Deck 50: Nutrition, Digestion, and Absorption
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/259
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 50: Nutrition, Digestion, and Absorption
1
The nutritional disease kwashiorkor, in which the body starts to metabolize some of the molecules of its own body, results from a(n)
A) protein deficiency.
B) vitamin deficiency.
C) mineral deficiency.
D) overdose of fat-soluble vitamins.
E) overdose of thyroxine.
A) protein deficiency.
B) vitamin deficiency.
C) mineral deficiency.
D) overdose of fat-soluble vitamins.
E) overdose of thyroxine.
A
2
Supplementation with _______ helps prevent the nutritional deficiency disease called goiter.
A) fluoride
B) iodine
C) chromium
D) zinc
E) copper
A) fluoride
B) iodine
C) chromium
D) zinc
E) copper
B
3
Which statement about the essential amino acids is true?
A) Only a few animals have essential amino acids.
B) Ingesting a surplus of one essential amino acid can compensate for a shortage of another.
C) Certain combinations, such as beans and corn, supply all eight of the essential amino acids in humans.
D) Acetyl groups can be combined with amino groups to produce many of the essential amino acids.
E) Human infants and adults require all the same essential amino acids.
A) Only a few animals have essential amino acids.
B) Ingesting a surplus of one essential amino acid can compensate for a shortage of another.
C) Certain combinations, such as beans and corn, supply all eight of the essential amino acids in humans.
D) Acetyl groups can be combined with amino groups to produce many of the essential amino acids.
E) Human infants and adults require all the same essential amino acids.
C
4
Organisms that derive their energy and molecular nutrients from other organisms are called
A) autotrophs.
B) herbivores.
C) heterotrophs.
D) photosynthetic.
E) protists.
A) autotrophs.
B) herbivores.
C) heterotrophs.
D) photosynthetic.
E) protists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Numerous organisms in deep-sea thermal vents, far below the surface and away from any light, survive by harvesting the chemical energy stored in the bonds of inorganic molecules that rise from the interior of Earth.These organisms can be described as
A) autotrophs.
B) heterotrophs.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) predators.
A) autotrophs.
B) heterotrophs.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
During periods of starvation, stored fuels are used in which order?
A) Fats, glycogen, proteins
B) Glycogen, proteins, fats
C) Proteins, fats, glycogen
D) Fats, proteins, glycogen
E) Glycogen, fats, proteins
A) Fats, glycogen, proteins
B) Glycogen, proteins, fats
C) Proteins, fats, glycogen
D) Fats, proteins, glycogen
E) Glycogen, fats, proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The energy content of food is described in terms of calories because
A) the amount of energy in food depends on the temperature.
B) food heats up as it is being digested.
C) the energy in food ultimately becomes mostly heat.
D) heat is the main product of digestion.
E) heat is the main product of respiration.
A) the amount of energy in food depends on the temperature.
B) food heats up as it is being digested.
C) the energy in food ultimately becomes mostly heat.
D) heat is the main product of digestion.
E) heat is the main product of respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Of the food components listed, which provides the least amount of metabolic energy for animals?
A) Carbohydrates
B) Nucleic acids
C) Proteins
D) Fats
E) Sugars
A) Carbohydrates
B) Nucleic acids
C) Proteins
D) Fats
E) Sugars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Certain amino acids are essential to the diet of animals because they
A) prevent overnourishment.
B) are cofactors and coenzymes that are required for normal physiological function.
C) cannot be directly synthesized by animals through the transfer of an amino group to an appropriate carbon skeleton.
D) are needed to make storable fats for use during hibernation and migration.
E) are the most important source of stored energy.
A) prevent overnourishment.
B) are cofactors and coenzymes that are required for normal physiological function.
C) cannot be directly synthesized by animals through the transfer of an amino group to an appropriate carbon skeleton.
D) are needed to make storable fats for use during hibernation and migration.
E) are the most important source of stored energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which disease differs from the others in terms of the kind of deficiency that causes it?
A) Pellagra
B) Rickets
C) Goiter
D) Pernicious anemia
E) Beriberi
A) Pellagra
B) Rickets
C) Goiter
D) Pernicious anemia
E) Beriberi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which type of food is least likely to help a patient who complains of night blindness?
A) Fruits
B) Vegetables
C) Liver
D) Dairy products
E) Whole grains
A) Fruits
B) Vegetables
C) Liver
D) Dairy products
E) Whole grains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Certain amino acids are called essential amino acids because they
A) are required for making protein.
B) cannot be made from other amino acids and must be obtained from food.
C) are those required by all animals.
D) are essential as an energy source.
E) are required for making nucleic acids.
A) are required for making protein.
B) cannot be made from other amino acids and must be obtained from food.
C) are those required by all animals.
D) are essential as an energy source.
E) are required for making nucleic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Researchers recently reported that the green sea slug, Elysia chlorotica, can incorporate genes from algae, allowing them to use solar energy to meet their energy needs.Sea slugs can therefore be described as
A) predators.
