Deck 3: Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Lipids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/246
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Lipids
1
Three different proteins, A, B, and C, from a plant were studied.In each case, a glycine residue was changed to an alanine.Changes in the biological activities of the mutated proteins were then measured, and the results are shown in the table below. 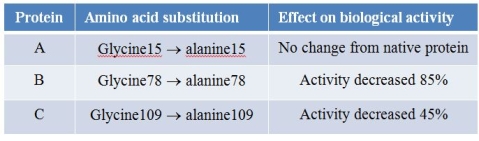 Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is supported by the data?
Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is supported by the data?
A) Each unique amino acid sequence results in a protein with a unique function.
B) A protein's function changes only when changes in primary structure alter its tertiary structure.
C) Substitution of a nonpolar amino acid for another nonpolar amino acid is sufficient to allow a protein to retain its biological activity.
D) Amino acids located at the beginning of a polypeptide chain have less importance in determining biological function than amino acids in the middle or far end of the chain.
E) Every amino acid substitution in a protein's primary structure leads to a change in the protein's function.
 Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is supported by the data?
Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is supported by the data?A) Each unique amino acid sequence results in a protein with a unique function.
B) A protein's function changes only when changes in primary structure alter its tertiary structure.
C) Substitution of a nonpolar amino acid for another nonpolar amino acid is sufficient to allow a protein to retain its biological activity.
D) Amino acids located at the beginning of a polypeptide chain have less importance in determining biological function than amino acids in the middle or far end of the chain.
E) Every amino acid substitution in a protein's primary structure leads to a change in the protein's function.
B
2
Refer to the diagram below, showing a condensation reaction. 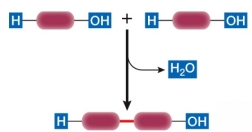 This reaction does not occur during the formation of a(n)
This reaction does not occur during the formation of a(n)
A) peptide bond.
B) glycosidic linkage.
C) disulfide bond.
D) ester linkage.
E) disaccharide from two monosaccharides.
 This reaction does not occur during the formation of a(n)
This reaction does not occur during the formation of a(n)A) peptide bond.
B) glycosidic linkage.
C) disulfide bond.
D) ester linkage.
E) disaccharide from two monosaccharides.
C
3
A protein contains a section partially embedded in a cell membrane and another section that extends out into the external environment.Which statement could be true about this protein?
A) The protein is composed of a chain of alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids.
B) The protein is composed of a chain with a long stretch of hydrophobic amino acids and then another stretch of hydrophilic amino acids.
C) The protein has two subunits, each containing alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids.
D) The protein is composed of either all hydrophobic amino acids or all hydrophilic amino acids, but not both.
E) The protein is composed of a mix of hydrophobic amino acids and hydrophilic amino acids covalently modified and so converted to hydrophobic residues.
A) The protein is composed of a chain of alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids.
B) The protein is composed of a chain with a long stretch of hydrophobic amino acids and then another stretch of hydrophilic amino acids.
C) The protein has two subunits, each containing alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids.
D) The protein is composed of either all hydrophobic amino acids or all hydrophilic amino acids, but not both.
E) The protein is composed of a mix of hydrophobic amino acids and hydrophilic amino acids covalently modified and so converted to hydrophobic residues.
B
4
A student claims that all triglycerides have the exact same properties, since they are all composed of the same units: a glycerol molecule and three fatty acids.Which statement provides the best response to this claim?
A) The claim is correct because all triglycerides have the same pattern of ester linkages between fatty acids and glycerol.
B) The claim is correct because all fatty acid tails consist of long hydrocarbon tails that contribute to the nonpolar nature of triglycerides as a class.
C) The claim is incorrect because triglycerides can assume different shapes due to random motion of their hydrocarbon chains.
D) The claim is incorrect because the hydrocarbon chains of triglycerides vary in length and number of double bonds.
E) The claim is incorrect because triglycerides are found in many different types of organisms.
A) The claim is correct because all triglycerides have the same pattern of ester linkages between fatty acids and glycerol.
B) The claim is correct because all fatty acid tails consist of long hydrocarbon tails that contribute to the nonpolar nature of triglycerides as a class.
C) The claim is incorrect because triglycerides can assume different shapes due to random motion of their hydrocarbon chains.
D) The claim is incorrect because the hydrocarbon chains of triglycerides vary in length and number of double bonds.
E) The claim is incorrect because triglycerides are found in many different types of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Each amino acid has a unique _______ group.
A) amino
B) hydroxyl
C) carboxyl
D) R
E) phosphate
A) amino
B) hydroxyl
C) carboxyl
D) R
E) phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Molecules containing a large number of hydroxyl groups are
A) basic.
B) structurally less stable than those with fewer hydroxyls.
C) complex macromolecules.
D) nonpolar.
E) soluble in water.
A) basic.
B) structurally less stable than those with fewer hydroxyls.
C) complex macromolecules.
D) nonpolar.
E) soluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All amino acids have an optical isomer except
A) arginine.
B) cysteine.
C) alanine.
D) glycine.
E) methionine.
A) arginine.
B) cysteine.
C) alanine.
D) glycine.
E) methionine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which description applies to polysaccharides, polypeptides, and polynucleotides?
A) They contain simple sugars.
B) They are broken down in hydrolysis reactions.
C) They are located in cell membranes.
D) They contain nitrogen.
E) Their molecular weights are less than 30,000 Da.
A) They contain simple sugars.
B) They are broken down in hydrolysis reactions.
C) They are located in cell membranes.
D) They contain nitrogen.
E) Their molecular weights are less than 30,000 Da.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Aldehydes and ketones are very similar in that they both contain
A) phosphorus atoms.
B) sulfur atoms.
C) a keto group.
D) nitrogen atoms.
E) two R groups.
A) phosphorus atoms.
B) sulfur atoms.
C) a keto group.
D) nitrogen atoms.
E) two R groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the figure below. 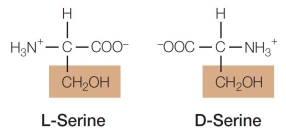 The molecules in the figure are
The molecules in the figure are
A) structural isomers.
B) optical isomers.
