Deck 47: Musculoskeletal Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/259
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 47: Musculoskeletal Systems
1
An individual sarcomere unit consists primarily of
A) a stack of actin fibers, only.
B) a stack of myosin units, only.
C) overlapping actin and membrane.
D) overlapping myosin and membrane.
E) overlapping actin and myosin.
A) a stack of actin fibers, only.
B) a stack of myosin units, only.
C) overlapping actin and membrane.
D) overlapping myosin and membrane.
E) overlapping actin and myosin.
E
2
Which statement about the interaction between actin and myosin molecules is true?
A) Globular myosin heads bind to actin filaments.
B) Globular actin heads bind to myosin filaments.
C) They are connected to one another by other proteins.
D) Myosin filaments bend to connect to actin.
E) Actin filaments bend to connect to myosin.
A) Globular myosin heads bind to actin filaments.
B) Globular actin heads bind to myosin filaments.
C) They are connected to one another by other proteins.
D) Myosin filaments bend to connect to actin.
E) Actin filaments bend to connect to myosin.
A
3
Refer to the figure showing the components of a sarcomere. 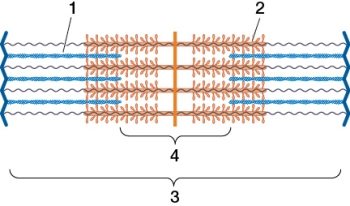 Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
A) Structure 1 consists of three chains made of monomers.
B) Structure 1 shortens in length as contraction occurs.
C) Structure 2 includes "heads" that hydrolyze ATP.
D) Structure 3 increases in length as contraction occurs.
E) Structure 4 increases in length as contraction occurs.
 Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?A) Structure 1 consists of three chains made of monomers.
B) Structure 1 shortens in length as contraction occurs.
C) Structure 2 includes "heads" that hydrolyze ATP.
D) Structure 3 increases in length as contraction occurs.
E) Structure 4 increases in length as contraction occurs.
C
4
Which muscle type(s) has/have the least regular arrangements of actin and myosin?
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about the structure of skeletal muscle is true?
A) The light bands of the sarcomere are the regions where actin and myosin filaments overlap.
B) When a muscle contracts, the A bands of the sarcomere lengthen.
C) The myosin filaments are anchored in the Z lines.
D) When a muscle contracts, the H zone of the sarcomere shortens.
E) The sarcoplasm of the muscle cell is contained within the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
A) The light bands of the sarcomere are the regions where actin and myosin filaments overlap.
B) When a muscle contracts, the A bands of the sarcomere lengthen.
C) The myosin filaments are anchored in the Z lines.
D) When a muscle contracts, the H zone of the sarcomere shortens.
E) The sarcoplasm of the muscle cell is contained within the sarcoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The striated appearance of skeletal muscle is due to the
A) dark color of actin.
B) multiple nuclei per fiber.
C) regular arrangement of filaments relative to each other.
D) dense array of microtubules.
E) dense packing of ATP molecules.
A) dark color of actin.
B) multiple nuclei per fiber.
C) regular arrangement of filaments relative to each other.
D) dense array of microtubules.
E) dense packing of ATP molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle contraction?
A) It stores Ca2+ ions for release during contraction.
B) It surrounds and protects the muscle filaments.
C) It provides sites of ATP synthesis.
D) It depolarizes when stimulated by an impulse.
E) It synthesizes actin and myosin filaments.
A) It stores Ca2+ ions for release during contraction.
B) It surrounds and protects the muscle filaments.
C) It provides sites of ATP synthesis.
D) It depolarizes when stimulated by an impulse.
E) It synthesizes actin and myosin filaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Vertebrate skeletal muscles are categorized as excitable cells because
A) they can be stimulated by ATP.
B) they can be stimulated by an electric charge.
C) they can secrete neurotransmitter.
D) their membranes generate and conduct action potentials.
E) they can attain a high level of activity.
A) they can be stimulated by ATP.
B) they can be stimulated by an electric charge.
C) they can secrete neurotransmitter.
D) their membranes generate and conduct action potentials.
E) they can attain a high level of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which muscle type(s) has/have gap junctions?
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When animals die, the lack of ATP causes muscles to stiffen in rigor mortis because
A) muscles cannot contract without ATP.
B) actin and myosin cannot bind without ATP.
C) actin and myosin cannot separate without ATP.
D) ATP is required for synthesis of protein filaments.
E) ATP forms cross-bridges between filaments.
A) muscles cannot contract without ATP.
B) actin and myosin cannot bind without ATP.
C) actin and myosin cannot separate without ATP.
D) ATP is required for synthesis of protein filaments.
E) ATP forms cross-bridges between filaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which muscle type(s) has/have a pacemaking function?
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement about the molecular arrangement of actin and myosin in myofibrils is true?
A) A thin filament consists of myosin and tropomyosin.
B) Two chains of myosin monomers are twisted into a helix.
C) Two strands of tropomyosin lie in the grooves of the myosin.
D) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
E) The myosin heads have ATPase activity and interact with the actin.
A) A thin filament consists of myosin and tropomyosin.
B) Two chains of myosin monomers are twisted into a helix.
C) Two strands of tropomyosin lie in the grooves of the myosin.
D) Troponin forms the head of the myosin molecule.
E) The myosin heads have ATPase activity and interact with the actin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Myoblasts
A) communicate a muscle fiber's need for more O2.
B) lie in a ring around the muscle fibers, absorbing their metabolic waste.
C) are embryonic cells that fuse to form skeletal muscle fibers.
D) move through the muscle fibers, providing ATP where it is most needed.
E) are phagocytic, watching for and then attacking pathogens in the muscle fiber.
A) communicate a muscle fiber's need for more O2.
B) lie in a ring around the muscle fibers, absorbing their metabolic waste.
C) are embryonic cells that fuse to form skeletal muscle fibers.
D) move through the muscle fibers, providing ATP where it is most needed.