B) heterotrophs.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) autotrophs.
A) predators.
B) heterotrophs.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) autotrophs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Vitamins are essential nutrients for cells because they cannot be synthesized by the animal itself, and most
A) are used as an energy source.
B) function as enzymes to digest foods.
C) function as coenzymes or parts of coenzymes.
D) are metabolized into essential amino acids.
E) are essential macronutrients.
A) are used as an energy source.
B) function as enzymes to digest foods.
C) function as coenzymes or parts of coenzymes.
D) are metabolized into essential amino acids.
E) are essential macronutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which statement about energy storage is true?
A) Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscle as glucose.
B) Fat is not an important form of stored energy.
C) Fat has the lowest energy content per gram.
D) Protein is the most important energy storage component.
E) The total glycogen stores are usually not more than a day's energy requirements.
A) Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and muscle as glucose.
B) Fat is not an important form of stored energy.
C) Fat has the lowest energy content per gram.
D) Protein is the most important energy storage component.
E) The total glycogen stores are usually not more than a day's energy requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The major form of stored energy in animal bodies is _______ because it _______.
A) protein; is a long-term energy storage form
B) glycogen; breaks down into readily usable carbohydrates
C) glycogen; is lightweight
D) fat; has the highest energy content per gram
E) fat; is readily stored and dissolved in water
A) protein; is a long-term energy storage form
B) glycogen; breaks down into readily usable carbohydrates
C) glycogen; is lightweight
D) fat; has the highest energy content per gram
E) fat; is readily stored and dissolved in water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement about vitamins is true?
A) Vitamins, unlike essential amino acids and fatty acids, are not organic molecules.
B) Most vertebrates require the same vitamins.
C) Vitamins function mostly as building blocks for proteins.
D) Vitamins are required in relatively large amounts.
E) Humans require more water-soluble vitamins than fat-soluble vitamins.
A) Vitamins, unlike essential amino acids and fatty acids, are not organic molecules.
B) Most vertebrates require the same vitamins.
C) Vitamins function mostly as building blocks for proteins.
D) Vitamins are required in relatively large amounts.
E) Humans require more water-soluble vitamins than fat-soluble vitamins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which statement about undernourishment is true?
A) The swollen belly seen in a starving child is due to fat being preferentially stored in the abdomen.
B) Several weeks of fasting are required to deplete glycogen reserves.
C) A person can survive no more than a week without food.
D) The loss of blood proteins during starvation leads to edema.
E) During starvation, protein reserves are exhausted before the metabolism of body fat is accelerated.
A) The swollen belly seen in a starving child is due to fat being preferentially stored in the abdomen.
B) Several weeks of fasting are required to deplete glycogen reserves.
C) A person can survive no more than a week without food.
D) The loss of blood proteins during starvation leads to edema.
E) During starvation, protein reserves are exhausted before the metabolism of body fat is accelerated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Adventurers attempting to recreate the Polynesians' months- or years-long trips across the ocean would likely carry _______ with them to avoid the ascorbic acid deficiency called _______.
A) corn; beriberi
B) meat; kwashiorkor
C) liver; pellagra
D) citrus fruits; scurvy
E) dairy products; rickets
A) corn; beriberi
B) meat; kwashiorkor
C) liver; pellagra
D) citrus fruits; scurvy
E) dairy products; rickets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Most animals digest dietary proteins into their constituent amino acids and then synthesize new proteins because
A) all amino acids are essential and cannot be synthesized by animals.
B) though protein function is often species-specific, protein structure is not.
C) foreign proteins are considered invaders and are attacked by the immune system.
D) animals build proteins by first synthesizing acetyl groups from the breakdown products of protein.
E) though macromolecules such as proteins can pass freely into the intestinal cells, they cannot then be transported into the blood vessels.
A) all amino acids are essential and cannot be synthesized by animals.
B) though protein function is often species-specific, protein structure is not.
C) foreign proteins are considered invaders and are attacked by the immune system.
D) animals build proteins by first synthesizing acetyl groups from the breakdown products of protein.
E) though macromolecules such as proteins can pass freely into the intestinal cells, they cannot then be transported into the blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A fundamental difference between saprobes and detritivores is that
A) saprobes have long snouts that allow them access to food that is unavailable to detritivores.
B) saprobes absorb nutrients primarily from living organisms.
C) detritivores are primarily bacteria.
D) detritivores seek out dead organic items and actively eat them.
E) detritivores include fungi but no animal species.
A) saprobes have long snouts that allow them access to food that is unavailable to detritivores.
B) saprobes absorb nutrients primarily from living organisms.
C) detritivores are primarily bacteria.
D) detritivores seek out dead organic items and actively eat them.
E) detritivores include fungi but no animal species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The nutritional disease beriberi results from a(n)
A) protein deficiency.
B) vitamin deficiency.
C) calorie deficiency.
D) overdose of fat-soluble vitamins.
E) overdose of thyroxine.
A) protein deficiency.
B) vitamin deficiency.