C) hydrophobic.
D) monosaccharides.
E) fatty acids.
 The molecules in the figure are
The molecules in the figure areA) structural isomers.
B) optical isomers.
C) hydrophobic.
D) monosaccharides.
E) fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Two biologically important polymers of glucose contain the same number of monomers and have the same mass, yet one is soluble in water and the other is not.This can be explained by the fact that the two polymers
A) differ in their proportions of glucose units existing in ring form versus straight-chain form.
B) differ in the amount of hydrogen bonding taking place between glucose residues in their chains.
C) were biosynthesized in different cells by different enzymes.
D) contain glycosidic linkages between different oxygen and carbon atoms in the monomeric units.
E) have different biological functions.
A) differ in their proportions of glucose units existing in ring form versus straight-chain form.
B) differ in the amount of hydrogen bonding taking place between glucose residues in their chains.
C) were biosynthesized in different cells by different enzymes.
D) contain glycosidic linkages between different oxygen and carbon atoms in the monomeric units.
E) have different biological functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In condensation reactions, the atoms that make up a water molecule are derived from
A) oxygen.
B) one of the reactants.
C) both reactants.
D) carbohydrates.
E) the enzyme.
A) oxygen.
B) one of the reactants.
C) both reactants.
D) carbohydrates.
E) the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All of the following are macromolecules except
A) RNA.
B) DNA.
C) glycogen.
D) protein.
E) salt.
A) RNA.
B) DNA.
C) glycogen.
D) protein.
E) salt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two identical samples of a purified protein were subjected to different treatment steps.The biological activity of the protein after each step was measured, as summarized in the table below. 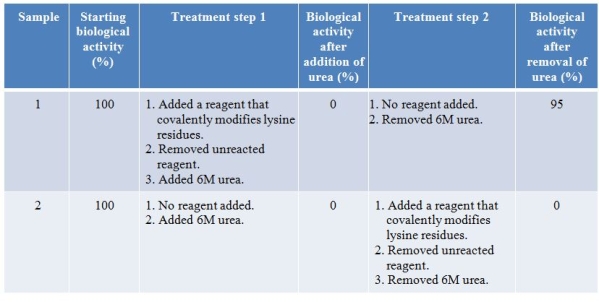 Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is consistent with the data?
Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is consistent with the data?
A) Lysine residues in a protein cannot be modified without a change to the protein's function.
B) After being denatured, proteins cannot refold back to their original shapes.
C) Amino acids buried in a protein's interior can be more critical to stabilizing the protein's three-dimensional structure than amino acids on the exterior.
D) Lysine residues are not as important as other amino acid residues in stabilizing a protein's three-dimensional structure.
E) A protein's ability to fold properly requires that all amino acids be intact and without modification.
 Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is consistent with the data?
Which statement about structure-function relationships in proteins is consistent with the data?A) Lysine residues in a protein cannot be modified without a change to the protein's function.
B) After being denatured, proteins cannot refold back to their original shapes.
C) Amino acids buried in a protein's interior can be more critical to stabilizing the protein's three-dimensional structure than amino acids on the exterior.
D) Lysine residues are not as important as other amino acid residues in stabilizing a protein's three-dimensional structure.
E) A protein's ability to fold properly requires that all amino acids be intact and without modification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A functional group that releases energy when removed by hydrolysis is the _______ group.
A) phosphate
B) amino
C) sulfhydryl
D) hydroxyl
E) saccharide
A) phosphate
B) amino
C) sulfhydryl
D) hydroxyl
E) saccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The amino acid sequence of a protein isolated from human blood cells is the same as the amino acid sequence of a protein isolated from chimpanzees.Which statement related to this observation is accurate?
A) Humans and chimpanzees are so closely related that all of their protein sequences are identical.
B) The two proteins serve the same function in both humans and chimpanzees because their structures are the same.
C) The folding is likely to differ in the polypeptide chains in the two cases because they exist in cells of different organisms.
D) The two proteins will have the same properties, since they have the same primary structure, but different functions, since they come from different species.
E) The biological properties of the two proteins must differ, since they were isolated from two different species.
A) Humans and chimpanzees are so closely related that all of their protein sequences are identical.
B) The two proteins serve the same function in both humans and chimpanzees because their structures are the same.
C) The folding is likely to differ in the polypeptide chains in the two cases because they exist in cells of different organisms.
D) The two proteins will have the same properties, since they have the same primary structure, but different functions, since they come from different species.
E) The biological properties of the two proteins must differ, since they were isolated from two different species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Polymerization reactions in which polysaccharides are synthesized from monosaccharides
A) require the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the monosaccharides.
B) release phosphate.
C) are hydrolysis reactions.
D) depend on van der Waals forces to hold the monosaccharides together.
E) result in the formation of water.
A) require the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the monosaccharides.
B) release phosphate.
C) are hydrolysis reactions.
D) depend on van der Waals forces to hold the monosaccharides together.
E) result in the formation of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is not a correct monomers → polymer construction?
A) Monosaccharides → polysaccharide
B) Amino acids → protein
C) Celluloses → triglyceride
D) Nucleotides → nucleic acid
E) Monosaccharides → oligosaccharide
A) Monosaccharides → polysaccharide
B) Amino acids → protein
C) Celluloses → triglyceride
D) Nucleotides → nucleic acid
E) Monosaccharides → oligosaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Refer to the table below. 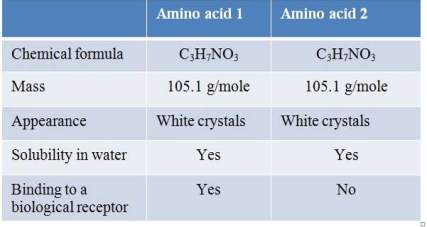 Which statement about amino acids 1 and 2 is valid, given all of the data provided in the table?
Which statement about amino acids 1 and 2 is valid, given all of the data provided in the table?
A) They are identical in structure.
B) They have different R groups.
C) They are optical isomers.
D) They have opposite charges.
E) They contain different types of bonds.
 Which statement about amino acids 1 and 2 is valid, given all of the data provided in the table?
