggs during each ovarian cycle.
E) woman will have only anovulatory (non-ovulatory) cycles and will therefore be infertile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



