Deck 45: Sensory Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/249
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 45: Sensory Systems
1
Some prescription drugs have the side effect of interfering with the senses of taste and smell.One explanation for this side effect is that these drugs may
A) bind to chemoreceptors in the nasal cavity and tongue.
B) inactivate an electroreceptor.
C) diminish the stretch response.
D) chemically block a pressure-sensitive cation channel.
E) increase the activity of thermoreceptors.
A) bind to chemoreceptors in the nasal cavity and tongue.
B) inactivate an electroreceptor.
C) diminish the stretch response.
D) chemically block a pressure-sensitive cation channel.
E) increase the activity of thermoreceptors.
A
2
A(n) _______ is a change in the membrane potential of a sensory receptor cell in response to a stimulus.
A) receptor potential
B) action potential
C) all-or-none signal
D) transduction signal
E) sensory potential
A) receptor potential
B) action potential
C) all-or-none signal
D) transduction signal
E) sensory potential
receptor potential
3
Which statement about receptor potentials is false?
A) They are graded membrane potentials.
B) A receptor potential represents a change in membrane potential of a receptor cell caused by a specific stimulus.
C) They must generate action potentials to signal over long distances.
D) The generation of receptor potentials is the last step in sensory adaptation.
E) They spread only short distances.
A) They are graded membrane potentials.
B) A receptor potential represents a change in membrane potential of a receptor cell caused by a specific stimulus.
C) They must generate action potentials to signal over long distances.
D) The generation of receptor potentials is the last step in sensory adaptation.
E) They spread only short distances.
D
4
The magnitude of a receptor potential in the stretch receptor of a crayfish
A) depends on the strength of the incoming action potential.
B) remains high even after a long period of stimulation.
C) is the same for all types of stimuli.
D) depends on the amount of neurotransmitter released.
E) depends on how much the muscle is stretched.
A) depends on the strength of the incoming action potential.
B) remains high even after a long period of stimulation.
C) is the same for all types of stimuli.
D) depends on the amount of neurotransmitter released.
E) depends on how much the muscle is stretched.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If you brush against a doorway as you enter a room, you will trigger
A) an electric current that opens a calcium channel.
B) the opening of a pressure-sensitive cation channel.
C) a G protein.
D) a second messenger system.
E) a signal transduction cascade.
A) an electric current that opens a calcium channel.
B) the opening of a pressure-sensitive cation channel.
C) a G protein.
D) a second messenger system.
E) a signal transduction cascade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The intensity of a given sensation
A) depends on which area of the brain receives action potentials.
B) is determined by the frequency of action potentials.
C) reflects the type of sensory receptor cell.
D) is determined by the amplitude of action potentials.
E) reflects whether stimuli directly or indirectly open or close ion channels.
A) depends on which area of the brain receives action potentials.
B) is determined by the frequency of action potentials.
C) reflects the type of sensory receptor cell.
D) is determined by the amplitude of action potentials.
E) reflects whether stimuli directly or indirectly open or close ion channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Drugs that block G proteins will affect
A) mechanoreceptors and thermoreceptors.
B) electroreceptors and mechanoreceptors.
C) thermoreceptors and electroreceptors.
D) chemoreceptors and photoreceptors.
E) electroreceptors and chemoreceptors.
A) mechanoreceptors and thermoreceptors.
B) electroreceptors and mechanoreceptors.
C) thermoreceptors and electroreceptors.
D) chemoreceptors and photoreceptors.
E) electroreceptors and chemoreceptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Sensory receptor cells transduce specific physical or chemical stimuli
A) from an action potential to a receptor potential.
B) into a change in membrane potential.
C) from an action potential into a synaptic signal.
D) by summing local potentials.
E) by amplification of the stimulus.
A) from an action potential to a receptor potential.
B) into a change in membrane potential.
C) from an action potential into a synaptic signal.
D) by summing local potentials.
E) by amplification of the stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which sensory receptor proteins respond to stimuli by directly opening or closing ion channels?
A) Photoreceptors and mechanoreceptors
B) Chemoreceptors and thermoreceptors
C) Thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors
D) Chemoreceptors and electroreceptors
E) Photoreceptors and electroreceptors
A) Photoreceptors and mechanoreceptors
B) Chemoreceptors and thermoreceptors
C) Thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors
D) Chemoreceptors and electroreceptors
E) Photoreceptors and electroreceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
_______ are cells of the nervous system that transduce physical or chemical stimuli into receptor potentials, which generate action potentials for transmission to other parts of the nervous system for processing and interpretation.
A) Receptor proteins
B) Effectors
C) Glial cells
D) Ion channels
E) Sensory receptor cells
A) Receptor proteins
B) Effectors
C) Glial cells
D) Ion channels
E) Sensory receptor cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Bright light shining into one's eye will directly trigger
A) an electric current that opens calcium channels.
B) the opening of a cation channel.
C) chemoreceptor binding.
D) the opening of voltage-gated channels.
E) a G protein and second messenger.
A) an electric current that opens calcium channels.
B) the opening of a cation channel.
C) chemoreceptor binding.
D) the opening of voltage-gated channels.
E) a G protein and second messenger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The receptor potential of a stretch receptor in the muscle of a crayfish
A) is generated by an action potential from the same cell.
B) spreads when ion channels in the cell's dendrites are opened.
C) starts at the axon.
D) decreases when the muscle is stretched.
E) is created by the opening of ion channels in the axon.
A) is generated by an action potential from the same cell.
B) spreads when ion channels in the cell's dendrites are opened.
C) starts at the axon.
D) decreases when the muscle is stretched.
E) is created by the opening of ion channels in the axon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An ice cube placed on your hand will cause some cells to fire action potentials more frequently and other cells to reduce the number fired.What explains the different responses?
