Deck 6: Cell Membranes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/246
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Cell Membranes
1
In a biological membrane, the phospholipids are arranged in a _______, with the _______.
A) bilayer; fatty acid tails pointing toward each other
B) bilayer; fatty acid tails facing outward
C) single layer; fatty acid tails facing the interior of the cell
D) single layer; phosphorus-containing region facing the interior of the cell
E) bilayer; phosphorus groups in the interior of the membrane
A) bilayer; fatty acid tails pointing toward each other
B) bilayer; fatty acid tails facing outward
C) single layer; fatty acid tails facing the interior of the cell
D) single layer; phosphorus-containing region facing the interior of the cell
E) bilayer; phosphorus groups in the interior of the membrane
A
2
Refer to the figure below showing results from an analysis of the fluidity of neutrophil membranes as a function of their cholesterol content.Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell in humans. 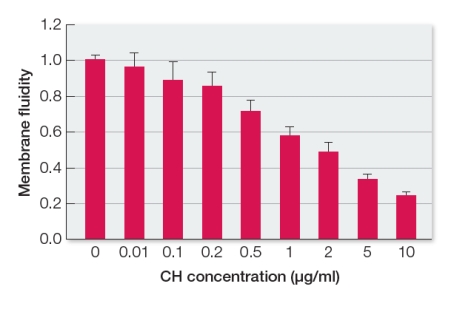 Which statement is consistent with these data?
Which statement is consistent with these data?
A) Cholesterol has a negligible influence on cell membrane fluidity.
B) The greater the cholesterol content in a membrane, the more fluid the membrane is.
C) A membrane with less cholesterol is more fluid than a membrane with more cholesterol.
D) Membrane fluidity increases with increasing cholesterol concentration.
E) There is an inverse relationship between membrane fluidity and cholesterol content.
 Which statement is consistent with these data?
Which statement is consistent with these data?A) Cholesterol has a negligible influence on cell membrane fluidity.
B) The greater the cholesterol content in a membrane, the more fluid the membrane is.
C) A membrane with less cholesterol is more fluid than a membrane with more cholesterol.
D) Membrane fluidity increases with increasing cholesterol concentration.
E) There is an inverse relationship between membrane fluidity and cholesterol content.
C
3
One student mentioned to another that the fluidity of a cell membrane can be changed by changing the membrane's lipid composition.The second student expressed doubt about this claim.What evidence could the first student find in a research journal to support his claim?
A) A comparison of lipid compositions of membranes in different cells within the same organism
B) An analysis of the change in fatty acid compositions of liver cell membranes in juvenile fish as they mature into adults
C) Results from cell fusion experiments between the same two cells that measure diffusion rates of different membrane proteins
D) Measurement of diffusion rates of the same protein in cell membranes containing different percentages of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
E) An analysis of the saturated and unsaturated fatty acid content in membranes of skin cells from a single population of cane toads
A) A comparison of lipid compositions of membranes in different cells within the same organism
B) An analysis of the change in fatty acid compositions of liver cell membranes in juvenile fish as they mature into adults
C) Results from cell fusion experiments between the same two cells that measure diffusion rates of different membrane proteins
D) Measurement of diffusion rates of the same protein in cell membranes containing different percentages of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
E) An analysis of the saturated and unsaturated fatty acid content in membranes of skin cells from a single population of cane toads
D
4
Refer to the figure below. 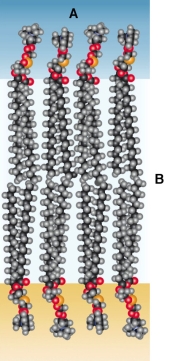 Which statement about the lipid bilayer shown in the figure is false?
Which statement about the lipid bilayer shown in the figure is false?
A) The area labeled A contains hydrophilic portions of fatty acids.
B) The area labeled A contains polar groups that can interact with water.
C) The area labeled B contains hydrophobic regions of fatty acids.
D) The area labeled B allows for the movement of charged particles.
E) The area labeled B allows for the diffusion of lipid-soluble particles.
 Which statement about the lipid bilayer shown in the figure is false?
Which statement about the lipid bilayer shown in the figure is false?A) The area labeled A contains hydrophilic portions of fatty acids.
B) The area labeled A contains polar groups that can interact with water.
C) The area labeled B contains hydrophobic regions of fatty acids.
D) The area labeled B allows for the movement of charged particles.
E) The area labeled B allows for the diffusion of lipid-soluble particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The hydrophilic regions of a membrane protein would most likely be found
A) only in cell membranes.
B) associated with the fatty acid region of the lipids.
C) in the interior of the membrane.
D) exposed on the surface of the membrane.
E) either on the surface or inserted into the interior of the membrane.
A) only in cell membranes.
B) associated with the fatty acid region of the lipids.
C) in the interior of the membrane.
D) exposed on the surface of the membrane.
E) either on the surface or inserted into the interior of the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The plasma membrane of the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae is able to remain fluid when it is extremely cold.The bacterium most likely accomplishes this by
A) increasing the number of cholesterol molecules present.
B) closing protein channels.
C) decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins present.
D) replacing saturated fatty acids with unsaturated fatty acids.
E) using fatty acids with longer tails.
A) increasing the number of cholesterol molecules present.
B) closing protein channels.
C) decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins present.
D) replacing saturated fatty acids with unsaturated fatty acids.
E) using fatty acids with longer tails.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ion channels are formed by a particular kind of membrane protein that allows the passage of a specific ion under certain conditions.This type of protein is most likely a(n)
A) peripheral protein with additional hydrophobic domains.
B) integral protein with a transmembrane domain.
C) phospholipid with hydrophilic domains.
D) enzyme with an asymmetrical arrangement on either side of the plasma membrane.
E) membrane protein that is able to move freely within the phospholipid bilayer.
A) peripheral protein with additional hydrophobic domains.
B) integral protein with a transmembrane domain.
C) phospholipid with hydrophilic domains.
D) enzyme with an asymmetrical arrangement on either side of the plasma membrane.
E) membrane protein that is able to move freely within the phospholipid bilayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a cell membrane lacking integral proteins is prepared by the freeze-fracture technique and examined under the electron microscope, the exposed interior of the membrane bilayer will
A) reveal a bumpy surface.
