Deck 8: Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/246
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism
1
Suppose that, in a closed system, there is an input of energy as 1 kJ of light.The light energy is converted to glucose, then ATP, and finally to mechanical energy.Which statement about the amount of mechanical energy available is true?
A) There is 1 kJ of mechanical energy available to do work.
B) The amount of usable energy decreases with each conversion, so less than 1 kJ of energy is available for mechanical work.
C) All of the reactions involved are anabolic, so there is 0.25 kJ of mechanical energy available.
D) All of the reactions involved are exergonic, so the number of kilojoules of mechanical energy produced is greater than the 1 kJ input.
E) All of the reactions involved are endergonic, so without constant input of energy, no mechanical energy is produced.
A) There is 1 kJ of mechanical energy available to do work.
B) The amount of usable energy decreases with each conversion, so less than 1 kJ of energy is available for mechanical work.
C) All of the reactions involved are anabolic, so there is 0.25 kJ of mechanical energy available.
D) All of the reactions involved are exergonic, so the number of kilojoules of mechanical energy produced is greater than the 1 kJ input.
E) All of the reactions involved are endergonic, so without constant input of energy, no mechanical energy is produced.
B
2
Which of the following is neither created nor destroyed during its conversion?
A) Entropy
B) Energy
C) Free energy only
D) Thermal energy only
E) Potential energy only
A) Entropy
B) Energy
C) Free energy only
D) Thermal energy only
E) Potential energy only
B
3
The first law of thermodynamics states that the total energy in the universe is
A) decreasing.
B) increasing.
C) constant.
D) being converted to free energy.
E) being converted to matter.
A) decreasing.
B) increasing.
C) constant.
D) being converted to free energy.
E) being converted to matter.
C
4
The G of a reaction tells us all of the following except
A) the rate of the reaction.
B) the direction of the reaction.
C) whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic.
D) whether the reaction requires or releases energy.
E) whether a higher free energy is in the product or in the reactants.
A) the rate of the reaction.
B) the direction of the reaction.
C) whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic.
D) whether the reaction requires or releases energy.
E) whether a higher free energy is in the product or in the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about the exergonic hydrolysis of maltose to glucose is true?
A) The reaction requires the input of free energy.
B) The free energy of glucose is larger than the free energy of maltose.
C) The reaction is not spontaneous.
D) The reaction releases free energy.
E) At equilibrium, the concentration of maltose is higher than the concentration of glucose.
A) The reaction requires the input of free energy.
B) The free energy of glucose is larger than the free energy of maltose.
C) The reaction is not spontaneous.
D) The reaction releases free energy.
E) At equilibrium, the concentration of maltose is higher than the concentration of glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The standard free energy change for the hydrolysis of GTP (guanosine triphosphate) to GDP + Pi is -7.3 kcal/mol, similar to that for ATP.From this information, one can conclude that the
A) reaction will never reach equilibrium.
B) free energy of GDP and phosphate is higher than the free energy of GTP.
C) reaction requires energy.
D) reaction is endergonic.
E) reaction is exergonic.
A) reaction will never reach equilibrium.
B) free energy of GDP and phosphate is higher than the free energy of GTP.
C) reaction requires energy.
D) reaction is endergonic.
E) reaction is exergonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In thermodynamic terms, water held back by a dam represents _______ energy.
A) electrical
B) irrigation
C) potential
D) kinetic
E) heat
A) electrical
B) irrigation
C) potential
D) kinetic
E) heat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the temperature of a reaction with a G of ‒7.1 kJ/mol increases, what will happen to the G of the reaction?
A) It will stay the same.
B) It will equal zero.
C) It will also increase.
D) It will decrease.
E) Not enough information is provided to make a determination.
A) It will stay the same.
B) It will equal zero.
C) It will also increase.
D) It will decrease.
E) Not enough information is provided to make a determination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The sum total of all chemical reactions in a living organism is called its
A) energetics.
B) activity.
C) digestive power.
D) entropy.
E) metabolism.
A) energetics.
B) activity.
C) digestive power.
D) entropy.
E) metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following represents kinetic energy?
A) Chemical bonds
B) Concentration gradient
C) Electric charge imbalance
D) Muscle contraction
E) Separation of opposite charges
A) Chemical bonds
B) Concentration gradient
C) Electric charge imbalance
D) Muscle contraction
E) Separation of opposite charges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
During photosynthesis, plants use light energy to synthesize sugars, using the carbon in carbon dioxide.They do not make new energy in this process; they merely convert it from light energy to chemical energy.Photosynthesis is thus an illustration of
A) increasing entropy.
B) chemical equilibrium.
C) the first law of thermodynamics.
D) the second law of thermodynamics.
E) a spontaneous reaction.
A) increasing entropy.
B) chemical equilibrium.
C) the first law of thermodynamics.
D) the second law of thermodynamics.
E) a spontaneous reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Free energy is
A) enthalpy.
B) entropy.
C) usable energy.
D) always positive.
E) always negative.
A) enthalpy.
B) entropy.
C) usable energy.
D) always positive.
E) always negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Refer to the table below. 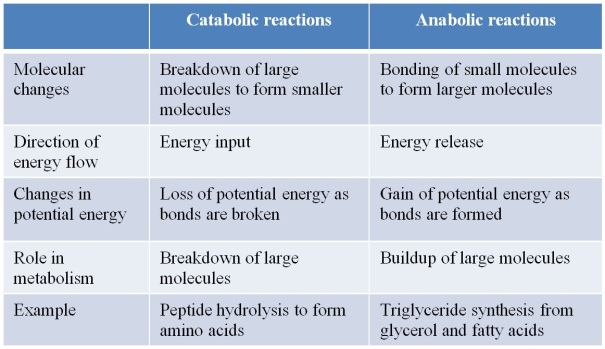 A student constructed the table to summarize characteristics that distinguish anabolic reactions from catabolic reactions.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?
A student constructed the table to summarize characteristics that distinguish anabolic reactions from catabolic reactions.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?
A) The table is correct as shown.
B) The entries concerning molecular changes and role in metabolism are incorrect and should be reversed.
C) The entries concerning direction of energy flow are incorrect and should be reversed.
D) The entries concerning changes in potential energy are incorrect and should be reversed.
E) The examples used are incorrect and should be reversed.
 A student constructed the table to summarize characteristics that distinguish anabolic reactions from catabolic reactions.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?
A student constructed the table to summarize characteristics that distinguish anabolic reactions from catabolic reactions.Which statement best evaluates the accuracy of the student's work?A) The table is correct as shown.
B) The entries concerning molecular changes and role in metabolism are incorrect and should be reversed.
C) The entries concerning direction of energy flow are incorrect and should be reversed.
D) The entries concerning changes in potential energy are incorrect and should be reversed.
E) The examples used are incorrect and should be reversed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the figure below showing the change in free energy resulting from a chemical reaction. 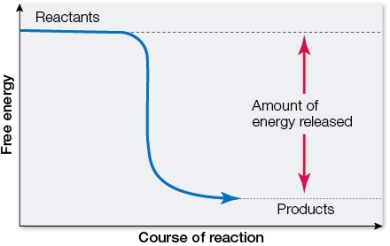 Which statement about the reaction is true?
Which statement about the reaction is true?
A) It is an endergonic reaction.
B) The reactants have less energy than the products.
C) G is negative.
D) It is an example of a condensation reaction.
E) It is an anabolic reaction.
 Which statement about the reaction is true?
Which statement about the reaction is true?A) It is an endergonic reaction.
B) The reactants have less energy than the products.
C) G is negative.
D) It is an example of a condensation reaction.
E) It is an anabolic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The G of ATP hydrolysis is negative, and the change in entropy is positive.The reaction, therefore,
A) requires energy.
B) is endergonic.
C) is exergonic.
D) will not reach equilibrium.
E) decreases the disorder in the system.
A) requires energy.
B) is endergonic.
C) is exergonic.
D) will not reach equilibrium.