Which statement about amino acids 1 and 2 is valid, given all of the data provided in the table?A) They are identical in structure.
B) They have different R groups.
C) They are optical isomers.
D) They have opposite charges.
E) They contain different types of bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the figure below. 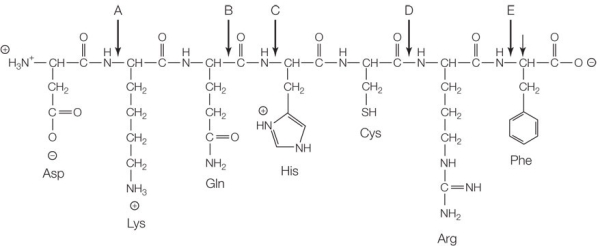 Which of the following is broken during hydrolysis reactions that release the molecule's monomers as products?
Which of the following is broken during hydrolysis reactions that release the molecule's monomers as products?
A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D
E) Bond E
 Which of the following is broken during hydrolysis reactions that release the molecule's monomers as products?
Which of the following is broken during hydrolysis reactions that release the molecule's monomers as products?A) Bond A
B) Bond B
C) Bond C
D) Bond D
E) Bond E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The amino acids of the protein keratin are arranged in a helix.This secondary structure is stabilized by
A) covalent bonds.
B) peptide bonds.
C) glycosidic linkages.
D) polar bonds.
E) hydrogen bonds.
A) covalent bonds.
B) peptide bonds.
C) glycosidic linkages.
D) polar bonds.
E) hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Aspartate and glutamate can form hydrogen bonds with water because they
A) are hydrophobic.
B) have sulfur atoms in their side chains.
C) have electrically charged side chains.
D) are nonpolar.
E) form only left-handed isomers.
A) are hydrophobic.
B) have sulfur atoms in their side chains.
C) have electrically charged side chains.
D) are nonpolar.
E) form only left-handed isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The shape of a folded protein is determined by
A) its tertiary structure.
B) the sequence of its amino acids.
C) whether the peptide bonds have or linkages.
D) the number of peptide bonds.
E) the base-pairing rules.
A) its tertiary structure.
B) the sequence of its amino acids.
C) whether the peptide bonds have or linkages.
D) the number of peptide bonds.
E) the base-pairing rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An amino acid can be classified by the
A) number of amino groups it contains.
B) number of central carbon atoms it contains.
C) number of peptide bonds it can form.
D) number of disulfide bridges it can form.
E) characteristics of its side chains, or R groups.
A) number of amino groups it contains.
B) number of central carbon atoms it contains.
C) number of peptide bonds it can form.
D) number of disulfide bridges it can form.
E) characteristics of its side chains, or R groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If an amino acid involved in the ability of an enzyme to bind a substrate were changed from a tyrosine to a phenylalanine, what would happen to the enzyme?
A) Nothing would change, because both residues have the same properties.
B) The change in amino acid would cause disulfide bonds to form, thus increasing its binding ability.
C) Nothing would change, because both residues have polar side chains.
D) Quaternary structure would be affected, because subunits would not be able to bind together.
E) The ability of the substrate to bind to the enzyme would be affected because of the change in R groups.
A) Nothing would change, because both residues have the same properties.
B) The change in amino acid would cause disulfide bonds to form, thus increasing its binding ability.
C) Nothing would change, because both residues have polar side chains.
D) Quaternary structure would be affected, because subunits would not be able to bind together.
E) The ability of the substrate to bind to the enzyme would be affected because of the change in R groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the diagram below, showing a condensation reaction. 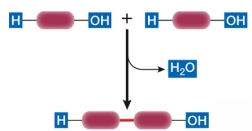 This reaction occurs during the formation of which protein structure?
This reaction occurs during the formation of which protein structure?
A) Peptide backbone
B) helix
C) pleated sheet
D) Disulfide bridge
E) Ionic bond
 This reaction occurs during the formation of which protein structure?
This reaction occurs during the formation of which protein structure?A) Peptide backbone
B) helix
C) pleated sheet
D) Disulfide bridge
E) Ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a hydrophilic amino acid on the surface of an enzyme were changed to a hydrophobic amino acid, which result would be possible?
A) The activity of the enzyme would remain unchanged.
B) The folding pattern of the enzyme's polypeptide chain would change.
C) The function of the enzyme could be expanded to allow it to bind many new substrates.
D) The tertiary structure would be stabilized by new hydrophobic interactions.
E) The protein's ability to form peptide bonds could be affected.
A) The activity of the enzyme would remain unchanged.
B) The folding pattern of the enzyme's polypeptide chain would change.
C) The function of the enzyme could be expanded to allow it to bind many new substrates.
D) The tertiary structure would be stabilized by new hydrophobic interactions.
E) The protein's ability to form peptide bonds could be affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A macromolecule that is isolated from the bone of dinosaurs and found to have nitrogen-carbon-carbon repeats would be classified as a(n)
A) polysaccharide.
B) oligosaccharide.
C) polypeptide.
D) triglyceride.
E) lipid.
A) polysaccharide.
B) oligosaccharide.
C) polypeptide.
D) triglyceride.
E) lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If all of the cysteine residues of a protein were changed to threonines,
A) the structure of the protein would not change, because both residues have hydrophobic properties.
B) the protein would lose activity, but the structure would remain the same.
C) the protein would lose peptide bond formation, and thus it would lose its primary structure.
D) the protein would lose disulfide bond formation, which would affect the stability of its tertiary structure.
E) the hydrogen bonds would be lost, affecting α helix and β pleated sheet formation.
A) the structure of the protein would not change, because both residues have hydrophobic properties.
B) the protein would lose activity, but the structure would remain the same.
C) the protein would lose peptide bond formation, and thus it would lose its primary structure.
D) the protein would lose disulfide bond formation, which would affect the stability of its tertiary structure.
E) the hydrogen bonds would be lost, affecting α helix and β pleated sheet formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The tertiary structure of a protein is determined by its
A) interactions among R groups.
B) right-handed coil.
C) size.
D) branching.
E) glycosidic linkages.
A) interactions among R groups.
B) right-handed coil.
C) size.
D) branching.