C) calorie deficiency.
D) overdose of fat-soluble vitamins.
E) overdose of thyroxine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The root of a typical mammalian tooth contains _______, but not _______.
A) enamel and cement; a pulp cavity
B) enamel and a pulp cavity; dentine
C) dentine and a pulp cavity; but not enamel
D) dentine and enamel; a pulp cavity
E) cement and dentine; a pulp cavity
A) enamel and cement; a pulp cavity
B) enamel and a pulp cavity; dentine
C) dentine and a pulp cavity; but not enamel
D) dentine and enamel; a pulp cavity
E) cement and dentine; a pulp cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Primates can eat citrus fruit to prevent scurvy, which is due to a deficiency of
A) niacin.
B) thiamin.
C) calciferol.
D) ascorbic acid.
E) biotin.
A) niacin.
B) thiamin.
C) calciferol.
D) ascorbic acid.
E) biotin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Prairie dogs feed on a variety of grasses and herbs, and black-footed ferrets feed almost exclusively on prairie dogs.Both of these animals can be described as
A) heterotrophs.
B) saprobes.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) autotrophs.
A) heterotrophs.
B) saprobes.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) autotrophs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The anti-acne medication Retin-A, also used for reduction of wrinkles, has the active ingredient all-trans retinoic acid.If ingested, it can be toxic, but surprisingly it is chemically related to other forms of vitamin A you get on a daily basis primarily from
A) fruits and vegetables.
B) meat.
C) sunshine.
D) intestinal bacteria.
E) wheat.
A) fruits and vegetables.
B) meat.
C) sunshine.
D) intestinal bacteria.
E) wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement about vitamin C is true?
A) It is a fat-soluble vitamin.
B) It is obtained primarily from meat in the Western diet.
C) It is not an essential vitamin for humans because their skin can make it when exposed to sunlight.
D) It is necessary for wound healing.
E) An excess of vitamin C is stored in fat tissue.
A) It is a fat-soluble vitamin.
B) It is obtained primarily from meat in the Western diet.
C) It is not an essential vitamin for humans because their skin can make it when exposed to sunlight.
D) It is necessary for wound healing.
E) An excess of vitamin C is stored in fat tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
People living in impoverished regions, as well as people with alcohol addiction, frequently have a niacin deficiency disease called
A) beriberi.
B) kwashiorkor.
C) pellagra.
D) scurvy.
E) rickets.
A) beriberi.
B) kwashiorkor.
C) pellagra.
D) scurvy.
E) rickets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which vitamin is most likely deficient in a person who eats liver regularly, yet presents with anemia?
A) Pantothenic acid
B) Biotin
C) Vitamin B12
D) Vitamin E
E) Folic acid
A) Pantothenic acid
B) Biotin
C) Vitamin B12
D) Vitamin E
E) Folic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A mammal with a diet of grain and leaves would be expected to have which kind of teeth?
A) Prominent canine teeth and small molars
B) Prominent molars and small canines
C) Prominent molars and small premolars
D) A balanced set of incisors, molars, and canines
E) Prominent canine teeth and small incisors
A) Prominent canine teeth and small molars
B) Prominent molars and small canines
C) Prominent molars and small premolars
D) A balanced set of incisors, molars, and canines
E) Prominent canine teeth and small incisors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The nutritional deficiency disease rickets is caused by an inadequate supply of the fat-soluble vitamin
A) A (retinol).
B) D (calciferol).
C) E (tocopherol).
D) K (menadione).
E) B7 (biotin).
A) A (retinol).
B) D (calciferol).
C) E (tocopherol).
D) K (menadione).
E) B7 (biotin).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A person who consumes a diet high in whole grains but exhibits pernicious anemia most likely is deficient in
A) pantothenic acid.
B) biotin.
C) vitamin B12.
D) vitamin E.
E) folic acid.
A) pantothenic acid.
B) biotin.
C) vitamin B12.
D) vitamin E.
E) folic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The nutritional deficiency disease beriberi is caused by an inadequate supply of the water-soluble vitamin
A) B1 (thiamin).
B) B2 (riboflavin).
C) B12 (cobalamin).
D) folic acid.
E) C (ascorbic acid).
A) B1 (thiamin).
B) B2 (riboflavin).
C) B12 (cobalamin).
D) folic acid.
E) C (ascorbic acid).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement about vitamin D is true?
A) The Inuit peoples of the Arctic obtain it primarily from sunlight.
B) People of middle latitudes obtain it primarily from drinking water.
C) Most people obtain it primarily from protein molecules that absorb sunlight.
D) Most people obtain it primarily from water-soluble components of foods.
E) People in tropical latitudes can obtain it primarily from sunlight.
A) The Inuit peoples of the Arctic obtain it primarily from sunlight.
B) People of middle latitudes obtain it primarily from drinking water.
C) Most people obtain it primarily from protein molecules that absorb sunlight.
D) Most people obtain it primarily from water-soluble components of foods.