A) Thermoreceptors will detect the cold and slow down the rate of firing.
B) A pressure-sensitive channel will increase its firing rate due to the weight of the ice cube.
C) Some sensory cells will interpret the ice cube as painful and slow down their firing rate.
D) There are both warm- and cold-sensitive receptors in the skin.
E) Only the receptors that the ice cube actually touches will slow down their firing rate.
A) Thermoreceptors will detect the cold and slow down the rate of firing.
B) A pressure-sensitive channel will increase its firing rate due to the weight of the ice cube.
C) Some sensory cells will interpret the ice cube as painful and slow down their firing rate.
D) There are both warm- and cold-sensitive receptors in the skin.
E) Only the receptors that the ice cube actually touches will slow down their firing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which behavior results from the adaptation of sensory cells?
A) Going into a deep sleep
B) Discriminating different colors
C) Ignoring your shoes as you walk
D) Detecting high-pitched notes
E) Detecting sound and light simultaneously
A) Going into a deep sleep
B) Discriminating different colors
C) Ignoring your shoes as you walk
D) Detecting high-pitched notes
E) Detecting sound and light simultaneously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following best represents the order of the flow of information from a muscle in a crayfish that will ultimately generate an action potential in the crayfish stretch receptor neuron?
A) Stretch, opening of ion channels, receptor potential, opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels, action potential
B) Stretch, dendritic potential, opening of ion channels, receptor potential, action potential
C) Stretch, receptor potential, spread of potential in receptor neuron, neurotransmitter release, action potential
D) Stretch, neurotransmitter release, receptor potential, opening of ion channels, action potential
E) Stretch, opening of ion channels, neurotransmitter release, opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels, action potential
A) Stretch, opening of ion channels, receptor potential, opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels, action potential
B) Stretch, dendritic potential, opening of ion channels, receptor potential, action potential
C) Stretch, receptor potential, spread of potential in receptor neuron, neurotransmitter release, action potential
D) Stretch, neurotransmitter release, receptor potential, opening of ion channels, action potential
E) Stretch, opening of ion channels, neurotransmitter release, opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels, action potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A chemical damages dendrites of stretch receptors of a crayfish.What will be the result?
A) The ion channels will open when the muscle relaxes.
B) Stretching will not activate the opening of ion channels in stretch receptor dendrites.
C) Action potentials will spread from the cell body to the dendrites.
D) Sensory adaptation will occur.
E) Receptor potentials will travel down the axon.
A) The ion channels will open when the muscle relaxes.
B) Stretching will not activate the opening of ion channels in stretch receptor dendrites.
C) Action potentials will spread from the cell body to the dendrites.
D) Sensory adaptation will occur.
E) Receptor potentials will travel down the axon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To signal over long distances, receptor potentials must
A) generate ATP.
B) cause the release of hormones.
C) adapt.
D) generate action potentials.
E) generalize to other stimuli.
A) generate ATP.
B) cause the release of hormones.
C) adapt.
D) generate action potentials.
E) generalize to other stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the G proteins in photoreceptors are pharmacologically blocked, exposure of these photoreceptors to light will
A) raise the intracellular concentration of cations.
B) lower the intracellular concentration of cations.
C) cause electroreceptors to open ion channels.
D) cause a signaling cascade.
E) have no effect on these receptors.
A) raise the intracellular concentration of cations.
B) lower the intracellular concentration of cations.
C) cause electroreceptors to open ion channels.
D) cause a signaling cascade.
E) have no effect on these receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about sensory cells is false?
A) Sensory cells can produce gradually diminishing responses to repeated stimulation.
B) Sensory cells can respond equally to all types of stimuli.
C) Changes in stimulus strength can lead to changes in the frequency of action potentials generated by sensory cells.
D) Sensory cells display a phenomenon called adaptation.
E) Some sensory cells are assembled with other cell types that enhance their ability to collect, filter, and amplify stimuli.
A) Sensory cells can produce gradually diminishing responses to repeated stimulation.
B) Sensory cells can respond equally to all types of stimuli.
C) Changes in stimulus strength can lead to changes in the frequency of action potentials generated by sensory cells.
D) Sensory cells display a phenomenon called adaptation.
E) Some sensory cells are assembled with other cell types that enhance their ability to collect, filter, and amplify stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
All sensory systems process information as action potentials, so how are different stimuli recognized as different sensations?
A) The strength of the stimulus determines how it is interpreted by the central nervous system.
B) Action potentials are combined in the brain.
C) Sensory cells respond to only one type of stimulus.
D) Action potentials arrive at different parts of the central nervous system.
E) The strength of the stimulus determines the type of sensation.
A) The strength of the stimulus determines how it is interpreted by the central nervous system.
B) Action potentials are combined in the brain.
C) Sensory cells respond to only one type of stimulus.
D) Action potentials arrive at different parts of the central nervous system.
E) The strength of the stimulus determines the type of sensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A male silkworm moth locates a female at a distance by
A) flying toward a chemical signal.
B) flying toward a sound signal.
C) flying toward anything shaped like a female moth.
D) emitting a sound as the female approaches.
E) emitting a chemical as the female approaches.
A) flying toward a chemical signal.
B) flying toward a sound signal.
C) flying toward anything shaped like a female moth.
D) emitting a sound as the female approaches.
E) emitting a chemical as the female approaches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sensory _______ allows animals to ignore conditions that are unchanging yet remain sensitive to new information.
A) transduction
B) deprivation
C) adaptation
D) stimulation
E) processing
A) transduction
B) deprivation
C) adaptation
D) stimulation
E) processing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement about olfaction is false?