E) are phagocytic, watching for and then attacking pathogens in the muscle fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How do muscle fibers shorten during contraction?
A) Individual protein filaments contract.
B) Additional cross-bridges are formed between filaments.
C) Arrays of filaments overlap and slide past arrays of another type of filament.
D) Protein filaments coil more tightly.
E) Subunits of protein polymers detach themselves from the larger units.
A) Individual protein filaments contract.
B) Additional cross-bridges are formed between filaments.
C) Arrays of filaments overlap and slide past arrays of another type of filament.
D) Protein filaments coil more tightly.
E) Subunits of protein polymers detach themselves from the larger units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which muscle type(s) contain(s) intercalated disks?
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Refer to the figure showing the components of a sarcomere. 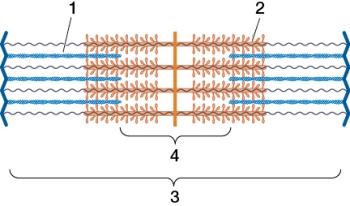 Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
A) Structure 2 consists of two chains made of monomers.
B) Structure 2 shortens in length as contraction occurs.
C) Structure 1 has a "head" that hydrolyzes ATP.
D) Structure 3 shortens in length as contraction occurs.
E) Structure 4 lengthens as contraction occurs.
 Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?A) Structure 2 consists of two chains made of monomers.
B) Structure 2 shortens in length as contraction occurs.
C) Structure 1 has a "head" that hydrolyzes ATP.
D) Structure 3 shortens in length as contraction occurs.
E) Structure 4 lengthens as contraction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Smooth muscle differs from both cardiac and skeletal muscle in that
A) it can act as a pacemaker for rhythmic contractions.
B) its contractions are not due to interactions between neighboring microfilaments.
C) its neighboring cells are electrically connected by gap junctions.
D) its neighboring cells are tightly coupled by intercalated discs.
E) its cell membranes are depolarized by stretching.
A) it can act as a pacemaker for rhythmic contractions.
B) its contractions are not due to interactions between neighboring microfilaments.
C) its neighboring cells are electrically connected by gap junctions.
D) its neighboring cells are tightly coupled by intercalated discs.
E) its cell membranes are depolarized by stretching.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which muscle type(s) use(s) calcium to trigger actin-myosin interactions for movement?
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which muscle type(s) has/have numerous nuclei per muscle cell?
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle
A) Smooth muscle only
B) Cardiac muscle only
C) Skeletal muscle only
D) Both smooth and cardiac muscle, but not skeletal muscle
E) Smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which event occurs during skeletal and cardiac muscle contraction?
A) The distance between Z lines increases.
B) The sarcomeres lengthen.
C) The width of the H zone increases.
D) The width of the I band increases.
E) The area of actin and myosin overlap increases.
A) The distance between Z lines increases.
B) The sarcomeres lengthen.
C) The width of the H zone increases.
D) The width of the I band increases.
E) The area of actin and myosin overlap increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure showing molecules found in sarcomeres. 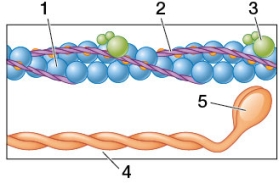 Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
A) Structure 1 has ATPase activity.
B) Structure 2 blocks myosin-binding sites.
C) Structure 3 has one subunit that binds myosin.
D) Structure 4 shortens in length as the sarcomere contracts.
E) Structure 5 binds calcium.
 Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?
Which statement about the structures shown in the figure is true?A) Structure 1 has ATPase activity.
B) Structure 2 blocks myosin-binding sites.
C) Structure 3 has one subunit that binds myosin.
D) Structure 4 shortens in length as the sarcomere contracts.
E) Structure 5 binds calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the role of Ca2+ in the control of muscle contraction?
A) It causes depolarization of the T tubule system.
B) It changes the conformation of troponin, which ultimately results in myosin-binding sites being exposed.
C) It changes the conformation of myosin heads, causing actin and myosin filaments to slide past each other.
D) It binds to tropomyosin and breaks actin-myosin cross-bridges.
E) It blocks the ATP-binding site on myosin heads, enabling muscles to relax.
A) It causes depolarization of the T tubule system.
B) It changes the conformation of troponin, which ultimately results in myosin-binding sites being exposed.
C) It changes the conformation of myosin heads, causing actin and myosin filaments to slide past each other.
D) It binds to tropomyosin and breaks actin-myosin cross-bridges.
E) It blocks the ATP-binding site on myosin heads, enabling muscles to relax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement about slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscles is true?
A) One is smooth muscle and one is skeletal muscle.
B) They have different myosin variants because they express different genes for their myosin molecules.
C) One occurs only in mammals.
D) They typically have similar numbers of mitochondria per cell.
E) Those with low ATPase activity compensate by quickly recycling their actin-myosin bridges.
A) One is smooth muscle and one is skeletal muscle.
B) They have different myosin variants because they express different genes for their myosin molecules.
C) One occurs only in mammals.
D) They typically have similar numbers of mitochondria per cell.
E) Those with low ATPase activity compensate by quickly recycling their actin-myosin bridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The resting potential of smooth muscle cells is
A) not likely to fire action potentials.
B) affected by the stretching of the cells.
C) more negative than that of most cells.
D) unaffected by nearby potential change.
E) nearly zero.
A) not likely to fire action potentials.
B) affected by the stretching of the cells.
C) more negative than that of most cells.
D) unaffected by nearby potential change.
E) nearly zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Slow-twitch fibers
A) are also called glycolytic muscle.
B) are also called white muscle.
C) are well supplied with mitochondria.
D) contain less myoglobin than fast-twitch fibers within the same muscle.
E) are found in lower proportion in the leg muscles than breast muscles of farmed chickens.
A) are also called glycolytic muscle.
B) are also called white muscle.
C) are well supplied with mitochondria.
D) contain less myoglobin than fast-twitch fibers within the same muscle.