E) People in tropical latitudes can obtain it primarily from sunlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A strictly vegan diet with no vitamin B12 supplements can lead to
A) beriberi.
B) pellagra.
C) pernicious anemia.
D) scurvy.
E) night blindness.
A) beriberi.
B) pellagra.
C) pernicious anemia.
D) scurvy.
E) night blindness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Organisms living in the lightless interiors of caves often rely on ingesting dead organic matter that washes in from the surface.They can therefore be described as
A) predators.
B) omnivores.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) detritivores.
A) predators.
B) omnivores.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) detritivores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which character is primarily an herbivorous feeding adaptation?
A) A spiderweb
B) Rattlesnake venom
C) Bat echolocation
D) An elephant's trunk
E) A jellyfish tentacle
A) A spiderweb
B) Rattlesnake venom
C) Bat echolocation
D) An elephant's trunk
E) A jellyfish tentacle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Research in recent years has described the existence of a diverse community of heterotrophs in the deepest parts of the ocean.These organisms ingest dead organic matter that falls down from the surface, and therefore can be described as
A) predators.
B) omnivores.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) detritivores.
A) predators.
B) omnivores.
C) carnivores.
D) herbivores.
E) detritivores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
_______ ingest both plant and animal food and process their food through _______ digestion.
A) Predators; intracellular
B) Omnivores; intracellular
C) Carnivores; intracellular
D) Herbivores; extracellular
E) Omnivores; extracellular
A) Predators; intracellular
B) Omnivores; intracellular
C) Carnivores; intracellular
D) Herbivores; extracellular
E) Omnivores; extracellular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A filter feeder acquires food items by
A) restraining prey with poison.
B) restraining prey using claws and jaws.
C) ingesting mud and extracting particles.
D) filtering food substances from the blood.
E) extracting particles suspended in water.
A) restraining prey with poison.
B) restraining prey using claws and jaws.
C) ingesting mud and extracting particles.
D) filtering food substances from the blood.
E) extracting particles suspended in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the figure showing the digestive systems of an earthworm and a cockroach. 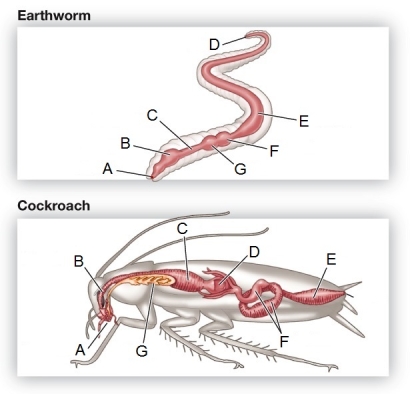 Identify the structure in each organism that is the primary site of nutrient absorption.
Identify the structure in each organism that is the primary site of nutrient absorption.
A) B in earthworm and A in cockroach
B) C in earthworm and B in cockroach
C) G in earthworm and C in cockroach
D) E in earthworm and F in cockroach
E) D in earthworm and D in cockroach
 Identify the structure in each organism that is the primary site of nutrient absorption.
Identify the structure in each organism that is the primary site of nutrient absorption.A) B in earthworm and A in cockroach
B) C in earthworm and B in cockroach
C) G in earthworm and C in cockroach
D) E in earthworm and F in cockroach
E) D in earthworm and D in cockroach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the figure showing the intestinal surface area of various organisms. 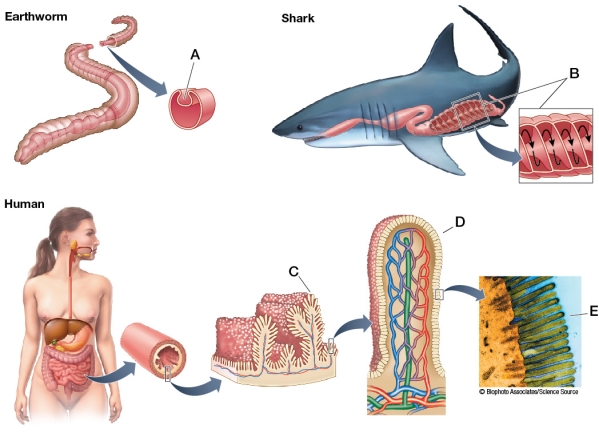 All of the structures labeled in the figure function to increase the surface area available for absorption.Which structure is correctly matched with its name?
All of the structures labeled in the figure function to increase the surface area available for absorption.Which structure is correctly matched with its name?
A) A: Spiral valve
B) B: Typhlosole
C) C: Large intestine
D) D: Villus
E) E: Lacteal
 All of the structures labeled in the figure function to increase the surface area available for absorption.Which structure is correctly matched with its name?
All of the structures labeled in the figure function to increase the surface area available for absorption.Which structure is correctly matched with its name?A) A: Spiral valve
B) B: Typhlosole
C) C: Large intestine
D) D: Villus
E) E: Lacteal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which structure of the vertebrate gut is a membrane covering the abdominal organs and lubricating them so they easily slide against one another?