A) In general, mammals depend less on olfaction than on vision as their dominant sensory modality.
B) Olfactory stimuli are recognized by the interaction between odorant molecules and receptor proteins on olfactory cilia.
C) The more odorant molecules that bind to receptors, the more action potentials that are generated.
D) The greater the number of action potentials generated by an olfactory receptor, the greater the intensity of the perceived smell.
E) The perception of different smells results from the activation of different combinations of olfactory receptors.
A) In general, mammals depend less on olfaction than on vision as their dominant sensory modality.
B) Olfactory stimuli are recognized by the interaction between odorant molecules and receptor proteins on olfactory cilia.
C) The more odorant molecules that bind to receptors, the more action potentials that are generated.
D) The greater the number of action potentials generated by an olfactory receptor, the greater the intensity of the perceived smell.
E) The perception of different smells results from the activation of different combinations of olfactory receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The pathway for olfactory information flowing from the nasal cavity to the brain is
A) olfactory cilia, glomeruli, mucus.
B) glomeruli, mucus, olfactory microvilli.
C) microvilli, mucus, glomeruli.
D) mucus, olfactory cilia, glomeruli.
E) mucus, microvilli, glomeruli.
A) olfactory cilia, glomeruli, mucus.
B) glomeruli, mucus, olfactory microvilli.
C) microvilli, mucus, glomeruli.
D) mucus, olfactory cilia, glomeruli.
E) mucus, microvilli, glomeruli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The greatest intensity of perceived smell comes from the
A) enzyme that binds with the most odorant molecules.
B) odorant that binds to the most receptors.
C) greatest variety of odorant molecules.
D) greatest threshold of depolarization.
E) greatest number of odorant molecules entering the cell.
A) enzyme that binds with the most odorant molecules.
B) odorant that binds to the most receptors.
C) greatest variety of odorant molecules.
D) greatest threshold of depolarization.
E) greatest number of odorant molecules entering the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Destruction of the accessory olfactory bulbs of a rat would cause which of the following outcomes?
A) Inability to integrate information from the vomeronasal organ
B) Delays in finding food
C) Inability to integrate information from the main olfactory system
D) Inability to detect predators
E) Enhanced ability to detect pheromones
A) Inability to integrate information from the vomeronasal organ
B) Delays in finding food
C) Inability to integrate information from the main olfactory system
D) Inability to detect predators
E) Enhanced ability to detect pheromones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The olfactory bulb is part of the
A) brain.
B) nasal epithelium.
C) organ of Corti.
D) cochlea.
E) vomeronasal organ.
A) brain.
B) nasal epithelium.
C) organ of Corti.
D) cochlea.
E) vomeronasal organ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Destruction of the vomeronasal organ of a male mouse would prevent all of the following except
A) determination of the sex of another mouse encountered in a runway.
B) detection of a cat nearby.
C) identification of an individual mouse.
D) determination of the strain of another mouse.
E) assessing the sexual receptivity of a female mouse.
A) determination of the sex of another mouse encountered in a runway.
B) detection of a cat nearby.
C) identification of an individual mouse.
D) determination of the strain of another mouse.
E) assessing the sexual receptivity of a female mouse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
As a male silkworm moth nears a female that is releasing pheromone,
A) he can locate the female by following a concentration gradient of the pheromone.
B) the action potentials in his antennal nerve decrease.
C) fewer pheromone-sensitive hairs are stimulated per second.
D) the female starts to release more pheromone.
E) he switches from pheromone detection to hearing for locating the female.
A) he can locate the female by following a concentration gradient of the pheromone.
B) the action potentials in his antennal nerve decrease.
C) fewer pheromone-sensitive hairs are stimulated per second.
D) the female starts to release more pheromone.
E) he switches from pheromone detection to hearing for locating the female.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure. 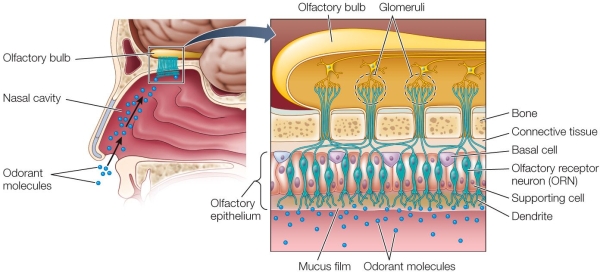 In the human olfactory system, a single glomerulus receives input from
In the human olfactory system, a single glomerulus receives input from
A) an olfactory receptor.
B) a basal cell.
C) an odorant molecule.
D) receptor cells of the same type.
E) a branch of the olfactory nerve.
 In the human olfactory system, a single glomerulus receives input from
In the human olfactory system, a single glomerulus receives input fromA) an olfactory receptor.
B) a basal cell.
C) an odorant molecule.
D) receptor cells of the same type.
E) a branch of the olfactory nerve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the figure. 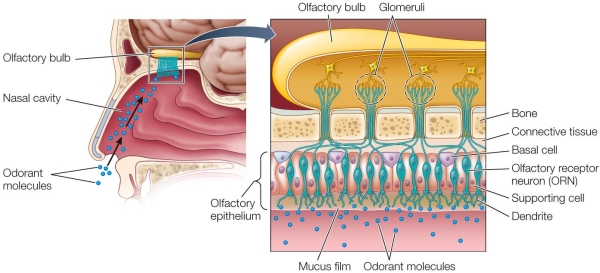 In the human olfactory system, odorant molecules in the environment bind to receptors on the
In the human olfactory system, odorant molecules in the environment bind to receptors on the
A) olfactory bulb.
B) glomeruli.
C) nasal cavity.
D) olfactory cell axon.
E) olfactory cilia.