E) glycosidic linkages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many different types of tripeptides (molecules of three amino acids linked together) can be synthesized from the 20 common amino acids?
A) 3
B) 20
C) 60
D) 900
E) 8,000
A) 3
B) 20
C) 60
D) 900
E) 8,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A pleated sheet organization in a polypeptide chain is an example of _______ structure.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) coiled
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) coiled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During the formation of a peptide linkage, a(n) _______ is formed.
A) molecule of water
B) disulfide bridge
C) hydrophobic bond
D) hydrophilic bond
E) ionic bond
A) molecule of water
B) disulfide bridge
C) hydrophobic bond
D) hydrophilic bond
E) ionic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What type of amino acid side chains would you expect to find on the surface of a protein embedded in a cell membrane?
A) Short
B) Hydrophobic
C) Hydrophilic
D) Charged
E) Polar, but not charged
A) Short
B) Hydrophobic
C) Hydrophilic
D) Charged
E) Polar, but not charged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which amino acid is small enough to fit into tight corners of protein molecules?
A) Proline
B) Glycine
C) Cysteine
D) Asparagine
E) Glutamine
A) Proline
B) Glycine
C) Cysteine
D) Asparagine
E) Glutamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Leucine and valine have side chains that do not interact with water; therefore, they
A) are hydrophilic.
B) are nonpolar.
C) have sulfur atoms in their side chains.
D) are electrically charged.
E) form only left-handed isomers.
A) are hydrophilic.
B) are nonpolar.
C) have sulfur atoms in their side chains.
D) are electrically charged.
E) form only left-handed isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the figure below. 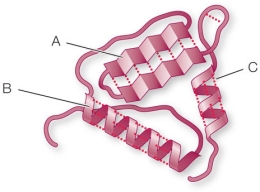 What level of protein structure is illustrated in sections A and B of this polypeptide, and what types of forces indicated by the letter C stabilize these sections?
What level of protein structure is illustrated in sections A and B of this polypeptide, and what types of forces indicated by the letter C stabilize these sections?
A) Primary structure, disulfide bridges
B) Secondary structure, hydrogen bonds
C) Secondary structure, salt bridges
D) Tertiary structure, salt bridges
E) Tertiary structure, hydrogen bonds
 What level of protein structure is illustrated in sections A and B of this polypeptide, and what types of forces indicated by the letter C stabilize these sections?
What level of protein structure is illustrated in sections A and B of this polypeptide, and what types of forces indicated by the letter C stabilize these sections?A) Primary structure, disulfide bridges
B) Secondary structure, hydrogen bonds
C) Secondary structure, salt bridges
D) Tertiary structure, salt bridges
E) Tertiary structure, hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A peptide bond forms between a(n) _______ group on one molecule and a(n) _______ group on the other molecule.
A) amino; carboxyl
B) amino; R
C) hydrogen; carboxyl
D) R; hydrogen
E) carboxyl; R
A) amino; carboxyl
B) amino; R
C) hydrogen; carboxyl
D) R; hydrogen
E) carboxyl; R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose you want to construct a protein that is 50 amino acids long.What is the theoretical number of different proteins you could make?
A) 1050
B) 2050
C) 20 × 50
D) 5020
E) 50 × 50
A) 1050
B) 2050
C) 20 × 50
D) 5020
E) 50 × 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The magnesium chelatase protein has quaternary structure.This means that magnesium chelatase
A) is composed of subunits.
B) binds to the surface of membranes.
C) forms part of a quadruple complex.
D) changes over time.
E) has fourfold symmetry.
A) is composed of subunits.
B) binds to the surface of membranes.
C) forms part of a quadruple complex.
D) changes over time.
E) has fourfold symmetry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A molecule with the formula C15H30O15 is most likely a
A) hydrocarbon.
B) carbohydrate.
C) lipid.
D) protein.
E) nucleic acid.
A) hydrocarbon.
B) carbohydrate.
C) lipid.
D) protein.
E) nucleic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 1 shows a protein enzyme labeled E that catalyzes a chemical reaction involving the substrate molecule labeled C.Figure 2 shows how another molecule, labeled D, binds to a site on the protein that is distinct from the catalytic site. 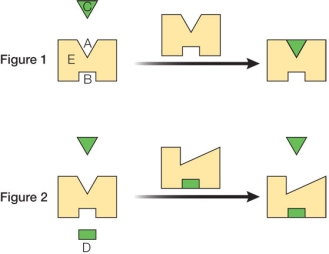 Based on the activities shown, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to bind molecule D?
Based on the activities shown, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to bind molecule D?
A) It gains a new chemical reaction that it can catalyze.
B) It gains the ability to bind a broader range of molecules at its catalytic site.
C) It gains a mechanism for preventing the protein from being degraded.
D) It gains a means for turning the biological activity of the protein on and off.
E) It gains the ability to diffuse through cell membranes.
 Based on the activities shown, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to bind molecule D?
Based on the activities shown, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to bind molecule D? A) It gains a new chemical reaction that it can catalyze.
B) It gains the ability to bind a broader range of molecules at its catalytic site.
C) It gains a mechanism for preventing the protein from being degraded.
D) It gains a means for turning the biological activity of the protein on and off.
E) It gains the ability to diffuse through cell membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When a cysteine residue in a protein is replaced with serine, the protein folds normally and exhibits 95 percent of its normal biological activity.However, when this same cysteine residue is replaced with glycine, the protein does not fold normally and exhibits only 35 percent of its normal biological activity.Which hypothesis is both reasonable and consistent with these observations?
A) A hydrogen bond between the cysteine side chain and another residue in the interior of the protein helps stabilize the protein's tertiary structure.
B) The cysteine side chain is exposed to the external environment, where it forms salt bridges with ions dissolved in the water surrounding the protein.
C) The cysteine residue forms a disulfide bridge with another cysteine in the polypeptide chain to stabilize the protein's tertiary structure.
D) A salt bridge between the cysteine side chain and an acidic residue in the interior of the protein helps stabilize the protein's tertiary structure.
E) The cysteine side chain is located in a tight bend in the polypeptide chain, where only a small side chain can be accommodated.