A) Peritoneum
B) Mucosal layer
C) Submucosal layer
D) Circular muscle layer
E) Longitudinal muscle layer
A) Peritoneum
B) Mucosal layer
C) Submucosal layer
D) Circular muscle layer
E) Longitudinal muscle layer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which structure serves to increase surface area for nutrient absorption?
A) A human's esophagus
B) An earthworm's crop
C) A shark's spiral valve
D) A bird's gizzard
E) A human's lacteals
A) A human's esophagus
B) An earthworm's crop
C) A shark's spiral valve
D) A bird's gizzard
E) A human's lacteals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In humans, which structure is closed off from food when food is swallowed?
A) Epiglottis
B) Larynx
C) Soft palate
D) Pharynx
E) Esophagus
A) Epiglottis
B) Larynx
C) Soft palate
D) Pharynx
E) Esophagus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure showing the digestive systems of an earthworm and a cockroach. 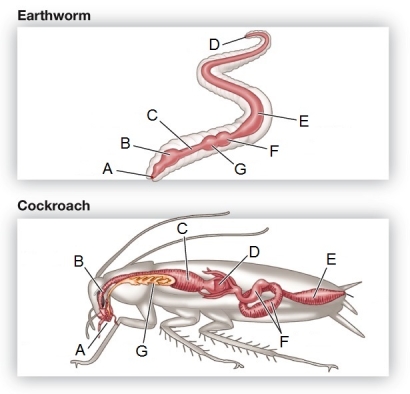 Which component of the digestive system is found in only one of the organisms in the figure?
Which component of the digestive system is found in only one of the organisms in the figure?
A) Mandibles
B) Esophagus
C) Crop
D) Gizzard
E) Anus
 Which component of the digestive system is found in only one of the organisms in the figure?
Which component of the digestive system is found in only one of the organisms in the figure?A) Mandibles
B) Esophagus
C) Crop
D) Gizzard
E) Anus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Nematocysts are an adaptation used by _______ to inject toxin into a victim.
A) jellyfish
B) spiders
C) snakes
D) short-tailed shrews
E) pufferfish
A) jellyfish
B) spiders
C) snakes
D) short-tailed shrews
E) pufferfish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure showing a portion of the human stomach. 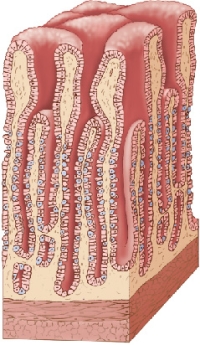 The part of the stomach shown in the figure does not show
The part of the stomach shown in the figure does not show
A) pepsinogen-producing cells.
B) gastric pits.
C) a significant surface area, functioning primarily in absorption.
D) gastric mucosa.
E) parietal cells producing H+ concentration gradients.
 The part of the stomach shown in the figure does not show
The part of the stomach shown in the figure does not showA) pepsinogen-producing cells.
B) gastric pits.
C) a significant surface area, functioning primarily in absorption.
D) gastric mucosa.
E) parietal cells producing H+ concentration gradients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Movement of food from the stomach into the esophagus is normally prevented by
A) the esophageal sphincter.
B) reverse peristalsis.
C) the pyloric sphincter.
D) peristalsis.
E) the pharynx.
A) the esophageal sphincter.
B) reverse peristalsis.
C) the pyloric sphincter.
D) peristalsis.
E) the pharynx.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the figure showing the intestinal surface area of various organisms. 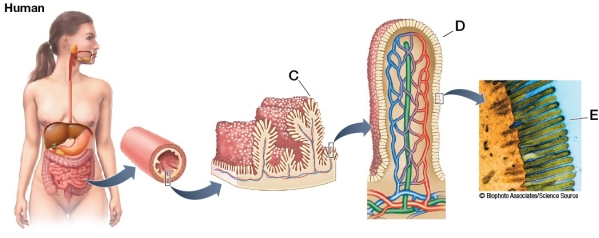 In the figure of the human intestine, what is the structure labeled E, and what is its function?
In the figure of the human intestine, what is the structure labeled E, and what is its function?
A) Villus; contracts, contributing to the wave of peristalsis
B) Mucosa; produces mucus
C) Peritoneum; protects the surface of the intestine
D) Microvillus; increases absorptive surface area
E) Cilium; moves chyme through the intestine
 In the figure of the human intestine, what is the structure labeled E, and what is its function?
In the figure of the human intestine, what is the structure labeled E, and what is its function?A) Villus; contracts, contributing to the wave of peristalsis
B) Mucosa; produces mucus
C) Peritoneum; protects the surface of the intestine
D) Microvillus; increases absorptive surface area
E) Cilium; moves chyme through the intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the key adaptation of most vertebrates that serves to increase absorptive area?
A) The length of the intestine
B) The typhlosole infolding of the intestine
C) The capillary bed underlying the intestine
D) The lymphatic vessels
E) The spiral channel
A) The length of the intestine
B) The typhlosole infolding of the intestine
C) The capillary bed underlying the intestine
D) The lymphatic vessels
E) The spiral channel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The gut of a vertebrate is often described as an elongated tube consisting of four layers of different cell types.Which represents the correct order of those layers, from innermost (lumen-facing) to outermost?