 In the human olfactory system, odorant molecules in the environment bind to receptors on the
In the human olfactory system, odorant molecules in the environment bind to receptors on theA) olfactory bulb.
B) glomeruli.
C) nasal cavity.
D) olfactory cell axon.
E) olfactory cilia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which statement about olfaction is false?
A) Humans can discriminate many more odorants than there are olfactory receptors.
B) Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses only one type of receptor.
C) Different regions of a complex odorant molecule can bind to different receptor proteins.
D) Each glomerulus in the olfactory bulb contains axons from olfactory receptor neurons that express different receptor proteins.
E) Each olfactory receptor protein is found in a limited number of olfactory receptor neurons in the nasal epithelium.
A) Humans can discriminate many more odorants than there are olfactory receptors.
B) Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses only one type of receptor.
C) Different regions of a complex odorant molecule can bind to different receptor proteins.
D) Each glomerulus in the olfactory bulb contains axons from olfactory receptor neurons that express different receptor proteins.
E) Each olfactory receptor protein is found in a limited number of olfactory receptor neurons in the nasal epithelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All of the following might use pheromones to communicate with one another except
A) a mother rat and her offspring.
B) a bat preying on a moth.
C) a female mouse and male mouse.
D) members of a termite colony.
E) members of a naked mole-rat colony.
A) a mother rat and her offspring.
B) a bat preying on a moth.
C) a female mouse and male mouse.
D) members of a termite colony.
E) members of a naked mole-rat colony.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sensory adaptation would likely occur when you are exposed to
A) background noise.
B) a painful stimulus.
C) a single light touch that is quickly withdrawn.
D) changing visual images.
E) varying amounts of pressure.
A) background noise.
B) a painful stimulus.
C) a single light touch that is quickly withdrawn.
D) changing visual images.
E) varying amounts of pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement about chemoreception in snakes is false?
A) Snakes use their forked tongue to smell the environment.
B) Information from the tongue of a snake is interpreted in the main olfactory bulbs.
C) The tongue provides olfactory information more rapidly than does the flow of air to the lungs.
D) The tongue brings olfactory molecules to the vomeronasal organ.
E) Information provided by the tongue aids in communicating with conspecifics and in hunting prey.
A) Snakes use their forked tongue to smell the environment.
B) Information from the tongue of a snake is interpreted in the main olfactory bulbs.
C) The tongue provides olfactory information more rapidly than does the flow of air to the lungs.
D) The tongue brings olfactory molecules to the vomeronasal organ.
E) Information provided by the tongue aids in communicating with conspecifics and in hunting prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
As a male silkworm moth nears a female that is releasing the pheromone bombykol,
A) the female starts to release more bombykol.
B) the frequency of action potentials in his antennal nerve increases.
C) the diffusion coefficient of bombykol increases.
D) a larger number of the bombykol-sensitive hairs undergo sensory adaptation.
E) the receptor potential in bombykol-sensitive hairs is reduced.
A) the female starts to release more bombykol.
B) the frequency of action potentials in his antennal nerve increases.
C) the diffusion coefficient of bombykol increases.
D) a larger number of the bombykol-sensitive hairs undergo sensory adaptation.
E) the receptor potential in bombykol-sensitive hairs is reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How is information from a complex odorant molecule transmitted to the olfactory bulb?
A) The frequency of action potentials in olfactory receptor neurons is dramatically increased.
B) Different regions of the odorant molecule can bind to different receptor proteins and activate a unique combination of glomeruli in the olfactory bulb.
C) The odorant molecule combines with other odorants to amplify the smell.
D) The odorant molecule activates one glomerulus in both olfactory bulbs.
E) The odorant molecule increases its binding to one type of receptor.
A) The frequency of action potentials in olfactory receptor neurons is dramatically increased.
B) Different regions of the odorant molecule can bind to different receptor proteins and activate a unique combination of glomeruli in the olfactory bulb.
C) The odorant molecule combines with other odorants to amplify the smell.
D) The odorant molecule activates one glomerulus in both olfactory bulbs.
E) The odorant molecule increases its binding to one type of receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Pheromones are involved in all of the following except
A) defining territory boundaries for neighboring conspecifics.
B) attracting a mate.
C) delaying reproduction in individuals of another species.
D) marking a trail to food for colony members.
E) communicating alarm to family members.
A) defining territory boundaries for neighboring conspecifics.
B) attracting a mate.
C) delaying reproduction in individuals of another species.
D) marking a trail to food for colony members.
E) communicating alarm to family members.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When a male cat smells the urine of a female cat, he may exhibit the flehmen response, a behavior in which he curls back his upper lip and breathes in deeply.Olfactory molecules from the urine travel in nasal fluid over chemoreceptors of the _______, which is a structure located on the septum dividing the two nostrils.
A) gustatory nucleus
B) fovea
C) vomeronasal organ
D) organ of Corti
E) Ruffini endings
A) gustatory nucleus
B) fovea
C) vomeronasal organ
D) organ of Corti
E) Ruffini endings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
You are a physician and one of your patients comes in and tells you she has a cold and has lost her sense of smell.You explain that she has lost her sense of smell because
A) cold viruses directly damage the microvilli on the dendrites of olfactory receptor neurons.
B) cold viruses interfere with the processing of olfactory information in the olfactory bulb of the nasal cavity.
C) the amount of mucus in her nose has increased, making it difficult for odorant molecules to diffuse through the protective mucus layer to reach olfactory receptors.
D) her vomeronasal organ has been damaged.
E) the olfactory bulb is swollen, making it impossible for olfactory information to reach the brain.
A) cold viruses directly damage the microvilli on the dendrites of olfactory receptor neurons.