A) A hydrogen bond between the cysteine side chain and another residue in the interior of the protein helps stabilize the protein's tertiary structure.
B) The cysteine side chain is exposed to the external environment, where it forms salt bridges with ions dissolved in the water surrounding the protein.
C) The cysteine residue forms a disulfide bridge with another cysteine in the polypeptide chain to stabilize the protein's tertiary structure.
D) A salt bridge between the cysteine side chain and an acidic residue in the interior of the protein helps stabilize the protein's tertiary structure.
E) The cysteine side chain is located in a tight bend in the polypeptide chain, where only a small side chain can be accommodated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Starch and glycogen, which are both polysaccharides, differ in their functions in that starch is _______, whereas glycogen _______.
A) the main component for plant structural support; is an energy source for animals
B) a structural material found in plants and animals; forms external skeletons in animals
C) the principal energy storage compound of plants; is the main energy storage of animals
D) a temporary compound used to store glucose; is a highly stable compound that stores complex lipids
E) the main energy storage of animals; is a temporary compound used to store glucose
A) the main component for plant structural support; is an energy source for animals
B) a structural material found in plants and animals; forms external skeletons in animals
C) the principal energy storage compound of plants; is the main energy storage of animals
D) a temporary compound used to store glucose; is a highly stable compound that stores complex lipids
E) the main energy storage of animals; is a temporary compound used to store glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The main function of cellulose, the most abundant organic compound on Earth, is
A) to store genetic information.
B) as a storage compound for energy in plant cells.
C) as a storage compound for energy in animal cells.
D) as a component of biological membranes.
E) to provide mechanical strength to plant cell walls.
A) to store genetic information.
B) as a storage compound for energy in plant cells.
C) as a storage compound for energy in animal cells.
D) as a component of biological membranes.
E) to provide mechanical strength to plant cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A simple sugar with the formula C5H10O5 can be classified as a
A) hexose.
B) polysaccharide.
C) disaccharide.
D) pentose.
E) lipid.
A) hexose.
B) polysaccharide.
C) disaccharide.
D) pentose.
E) lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A carbohydrate with 12 oxygen molecules would have _______ hydrogen molecules.
A) 6
B) 12
C) 18
D) 24
E) 36
A) 6
B) 12
C) 18
D) 24
E) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Glucose and fructose both have the formula C6H12O6, but the atoms in these two compounds are arranged differently.Glucose and fructose are therefore
A) isomers.
B) polysaccharides.
C) stereosaccharides.
D) pentoses.
E) isotopes.
A) isomers.
B) polysaccharides.
C) stereosaccharides.
D) pentoses.
E) isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure A shows a protein consisting of two identical subunits.Figure B shows the same protein after each subunit has been covalently modified with a phosphate group. 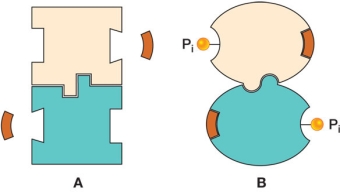 Based on the activities shown in the diagrams, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to undergo a reversible phosphorylation-dephosphorylation reaction?
Based on the activities shown in the diagrams, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to undergo a reversible phosphorylation-dephosphorylation reaction?
A) It gains the ability to resist denaturation.
B) It gains the ability to undergo reversible subunit dissociation.
C) It gains a mechanism for regulating substrate binding.
D) It gains a broader range of molecules that will bind to its binding sites.
E) It gains a broader range of biological functions that it can carry out.
 Based on the activities shown in the diagrams, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to undergo a reversible phosphorylation-dephosphorylation reaction?
Based on the activities shown in the diagrams, what biological advantage does this protein gain by having the ability to undergo a reversible phosphorylation-dephosphorylation reaction?A) It gains the ability to resist denaturation.
B) It gains the ability to undergo reversible subunit dissociation.
C) It gains a mechanism for regulating substrate binding.
D) It gains a broader range of molecules that will bind to its binding sites.
E) It gains a broader range of biological functions that it can carry out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When an organism is exposed to extreme heat, _______ can help return its enzymes to their proper functions.
A) hydrolysis reactions
B) condensation reactions
C) protein chaperones
D) amino acids
E) carbohydrates
A) hydrolysis reactions
B) condensation reactions
C) protein chaperones
D) amino acids
E) carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A research team tracked the carbon atoms in glucose molecules to see where they ended up when the glucose was taken up and metabolized by human cells grown in culture.The team found that 9 percent of the carbon atoms ended up in proteins.This result provides evidence for which biological function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
A) Energy storage
B) Energy source
C) Energy transport
D) Carbon skeleton source
E) Structural support
A) Energy storage
B) Energy source
C) Energy transport
D) Carbon skeleton source
E) Structural support

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A type of protein that functions by helping other proteins fold correctly is called a
A) foldzyme.
B) renaturing protein.
C) chaperone.
D) hemoglobin.
E) denaturing protein.
A) foldzyme.
B) renaturing protein.
C) chaperone.
D) hemoglobin.
E) denaturing protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to the figure below of a hemoglobin protein. 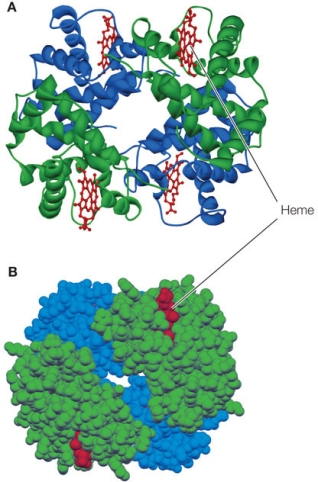 The hemoglobin protein has four subunits.If it were exposed to high temperatures, it would most likely
The hemoglobin protein has four subunits.If it were exposed to high temperatures, it would most likely
A) remain unchanged, since it is protected by the interaction of the R subunits.
B) become covalently modified.
C) become denatured into four peptide backbones.
D) release amino acids when the peptide bonds break.
E) show increased function in activity assays.
 The hemoglobin protein has four subunits.If it were exposed to high temperatures, it would most likely
The hemoglobin protein has four subunits.If it were exposed to high temperatures, it would most likelyA) remain unchanged, since it is protected by the interaction of the R subunits.