B) show hydrophobic side chains.
C) show an asymmetric distribution of proteins.
D) show cytoskeletal anchors.
E) look smooth.
A) reveal a bumpy surface.
B) show hydrophobic side chains.
C) show an asymmetric distribution of proteins.
D) show cytoskeletal anchors.
E) look smooth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Experimental results from five different studies on cell membranes are given.Which results could be used as evidence to support the claim that temperature affects a membrane's fluidity?
A) Results from freeze-fracture imaging of cell membranes isolated from blood cells of Arctic and desert rabbits
B) A comparison of diffusion rates of different membrane proteins at 37°C in the cell membranes of liver cells from mice
C) A chemical analysis of the saturated and unsaturated fatty acid content in membranes of intestinal cells from a single population of tropical frogs
D) A comparison of lipid compositions of membranes in different cells within the same organism
E) An analysis of the change in fatty acid compositions of liver cell membranes in a fish species before and after they migrate from warm to cold waters
A) Results from freeze-fracture imaging of cell membranes isolated from blood cells of Arctic and desert rabbits
B) A comparison of diffusion rates of different membrane proteins at 37°C in the cell membranes of liver cells from mice
C) A chemical analysis of the saturated and unsaturated fatty acid content in membranes of intestinal cells from a single population of tropical frogs
D) A comparison of lipid compositions of membranes in different cells within the same organism
E) An analysis of the change in fatty acid compositions of liver cell membranes in a fish species before and after they migrate from warm to cold waters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Membrane proteins are asymmetrically distributed according to the function of the membrane and its lipid composition.Which statement about peripheral membrane proteins is true?
A) They do not contain any hydrophilic regions.
B) They are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
C) They are able to move freely within the plasma membrane.
D) Their charged regions interact with other proteins or with phospholipids.
E) Their hydrophobic side chains interact with the lipid bilayer.
A) They do not contain any hydrophilic regions.
B) They are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
C) They are able to move freely within the plasma membrane.
D) Their charged regions interact with other proteins or with phospholipids.
E) Their hydrophobic side chains interact with the lipid bilayer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The LDL receptor is an integral membrane protein that extends both outside and into the interior of the cell.The amino acid side chains (R groups) in the region of the protein that crosses the membrane are most likely
A) polar.
B) hydrophilic.
C) hydrophobic.
D) carbohydrates.
E) lipids.
A) polar.
B) hydrophilic.
C) hydrophobic.
D) carbohydrates.
E) lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which observation can be used as evidence that the cell membrane has a fluid nature?
A) In the laboratory, two cells from different species can be fused together to make one large cell.
B) Images obtained using freeze-fracture electron microscopy reveal that the membrane contains embedded proteins.
C) Chemical analysis reveals that cell membranes contain phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol as major components.
D) Analysis of the amino acids present in protein regions embedded in cell membranes show that they mainly have hydrophobic side chains.
E) The cholesterol content in cell membranes varies depending on cell type, and it is generally higher than in organelle membranes.
A) In the laboratory, two cells from different species can be fused together to make one large cell.
B) Images obtained using freeze-fracture electron microscopy reveal that the membrane contains embedded proteins.
C) Chemical analysis reveals that cell membranes contain phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol as major components.
D) Analysis of the amino acids present in protein regions embedded in cell membranes show that they mainly have hydrophobic side chains.
E) The cholesterol content in cell membranes varies depending on cell type, and it is generally higher than in organelle membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The compounds in a biological membrane that form a barrier to the movement of hydrophilic materials across the membrane are
A) integral membrane proteins.
B) carbohydrates.
C) lipids.
D) nucleic acids.
E) peripheral membrane proteins.
A) integral membrane proteins.
B) carbohydrates.
C) lipids.
D) nucleic acids.
E) peripheral membrane proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The membrane components that enable a biological membrane to have fluidity are
A) integral membrane proteins.
B) carbohydrates.
C) oligosaccharides.
D) peripheral membrane proteins.
E) lipids.
A) integral membrane proteins.
B) carbohydrates.
C) oligosaccharides.
D) peripheral membrane proteins.
E) lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A biologist wants to compare the fluidity of membranes from different human cells.Which data will provide information that can be used for this analysis?
A) Integral membrane protein and peripheral membrane protein content
B) Cholesterol content and phospholipid fatty acid composition and content
C) Mass percentage of membrane proteins and mass percentage of lipids
D) Integral membrane protein densities in different locations of a membrane
E) Glycolipid and glycoprotein content and distribution in a membrane
A) Integral membrane protein and peripheral membrane protein content
B) Cholesterol content and phospholipid fatty acid composition and content
C) Mass percentage of membrane proteins and mass percentage of lipids
D) Integral membrane protein densities in different locations of a membrane
E) Glycolipid and glycoprotein content and distribution in a membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Protein movement within a membrane may be restricted by
A) glycolipids and glycoproteins.
B) cell fusion.
C) the cytoskeleton.
D) cell adhesion.
E) peripheral membrane proteins.
A) glycolipids and glycoproteins.
B) cell fusion.
C) the cytoskeleton.
D) cell adhesion.
E) peripheral membrane proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the table below. 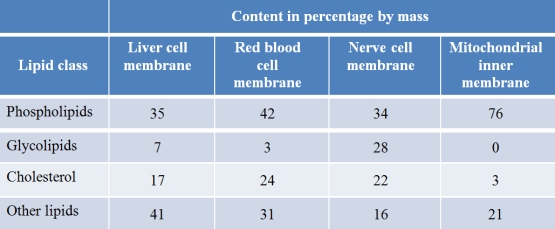 According to the data presented in the table, biological membranes differ in composition because of differences in
According to the data presented in the table, biological membranes differ in composition because of differences in
A) gene expression.
B) anatomical location.
C) lipid arrangement.
D) biological origin.
E) biological function.
 According to the data presented in the table, biological membranes differ in composition because of differences in
According to the data presented in the table, biological membranes differ in composition because of differences inA) gene expression.
B) anatomical location.
C) lipid arrangement.
D) biological origin.