B) cold viruses interfere with the processing of olfactory information in the olfactory bulb of the nasal cavity.
C) the amount of mucus in her nose has increased, making it difficult for odorant molecules to diffuse through the protective mucus layer to reach olfactory receptors.
D) her vomeronasal organ has been damaged.
E) the olfactory bulb is swollen, making it impossible for olfactory information to reach the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
_______ receptors allow sodium ions to diffuse into taste bud sensory cells through open sodium ion channels.
A) Sweet
B) Salty
C) Bitter
D) Sour
E) Umami
A) Sweet
B) Salty
C) Bitter
D) Sour
E) Umami

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the mammalian auditory system, ear ossicles transmit signals from the _______ to the _______.
A) oval window; round window
B) round window; tympanic membrane
C) oval window; basilar membrane
D) cochlea; auditory nerve
E) tympanic membrane; oval window
A) oval window; round window
B) round window; tympanic membrane
C) oval window; basilar membrane
D) cochlea; auditory nerve
E) tympanic membrane; oval window

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement about muscle spindles is true?
A) They allow for adjustment of the strength of muscle contraction to the load put on the muscle.
B) They are found in tendons and ligaments.
C) They possess hair cells that serve as mechanoreceptors.
D) They are innervated by motor neurons.
E) They are found in cardiac muscle.
A) They allow for adjustment of the strength of muscle contraction to the load put on the muscle.
B) They are found in tendons and ligaments.
C) They possess hair cells that serve as mechanoreceptors.
D) They are innervated by motor neurons.
E) They are found in cardiac muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement about gustation is false?
A) Taste buds are distributed more broadly over the body in terrestrial animals than in aquatic animals.
B) Taste buds are shed and replaced, but the sensory neurons associated with them are not.
C) Microvilli of taste bud sensory cells contain membrane receptor proteins.
D) Humans perceive five taste classes.
E) Despite different mechanisms of taste transduction by the receptors of taste bud sensory cells, all of these sensory cells release neurotransmitter onto sensory neurons, which carry information to the central nervous system.
A) Taste buds are distributed more broadly over the body in terrestrial animals than in aquatic animals.
B) Taste buds are shed and replaced, but the sensory neurons associated with them are not.
C) Microvilli of taste bud sensory cells contain membrane receptor proteins.
D) Humans perceive five taste classes.
E) Despite different mechanisms of taste transduction by the receptors of taste bud sensory cells, all of these sensory cells release neurotransmitter onto sensory neurons, which carry information to the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The sound of the alarm clock in the morning triggers a(n) _______ in the sleeper.
A) mechanoreceptor
B) thermoreceptor
C) electroreceptor
D) chemoreceptor
E) photoreceptor
A) mechanoreceptor
B) thermoreceptor
C) electroreceptor
D) chemoreceptor
E) photoreceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If you wanted to specifically block the binding of molecules to receptors of taste bud sensory cells, you would destroy the
A) cilia.
B) vomeronasal organ.
C) microvilli.
D) supporting cells.
E) sensory neurons carrying information to the central nervous system.
A) cilia.
B) vomeronasal organ.
C) microvilli.
D) supporting cells.
E) sensory neurons carrying information to the central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Refer to the figure, which shows the structures of the middle ear. 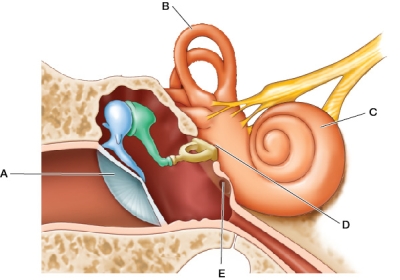 Vibrations from the structure labeled A are transmitted to the oval window via the
Vibrations from the structure labeled A are transmitted to the oval window via the
A) eustachian tube.
B) ossicles.
C) semicircular canals.
D) round window.
E) malleus.
 Vibrations from the structure labeled A are transmitted to the oval window via the
Vibrations from the structure labeled A are transmitted to the oval window via theA) eustachian tube.
B) ossicles.
C) semicircular canals.
D) round window.
E) malleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Meissner's corpuscles
A) adapt very slowly to pressure.
B) sense changes in light touch.
C) sense deep pressure.
D) excel at providing information about vibrating stimuli at low frequencies.
E) are found primarily in hairy skin.
A) adapt very slowly to pressure.
B) sense changes in light touch.
C) sense deep pressure.
D) excel at providing information about vibrating stimuli at low frequencies.
E) are found primarily in hairy skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which receptors are located deep in the skin and are adapted specifically for sensing pressure?
A) Meissner's corpuscles
B) Free nerve endings
C) Tactile receptors
D) Sweat glands
E) Pacinian corpuscles
A) Meissner's corpuscles
B) Free nerve endings
C) Tactile receptors
D) Sweat glands
E) Pacinian corpuscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the figure, which shows the structures of the middle ear. 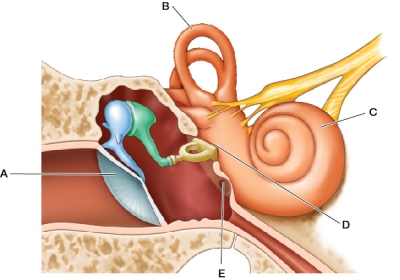 Vibrations sensed at the structure labeled _______ initiate pressure waves in the cochlea.
Vibrations sensed at the structure labeled _______ initiate pressure waves in the cochlea.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 Vibrations sensed at the structure labeled _______ initiate pressure waves in the cochlea.
Vibrations sensed at the structure labeled _______ initiate pressure waves in the cochlea.A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In casinos, gamblers often roll the dice around in their hands before throwing them.Which type of mechanoreceptor is giving them information about the shape of the dice?