E) are found in lower proportion in the leg muscles than breast muscles of farmed chickens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Muscle tone is the condition in which
A) different muscles are taking responsibility for maintaining posture.
B) the muscle has generated maximum tension.
C) the muscle will eventually exhaust its supply of ATP.
D) a small but changing number of motor units are active in a muscle.
E) the maximum number of action potentials is being received by the muscle.
A) different muscles are taking responsibility for maintaining posture.
B) the muscle has generated maximum tension.
C) the muscle will eventually exhaust its supply of ATP.
D) a small but changing number of motor units are active in a muscle.
E) the maximum number of action potentials is being received by the muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is a feature of cardiac muscle that helps the heart withstand high pressures without tearing?
A) Branching and intertwined fibers
B) Fibers arranged in parallel
C) A single nucleus possessed by each fiber
D) Gap junctions between fibers
E) The pacemaking functions of some fibers
A) Branching and intertwined fibers
B) Fibers arranged in parallel
C) A single nucleus possessed by each fiber
D) Gap junctions between fibers
E) The pacemaking functions of some fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When troponin binds calcium,
A) it allows tropomyosin to bind actin.
B) ion channels open, and sodium rushes into the muscle cells.
C) it changes conformation, twisting tropomyosin and exposing the actin-myosin binding site.
D) it changes conformation, exposing the ATP binding site and allowing the actin-myosin bond to break.
E) it binds to calmodulin and starts a cascade by activating myosin kinase.
A) it allows tropomyosin to bind actin.
B) ion channels open, and sodium rushes into the muscle cells.
C) it changes conformation, twisting tropomyosin and exposing the actin-myosin binding site.
D) it changes conformation, exposing the ATP binding site and allowing the actin-myosin bond to break.
E) it binds to calmodulin and starts a cascade by activating myosin kinase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When an action potential arrives at the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane.Which of the following represents the correct order of the next series of events?
A) Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, an action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, and myosin binds actin.
B) An action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and myosin binds actin.
C) An action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, calcium is taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and myosin binds actin.
D) An action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, ATP binds to myosin, and myosin binds actin.
E) A T tubule is depolarized, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, an action potential is created in the muscle cell, and myosin binds actin.
A) Calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, an action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, and myosin binds actin.
B) An action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and myosin binds actin.
C) An action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, calcium is taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and myosin binds actin.
D) An action potential travels down the T tubules, depolarization spreads through the T tubule, ATP binds to myosin, and myosin binds actin.
E) A T tubule is depolarized, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, an action potential is created in the muscle cell, and myosin binds actin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Skeletal muscle fibers show a range of responses to different levels of stimulation because
A) each muscle fiber contraction is "all or none."
B) the availability of Ca2+ sets an upper limit to the strength of the contraction.
C) a new contraction can occur only after the resting condition is reached.
D) following stimulation, the fibers stay contracted.
E) individual twitches in quick succession in the same fiber can undergo summation.
A) each muscle fiber contraction is "all or none."
B) the availability of Ca2+ sets an upper limit to the strength of the contraction.
C) a new contraction can occur only after the resting condition is reached.
D) following stimulation, the fibers stay contracted.
E) individual twitches in quick succession in the same fiber can undergo summation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement about skeletal muscle contraction is true?
A) A single action potential at the neuromuscular junction is not sufficient to cause a muscle to twitch.
B) An action potential in the muscle cell activates contraction by releasing Na+ into the sarcoplasm.
C) Twitches are able to sum when Ca2+ is quickly removed from the sarcoplasm between action potentials.
D) Summation of twitches leads to a graded increase in the tension that can be generated by a single muscle fiber.
E) The tension generated by a muscle is invariable.
A) A single action potential at the neuromuscular junction is not sufficient to cause a muscle to twitch.
B) An action potential in the muscle cell activates contraction by releasing Na+ into the sarcoplasm.
C) Twitches are able to sum when Ca2+ is quickly removed from the sarcoplasm between action potentials.
D) Summation of twitches leads to a graded increase in the tension that can be generated by a single muscle fiber.
E) The tension generated by a muscle is invariable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Fast-twitch skeletal muscle fibers, called white muscle, are characterized by
A) a high concentration of myoglobin.
B) abundant mitochondria.
C) the rapid development of high tension.
D) the ability to sustain activity for a long time.
E) a higher oxygen requirement than that of slow-twitch fibers.
A) a high concentration of myoglobin.
B) abundant mitochondria.
C) the rapid development of high tension.
D) the ability to sustain activity for a long time.
E) a higher oxygen requirement than that of slow-twitch fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which feature represents one similarity between fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibers within a muscle?
A) Number of mitochondria
B) Amount of myoglobin
C) Amount of glycogen and fat
D) Number of neuromuscular junctions
E) Level of ATPase activity
A) Number of mitochondria
B) Amount of myoglobin
C) Amount of glycogen and fat
D) Number of neuromuscular junctions
E) Level of ATPase activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement about smooth muscle is true?
A) Smooth muscle of the gut is under voluntary control.
B) Smooth muscle cells are multinucleated.
C) Smooth muscle appears striated when viewed with the microscope.
D) Gap junctions are common in smooth muscle.
E) Stretched smooth muscle cells do not contract.
A) Smooth muscle of the gut is under voluntary control.
B) Smooth muscle cells are multinucleated.
C) Smooth muscle appears striated when viewed with the microscope.
D) Gap junctions are common in smooth muscle.
E) Stretched smooth muscle cells do not contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the figure. 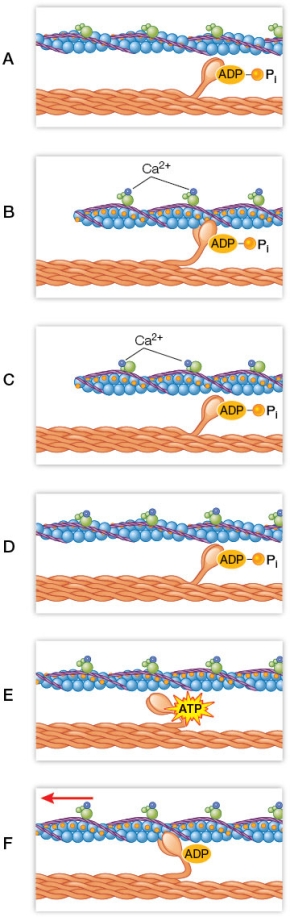 Based on the figure, which of the following represents the stages of muscle contraction in the correct order?