E) biological function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How do the cell membranes of a hibernating animal change in colder temperatures?
A) Cholesterol content is increased.
B) Saturated fatty acids are more tightly packed.
C) Integral membrane proteins increase in number.
D) Unsaturated fatty acids make up more of the lipid composition.
E) Fatty acids with longer tails increase in number.
A) Cholesterol content is increased.
B) Saturated fatty acids are more tightly packed.
C) Integral membrane proteins increase in number.
D) Unsaturated fatty acids make up more of the lipid composition.
E) Fatty acids with longer tails increase in number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which membrane protein type would likely be removed most easily from a cell membrane in a laboratory experiment?
A) Integral proteins
B) Channel proteins
C) Peripheral proteins
D) Transmembrane proteins
E) Gated channels
A) Integral proteins
B) Channel proteins
C) Peripheral proteins
D) Transmembrane proteins
E) Gated channels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the hydrophilic side chains of a transmembrane protein were removed, the protein would most likely
A) remain within the phospholipid bilayer.
B) extend farther into the cytoplasm.
C) protrude into the extracellular space.
D) remain anchored to the cytoskeleton.
E) become a peripheral protein.
A) remain within the phospholipid bilayer.
B) extend farther into the cytoplasm.
C) protrude into the extracellular space.
D) remain anchored to the cytoskeleton.
E) become a peripheral protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the figure below. 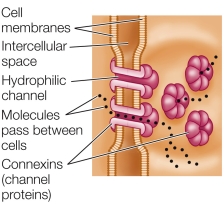 The type of cell junction shown is most efficient in
The type of cell junction shown is most efficient in
A) animal cells that require a tight structure.
B) animal cells that conduct electrical activity, as in the heart.
C) muscles, where rapid reflexes are required.
D) epithelial cells that line animal body cavities.
E) skin cells that receive stress.
 The type of cell junction shown is most efficient in
The type of cell junction shown is most efficient inA) animal cells that require a tight structure.
B) animal cells that conduct electrical activity, as in the heart.
C) muscles, where rapid reflexes are required.
D) epithelial cells that line animal body cavities.
E) skin cells that receive stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Scientists have been able to engineer young laboratory mice to have a defective gene for a particular integrin protein only in epidermal skin cells.These mice develop into adults with severe hair loss and skin blistering.Which statement explains the connection between the mutation and the observed physical problems of the mice?
A) A membrane protein receptor is absent, causing loss of cell signaling.
B) The mice cannot produce any extracellular matrix proteins.
C) Cell-cell communication is lost because of a lost cell junction.
D) Epidermal cells cannot express their genes properly.
E) Epidermal cells cannot connect to the extracellular matrix.
A) A membrane protein receptor is absent, causing loss of cell signaling.
B) The mice cannot produce any extracellular matrix proteins.
C) Cell-cell communication is lost because of a lost cell junction.
D) Epidermal cells cannot express their genes properly.
E) Epidermal cells cannot connect to the extracellular matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Cell adhesion occurs through the interactions of
A) glycoproteins and glycolipids.
B) cholesterol and fatty acids.
C) phospholipids and glycerol.
D) oligosaccharides and oligonucleotides.
E) integral proteins and cholesterol.
A) glycoproteins and glycolipids.
B) cholesterol and fatty acids.
C) phospholipids and glycerol.
D) oligosaccharides and oligonucleotides.
E) integral proteins and cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which type of molecule can function as a recognition signal for interactions between cells?
A) RNA
B) Phospholipids
C) Cholesterol
D) Fatty acids
E) Glycolipids
A) RNA
B) Phospholipids
C) Cholesterol
D) Fatty acids
E) Glycolipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Integrin on the cell surface of a white blood cell binds reversibly with the extracellular matrix of blood vessel walls.This reversibility allows for
A) communication between cells.
B) homotypic binding.
C) heterotypic movement.
D) cell movement.
E) passage of dissolved materials.
A) communication between cells.
B) homotypic binding.
C) heterotypic movement.
D) cell movement.
E) passage of dissolved materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure below.  The type of cell junction shown is most efficient in
The type of cell junction shown is most efficient in
A) animal cells that must exchange a lot of material with adjacent cells.
B) animal cells that conduct electrical activity, as in the heart.
C) muscles, where rapid reflexes are required.
D) epithelial cells that line animal body cavities.
E) skin cells that receive stress.
 The type of cell junction shown is most efficient in
The type of cell junction shown is most efficient inA) animal cells that must exchange a lot of material with adjacent cells.
B) animal cells that conduct electrical activity, as in the heart.
C) muscles, where rapid reflexes are required.
D) epithelial cells that line animal body cavities.
E) skin cells that receive stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Heart muscle cells beat in unison because of the rapid spread of electrical current through
A) tight junctions.
B) desmosomes.
C) gap junctions.
D) integral membrane proteins.
E) neurons.
A) tight junctions.
B) desmosomes.
C) gap junctions.
D) integral membrane proteins.
E) neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You are monitoring the diffusion of a molecule across a membrane.Of the options listed below, the fastest rate of diffusion would result from an internal concentration of _______ M and an external concentration of _______ M.
A) 5; 60
B) 35; 40
C) 50; 40
D) 50; 50
E) 100; 120
A) 5; 60
B) 35; 40
C) 50; 40
D) 50; 50
E) 100; 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You are working in a lab that is studying cell recognition and cell attachment in a red sponge.You need to culture individual cells in a medium that promotes cell recognition and attachment of isolated cells.Which of the following would you add to the culture medium?
A) Cellulose beads
B) Glycolipids
C) Glycoproteins from a different species of sponge
D) A species-specific polysaccharide
E) Complementary binding surfaces
A) Cellulose beads
B) Glycolipids
C) Glycoproteins from a different species of sponge
D) A species-specific polysaccharide
E) Complementary binding surfaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Osmosis is a specific form of
A) diffusion.
B) facilitated transport.
C) active transport.
D) secondary active transport.
E) movement of water by carrier proteins.
A) diffusion.
B) facilitated transport.
C) active transport.
D) secondary active transport.
E) movement of water by carrier proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Two membrane components that serve as cell recognition sites are
A) peripheral and integral membrane proteins.
B) hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains.
C) carbohydrates and proteins.
D) glycolipids and glycoproteins.
E) amino acids and lipids.
A) peripheral and integral membrane proteins.
B) hydrophilic and hydrophobic domains.
C) carbohydrates and proteins.
D) glycolipids and glycoproteins.
E) amino acids and lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sponges are multicellular organisms whose bodies allow water to circulate freely.If isolated cells from one species were added to a solution of isolated cells from another species, what would you expect in terms of binding among the cells?
A) Cells from both species would bind to one another.
B) Cells from one species would bind only to others of the same species.
C) Cell binding would occur according to which type of cell was present in greater numbers.
D) The cells would bind according to size, with no difference in species.
E) The cells would remain isolated without binding between any groups.
A) Cells from both species would bind to one another.
B) Cells from one species would bind only to others of the same species.
C) Cell binding would occur according to which type of cell was present in greater numbers.
D) The cells would bind according to size, with no difference in species.
E) The cells would remain isolated without binding between any groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A student claims that cell recognition and cell adhesion refer to the same function.Which statement best evaluates this claim?
A) This statement is accurate, because cell recognition and cell adhesion rely on the ability of molecules from different cells to have complementary surfaces.
B) This statement is accurate, because cell recognition and cell adhesion are both abolished if molecules on different cells are prevented from interacting.
C) This statement is not accurate, because cell recognition is the basis for cell adhesion, as well as for many other functions.
D) This statement is not accurate, because cell adhesion is the basis for cell recognition as well as for many other functions.
E) This statement is not accurate, because cell recognition and cell adhesion have no overlap in function.
A) This statement is accurate, because cell recognition and cell adhesion rely on the ability of molecules from different cells to have complementary surfaces.
B) This statement is accurate, because cell recognition and cell adhesion are both abolished if molecules on different cells are prevented from interacting.
C) This statement is not accurate, because cell recognition is the basis for cell adhesion, as well as for many other functions.
D) This statement is not accurate, because cell adhesion is the basis for cell recognition as well as for many other functions.
E) This statement is not accurate, because cell recognition and cell adhesion have no overlap in function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In animal cell junctions, _______ seal intercellular spaces, _______ reinforce attachments, and _______ allow for communication between cells.
A) keratins; desmosomes; connexins
B) tight junctions; desmosomes; gap junctions
C) cell recognition molecules; adhesion molecules; tight junctions
D) junction proteins; adhesion molecules; connexins
E) desmosomes; gap junctions; tight junctions
A) keratins; desmosomes; connexins
B) tight junctions; desmosomes; gap junctions
C) cell recognition molecules; adhesion molecules; tight junctions
D) junction proteins; adhesion molecules; connexins
E) desmosomes; gap junctions; tight junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A group of transmembrane proteins involved in maintaining animal cell structure via their interactions with the cytoskeleton are known as
A) integrins.
B) desmosomes.
C) seal tissues.
D) connexins.
E) keratins.
A) integrins.
B) desmosomes.
C) seal tissues.
D) connexins.
E) keratins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
You are studying the effects of different substances on frog heart muscle cells.You treat the cells with a substance that blocks gap junctions.What do you expect will occur?
A) The cells will not be able to maintain their structure.
B) The gap junctions will not be able to provide stability.
C) The electric current will not spread evenly to adjacent heart cells.
D) Nutrients will not pass between the cells.
E) Nerve impulses will not be transmitted to the cells.
A) The cells will not be able to maintain their structure.
B) The gap junctions will not be able to provide stability.
C) The electric current will not spread evenly to adjacent heart cells.
D) Nutrients will not pass between the cells.
E) Nerve impulses will not be transmitted to the cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If tight junctions were replaced by desmosomes in cells lining the bladder,
A) dissolved substances would move freely through the extracellular matrix.
B) membrane protein migration would be restricted.
C) intercellular spaces would be sealed off.
D) the number of gap junctions would increase.
E) pressure on the desmosomes would increase.
A) dissolved substances would move freely through the extracellular matrix.
B) membrane protein migration would be restricted.
C) intercellular spaces would be sealed off.
D) the number of gap junctions would increase.
E) pressure on the desmosomes would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which factor does not affect the rate of diffusion of a substance?
A) Temperature of the solution
B) Concentration gradient
C) Density of the solution
D) Presence of other solutes in the solution
E) Molecular diameter of the diffusing material
A) Temperature of the solution
B) Concentration gradient
C) Density of the solution
D) Presence of other solutes in the solution
E) Molecular diameter of the diffusing material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which is the name of a specialized cell junction that allows rapid spread of electric current via the flow of ions between animal cells?
A) Gap junction
B) Tight junction
C) Desmosome
D) Connexin
E) Integrin
A) Gap junction
B) Tight junction
C) Desmosome
D) Connexin
E) Integrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A biologist hypothesizes that a particular membrane protein is distributed throughout the cell and anchored to the cytoskeleton.Which experimental technique could provide evidence to test the biologist's hypothesis, and why?
A) Freeze-fracturing techniques, because they can be used to identify cell locations of membrane proteins
B) Freeze-fracturing techniques, because they can distinguish between integral and peripheral proteins
C) Cell fusion techniques, because they can be used to analyze the diffusion rate of a membrane protein
D) Cell fusion techniques, because they can be used to determine the fluidity of a membrane
E) Cell fusion techniques, because they can distinguish between membrane proteins of different sizes by their diffusion rates
A) Freeze-fracturing techniques, because they can be used to identify cell locations of membrane proteins
B) Freeze-fracturing techniques, because they can distinguish between integral and peripheral proteins
C) Cell fusion techniques, because they can be used to analyze the diffusion rate of a membrane protein
D) Cell fusion techniques, because they can be used to determine the fluidity of a membrane
E) Cell fusion techniques, because they can distinguish between membrane proteins of different sizes by their diffusion rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a hospital patient is mistakenly administered pure water instead of a saline solution that is isotonic to blood during intravenous (IV) therapy, the patient's red blood cells will
A) shrink and collapse.
B) release water to the plasma along its concentration gradient.
C) absorb water from the plasma and eventually burst.