A) Meissner's corpuscles
B) Merkel's discs
C) Ruffini endings
D) Pacinian corpuscles
E) Free nerve endings
A) Meissner's corpuscles
B) Merkel's discs
C) Ruffini endings
D) Pacinian corpuscles
E) Free nerve endings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Hair cells are not associated with which of the following structures?
A) Vestibular system
B) Organ of Corti
C) Cochlea
D) Muscle spindle
E) Semicircular canal
A) Vestibular system
B) Organ of Corti
C) Cochlea
D) Muscle spindle
E) Semicircular canal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following does not characterize hair cells?
A) They contain fingerlike extensions of the cell membrane.
B) They are mechanoreceptors.
C) They are found in the vertebrate auditory and vestibular systems.
D) They depolarize when stereocilia bend in one direction and hyperpolarize when they bend in the opposite direction.
E) They are one of many types of tactile receptors found in the skin, where they wrap around hair follicles.
A) They contain fingerlike extensions of the cell membrane.
B) They are mechanoreceptors.
C) They are found in the vertebrate auditory and vestibular systems.
D) They depolarize when stereocilia bend in one direction and hyperpolarize when they bend in the opposite direction.
E) They are one of many types of tactile receptors found in the skin, where they wrap around hair follicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Golgi tendon organ is a type of mechanoreceptor found in tendons and ligaments.Action potentials from this structure inhibit spinal cord motor neurons.The main function of this structure is to
A) monitor the force of muscle contraction.
B) provide information about deep pressure.
C) innervate muscles.
D) activate the Golgi apparatus within muscle cells.
E) signal muscle contraction.
A) monitor the force of muscle contraction.
B) provide information about deep pressure.
C) innervate muscles.
D) activate the Golgi apparatus within muscle cells.
E) signal muscle contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which taste receptor would be activated by the direct effect of hydrogen ions on sodium channels?
A) Sweet
B) Salty
C) Bitter
D) Sour
E) Umami
A) Sweet
B) Salty
C) Bitter
D) Sour
E) Umami

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Ruffini endings
A) are found in the epidermis.
B) adapt rapidly.
C) adapt slowly and provide information about vibrating stimuli of low frequencies.
D) respond to pain, itch, and temperature.
E) respond when surface hairs are displaced.
A) are found in the epidermis.
B) adapt rapidly.
C) adapt slowly and provide information about vibrating stimuli of low frequencies.
D) respond to pain, itch, and temperature.
E) respond when surface hairs are displaced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which structure of the mammalian auditory system transduces (converts) pressure changes into action potentials that are carried by the auditory nerve to the brain?
A) Hair cells
B) Ear ossicles
C) Oval window
D) Tympanic membrane
E) Basilar membrane
A) Hair cells
B) Ear ossicles
C) Oval window
D) Tympanic membrane
E) Basilar membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Pacinian corpuscles
A) are found just below the epidermis.
B) respond to extended, steady pressure.
C) adapt rapidly and provide information about high-frequency vibrating stimuli.
D) have long, extensive dendritic processes.
E) are extremely sensitive to light touch.
A) are found just below the epidermis.
B) respond to extended, steady pressure.
C) adapt rapidly and provide information about high-frequency vibrating stimuli.
D) have long, extensive dendritic processes.
E) are extremely sensitive to light touch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Auditory information comes from hair cells in the _______ ear that are concentrated in the _______.
A) inner; organ of Corti
B) outer; tympanic membrane
C) inner; basilar membrane
D) middle; semicircular canals
E) middle; vestibular apparatus
A) inner; organ of Corti
B) outer; tympanic membrane
C) inner; basilar membrane
D) middle; semicircular canals
E) middle; vestibular apparatus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following does not characterize Merkel's discs?
A) They respond to touch.
B) They are found primarily in the epidermis.
C) They are found in hairy and non-hairy skin.
D) They adapt slowly.
E) They provide continuous information about objects touching the skin.
A) They respond to touch.
B) They are found primarily in the epidermis.
C) They are found in hairy and non-hairy skin.
D) They adapt slowly.
E) They provide continuous information about objects touching the skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the figure, which shows the human eye. 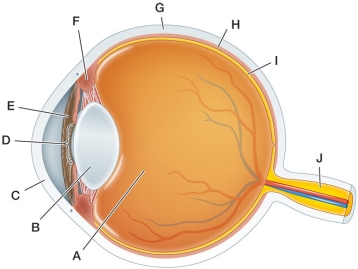 The three structures labeled A, B, and C bend light rays so that they are focused on the retina.These structures (from A to C) are the
The three structures labeled A, B, and C bend light rays so that they are focused on the retina.These structures (from A to C) are the
A) vitreous humor, lens, and cornea.
B) aqueous humor, lens, and cornea.
C) vitreous humor, lens, and retina.
D) aqueous humor, cornea, and pupil.
E) vitreous humor, cornea, and iris.
 The three structures labeled A, B, and C bend light rays so that they are focused on the retina.These structures (from A to C) are the
The three structures labeled A, B, and C bend light rays so that they are focused on the retina.These structures (from A to C) are theA) vitreous humor, lens, and cornea.
B) aqueous humor, lens, and cornea.
C) vitreous humor, lens, and retina.
D) aqueous humor, cornea, and pupil.
E) vitreous humor, cornea, and iris.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement about the events of photoreception is false?
A) As a rod cell hyperpolarizes, its release of neurotransmitter increases.
B) In the dark, most of the sodium channels of a rod cell are open.
C) cGMP keeps the sodium channels open.
D) Activated phosphodiesterase (PDE) catalyzes the reaction hydrolyzing cGMP into GMP.