Based on the figure, which of the following represents the stages of muscle contraction in the correct order?
A) A B C D E F
B) A F E D C B
C) D F E B C A
D) A C B F E D
E) D E F B C A
 Based on the figure, which of the following represents the stages of muscle contraction in the correct order?
Based on the figure, which of the following represents the stages of muscle contraction in the correct order?A) A B C D E F
B) A F E D C B
C) D F E B C A
D) A C B F E D
E) D E F B C A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Fast-twitch fibers
A) are also called red muscle.
B) fatigue rapidly.
C) have more mitochondria per cell than do slow-twitch fibers within the same muscle.
D) are also called oxidative muscle.
E) are found in higher proportion in the leg muscles of champion marathon runners than weight lifters.
A) are also called red muscle.
B) fatigue rapidly.
C) have more mitochondria per cell than do slow-twitch fibers within the same muscle.
D) are also called oxidative muscle.
E) are found in higher proportion in the leg muscles of champion marathon runners than weight lifters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure showing muscle cells. 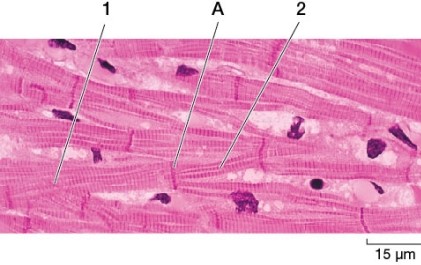 In the living tissue, if an action potential stimulates contraction of cell 1, will cell 2 also contract?
In the living tissue, if an action potential stimulates contraction of cell 1, will cell 2 also contract?
A) Yes, because an action potential in cell 1 will spread to cell 2 through gap junctions in structure A.
B) Yes, because the motor neuron A that innervates cell 1 also innervates cell 2.
C) No, because the action potential will be stopped by structure A, which separates cell 1 and cell 2.
D) Yes, because the smooth muscle cell labeled 1 will spread the action potential to cell 2 through the neuromuscular junction at A.
E) No, because the skeletal muscle cell labeled 1 is not physically connected to cell 2 through gap junctions.
 In the living tissue, if an action potential stimulates contraction of cell 1, will cell 2 also contract?
In the living tissue, if an action potential stimulates contraction of cell 1, will cell 2 also contract?A) Yes, because an action potential in cell 1 will spread to cell 2 through gap junctions in structure A.
B) Yes, because the motor neuron A that innervates cell 1 also innervates cell 2.
C) No, because the action potential will be stopped by structure A, which separates cell 1 and cell 2.
D) Yes, because the smooth muscle cell labeled 1 will spread the action potential to cell 2 through the neuromuscular junction at A.
E) No, because the skeletal muscle cell labeled 1 is not physically connected to cell 2 through gap junctions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
_______ chemically binds with calcium, and this complex activates myosin kinase in smooth muscle cells.
A) Myosin
B) Actin
C) Troponin
D) Cyclic AMP
E) Calmodulin
A) Myosin
B) Actin
C) Troponin
D) Cyclic AMP
E) Calmodulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does tropomyosin control muscle contraction?
A) It provides a bridge between actin and myosin.
B) It provides a site where ATP can be utilized.
C) Changes in its conformation expose actin-myosin binding sites.
D) It transmits an electric charge to the filaments.
E) Changes in its shape open membrane channels.
A) It provides a bridge between actin and myosin.
B) It provides a site where ATP can be utilized.
C) Changes in its conformation expose actin-myosin binding sites.
D) It transmits an electric charge to the filaments.
E) Changes in its shape open membrane channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The strength or weakness of a skeletal muscle contraction depends on
A) only the number of motor units activated.
B) only the frequency with which motor units fire.
C) only the number of muscle fibers stimulated.
D) only the number of motor units activated and the frequency with which motor units fire.
E) the number of motor units activated, the frequency with which motor units fire, and the number of muscle fibers stimulated.
A) only the number of motor units activated.
B) only the frequency with which motor units fire.
C) only the number of muscle fibers stimulated.
D) only the number of motor units activated and the frequency with which motor units fire.
E) the number of motor units activated, the frequency with which motor units fire, and the number of muscle fibers stimulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Bricklayers periodically need to carry heavy stacks of bricks from their truck to the work site, and they are quickly fatigued by this activity.An examination of the muscles used to perform this work would reveal
A) substantial fuel reserves.
B) low levels of ATPase activity.
C) an abundance of blood vessels.
D) relatively few mitochondria.
E) relatively high amounts of myoglobin.
A) substantial fuel reserves.
B) low levels of ATPase activity.
C) an abundance of blood vessels.
D) relatively few mitochondria.
E) relatively high amounts of myoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Anaerobic exercise such as weight lifting
A) increases endurance without increasing strength.
B) causes damage to muscle, none of which can be repaired.
C) induces the formation of new actin and myosin filaments in existing muscle fibers.
D) produces smaller muscle fibers but increases their number and hence creates bigger muscles.
E) causes satellite cells to increase the number of intercalated discs between the muscle fibers.
A) increases endurance without increasing strength.
B) causes damage to muscle, none of which can be repaired.
C) induces the formation of new actin and myosin filaments in existing muscle fibers.
D) produces smaller muscle fibers but increases their number and hence creates bigger muscles.
E) causes satellite cells to increase the number of intercalated discs between the muscle fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement about the effect of anaerobic exercise on muscles is true?
A) It increases the size of muscle fibers by increasing the number of actin and myosin filaments.