D) allow water to move through protein channels in the cell membrane in both directions.
E) lose their function, and the water level in the plasma will be maintained by white blood cells instead.
A) shrink and collapse.
B) release water to the plasma along its concentration gradient.
C) absorb water from the plasma and eventually burst.
D) allow water to move through protein channels in the cell membrane in both directions.
E) lose their function, and the water level in the plasma will be maintained by white blood cells instead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If a red blood cell with an internal salt concentration of about 0.85 percent is placed in a solution that is 4 percent salt,
A) the cell will lose water and shrivel.
B) the cell will gain water and burst.
C) the turgor pressure in the cell will increase greatly.
D) the turgor pressure in the cell will decrease greatly.
E) the cell will remain unchanged.
A) the cell will lose water and shrivel.
B) the cell will gain water and burst.
C) the turgor pressure in the cell will increase greatly.
D) the turgor pressure in the cell will decrease greatly.
E) the cell will remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When placed in water, wilted plants regain their leaf turgor because of the
A) active transport of salts from the water into the plant cells.
B) active transport of salts from the plant cells into the water.
C) osmosis of water into the plant cells.
D) osmosis of water out of the plant cells.
E) diffusion of water out of the plant cells.
A) active transport of salts from the water into the plant cells.
B) active transport of salts from the plant cells into the water.
C) osmosis of water into the plant cells.
D) osmosis of water out of the plant cells.
E) diffusion of water out of the plant cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the table below. 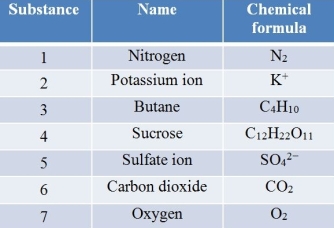 Which list contains every substance in the table that can be predicted to pass via simple diffusion across a biological membrane?
Which list contains every substance in the table that can be predicted to pass via simple diffusion across a biological membrane?
A) 6, 7
B) 1, 6, 7
C) 2, 3, 5
D) 1, 2, 3, 6
E) 1, 3, 6, 7
 Which list contains every substance in the table that can be predicted to pass via simple diffusion across a biological membrane?
Which list contains every substance in the table that can be predicted to pass via simple diffusion across a biological membrane?A) 6, 7
B) 1, 6, 7
C) 2, 3, 5
D) 1, 2, 3, 6
E) 1, 3, 6, 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the figure below. 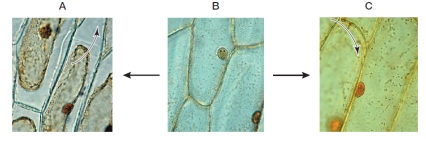 Which statement regarding the sequence of events shown in the figure is true?
Which statement regarding the sequence of events shown in the figure is true?
A) The cells in condition B have less turgor pressure than the cells in condition A.
B) The cells in condition A have been placed in a hypotonic solution.
C) The cells in condition C have been placed in a hypertonic solution.
D) The cells in condition C have been placed in an isotonic solution.
E) The cells in condition C have greater turgor pressure than the cells in condition B.
 Which statement regarding the sequence of events shown in the figure is true?
Which statement regarding the sequence of events shown in the figure is true?A) The cells in condition B have less turgor pressure than the cells in condition A.
B) The cells in condition A have been placed in a hypotonic solution.
C) The cells in condition C have been placed in a hypertonic solution.
D) The cells in condition C have been placed in an isotonic solution.
E) The cells in condition C have greater turgor pressure than the cells in condition B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If cells that normally contain aquaporins undergo a mutation that destroys aquaporin function, which outcome can be expected?
A) The cells will experience uncontrollable water loss.
B) The cells will experience uncontrollable sodium and potassium ion uptake.
C) The cells will lose the ability to take up or release sodium and potassium ions.
D) The cells' membranes will become impermeable to water.
E) The cells will have no means for any polar compounds to diffuse across their membranes.
A) The cells will experience uncontrollable water loss.
B) The cells will experience uncontrollable sodium and potassium ion uptake.
C) The cells will lose the ability to take up or release sodium and potassium ions.
D) The cells' membranes will become impermeable to water.
E) The cells will have no means for any polar compounds to diffuse across their membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Refer to the figure below. 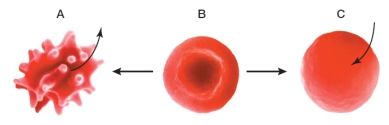 Which statement regarding the red blood cells in the figure is true?
Which statement regarding the red blood cells in the figure is true?
A) Cell C has been immersed in a hypertonic solution.
B) The concentration of solutes inside cell C is higher than in the solution surrounding the cell.
C) Cell A has been immersed in a hypotonic solution.
D) Osmosis occurs when a cell goes from condition B to C but not from condition B to A.
E) Diffusion of solutes out of the cell is causing the events shown in the transition from condition B to A.
 Which statement regarding the red blood cells in the figure is true?
Which statement regarding the red blood cells in the figure is true?A) Cell C has been immersed in a hypertonic solution.
B) The concentration of solutes inside cell C is higher than in the solution surrounding the cell.
C) Cell A has been immersed in a hypotonic solution.
D) Osmosis occurs when a cell goes from condition B to C but not from condition B to A.
E) Diffusion of solutes out of the cell is causing the events shown in the transition from condition B to A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which statement about the process of diffusion is true?
A) The concentration gradient of a solute depends on the size of the molecule.
B) Equilibrium in a solution is the end point of diffusion.
C) The net movement of particles depends on the temperature of the solution.
D) Diffusion is most efficient over long distances.
E) Diffusion can reduce selective permeability of a membrane.
A) The concentration gradient of a solute depends on the size of the molecule.
B) Equilibrium in a solution is the end point of diffusion.
C) The net movement of particles depends on the temperature of the solution.
D) Diffusion is most efficient over long distances.
E) Diffusion can reduce selective permeability of a membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which statement about osmosis is false?
A) Osmosis refers to the movement of water along a concentration gradient.
B) In osmosis, water moves in a direction from low solute concentrations to high solute concentrations.
C) The movement of water across a membrane can affect the turgor pressure of some cells.
D) If osmosis occurs across a membrane, then diffusion is not occurring.