A) Submucosa, cartilage, mucosa, endoplasmic reticulum
B) Smooth muscle layers, submucosa, mucosa, cartilage
C) Cartilage, smooth muscle layers, mucosa, circular muscle
D) Mucosa, submucosa, circular muscle, longitudinal muscle
E) Cartilage, mucosa, endoplasmic reticulum, submucosa
A) Submucosa, cartilage, mucosa, endoplasmic reticulum
B) Smooth muscle layers, submucosa, mucosa, cartilage
C) Cartilage, smooth muscle layers, mucosa, circular muscle
D) Mucosa, submucosa, circular muscle, longitudinal muscle
E) Cartilage, mucosa, endoplasmic reticulum, submucosa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The major function of the colon, or large intestine, is the
A) digestive breakdown of foods.
B) absorption of nutrients from foods.
C) housing of parasitic bacteria.
D) secretion of bile and enzymes.
E) reabsorption of ions and water.
A) digestive breakdown of foods.
B) absorption of nutrients from foods.
C) housing of parasitic bacteria.
D) secretion of bile and enzymes.
E) reabsorption of ions and water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the figure showing the digestive systems of an earthworm and a cockroach. 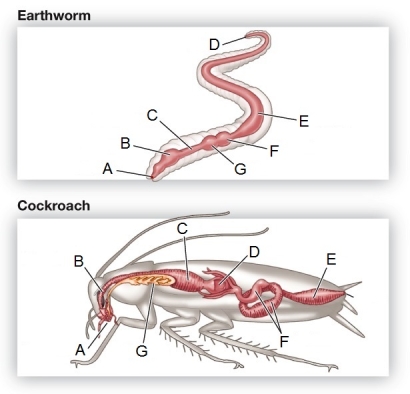 Identify the structure in each organism used for food storage and some minimal, initial digestion.
Identify the structure in each organism used for food storage and some minimal, initial digestion.
A) B in earthworm and A in cockroach
B) C in earthworm and B in cockroach
C) G in earthworm and C in cockroach
D) E in earthworm and F in cockroach
E) F in earthworm and D in cockroach
 Identify the structure in each organism used for food storage and some minimal, initial digestion.
Identify the structure in each organism used for food storage and some minimal, initial digestion.A) B in earthworm and A in cockroach
B) C in earthworm and B in cockroach
C) G in earthworm and C in cockroach
D) E in earthworm and F in cockroach
E) F in earthworm and D in cockroach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which teeth are most prominent in mammalian carnivores?
A) Incisors
B) Canines
C) Premolars
D) Molars
E) Cheek teeth
A) Incisors
B) Canines
C) Premolars
D) Molars
E) Cheek teeth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which structure is used as a storage chamber for food, but not for grinding food?
A) Radula
B) Gizzard
C) Crop
D) Mandible
E) Esophagus
A) Radula
B) Gizzard
C) Crop
D) Mandible
E) Esophagus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which example could be considered analogous to the vertebrate gut?
A) An assembly line producing cars
B) A junkyard where pieces of cars are removed one by one
C) A cornfield capturing sunlight to form carbohydrates
D) A migrating herd of wildebeest
E) A chef combining ingredients to produce a meal
A) An assembly line producing cars
B) A junkyard where pieces of cars are removed one by one
C) A cornfield capturing sunlight to form carbohydrates
D) A migrating herd of wildebeest
E) A chef combining ingredients to produce a meal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the figure showing the digestive systems of an earthworm and a cockroach. 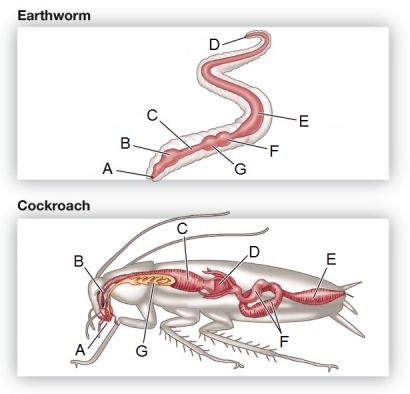 Identify the structure in each organism used for grinding food.
Identify the structure in each organism used for grinding food.
A) A in earthworm and A in cockroach
B) C in earthworm and B in cockroach
C) G in earthworm and C in cockroach
D) E in earthworm and F in cockroach
E) F in earthworm and D in cockroach
 Identify the structure in each organism used for grinding food.
Identify the structure in each organism used for grinding food.A) A in earthworm and A in cockroach
B) C in earthworm and B in cockroach
C) G in earthworm and C in cockroach
D) E in earthworm and F in cockroach
E) F in earthworm and D in cockroach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which layer of the vertebrate gut shows adaptations for increasing absorptive surface area?