B) It increases the number of mitochondria per muscle fiber.
C) It increases the enzymes involved in oxidative production of ATP.
D) It increases the density of capillaries delivering oxygen to the muscles.
E) It increases the production of myoglobin.
A) It increases the size of muscle fibers by increasing the number of actin and myosin filaments.
B) It increases the number of mitochondria per muscle fiber.
C) It increases the enzymes involved in oxidative production of ATP.
D) It increases the density of capillaries delivering oxygen to the muscles.
E) It increases the production of myoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The skeletal muscles in the legs of competitive cross-country skiers and long-distance runners are likely to have
A) all slow-twitch fibers.
B) all fast-twitch fibers.
C) about the same number of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers.
D) more fast-twitch fibers.
E) more slow-twitch fibers.
A) all slow-twitch fibers.
B) all fast-twitch fibers.
C) about the same number of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers.
D) more fast-twitch fibers.
E) more slow-twitch fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Shot-putters competing in track and field events rely on short, intense bursts of energy.An examination of the muscles used in this sport would reveal
A) substantial fuel reserves.
B) low levels of ATPase activity.
C) an abundance of blood vessels.
D) relatively few mitochondria.
E) relatively high amounts of myoglobin.
A) substantial fuel reserves.
B) low levels of ATPase activity.
C) an abundance of blood vessels.
D) relatively few mitochondria.
E) relatively high amounts of myoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
At a turkey dinner, you tell your host you would like to be served mostly fast-twitch muscle.To comply, your host serves you
A) a drumstick.
B) a thigh.
C) the gizzard.
D) the heart.
E) a slice of breast meat.
A) a drumstick.
B) a thigh.
C) the gizzard.
D) the heart.
E) a slice of breast meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A muscle reaches its maximum force of contraction when it is at _______ percent of its resting length.
A) 40
B) 60
C) 80
D) 100
E) 125 or greater
A) 40
B) 60
C) 80
D) 100
E) 125 or greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the slow-twitch muscle fiber of a world-class marathon runner, a weight lifter, and a 100-meter dash Olympian were compared, which would represent the correct order, from highest to lowest, of the percentage of slow-twitch muscle in their bodies?
A) Triathlete, marathon runner, weight lifter
B) Weight lifter, marathon runner, triathlete
C) Marathon runner, triathlete, weight lifter
D) Triathlete, weight lifter, marathon runner
E) Marathon runner, weight lifter, triathlete
A) Triathlete, marathon runner, weight lifter
B) Weight lifter, marathon runner, triathlete
C) Marathon runner, triathlete, weight lifter
D) Triathlete, weight lifter, marathon runner
E) Marathon runner, weight lifter, triathlete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A muscle's capacity to be shortened is limited by
A) bones, which eventually impede further contraction.
B) the amount of overlap of actin and myosin, which eventually causes myosin to push against the Z line.
C) the amount of overlap of actin and myosin, which eventually causes actin to push against the Z line.
D) the water component of its fibers' cytoplasm, which is incompressible.
E) the water content of the cartilage matrix of the joint the muscle is associated with.
A) bones, which eventually impede further contraction.
B) the amount of overlap of actin and myosin, which eventually causes myosin to push against the Z line.
C) the amount of overlap of actin and myosin, which eventually causes actin to push against the Z line.
D) the water component of its fibers' cytoplasm, which is incompressible.
E) the water content of the cartilage matrix of the joint the muscle is associated with.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The primary determinant regarding the proportion of fast- and slow-twitch fibers in a person's skeletal muscle is
A) diet.
B) exercise.
C) genetic heritage.
D) age.
E) geographic location.
A) diet.
B) exercise.
C) genetic heritage.
D) age.
E) geographic location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Wild turkeys have breast muscles that are capable of explosively fast flight, but only for short distances.These muscles most likely
A) fuel their rapid flight with high levels of mitochondria.
B) have surprisingly low rates of ATPase activity.
C) are fast-twitch muscles.
D) are slow-twitch muscles.
E) have substantial reserves of glycogen.
A) fuel their rapid flight with high levels of mitochondria.
B) have surprisingly low rates of ATPase activity.
C) are fast-twitch muscles.
D) are slow-twitch muscles.
E) have substantial reserves of glycogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Migrating birds often cross the Gulf of Mexico in a single flight thus their flight muscles demand extreme endurance.An examination of the muscles used to perform this activity would reveal
A) little to no myoglobin.
B) one-to-two nuclei per muscle fiber.
C) an abundance of blood vessels.
D) a high number of intercalated discs.
E) numerous gap junctions.
A) little to no myoglobin.
B) one-to-two nuclei per muscle fiber.
C) an abundance of blood vessels.
D) a high number of intercalated discs.
E) numerous gap junctions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which statement about fast-twitch fibers is true?
A) They are more common in the leg muscles of champion sprinters than in champion marathon runners.
B) They have more mitochondria than slow-twitch fibers in the same muscle.
C) They fatigue less rapidly than slow-twitch fibers do.
D) Their abundance is more a product of training than of genetics.
E) They are more common in postural muscles than in finger muscles.
A) They are more common in the leg muscles of champion sprinters than in champion marathon runners.
B) They have more mitochondria than slow-twitch fibers in the same muscle.
C) They fatigue less rapidly than slow-twitch fibers do.
D) Their abundance is more a product of training than of genetics.
E) They are more common in postural muscles than in finger muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Salmon returning to spawn in their native stream undertake a journey that requires extreme endurance.An examination of the muscles used to perform this activity would reveal
A) mostly smooth muscle fibers.
B) a high number of gap junctions.
C) mostly glycolytic fibers.
D) many mitochondria per cell.
E) pale color of the cells
A) mostly smooth muscle fibers.
B) a high number of gap junctions.
C) mostly glycolytic fibers.
D) many mitochondria per cell.
E) pale color of the cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Aerobic exercise like jogging causes changes in skeletal leg muscles, such as
A) increasing hemoglobin in fast-twitch muscles.