E) decreases the disorder in the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When energy is converted from one form to another, only some of the energy is usable.The unusable energy is released to a form associated with disorder.A measure of this disorder is referred to as
A) free energy.
B) entropy.
C) enthalpy.
D) thermodynamics.
E) equilibrium.
A) free energy.
B) entropy.
C) enthalpy.
D) thermodynamics.
E) equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Chemical equilibrium
A) is a static state where all motion stops.
B) represents a state of negative energy change.
C) represents a state of positive energy change.
D) is essential for normal cell functions.
E) is a state in which G = 0.
A) is a static state where all motion stops.
B) represents a state of negative energy change.
C) represents a state of positive energy change.
D) is essential for normal cell functions.
E) is a state in which G = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How does the second law of thermodynamics apply to living organisms?
A) It does not apply to living organisms; the complexity of organisms contradicts the second law.
B) As energy transformations occur, free energy increases and unusable energy decreases.
C) The potential energy of ATP is converted to kinetic energy, as with muscle contractions.
D) Living organisms require a constant input of energy to maintain complex structures and order.
E) All of the reactions in an organism require an input of energy.
A) It does not apply to living organisms; the complexity of organisms contradicts the second law.
B) As energy transformations occur, free energy increases and unusable energy decreases.
C) The potential energy of ATP is converted to kinetic energy, as with muscle contractions.
D) Living organisms require a constant input of energy to maintain complex structures and order.
E) All of the reactions in an organism require an input of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A plant makes sugars via photosynthesis and is consumed by an herbivore.The herbivore in turn breaks down the sugars, producing energy it then uses to build a nest.Which sequence represents the energy transformation of this pathway?
A) Light chemical mechanical
B) Chemical kinetic heat
C) Heat chemical potential
D) Light kinetic chemical
E) Mechanical heat potential
A) Light chemical mechanical
B) Chemical kinetic heat
C) Heat chemical potential
D) Light kinetic chemical
E) Mechanical heat potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the enzyme phosphohexoisomerase is added to a 0.3 M solution of fructose 6-phosphate and the reaction is allowed to proceed to equilibrium, the final concentrations are 0.2 M glucose 6-phosphate and 0.1 M fructose 6-phosphate.What would be the final concentration of glucose 6-phosphate if the initial concentration of fructose 6-phosphate were changed to 3 M?
A) 2 M
B) 3 M
C) 1 M
D) 0.5 M
E) 0.2 M
A) 2 M
B) 3 M
C) 1 M
D) 0.5 M
E) 0.2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In order for a coupled reaction to have a net G of ‒3.3 kcal/mol,
A) the exergonic reaction needs to release more energy than the endergonic reaction requires.
B) both reactions need to have the same G.
C) the G of the endergonic reaction needs to be more negative than the G of the exergonic reaction.
D) both reactions need to be exergonic.
E) both reactions need to be endergonic.
A) the exergonic reaction needs to release more energy than the endergonic reaction requires.
B) both reactions need to have the same G.
C) the G of the endergonic reaction needs to be more negative than the G of the exergonic reaction.
D) both reactions need to be exergonic.
E) both reactions need to be endergonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You make a solution of glucose 1-phosphate and allow it to isomerize to form glucose 6-phosphate.Eventually, you have an equilibrium mixture of the two isomers.What can you do to increase the concentration of glucose 6-phosphate in the solution?
A) Add more glucose.
B) Add more phosphate.
C) Add a higher concentration of reactant and allow it to make more product.
D) Add ATP as an energy source for the forward reaction ( G = ‒7.1 kJ/mol) to make more product.
E) Add an enzyme to lower the ΔG of the reaction so more product is made.
A) Add more glucose.
B) Add more phosphate.
C) Add a higher concentration of reactant and allow it to make more product.
D) Add ATP as an energy source for the forward reaction ( G = ‒7.1 kJ/mol) to make more product.
E) Add an enzyme to lower the ΔG of the reaction so more product is made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is a transition state in a chemical reaction?