A) Lumen
B) Mucosa
C) Submucosa
D) Serosa
E) Peritoneum
A) Lumen
B) Mucosa
C) Submucosa
D) Serosa
E) Peritoneum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which statement about movement of food in the gut is true?
A) There are two sphincters in the vertebrate gut, one at the anterior end and one at the posterior end.
B) Peristalsis is under voluntary control.
C) Smooth muscle of the gut contracts in response to being stretched.
D) Peristalsis begins when food enters the glottis.
E) The muscle in a sphincter is normally relaxed.
A) There are two sphincters in the vertebrate gut, one at the anterior end and one at the posterior end.
B) Peristalsis is under voluntary control.
C) Smooth muscle of the gut contracts in response to being stretched.
D) Peristalsis begins when food enters the glottis.
E) The muscle in a sphincter is normally relaxed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How does cotransport of sodium in a symporter facilitate glucose absorption?
A) Active transport of sodium ions aids in salt uptake.
B) When sodium ions diffuse into cells, glucose is carried along with it.
C) When sodium ions are pumped into cells, glucose moves out of the cells.
D) When sodium ions diffuse out of the cell, they are exchanged for glucose moving into cells.
E) ATP is used to actively transport glucose into cells along with sodium ions.
A) Active transport of sodium ions aids in salt uptake.
B) When sodium ions diffuse into cells, glucose is carried along with it.
C) When sodium ions are pumped into cells, glucose moves out of the cells.
D) When sodium ions diffuse out of the cell, they are exchanged for glucose moving into cells.
E) ATP is used to actively transport glucose into cells along with sodium ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the figure showing a portion of the human stomach. 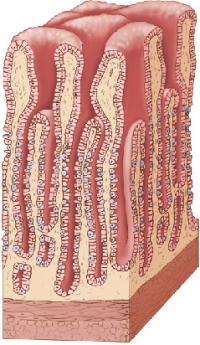 In humans, which event occurs prior to reaching the part of the stomach shown in the figure?
In humans, which event occurs prior to reaching the part of the stomach shown in the figure?
A) Secretion of amylase to hydrolyze carbohydrates
B) Killing of ingested microorganisms by HCL
C) Digestion of proteins by pepsin secretion
D) Production of an inactive digestive enzyme, or zymogen
E) Storage of food to allow slower digestion
 In humans, which event occurs prior to reaching the part of the stomach shown in the figure?
In humans, which event occurs prior to reaching the part of the stomach shown in the figure?A) Secretion of amylase to hydrolyze carbohydrates
B) Killing of ingested microorganisms by HCL
C) Digestion of proteins by pepsin secretion
D) Production of an inactive digestive enzyme, or zymogen
E) Storage of food to allow slower digestion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The acidic chyme in the small intestine is neutralized in part by
A) bicarbonate from the pancreas.
B) buffers from the jejunum.
C) bile from the liver.
D) trypsin activation.
E) a variety of zymogens.
A) bicarbonate from the pancreas.
B) buffers from the jejunum.
C) bile from the liver.
D) trypsin activation.
E) a variety of zymogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The inactive form of stomach enzymes is activated by
A) enterokinase.
B) ATP.
C) low pH.
D) the appropriate substrate molecule.
E) the presence of water.
A) enterokinase.
B) ATP.
C) low pH.
D) the appropriate substrate molecule.
E) the presence of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The major enzyme produced by the stomach is
A) amylase.
B) chyme.
C) hydrochloric acid (HCl).
D) pepsin.
E) trypsin.
A) amylase.
B) chyme.
C) hydrochloric acid (HCl).
D) pepsin.
E) trypsin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which protease is produced by the small intestine?
A) Dipeptidase
B) Chymotrypsin
C) Trypsin
D) Carboxypeptidase
E) Pepsin
A) Dipeptidase
B) Chymotrypsin
C) Trypsin
D) Carboxypeptidase
E) Pepsin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Chylomicrons are produced in the
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) lumen of the small intestine.
D) epithelial cells of the small intestine.
E) liver.
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) lumen of the small intestine.
D) epithelial cells of the small intestine.
E) liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Lipases are enzymes produced by the pancreas that break down
A) carbohydrates.
B) nucleic acids.
C) proteins.
D) fat molecules.
E) fatty acids.
A) carbohydrates.
B) nucleic acids.
C) proteins.
D) fat molecules.
E) fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The sweetness that you taste if you keep chewing a piece of bread is due to the action of the enzyme
A) amylase.
B) sucrase.
C) lactase.
D) maltase.
E) pepsin.
A) amylase.
B) sucrase.
C) lactase.
D) maltase.
E) pepsin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the stomach, pepsin activates pepsinogen molecules in a positive feedback process called
A) emulsification.
B) absorption.
C) autocatalysis.
D) rumination.
E) excretion.
A) emulsification.
B) absorption.
C) autocatalysis.
D) rumination.
E) excretion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which feature protects the walls of the stomach against the action of its own digestive juices?