B) decreasing the number of mitochondria in the muscle cells.
C) decreasing the enzymes involved in energy utilization.
D) increasing the density of capillaries.
E) increasing the number of glycolytic muscle fibers.
A) increasing hemoglobin in fast-twitch muscles.
B) decreasing the number of mitochondria in the muscle cells.
C) decreasing the enzymes involved in energy utilization.
D) increasing the density of capillaries.
E) increasing the number of glycolytic muscle fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement about fast-twitch and slow-twitch fibers is true?
A) In skeletal muscle, the most important factor determining the proportion of fast- and slow-twitch fibers is physical training.
B) Aerobic training increases the oxidative capacity of intermediate fibers.
C) A single muscle cell may contain fast- and slow-twitch fibers.
D) Fast-twitch fibers fatigue slowly.
E) Champion sprinters are likely to have a high proportion of slow-twitch fibers in their legs.
A) In skeletal muscle, the most important factor determining the proportion of fast- and slow-twitch fibers is physical training.
B) Aerobic training increases the oxidative capacity of intermediate fibers.
C) A single muscle cell may contain fast- and slow-twitch fibers.
D) Fast-twitch fibers fatigue slowly.
E) Champion sprinters are likely to have a high proportion of slow-twitch fibers in their legs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the figure showing the leg muscles of two athletes. 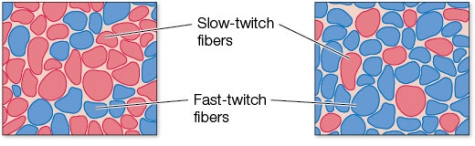 Investigators studying the leg muscles of Lance Armstrong, formerly recognized as the seven-time winner of the Tour de France bicycle marathon, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.
Investigators studying the leg muscles of Lance Armstrong, formerly recognized as the seven-time winner of the Tour de France bicycle marathon, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.
A) abundant slow-twitch; left
B) hyper-efficient slow-twitch; left
C) atrophied (neglected) slow-twitch; left
D) abundant fast-twitch; right
E) atrophied (neglected) fast-twitch; right
 Investigators studying the leg muscles of Lance Armstrong, formerly recognized as the seven-time winner of the Tour de France bicycle marathon, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.
Investigators studying the leg muscles of Lance Armstrong, formerly recognized as the seven-time winner of the Tour de France bicycle marathon, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.A) abundant slow-twitch; left
B) hyper-efficient slow-twitch; left
C) atrophied (neglected) slow-twitch; left
D) abundant fast-twitch; right
E) atrophied (neglected) fast-twitch; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Despite their lumbering appearance, alligators are capable of quick bursts of speed.This is most likely because their muscles
A) fuel their rapid movement with high levels of mitochondria.
B) have surprisingly low rates of ATPase activity.
C) are slow-twitch muscles.
D) are fast-twitch muscles.
E) have substantial reserves of glycogen.
A) fuel their rapid movement with high levels of mitochondria.
B) have surprisingly low rates of ATPase activity.
C) are slow-twitch muscles.
D) are fast-twitch muscles.
E) have substantial reserves of glycogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the figure showing the leg muscles of two athletes. 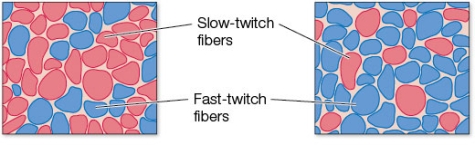 Investigators studying the leg muscles of Usain Bolt, the Olympian recognized as the fastest sprinter in the world for his performance in the 100-meter dash, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.
Investigators studying the leg muscles of Usain Bolt, the Olympian recognized as the fastest sprinter in the world for his performance in the 100-meter dash, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.
A) abundant slow-twitch; left
B) hyper-efficient slow-twitch; left
C) atrophied (neglected) slow-twitch; left
D) abundant fast-twitch; right
E) atrophied (neglected) fast-twitch; right
 Investigators studying the leg muscles of Usain Bolt, the Olympian recognized as the fastest sprinter in the world for his performance in the 100-meter dash, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.
Investigators studying the leg muscles of Usain Bolt, the Olympian recognized as the fastest sprinter in the world for his performance in the 100-meter dash, would likely find _______ muscle fibers, as shown in the panel on the _______.A) abundant slow-twitch; left
B) hyper-efficient slow-twitch; left
C) atrophied (neglected) slow-twitch; left
D) abundant fast-twitch; right
E) atrophied (neglected) fast-twitch; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Performing a chin-up is usually particularly difficult at the very end of the exercise because
A) when the muscle is fully contracted, it is exerting a maximum amount of force.
B) there is so much overlap between actin and myosin in the sarcomeres.
C) of psychological fatigue that is a metabolic by-product of the exertion.
D) of the necessary switch from fast- to slow-twitch fibers.
E) the sarcomeres cannot shorten beyond their resting length.
A) when the muscle is fully contracted, it is exerting a maximum amount of force.
B) there is so much overlap between actin and myosin in the sarcomeres.
C) of psychological fatigue that is a metabolic by-product of the exertion.
D) of the necessary switch from fast- to slow-twitch fibers.
E) the sarcomeres cannot shorten beyond their resting length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement best describes how an earthworm moves?
A) It stretches its longitudinal muscles and pushes its fluid-filled body cavity forward.
B) It forms pseudopods that ooze forward or backward.
C) It uses the coordinated beating of many cilia.
D) It alternates contractions of longitudinal and circular muscles.
E) It contracts longitudinal muscles, which puts pressure on the hydrostatic skeleton and causes it to extend.
A) It stretches its longitudinal muscles and pushes its fluid-filled body cavity forward.
B) It forms pseudopods that ooze forward or backward.
C) It uses the coordinated beating of many cilia.
D) It alternates contractions of longitudinal and circular muscles.
E) It contracts longitudinal muscles, which puts pressure on the hydrostatic skeleton and causes it to extend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement about exoskeletons is true?