E) The sodium channels of a rod cell close in proportion to the intensity of light received.
A) As a rod cell hyperpolarizes, its release of neurotransmitter increases.
B) In the dark, most of the sodium channels of a rod cell are open.
C) cGMP keeps the sodium channels open.
D) Activated phosphodiesterase (PDE) catalyzes the reaction hydrolyzing cGMP into GMP.
E) The sodium channels of a rod cell close in proportion to the intensity of light received.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following does not characterize visual accommodation in mammals?
A) It involves relaxation of ciliary muscles for distant vision.
B) It is accomplished by altering the shape of the lens.
C) It involves contraction of ciliary muscles for near vision.
D) It involves movement of the lens forward and backward.
E) It differs from accommodation in fishes and amphibians.
A) It involves relaxation of ciliary muscles for distant vision.
B) It is accomplished by altering the shape of the lens.
C) It involves contraction of ciliary muscles for near vision.
D) It involves movement of the lens forward and backward.
E) It differs from accommodation in fishes and amphibians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In diurnal mammals, light not captured by photosensors is
A) absorbed by a black-pigmented layer behind the retina.
B) reflected back onto the retina by an iridescent layer behind the retina.
C) absorbed by a black-pigmented layer in front of the retina.
D) reflected back onto the retina by an iridescent layer in front of the retina.
E) absorbed by the vitreous humor.
A) absorbed by a black-pigmented layer behind the retina.
B) reflected back onto the retina by an iridescent layer behind the retina.
C) absorbed by a black-pigmented layer in front of the retina.
D) reflected back onto the retina by an iridescent layer in front of the retina.
E) absorbed by the vitreous humor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which statement comparing the eyes of arthropods and the eyes of vertebrates is false?
A) An arthropod eye has many optical units, while a vertebrate eye has one optical unit.
B) The eyes of vertebrates produce detailed images, and the eyes of arthropods provide information about patterns in the environment.
C) The number of ommatidia in a compound eye varies dramatically among arthropods, but all vertebrate eyes have a single optical unit.
D) A vertebrate eye has a single narrow-angle lens, and an arthropod eye has many wide-angle lenses.
E) The images formed by arthropod eyes have low resolution compared with the high-resolution images formed by vertebrate eyes.
A) An arthropod eye has many optical units, while a vertebrate eye has one optical unit.
B) The eyes of vertebrates produce detailed images, and the eyes of arthropods provide information about patterns in the environment.
C) The number of ommatidia in a compound eye varies dramatically among arthropods, but all vertebrate eyes have a single optical unit.
D) A vertebrate eye has a single narrow-angle lens, and an arthropod eye has many wide-angle lenses.
E) The images formed by arthropod eyes have low resolution compared with the high-resolution images formed by vertebrate eyes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the figure, which shows the human eye. 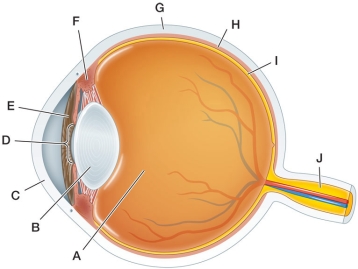 As we age, the structure labeled _______ becomes less elastic and we lose the ability to focus on close objects.
As we age, the structure labeled _______ becomes less elastic and we lose the ability to focus on close objects.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 As we age, the structure labeled _______ becomes less elastic and we lose the ability to focus on close objects.
As we age, the structure labeled _______ becomes less elastic and we lose the ability to focus on close objects.A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In a visual system, light is absorbed by rhodopsin, which causes
A) a change of shape in opsin, a photosensitive protein.
B) depolarization of the rhodopsin molecule, which results in the generation of an action potential.
C) first a change in the retinal molecule into a different isomer, and then a change in shape of the opsin protein.
D) oxidation of the rhodopsin molecule, a process known as bleaching.
E) an increase in the number of rod cells.
A) a change of shape in opsin, a photosensitive protein.
B) depolarization of the rhodopsin molecule, which results in the generation of an action potential.
C) first a change in the retinal molecule into a different isomer, and then a change in shape of the opsin protein.
D) oxidation of the rhodopsin molecule, a process known as bleaching.
E) an increase in the number of rod cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which statement about rhodopsin is false?
A) In vertebrate eyes, the retinal and the opsin never separate from each other.
B) When 11-cis-retinal absorbs light, it becomes all-trans-retinal.
C) Rhodopsin is a transmembrane protein.
D) Rhodopsin consists of a protein and a light-absorbing molecule.
E) Rhodopsin gives humans sensitivity to low light levels.
A) In vertebrate eyes, the retinal and the opsin never separate from each other.
B) When 11-cis-retinal absorbs light, it becomes all-trans-retinal.
C) Rhodopsin is a transmembrane protein.
D) Rhodopsin consists of a protein and a light-absorbing molecule.
E) Rhodopsin gives humans sensitivity to low light levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To bring distant objects into focus, mammals and birds
A) contract ciliary muscles to make the lens more round.
B) relax suspensory ligaments attached to the lens.
C) alter lens shape by relaxing ciliary muscles.
D) alter lens shape by moving the lens closer to the retina.
E) alter lens shape by moving the lens farther from the retina.
A) contract ciliary muscles to make the lens more round.
B) relax suspensory ligaments attached to the lens.
C) alter lens shape by relaxing ciliary muscles.
D) alter lens shape by moving the lens closer to the retina.
E) alter lens shape by moving the lens farther from the retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which statement about the auditory functioning of the cochlea is false?
A) The flexing of the round window follows the flexing of the oval window in a delayed fashion.
B) The hair cells on the organ of Corti move against the rigid tectorial membrane.
C) The intensity of the sound determines how many hair cells will be stimulated.