E) Water may move through membrane channels during the process of osmosis.
A) Osmosis refers to the movement of water along a concentration gradient.
B) In osmosis, water moves in a direction from low solute concentrations to high solute concentrations.
C) The movement of water across a membrane can affect the turgor pressure of some cells.
D) If osmosis occurs across a membrane, then diffusion is not occurring.
E) Water may move through membrane channels during the process of osmosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If equal volumes of differently colored solutions are poured into opposite sides of a shallow pool of water, what will be the result at equilibrium?
A) Each solution will be uniformly distributed in the side of the pool into which it was poured.
B) The solutions will be uniformly distributed throughout the pool.
C) Each solution will have moved against its concentration gradient.
D) The concentration of each solution will be higher in one side of the pool than in the other.
E) The solutions will have sunk to the bottom of the pool and remained separate.
A) Each solution will be uniformly distributed in the side of the pool into which it was poured.
B) The solutions will be uniformly distributed throughout the pool.
C) Each solution will have moved against its concentration gradient.
D) The concentration of each solution will be higher in one side of the pool than in the other.
E) The solutions will have sunk to the bottom of the pool and remained separate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The directions of ions as they move into and out of the cell are determined by the
A) ability of the ions to let go of their water.
B) ion concentration gradient.
C) number of channel proteins present.
D) size and charge of the ions.
E) presence of specific stimuli to open gated channel proteins.
A) ability of the ions to let go of their water.
B) ion concentration gradient.
C) number of channel proteins present.
D) size and charge of the ions.
E) presence of specific stimuli to open gated channel proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The process of osmosis allows water molecules to pass through specialized channels in membranes.Which statement about osmosis is true?
A) The direction of osmosis depends on temperature.
B) Water will move across a membrane to a region with less solute.
C) Water will move across a membrane to a region with more solute.
D) If the membrane does not allow solutes to pass, water will be equal on both sides.
E) A higher solute concentration on one side of a membrane indicates a higher water concentration on that side.
A) The direction of osmosis depends on temperature.
B) Water will move across a membrane to a region with less solute.
C) Water will move across a membrane to a region with more solute.
D) If the membrane does not allow solutes to pass, water will be equal on both sides.
E) A higher solute concentration on one side of a membrane indicates a higher water concentration on that side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that a new drug shows promise in treating cancer because it can enter cells by simple diffusion.Which statement about the drug is false?
A) It depends on a specific carrier protein to enter the cells.
B) Diffusion of the drug continues until its concentrations across membranes are in equilibrium.
C) The drug molecules move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
D) Diffusion of the drug molecules is a random process.
E) The rate of its diffusion is affected by temperature.
A) It depends on a specific carrier protein to enter the cells.
B) Diffusion of the drug continues until its concentrations across membranes are in equilibrium.
C) The drug molecules move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
D) Diffusion of the drug molecules is a random process.
E) The rate of its diffusion is affected by temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Channel proteins allow ions that would not normally pass through the cell membrane to pass through via the channel.The property of the channel protein that makes this possible is its pore, which is composed of
A) polar amino acid groups.
B) hydrophobic amino acid groups.
C) Ca2+.
D) carbohydrates.
E) nonpolar R groups.
A) polar amino acid groups.
B) hydrophobic amino acid groups.
C) Ca2+.
D) carbohydrates.
E) nonpolar R groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which helps ensure the diffusion of glucose into a cell that has a high energy need?
A) A glucose pump
B) Ion channels found in large muscle cells
C) A high number of carrier proteins specific for glucose
D) An extracellular environment high in glucose
E) Additional pores through which water can flow, carrying dissolved glucose
A) A glucose pump
B) Ion channels found in large muscle cells
C) A high number of carrier proteins specific for glucose
D) An extracellular environment high in glucose
E) Additional pores through which water can flow, carrying dissolved glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A molecule is present at two different concentrations on either side of a membrane.The molecule will have the greatest diffusion rate if the concentration is _______ M on one side and _______ M on the other.
A) 10; 20
B) 20; 30
C) 50; 60
D) 30; 30
E) 15; 50
A) 10; 20
B) 20; 30
C) 50; 60
D) 30; 30
E) 15; 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In facilitated diffusion, the diffusion rate of a specific molecule across a membrane does not continue to increase as the molecule's concentration difference across the membrane increases beyond a certain point.The reason is that
A) facilitated diffusion requires the use of ATP.
B) as the concentration difference increases, molecules interfere with one another.
C) the carrier proteins become saturated.
D) the transport protein is a channel protein.
E) the diffusion constant depends on the concentration difference.
A) facilitated diffusion requires the use of ATP.
B) as the concentration difference increases, molecules interfere with one another.
C) the carrier proteins become saturated.
D) the transport protein is a channel protein.
E) the diffusion constant depends on the concentration difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which strategy is paired with an appropriate consequence that would enable a cell to maintain homeostasis when placed in a vessel of pure water?
A) Reduce the number of aquaporins in the cell membrane to stop water from moving out of the cytoplasm and into the external environment.
B) Decrease the movement of salts out of the cytoplasm to stop water from moving into the cytoplasm.
C) Expend energy to pump water out of the cytoplasm and into the external environment as the internal fluid levels become too high.
D) Expend energy to pump salts into the cytoplasm from the external environment as the cytoplasm swells from water moving in by osmosis.
E) Allow water to diffuse across the cell membrane until equilibrium is reached.
A) Reduce the number of aquaporins in the cell membrane to stop water from moving out of the cytoplasm and into the external environment.
B) Decrease the movement of salts out of the cytoplasm to stop water from moving into the cytoplasm.
C) Expend energy to pump water out of the cytoplasm and into the external environment as the internal fluid levels become too high.
D) Expend energy to pump salts into the cytoplasm from the external environment as the cytoplasm swells from water moving in by osmosis.
E) Allow water to diffuse across the cell membrane until equilibrium is reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the figure below. 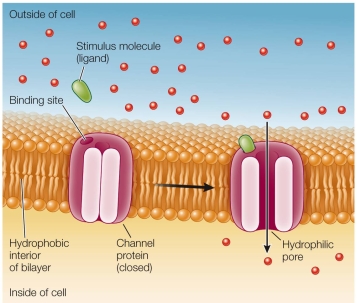 Which statement regarding channel proteins shown in the figure is false?