A) During molting, the old exoskeleton is reabsorbed and a new exoskeleton forms.
B) A clam shell is not an exoskeleton.
C) The arthropod cuticle is secreted by a layer of cells external to the exoskeleton.
D) The inner layer of the arthropod exoskeleton provides a surface for muscle attachment.
E) The arthropod exoskeleton is thickened at the joints.
A) During molting, the old exoskeleton is reabsorbed and a new exoskeleton forms.
B) A clam shell is not an exoskeleton.
C) The arthropod cuticle is secreted by a layer of cells external to the exoskeleton.
D) The inner layer of the arthropod exoskeleton provides a surface for muscle attachment.
E) The arthropod exoskeleton is thickened at the joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The glycolytic system by which muscles obtain ATP
A) relies on creatine phosphate.
B) is also referred to as the immediate system.
C) is the most efficient means of producing ATP.
D) produces lactic acid as a by-product.
E) completely metabolizes carbohydrates and fats.
A) relies on creatine phosphate.
B) is also referred to as the immediate system.
C) is the most efficient means of producing ATP.
D) produces lactic acid as a by-product.
E) completely metabolizes carbohydrates and fats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A major disadvantage of the glycolytic system for supplying ATP to muscle fibers is
A) the efficiency of glycolysis compared to aerobic respiration.
B) the long period of time that is required before it can start supplying ATP.
C) that it leads to the accumulation of lactic acid.
D) that it requires numerous mitochondria.
E) that it requires a large supply of oxygen, and therefore a high density of capillaries
A) the efficiency of glycolysis compared to aerobic respiration.
B) the long period of time that is required before it can start supplying ATP.
C) that it leads to the accumulation of lactic acid.
D) that it requires numerous mitochondria.
E) that it requires a large supply of oxygen, and therefore a high density of capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The three systems by which muscles obtain ATP
A) differ in the capacity and rate at which they produce ATP.
B) rely on the large amounts of ATP already present in the muscle itself.
C) produce similar amounts of ATP.
D) rely on reactions within mitochondria.
E) have similar time courses.
A) differ in the capacity and rate at which they produce ATP.
B) rely on the large amounts of ATP already present in the muscle itself.
C) produce similar amounts of ATP.
D) rely on reactions within mitochondria.
E) have similar time courses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which statement about the endoskeletons of vertebrates is true?
A) The muscles are attached to a nonliving support structure.
B) The rib bones are part of the appendicular skeleton.
C) They allow the animal to expand without molting.
D) They consist of bone, only.
E) Only one bone is required to form a joint.
A) The muscles are attached to a nonliving support structure.
B) The rib bones are part of the appendicular skeleton.
C) They allow the animal to expand without molting.
D) They consist of bone, only.
E) Only one bone is required to form a joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
An advantage of an endoskeleton over an exoskeleton is that an endoskeleton
A) provides muscle attachment sites.
B) provides protection.
C) grows as the animal grows.
D) supports the animal's weight.
E) gives structure to the animal.
A) provides muscle attachment sites.
B) provides protection.
C) grows as the animal grows.
D) supports the animal's weight.
E) gives structure to the animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
After the first 15 minutes of a 10-km run, the major energy requirements of the leg muscles are supplied by
A) preformed ATP.
B) glycolysis.
C) oxidative metabolism.
D) pyruvate and lactate.
E) the high-protein drink consumed right before the run.
A) preformed ATP.
B) glycolysis.
C) oxidative metabolism.
D) pyruvate and lactate.
E) the high-protein drink consumed right before the run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the graph showing the capacity of three systems that provide ATP for muscle contraction. 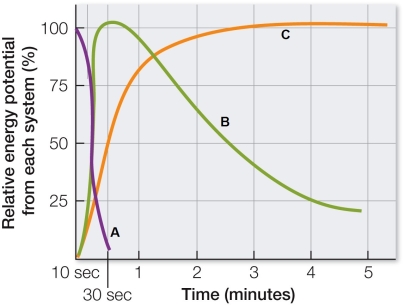 Based on the graph, which statement is true?
Based on the graph, which statement is true?
A) The system of curve A metabolizes carbohydrates to pyruvate and lactate.
B) The system of curve B comes on line within seconds but lacks sustained efficiency.
C) The system of curve B uses ATP produced by oxidative metabolism.
D) The system of curve C uses preformed ATP and creatine phosphate.
E) The system of curve C enables fast-twitch fibers to generate force quickly.
 Based on the graph, which statement is true?
Based on the graph, which statement is true?A) The system of curve A metabolizes carbohydrates to pyruvate and lactate.
B) The system of curve B comes on line within seconds but lacks sustained efficiency.
C) The system of curve B uses ATP produced by oxidative metabolism.
D) The system of curve C uses preformed ATP and creatine phosphate.
E) The system of curve C enables fast-twitch fibers to generate force quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a clown at a birthday party squeezes a long balloon to twist it into a poodle or a hat, the volume of air inside the balloon stretches the balloon and extends its length and stays constant.This example is analogous to the action of muscles on the
A) endoskeleton.
B) hydrostatic skeleton.
C) spandrel skeleton.
D) exoskeleton.
E) tendril skeleton.
A) endoskeleton.
B) hydrostatic skeleton.
C) spandrel skeleton.
D) exoskeleton.
E) tendril skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a benefit of the tough exoskeleton of arthropods that might help explain their tremendous evolutionary success?
A) It protects against abrasion and provides attachment sites for muscles.
B) It is soft and therefore allows for evaporation of water through the cuticle.
C) It is made up of a bony, calcium phosphate material called chitin.
D) It is stiff and prevents bending at the animals' joints.
E) It expands to accommodate the growing animal.
A) It protects against abrasion and provides attachment sites for muscles.
B) It is soft and therefore allows for evaporation of water through the cuticle.
C) It is made up of a bony, calcium phosphate material called chitin.