D) The frequency of the sound determines which hair cells will be stimulated.
E) Lower-frequency sounds result in the stimulation of hair cells closer to the round window.
A) The flexing of the round window follows the flexing of the oval window in a delayed fashion.
B) The hair cells on the organ of Corti move against the rigid tectorial membrane.
C) The intensity of the sound determines how many hair cells will be stimulated.
D) The frequency of the sound determines which hair cells will be stimulated.
E) Lower-frequency sounds result in the stimulation of hair cells closer to the round window.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The ear can distinguish different sound frequencies because different parts of the _______ respond differentially.
A) tympanic membrane
B) round window
C) oval window
D) tectorial membrane
E) basilar membrane
A) tympanic membrane
B) round window
C) oval window
D) tectorial membrane
E) basilar membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When an individual rod cell is stimulated with light, its membrane potential
A) becomes more negative.
B) becomes more positive.
C) becomes more positive than that of other neurons.
D) begins to generate action potentials.
E) begins to reduce membrane polarization.
A) becomes more negative.
B) becomes more positive.
C) becomes more positive than that of other neurons.
D) begins to generate action potentials.
E) begins to reduce membrane polarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following does not characterize the eyes of arthropods?
A) They contain multiple ommatidia per eye.
B) They provide information about patterns in the environment.
C) They provide high-resolution images.
D) They are more complex than the eyes of flatworms.
E) They have a narrow-angle lens associated with each optical unit.
A) They contain multiple ommatidia per eye.
B) They provide information about patterns in the environment.
C) They provide high-resolution images.
D) They are more complex than the eyes of flatworms.
E) They have a narrow-angle lens associated with each optical unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which statement about photoreceptors of the human retina is false?
A) Cone cells and rod cells differ in shape.
B) Rod cells are highly sensitive to light.
C) Cone cells provide high-acuity color vision.
D) The density of rods and cones varies across the retina.
E) Cones outnumber rods in the retina.
A) Cone cells and rod cells differ in shape.
B) Rod cells are highly sensitive to light.
C) Cone cells provide high-acuity color vision.
D) The density of rods and cones varies across the retina.
E) Cones outnumber rods in the retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In mammals, the semicircular ducts of the vestibular system participate in responses to changes in position and movement of the head.Which of the following statements about the semicircular ducts is true?
A) They lie within the vestibule.
B) They have openings to the external environment.
C) Mammals have two semicircular ducts.
D) Movement of fluid within the semicircular ducts bends hair cell stereocilia by pushing on a gelatinous cupula covering the hair cells.
E) Otoliths are found in the semicircular ducts.
A) They lie within the vestibule.
B) They have openings to the external environment.
C) Mammals have two semicircular ducts.
D) Movement of fluid within the semicircular ducts bends hair cell stereocilia by pushing on a gelatinous cupula covering the hair cells.
E) Otoliths are found in the semicircular ducts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
To test whether a group of hair cells depolarizes in response to a specific frequency, a researcher could produce the sound and then measure
A) the rate of action potentials in the hair cells.
B) the flexion of the basilar membrane.
C) the membrane potentials of the hair cells.
D) vibration in the tympanic membrane.
E) pressure waves transduced by the organ of Corti.
A) the rate of action potentials in the hair cells.
B) the flexion of the basilar membrane.
C) the membrane potentials of the hair cells.
D) vibration in the tympanic membrane.
E) pressure waves transduced by the organ of Corti.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In humans, which of the following is a possible result of damage to the basal end of the basilar membrane?
A) Temporal deafness
B) Conduction deafness
C) Failure of the tympanic window to conduct sound waves
D) Inability to detect high-frequency sounds
E) Inability to detect low-frequency sounds
A) Temporal deafness
B) Conduction deafness
C) Failure of the tympanic window to conduct sound waves
D) Inability to detect high-frequency sounds
E) Inability to detect low-frequency sounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Vertigo is a condition in which a person feels like she or he is spinning.Which structure is a likely location for the viral infection that often causes vertigo?
A) Eustachian tube
B) Cochlea
C) Vestibular system
D) Oval window
E) Tympanic membrane
A) Eustachian tube
B) Cochlea
C) Vestibular system
D) Oval window
E) Tympanic membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Refer to the figure, which shows the human eye.  The layers of the human eye from outermost to innermost include the structures labeled G, H, and I, which are the
The layers of the human eye from outermost to innermost include the structures labeled G, H, and I, which are the
A) retina, cornea, and pigmented epithelium.
B) sclera, pigmented epithelium, and retina.
C) cornea, retina, and iris.
D) retina, sclera, and pigmented epithelium.
E) sclera, ciliary muscle, and retina.
 The layers of the human eye from outermost to innermost include the structures labeled G, H, and I, which are the
The layers of the human eye from outermost to innermost include the structures labeled G, H, and I, which are theA) retina, cornea, and pigmented epithelium.
B) sclera, pigmented epithelium, and retina.
C) cornea, retina, and iris.
D) retina, sclera, and pigmented epithelium.
E) sclera, ciliary muscle, and retina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Fishes have a lateral line system consisting of canals under the surface of the skin.These canals contain sensory structures consisting of hair cells capped by a cupula.These structures look similar to those found in our semicircular ducts.When a fish swims, a stream of water flows through the lateral line canals.The most likely function of the lateral line sensory system is to sense
A) movements and pressure changes in the water.
B) the depth of the water.
C) chemical substances in the water.
D) electrical currents in the water.
E) spatial orientation based on gravity.
A) movements and pressure changes in the water.
B) the depth of the water.
C) chemical substances in the water.
D) electrical currents in the water.
E) spatial orientation based on gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