B) become covalently modified.
C) become denatured into four peptide backbones.
D) release amino acids when the peptide bonds break.
E) show increased function in activity assays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the figure showing one of the two cyclic forms of fructose. 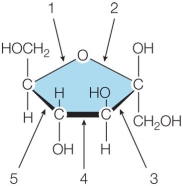 The covalent bond that results during cyclization of the straight-chain form is indicated by which number?
The covalent bond that results during cyclization of the straight-chain form is indicated by which number?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
 The covalent bond that results during cyclization of the straight-chain form is indicated by which number?
The covalent bond that results during cyclization of the straight-chain form is indicated by which number?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The atoms that make up carbohydrates are
A) C, H, and N.
B) C and H.
C) C, H, and P.
D) C, H, and O.
E) C, H, O, and N.
A) C, H, and N.
B) C and H.
C) C, H, and P.
D) C, H, and O.
E) C, H, O, and N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When an egg is exposed to extreme heat, it turns from a liquid into a solid.The egg remains solid when it cools.All of the following are reasons for this except:
A) Water has been removed from the egg proteins.
B) The hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions in the egg proteins have been broken.
C) Denatured proteins in the egg have lost secondary and tertiary structure.
D) Denatured proteins in the egg have aggregated.
E) Amino acid side chains have been chemically modified.
A) Water has been removed from the egg proteins.
B) The hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions in the egg proteins have been broken.
C) Denatured proteins in the egg have lost secondary and tertiary structure.
D) Denatured proteins in the egg have aggregated.
E) Amino acid side chains have been chemically modified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the figure below. 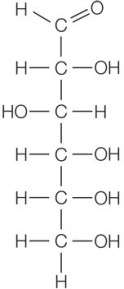 How many and what type(s) of atoms will occupy positions in the ring that forms when this molecule cyclizes?
How many and what type(s) of atoms will occupy positions in the ring that forms when this molecule cyclizes?
A) Four carbon atoms
B) Four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom
C) Five carbon atoms
D) Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom
E) Six carbon atoms
 How many and what type(s) of atoms will occupy positions in the ring that forms when this molecule cyclizes?
How many and what type(s) of atoms will occupy positions in the ring that forms when this molecule cyclizes?A) Four carbon atoms
B) Four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom
C) Five carbon atoms
D) Five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom
E) Six carbon atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which level(s) of protein structure would be destroyed by the addition of a denaturing reagent?
A) Primary only
B) Secondary only
C) Tertiary only
D) Secondary and tertiary
E) Primary, secondary, and tertiary
A) Primary only
B) Secondary only
C) Tertiary only
D) Secondary and tertiary
E) Primary, secondary, and tertiary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which is least likely to denature an enzyme?
A) Urea
B) Vinegar
C) Milk
D) Boiling water
E) Bleach
A) Urea
B) Vinegar
C) Milk
D) Boiling water
E) Bleach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the figure of a hemoglobin protein below. 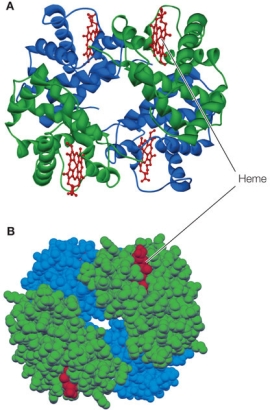 If a hemoglobin exposed to high temperatures is returned to normal temperature in the presence of chaperone proteins, it will refold _______ and _______ function.
If a hemoglobin exposed to high temperatures is returned to normal temperature in the presence of chaperone proteins, it will refold _______ and _______ function.
A) correctly; lose
B) correctly; regain
C) incorrectly; lose
D) incorrectly; regain
E) incorrectly; gain new
 If a hemoglobin exposed to high temperatures is returned to normal temperature in the presence of chaperone proteins, it will refold _______ and _______ function.
If a hemoglobin exposed to high temperatures is returned to normal temperature in the presence of chaperone proteins, it will refold _______ and _______ function.A) correctly; lose
B) correctly; regain
C) incorrectly; lose
D) incorrectly; regain
E) incorrectly; gain new

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the table below.  Using the fatty acids listed in the table, you are asked to create a triglyceride that has the highest possible melting point and also contains two different fatty acids.The fatty acids present in the triglyceride would include
Using the fatty acids listed in the table, you are asked to create a triglyceride that has the highest possible melting point and also contains two different fatty acids.The fatty acids present in the triglyceride would include
A) two stearic acids and one oleic acid.
B) two stearic acids and one elaidic acid.
C) two oleic acids and one elaidic acid.
D) two elaidic acids and one oleic acid.
E) two oleic acids and one stearic acid.
 Using the fatty acids listed in the table, you are asked to create a triglyceride that has the highest possible melting point and also contains two different fatty acids.The fatty acids present in the triglyceride would include
Using the fatty acids listed in the table, you are asked to create a triglyceride that has the highest possible melting point and also contains two different fatty acids.The fatty acids present in the triglyceride would includeA) two stearic acids and one oleic acid.
B) two stearic acids and one elaidic acid.
C) two oleic acids and one elaidic acid.
D) two elaidic acids and one oleic acid.
E) two oleic acids and one stearic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Transferrin is a protein that binds iron.It enters cells through transferrin receptors located on the cell membrane.A research group made a mutant transferrin receptor protein by replacing three asparagine residues with glycine.Results of their study are summarized in the table below. 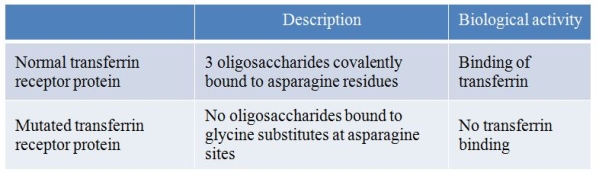 Which statement is consistent with these results?
Which statement is consistent with these results?
A) Iron binds to transferrin by recognizing oligosaccharides on the transferrin protein surface.
B) Iron binds to cells by recognizing oligosaccharides on the transferrin receptor surface.
C) Transferrin binds to the transferrin receptor protein on the cell surface by recognizing oligosaccharides attached to the receptor.