Which statement regarding channel proteins shown in the figure is false?
A) Channel proteins can assist polar molecules to cross the plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion.
B) The gated ion channel can allow ions to pass when stimulated to open.
C) The surface of a channel protein in contact with the bilayer would likely have hydrophilic amino acids.
D) Water plays a role in determining which ions are allowed to pass through an ion channel.
E) Aquaporins are channel proteins that facilitate the diffusion of water across membranes.
 Which statement regarding channel proteins shown in the figure is false?
Which statement regarding channel proteins shown in the figure is false?A) Channel proteins can assist polar molecules to cross the plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion.
B) The gated ion channel can allow ions to pass when stimulated to open.
C) The surface of a channel protein in contact with the bilayer would likely have hydrophilic amino acids.
D) Water plays a role in determining which ions are allowed to pass through an ion channel.
E) Aquaporins are channel proteins that facilitate the diffusion of water across membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The difference between osmosis and diffusion is that
A) diffusion is passive transport, whereas osmosis is active transport.
B) only in diffusion do molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
C) only diffusion refers to the movement of materials across a semipermeable membrane.
D) osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water, whereas diffusion is the movement of any molecule.
E) the process of osmosis varies according to the kinds of particles present.
A) diffusion is passive transport, whereas osmosis is active transport.
B) only in diffusion do molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
C) only diffusion refers to the movement of materials across a semipermeable membrane.
D) osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water, whereas diffusion is the movement of any molecule.
E) the process of osmosis varies according to the kinds of particles present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis all involve
A) the intake of large particles.
B) invagination of the plasma membrane.
C) the export of macromolecules.
D) the presence of receptor proteins.
E) the intake of fluids by the cell.
A) the intake of large particles.
B) invagination of the plasma membrane.
C) the export of macromolecules.
D) the presence of receptor proteins.
E) the intake of fluids by the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which is not involved in secondary active transport?
A) Energy
B) A coupled transporter
C) A concentration gradient
D) The bilayer membrane
E) A uniporter
A) Energy
B) A coupled transporter
C) A concentration gradient
D) The bilayer membrane
E) A uniporter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a cell were bathed in an extracellular solution high in Na+, what type of ion movement would maintain the proper balance of Na+ ions between the inside and the outside of the cell?
A) Active transport of Na+ against its concentration gradient
B) Facilitated diffusion of Na+ through ion channels
C) Secondary active transport of K+
D) Simple diffusion of Na+
E) Simple diffusion of K+
A) Active transport of Na+ against its concentration gradient
B) Facilitated diffusion of Na+ through ion channels
C) Secondary active transport of K+
D) Simple diffusion of Na+
E) Simple diffusion of K+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Both phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis
A) are methods used by a cell to expel materials into the environment.
B) involve vesicle formation as materials are taken up from the environment.
C) are nonspecific in terms of the materials they transport.
D) use membrane receptors as recognition sites for the molecules they target.
E) involve a process in which vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the cell membrane on the interior of a cell.
A) are methods used by a cell to expel materials into the environment.
B) involve vesicle formation as materials are taken up from the environment.
C) are nonspecific in terms of the materials they transport.
D) use membrane receptors as recognition sites for the molecules they target.
E) involve a process in which vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the cell membrane on the interior of a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What term is used to describe the nonspecific uptake of fluids and dissolved solutes by a cell?
A) Osmosis
B) Diffusion
C) Receptor-mediated endocytosis
D) Phagocytosis
E) Pinocytosis
A) Osmosis
B) Diffusion
C) Receptor-mediated endocytosis
D) Phagocytosis
E) Pinocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the intestine, Na+ and an amino acid bind to the same transport protein that moves the two substances in the same direction.This type of active transport involves
A) a symporter.
B) an antiporter.
C) secondary active transport.
D) facilitated transport.
E) a diffusion mechanism.
A) a symporter.
B) an antiporter.
C) secondary active transport.
D) facilitated transport.
E) a diffusion mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Both primary and secondary active transport
A) generate ATP.
B) are based on passive movement of Na+ ions.
C) include the passive movement of glucose molecules.
D) use ATP directly.
E) can move solutes against their concentration gradients.
A) generate ATP.
B) are based on passive movement of Na+ ions.
C) include the passive movement of glucose molecules.
D) use ATP directly.
E) can move solutes against their concentration gradients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Secondary active transport occurs in the small intestine, where the uptake of glucose is coupled to the transport of sodium ions into the cells lining this organ.This type of transport system is called
A) a uniporter.
B) a symporter.
C) an exchange channel.
D) diffusion.
E) an antiporter.
A) a uniporter.
B) a symporter.
C) an exchange channel.
D) diffusion.
E) an antiporter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which is an example of passive transport?
A) Facilitated diffusion
B) The sodium-potassium pump
C) Turgor pressure
D) ATP-driven transport
E) Endocytosis
A) Facilitated diffusion
B) The sodium-potassium pump
C) Turgor pressure
D) ATP-driven transport
E) Endocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Refer to the figure below, which is being created to illustrate secondary active transport. 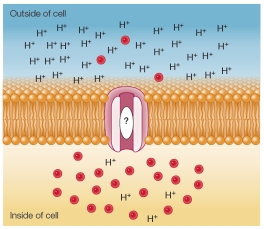 The small red circles represent the molecules being transported, and the H+ symbols represent hydrogen ions.The natural concentration gradient of the red molecules is shown.The hydrogen ion gradient was established by a membrane protein that is not shown.Given this information, which symbol should appear in the oval to indicate the direction of movement of hydrogen ions and red molecules?
The small red circles represent the molecules being transported, and the H+ symbols represent hydrogen ions.The natural concentration gradient of the red molecules is shown.The hydrogen ion gradient was established by a membrane protein that is not shown.Given this information, which symbol should appear in the oval to indicate the direction of movement of hydrogen ions and red molecules?