D) It is stiff and prevents bending at the animals' joints.
E) It expands to accommodate the growing animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the graph showing the capacity of three systems that provide ATP for muscle contraction. 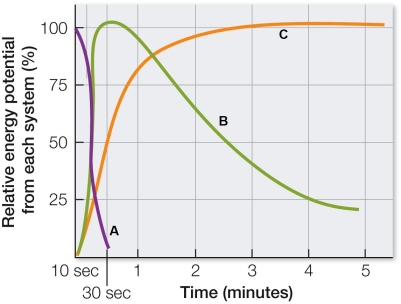 A marathon runner relies mostly on
A marathon runner relies mostly on
A) the system of curve A.
B) the system of curve B.
C) the system of curve C.
D) anaerobic production of ATP to meet the needs of muscles.
E) the system of curve A generating precursors for system B.
 A marathon runner relies mostly on
A marathon runner relies mostly onA) the system of curve A.
B) the system of curve B.
C) the system of curve C.
D) anaerobic production of ATP to meet the needs of muscles.
E) the system of curve A generating precursors for system B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which statement about the skeletal system of the clam is true?
A) It is an endoskeleton.
B) It consists of a shell made up primarily of protein and crystals of calcium carbonate.
C) Muscles attached to regions of the endoskeleton cause movement.
D) Muscles are attached to the endoskeleton by tendons.
E) Ligaments are used to attach muscles to the skeleton.
A) It is an endoskeleton.
B) It consists of a shell made up primarily of protein and crystals of calcium carbonate.
C) Muscles attached to regions of the endoskeleton cause movement.
D) Muscles are attached to the endoskeleton by tendons.
E) Ligaments are used to attach muscles to the skeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Insect flight muscles can contract as fast as _______ times per second, which is _______ hummingbird flight muscles.
A) 50; slower than
B) 100; slower than
C) 500; the same as
D) 1,000; the same as
E) 1,000; many times faster than
A) 50; slower than
B) 100; slower than
C) 500; the same as
D) 1,000; the same as
E) 1,000; many times faster than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is a major difference between strength training and aerobic exercise?
A) Only strength training increases endurance by creating more muscle fibers.
B) Only aerobic exercise increases the size of muscle fibers.
C) Only strength training increases the production of myoglobin.
D) Only aerobic exercise increases the oxidative capacity of muscles.
E) Only strength training increases the density of capillaries delivering oxygen to the muscles.
A) Only strength training increases endurance by creating more muscle fibers.
B) Only aerobic exercise increases the size of muscle fibers.
C) Only strength training increases the production of myoglobin.
D) Only aerobic exercise increases the oxidative capacity of muscles.
E) Only strength training increases the density of capillaries delivering oxygen to the muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is not one of the systems that supplies muscles with the ATP needed for contraction?
A) Immediate system
B) System that creates lactate
C) Glycolytic system
D) Oxidative system
E) Haversian system
A) Immediate system
B) System that creates lactate
C) Glycolytic system
D) Oxidative system
E) Haversian system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The total energy supply in all the muscles of the human body (in the form of ATP and creatine phosphate) is about 10 kilocalories.When a human is sitting at rest, how long does it take the body to metabolize this amount of energy?
A) 1 second
B) 30 seconds
C) 3 minutes
D) 10 minutes
E) 30 minutes
A) 1 second
B) 30 seconds
C) 3 minutes
D) 10 minutes
E) 30 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the graph showing the capacity of three systems that provide ATP for muscle contraction. 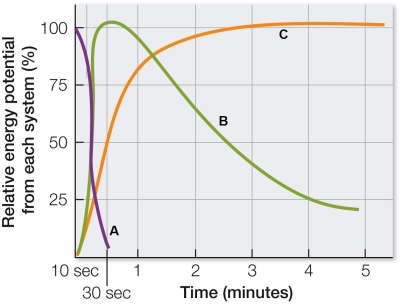 A short-distance world-record champion running a 400-meter race in 43 seconds relies mostly on
A short-distance world-record champion running a 400-meter race in 43 seconds relies mostly on
A) the system of curve A.
B) the system of curve B.
C) the system of curve C.
D) the anaerobic production of ATP to meet the needs of muscles.
E) both the systems of curve A and B.
 A short-distance world-record champion running a 400-meter race in 43 seconds relies mostly on
A short-distance world-record champion running a 400-meter race in 43 seconds relies mostly onA) the system of curve A.
B) the system of curve B.
C) the system of curve C.
D) the anaerobic production of ATP to meet the needs of muscles.
E) both the systems of curve A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which statement about skeletons is true?
A) No skeleton consists entirely of cartilage.
B) Hydrostatic skeletons are not useful in the function of locomotion.
C) An advantage of an exoskeleton is that it can continue to grow throughout the life of the animal.
D) Unlike bones, external skeletons must remain flexible and therefore do not contain calcium carbonate crystals.
E) The two categories of bone are membranous bone and cartilage bone, based on how the bones are formed.
A) No skeleton consists entirely of cartilage.
B) Hydrostatic skeletons are not useful in the function of locomotion.
C) An advantage of an exoskeleton is that it can continue to grow throughout the life of the animal.
D) Unlike bones, external skeletons must remain flexible and therefore do not contain calcium carbonate crystals.
E) The two categories of bone are membranous bone and cartilage bone, based on how the bones are formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Satellite cells are characterized in part by their ability to
A) communicate a muscle fiber's need for more O2.
B) lie in a ring around the muscle fibers, absorbing their metabolic waste.
C) produce new muscle fibers.
D) move through the fibers, providing ATP where it is most needed.
E) phagocytize, watching for and then attacking pathogens in the muscle fiber.
A) communicate a muscle fiber's need for more O2.
B) lie in a ring around the muscle fibers, absorbing their metabolic waste.
C) produce new muscle fibers.
D) move through the fibers, providing ATP where it is most needed.
E) phagocytize, watching for and then attacking pathogens in the muscle fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