D) Asparagine residues provide the critical recognition sites for iron to bind to and enter cells.
E) Transferrin recognizes asparagine residues on the transferrin receptor protein to bind and enter cells.
 Which statement is consistent with these results?
Which statement is consistent with these results?A) Iron binds to transferrin by recognizing oligosaccharides on the transferrin protein surface.
B) Iron binds to cells by recognizing oligosaccharides on the transferrin receptor surface.
C) Transferrin binds to the transferrin receptor protein on the cell surface by recognizing oligosaccharides attached to the receptor.
D) Asparagine residues provide the critical recognition sites for iron to bind to and enter cells.
E) Transferrin recognizes asparagine residues on the transferrin receptor protein to bind and enter cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which statement about lipids is true?
A) They are readily soluble in water.
B) They function as catalysts of chemical reactions.
C) They absorb large amounts of energy when broken down.
D) They may form two layers when mixed with organic solvents.
E) They can act as an energy storehouse.
A) They are readily soluble in water.
B) They function as catalysts of chemical reactions.
C) They absorb large amounts of energy when broken down.
D) They may form two layers when mixed with organic solvents.
E) They can act as an energy storehouse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the figures below. 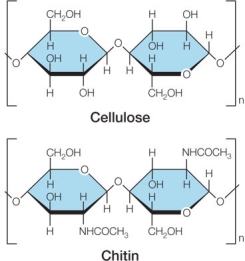 A student claims that adding functional groups onto carbohydrates does not provide any biological advantage.Which statement best evaluates this claim, using cellulose and chitin as evidence for the student's argument?
A student claims that adding functional groups onto carbohydrates does not provide any biological advantage.Which statement best evaluates this claim, using cellulose and chitin as evidence for the student's argument?
A) The student's claim is valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which both serve the same biological role even though one has a chemical modification and the other does not.
B) The student's claim is valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which require different enzymes for their synthesis and breakdown and thus create additional demands on cells.
C) The student's claim is not valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which allow the same organism to have greater flexibility in the type of structural polysaccharide it can build.
D) The student's claim is not valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which have different properties that enable different structures to develop in different organisms.
E) The student's claim is not valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which have vastly different biological functions as the result of chemical modification in one and not the other.
 A student claims that adding functional groups onto carbohydrates does not provide any biological advantage.Which statement best evaluates this claim, using cellulose and chitin as evidence for the student's argument?
A student claims that adding functional groups onto carbohydrates does not provide any biological advantage.Which statement best evaluates this claim, using cellulose and chitin as evidence for the student's argument?A) The student's claim is valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which both serve the same biological role even though one has a chemical modification and the other does not.
B) The student's claim is valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which require different enzymes for their synthesis and breakdown and thus create additional demands on cells.
C) The student's claim is not valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which allow the same organism to have greater flexibility in the type of structural polysaccharide it can build.
D) The student's claim is not valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which have different properties that enable different structures to develop in different organisms.
E) The student's claim is not valid, as shown by cellulose and chitin, which have vastly different biological functions as the result of chemical modification in one and not the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the graph below, showing data collected from harbor porpoises in eastern Scotland. 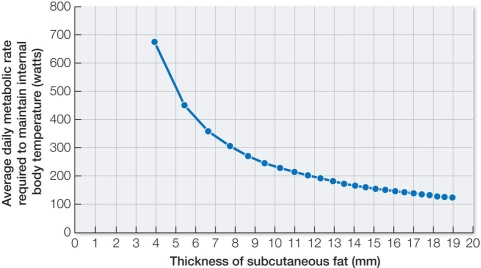 Based on these data, which biological function is associated with the lipids found in fats under the skin (subcutaneous fats) in harbor porpoises?
Based on these data, which biological function is associated with the lipids found in fats under the skin (subcutaneous fats) in harbor porpoises?
A) Thermal insulation
B) Energy storage
C) Light energy harvesting
D) Water retention
E) Regulation of cell metabolism
 Based on these data, which biological function is associated with the lipids found in fats under the skin (subcutaneous fats) in harbor porpoises?
Based on these data, which biological function is associated with the lipids found in fats under the skin (subcutaneous fats) in harbor porpoises?A) Thermal insulation
B) Energy storage
C) Light energy harvesting
D) Water retention
E) Regulation of cell metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Lipids play important roles in a number of functions.Which is not one of those functions?
A) Vision
B) Energy storage
C) Membrane structure
D) Storage of genetic information
E) Chemical signaling
A) Vision
B) Energy storage
C) Membrane structure
D) Storage of genetic information
E) Chemical signaling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The monomers that make up polymeric carbohydrates like starch are called
A) nucleotides.
B) trisaccharides.
C) monosaccharides.
D) nucleosides.
E) fatty acids.
A) nucleotides.
B) trisaccharides.
C) monosaccharides.
D) nucleosides.
E) fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Starch and glycogen are similar in that they both
A) store genetic information.
B) are polymers of amino acids.
C) are composed of fructose monomers.
D) contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
E) denature into a peptide backbone.
A) store genetic information.
B) are polymers of amino acids.
C) are composed of fructose monomers.
D) contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
E) denature into a peptide backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the figure below. 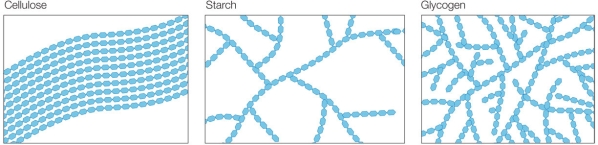 Cellulose and glycogen are not soluble in water, but starch is.What feature explains these differences?
Cellulose and glycogen are not soluble in water, but starch is.What feature explains these differences?
A) Type of sugar monomers
B) Type of glycosidic bonds
C) Number of monomers
D) Amount of branching
E) Type of sugar anomer (alpha or beta)
 Cellulose and glycogen are not soluble in water, but starch is.What feature explains these differences?
Cellulose and glycogen are not soluble in water, but starch is.What feature explains these differences?A) Type of sugar monomers
B) Type of glycosidic bonds
C) Number of monomers
D) Amount of branching
E) Type of sugar anomer (alpha or beta)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Unsaturated fatty acids do not pack together because of the _______ in their hydrocarbon chains.