A) An antienzyme chemical formed by the gastric glands
B) The nervous reactions of the lining of the stomach
C) Control by a center in the medulla of the brain
D) A mucus coating on the stomach's inner surface
E) Alkaline secretions of the gastric glands that neutralize the acidic secretions
A) An antienzyme chemical formed by the gastric glands
B) The nervous reactions of the lining of the stomach
C) Control by a center in the medulla of the brain
D) A mucus coating on the stomach's inner surface
E) Alkaline secretions of the gastric glands that neutralize the acidic secretions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Most absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract takes place in the
A) stomach.
B) small intestine.
C) large intestine.
D) liver.
E) pancreas.
A) stomach.
B) small intestine.
C) large intestine.
D) liver.
E) pancreas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which statement about digestion in the small intestine is true?
A) Most digestion occurs in the stomach and most absorption occurs in the small intestine.
B) Fat in the small intestine is emulsified by bile that is produced by the gallbladder and stored in the liver.
C) Bile molecules in the small intestine have one end that is lipophobic and one end that is hydrophilic.
D) The pancreas secretes zymogens and bicarbonate ions into the duodenum of the small intestine.
E) Enterokinase is secreted by the pancreas to activate enzymes in the small intestine.
A) Most digestion occurs in the stomach and most absorption occurs in the small intestine.
B) Fat in the small intestine is emulsified by bile that is produced by the gallbladder and stored in the liver.
C) Bile molecules in the small intestine have one end that is lipophobic and one end that is hydrophilic.
D) The pancreas secretes zymogens and bicarbonate ions into the duodenum of the small intestine.
E) Enterokinase is secreted by the pancreas to activate enzymes in the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If the acidity of the stomach is neutralized by antacids and acid-blockers,
A) pepsin will not be converted to pepsinogen.
B) a person will be more prone to ulcers.
C) micelles will not contain enterokinase.
D) pepsinogen will not be converted to pepsin.
E) carboxypeptidase will not break proteins down to peptides and amino acids.
A) pepsin will not be converted to pepsinogen.
B) a person will be more prone to ulcers.
C) micelles will not contain enterokinase.
D) pepsinogen will not be converted to pepsin.
E) carboxypeptidase will not break proteins down to peptides and amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Bile aids in the breakdown of lipids by
A) hydrolyzing lipids.
B) activating hydrolytic enzymes.
C) aggregating droplets of lipids.
D) emulsifying lipids.
E) making lipids water soluble.
A) hydrolyzing lipids.
B) activating hydrolytic enzymes.
C) aggregating droplets of lipids.
D) emulsifying lipids.
E) making lipids water soluble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The enzyme lactase
A) cleaves lactose into fructose and galactose.
B) is produced by the stomach.
C) is absent in many humans after childhood.
D) cleaves milk proteins.
E) can be produced by bacteria in the stomach causing bloating.
A) cleaves lactose into fructose and galactose.
B) is produced by the stomach.
C) is absent in many humans after childhood.
D) cleaves milk proteins.
E) can be produced by bacteria in the stomach causing bloating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Bile produced in the liver is associated with which activity?
A) Breakdown of fat globules into small fat particles in the small intestine
B) Digestive action of pancreatic amylase
C) Breakdown of fat globules into small fat particles in the stomach
D) Digestion of proteins into amino acids
E) Breakdown of fat globules into small fat particles in the large intestine
A) Breakdown of fat globules into small fat particles in the small intestine
B) Digestive action of pancreatic amylase
C) Breakdown of fat globules into small fat particles in the stomach
D) Digestion of proteins into amino acids
E) Breakdown of fat globules into small fat particles in the large intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Pepsinogen is converted into pepsin by
A) low pH.
B) chyme.
C) enterokinase.
D) trypsinogen.
E) amylase from the salivary glands.
A) low pH.
B) chyme.
C) enterokinase.
D) trypsinogen.
E) amylase from the salivary glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which statement about digestion is true?
A) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of proteins are secreted by the pancreas.
B) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of proteins cleave dipeptides into amino acids.
C) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of common disaccharides are produced by the stomach epithelial cells.
D) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of common trisaccharides produce absorbable disaccharides.
E) Unabsorbed lactose is metabolized by bacteria in the small intestine.
A) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of proteins are secreted by the pancreas.
B) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of proteins cleave dipeptides into amino acids.
C) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of common disaccharides are produced by the stomach epithelial cells.
D) Enzymes that carry out the final step in the digestion of common trisaccharides produce absorbable disaccharides.
E) Unabsorbed lactose is metabolized by bacteria in the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which function is served by the HCl secreted in the stomach?
A) Formation of chylomicrons
B) Proper pH for the digestive enzyme of the stomach
C) Breakdown of ingested fats
D) Activation of the zymogens secreted by the pancreas
E) Protection of most ingested microorganisms
A) Formation of chylomicrons
B) Proper pH for the digestive enzyme of the stomach
C) Breakdown of ingested fats
D) Activation of the zymogens secreted by the pancreas
E) Protection of most ingested microorganisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 259 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