A)
B)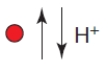
C)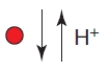
D)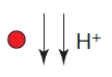
E)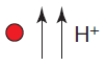
 The small red circles represent the molecules being transported, and the H+ symbols represent hydrogen ions.The natural concentration gradient of the red molecules is shown.The hydrogen ion gradient was established by a membrane protein that is not shown.Given this information, which symbol should appear in the oval to indicate the direction of movement of hydrogen ions and red molecules?
The small red circles represent the molecules being transported, and the H+ symbols represent hydrogen ions.The natural concentration gradient of the red molecules is shown.The hydrogen ion gradient was established by a membrane protein that is not shown.Given this information, which symbol should appear in the oval to indicate the direction of movement of hydrogen ions and red molecules?A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the figure below. 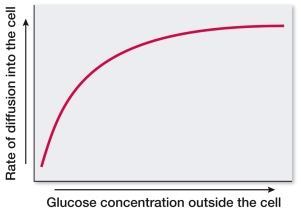 According to the graph, as the number of glucose molecules increases, the rate of diffusion across a membrane
According to the graph, as the number of glucose molecules increases, the rate of diffusion across a membrane
A) increases indefinitely.
B) decreases.
C) increases until a plateau is reached.
D) can either increase or decrease.
E) remains unchanged.
 According to the graph, as the number of glucose molecules increases, the rate of diffusion across a membrane
According to the graph, as the number of glucose molecules increases, the rate of diffusion across a membraneA) increases indefinitely.
B) decreases.
C) increases until a plateau is reached.
D) can either increase or decrease.
E) remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In passive transport, molecules move
A) against their concentration gradient.
B) more slowly than in active transport.
C) toward a region of higher concentration.
D) so as to reduce differences in concentration across a membrane.
E) until a state of equilibrium is reached and movement stops.
A) against their concentration gradient.
B) more slowly than in active transport.
C) toward a region of higher concentration.
D) so as to reduce differences in concentration across a membrane.
E) until a state of equilibrium is reached and movement stops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the figure below, which is being created to illustrate secondary active transport. 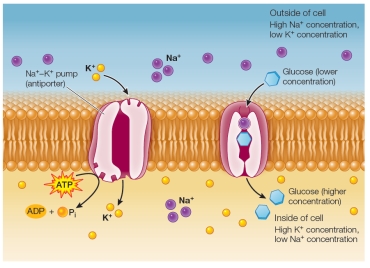 What is missing from the figure?
What is missing from the figure?
A) A concentration gradient
B) Arrows showing movement of sodium ions
C) A coupled transporter acting to create a concentration gradient
D) Arrows showing movement of glucose molecules
E) A source of energy for sodium ion transport
 What is missing from the figure?
What is missing from the figure?A) A concentration gradient
B) Arrows showing movement of sodium ions
C) A coupled transporter acting to create a concentration gradient
D) Arrows showing movement of glucose molecules
E) A source of energy for sodium ion transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Facilitated diffusion and active transport both
A) require ATP.
B) require the use of proteins as carriers or channels.
C) carry ions and not small molecules.
D) increase without limit as the concentration gradient increases.
E) depend on the solubility of the solute in lipids.
A) require ATP.
B) require the use of proteins as carriers or channels.
C) carry ions and not small molecules.
D) increase without limit as the concentration gradient increases.
E) depend on the solubility of the solute in lipids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For each molecule of ATP consumed during active transport of sodium and potassium, there is an import of _______ ion(s) and an export of _______ ion(s).
A) two Na+; three K+
B) two Na+; one K+
C) one K+; three Na+
D) two K+; three Na+
E) three K+; two Na+
A) two Na+; three K+
B) two Na+; one K+
C) one K+; three Na+
D) two K+; three Na+
E) three K+; two Na+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Refer to the figure below showing concentrations of three ions inside and outside a cell, as well as the direction of transport of each ion facilitated by a membrane protein. 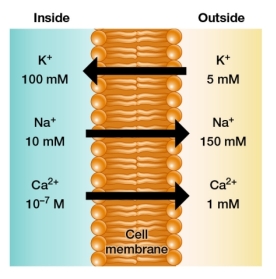 Which ions are moved by active transport and why?
Which ions are moved by active transport and why?
A) K+ and Na+, because they are present in millimolar concentrations in the cell
B) Ca2+, because it is present in concentrations below the micromolar level in the cell
C) K+, because it is being moved into the cell and not out of the cell
D) K+, Na+, and Ca2+, because they are charged particles
E) K+, Na+, and Ca2+, because they are moving from lower to higher concentration
 Which ions are moved by active transport and why?
Which ions are moved by active transport and why?A) K+ and Na+, because they are present in millimolar concentrations in the cell
B) Ca2+, because it is present in concentrations below the micromolar level in the cell
C) K+, because it is being moved into the cell and not out of the cell
D) K+, Na+, and Ca2+, because they are charged particles
E) K+, Na+, and Ca2+, because they are moving from lower to higher concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The sodium‒potassium pump found in animal cells is a(n)
A) uniporter.
B) carrier protein.
C) symporter.
D) peripheral membrane protein.
E) antiporter.
A) uniporter.
B) carrier protein.
C) symporter.
D) peripheral membrane protein.
E) antiporter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Regardless of the specific type of molecule or particle being transported, endocytosis always involves
A) phagocytosis.
B) pinocytosis.
C) receptor proteins.
D) membrane invagination.
E) phagosomes.
A) phagocytosis.
B) pinocytosis.
C) receptor proteins.
D) membrane invagination.
E) phagosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Transporters that move two substances at once are known as
A) uniporters.
B) facilitated transporters.
C) secondary active transporters.
D) coupled transporters.
E) directional transporters.
A) uniporters.
B) facilitated transporters.
C) secondary active transporters.
D) coupled transporters.
E) directional transporters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The sodium‒potassium pump changes shape in response to
A) the binding of ions.
B) the hydrolysis of ATP and phosphorylation.
C) the release of Na+ ions outside the cell.
D) the influx of K+ ions.
E) secondary active transport.
A) the binding of ions.
B) the hydrolysis of ATP and phosphorylation.
C) the release of Na+ ions outside the cell.
D) the influx of K+ ions.
E) secondary active transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