A) double bonds
B) glycosidic linkages
C) peptide bonds
D) disulfide bridges
E) van der Waals forces
A) double bonds
B) glycosidic linkages
C) peptide bonds
D) disulfide bridges
E) van der Waals forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the figure below.  This compound was found covering the surface of a plant leaf.Which is the most likely biological function for this compound, given its structure and location in a plant?
This compound was found covering the surface of a plant leaf.Which is the most likely biological function for this compound, given its structure and location in a plant?
A) Water retention
B) Regulation of cell metabolism
C) Thermal insulation
D) Light energy harvesting
E) Energy storage
 This compound was found covering the surface of a plant leaf.Which is the most likely biological function for this compound, given its structure and location in a plant?
This compound was found covering the surface of a plant leaf.Which is the most likely biological function for this compound, given its structure and location in a plant?A) Water retention
B) Regulation of cell metabolism
C) Thermal insulation
D) Light energy harvesting
E) Energy storage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Oil and water do not mix easily because _______ cause the fat molecules of the oil to aggregate together in water.
A) van der Waals forces
B) covalent bonds
C) disulfide bonds
D) ester linkages
E) glycosidic linkages
A) van der Waals forces
B) covalent bonds
C) disulfide bonds
D) ester linkages
E) glycosidic linkages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the figure below. 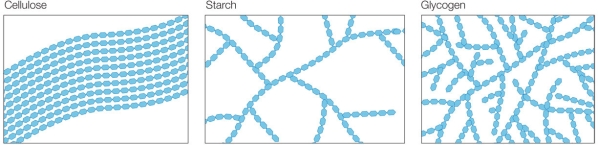 Rank the three structures shown, from lowest to highest density.
Rank the three structures shown, from lowest to highest density.
A) Cellulose, starch, glycogen
B) Starch, cellulose, glycogen
C) Glycogen, starch, cellulose
D) Cellulose, glycogen, starch
E) Starch, glycogen, cellulose
 Rank the three structures shown, from lowest to highest density.
Rank the three structures shown, from lowest to highest density.A) Cellulose, starch, glycogen
B) Starch, cellulose, glycogen
C) Glycogen, starch, cellulose
D) Cellulose, glycogen, starch
E) Starch, glycogen, cellulose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Why does a starchy food like bread become hard when it dries out?
A) In the absence of water, unbranched starch molecules aggregate together by forming hydrogen bonds.
B) Cellulose molecules in the cells aggregate in the absence of water.
C) The release of carbon dioxide from drying starch causes the food to harden.
D) The remaining water and heat cause the polysaccharide chains to bind together.
E) Mold growth interferes with α linkages, causing the food to harden.
A) In the absence of water, unbranched starch molecules aggregate together by forming hydrogen bonds.
B) Cellulose molecules in the cells aggregate in the absence of water.
C) The release of carbon dioxide from drying starch causes the food to harden.
D) The remaining water and heat cause the polysaccharide chains to bind together.
E) Mold growth interferes with α linkages, causing the food to harden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Lipids are
A) hydrophobic.
B) soluble in water.
C) absent from cell membranes.
D) composed of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen.
E) important for transmission of biological information.
A) hydrophobic.
B) soluble in water.
C) absent from cell membranes.
D) composed of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen.
E) important for transmission of biological information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A triglyceride contains fatty acids and
A) glycerol.
B) a base.
C) an amino acid.
D) a phosphate.
E) glucose.
A) glycerol.
B) a base.
C) an amino acid.
D) a phosphate.
E) glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
On the label of a shortening container are the words "hydrogenated vegetable oil." This means that during processing, the number of carbon-carbon double bonds in the oil was decreased and the
A) oil now has a lower melting point.
B) fatty acid chains now have more "kinks."
C) oil is now a derivative carbohydrate.
D) oil is now solid at room temperature.
E) fatty acid is now a triglyceride.
A) oil now has a lower melting point.
B) fatty acid chains now have more "kinks."
C) oil is now a derivative carbohydrate.
D) oil is now solid at room temperature.
E) fatty acid is now a triglyceride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Starch and glycogen are different in that only one of them
A) is a polymer of glucose.
B) contains ribose.
C) is made in plants.
D) is an energy storage molecule.
E) can be digested by humans.
A) is a polymer of glucose.
B) contains ribose.
C) is made in plants.
D) is an energy storage molecule.
E) can be digested by humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which statement about fatty acids is true?
A) They contain three fats bonded to a glycerol.
B) They are composed of a hydrocarbon tail and a carboxyl group.
C) They are carbohydrates linked to a hydrocarbon chain.
D) They contain glycerol and a carboxyl group.
E) They become saturated at low pH.
A) They contain three fats bonded to a glycerol.
B) They are composed of a hydrocarbon tail and a carboxyl group.
C) They are carbohydrates linked to a hydrocarbon chain.
D) They contain glycerol and a carboxyl group.
E) They become saturated at low pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the diagram of a polysaccharide below. 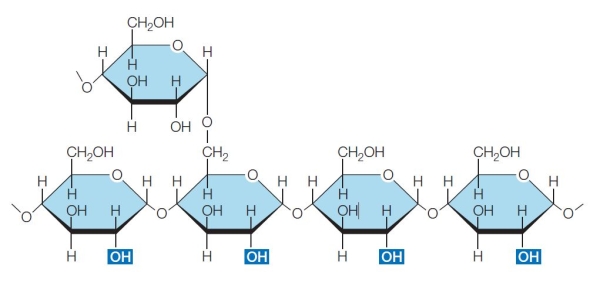 The monosaccharides shown in the diagram are linked by
The monosaccharides shown in the diagram are linked by
A) disulfide bridges.
B) glycosidic linkages.
C) peptide bonds.
D) noncovalent bonds.
E) ionic bonds.
 The monosaccharides shown in the diagram are linked by
The monosaccharides shown in the diagram are linked byA) disulfide bridges.
B) glycosidic linkages.
C) peptide bonds.
D) noncovalent bonds.
E) ionic bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