A) The place where a substrate molecule binds to an enzyme
B) A reactant with potential energy that is higher than that of the product
C) The combination of a substrate and an enzyme
D) The state at which the bonds of reactants are unstable
E) The active site where reactants are oriented
A) The place where a substrate molecule binds to an enzyme
B) A reactant with potential energy that is higher than that of the product
C) The combination of a substrate and an enzyme
D) The state at which the bonds of reactants are unstable
E) The active site where reactants are oriented

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A readily reversible reaction, in which reactants and products have almost equal free energies, is indicated by a
A) slightly negative G.
B) change in free energy.
C) negative G.
D) G near zero.
E) large positive G.
A) slightly negative G.
B) change in free energy.
C) negative G.
D) G near zero.
E) large positive G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate is a reaction with a G of +4.0 kcal/mol.What is required for this reaction to take place?
A) The input of energy from hydrolysis of ATP
B) An increase in glucose concentration to push the reaction toward the product
C) The coupling of this reaction with an endergonic reaction
D) The addition of a noncompetitive inhibitor
E) Nothing is required; this is a spontaneous reaction.
A) The input of energy from hydrolysis of ATP
B) An increase in glucose concentration to push the reaction toward the product
C) The coupling of this reaction with an endergonic reaction
D) The addition of a noncompetitive inhibitor
E) Nothing is required; this is a spontaneous reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which statement about ATP is true?
A) The hydrolysis of ATP is endergonic.
B) ATP consists of adenine bonded to deoxyribose.
C) ATP releases a large amount of light energy when hydrolyzed.
D) An active cell requires about 100 molecules of ATP per second.
E) On average, ATP is consumed within 1 second of its formation.
A) The hydrolysis of ATP is endergonic.
B) ATP consists of adenine bonded to deoxyribose.
C) ATP releases a large amount of light energy when hydrolyzed.
D) An active cell requires about 100 molecules of ATP per second.
E) On average, ATP is consumed within 1 second of its formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Most enzymes are which type of macromolecule?
A) Protein
B) Carbohydrate
C) Lipid
D) Nucleic acid
E) Hydrocarbon
A) Protein
B) Carbohydrate
C) Lipid
D) Nucleic acid
E) Hydrocarbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Knowing the change in free energy ( G) of a reaction tells us
A) the equilibrium point of the reaction.
B) the rate of the reaction.
C) how quickly equilibrium will be reached.
D) the optimum temperature for the reaction.
E) the activation energy.
A) the equilibrium point of the reaction.
B) the rate of the reaction.
C) how quickly equilibrium will be reached.
D) the optimum temperature for the reaction.
E) the activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which reaction will go the furthest toward completion?
A) A reaction with a G of zero
B) A reaction with a G of +2 kcal/mol
C) A reaction with a G of +12 kcal/mol
D) A reaction with a G of ‒2 kcal/mol
E) A reaction with a G of ‒12 kcal/mol
A) A reaction with a G of zero
B) A reaction with a G of +2 kcal/mol
C) A reaction with a G of +12 kcal/mol
D) A reaction with a G of ‒2 kcal/mol
E) A reaction with a G of ‒12 kcal/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When ATP is hydrolyzed, the reaction produces all of the following except
A) AMP.
B) ADP.
C) phosphate ions.
D) pyrophosphate ions.
E) water.
A) AMP.
B) ADP.
C) phosphate ions.
D) pyrophosphate ions.
E) water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Refer to the table below. 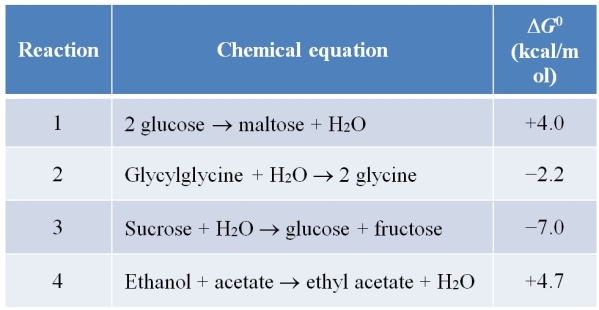 Predict which reactions are most likely to be coupled to ATP hydrolysis in a cell.
Predict which reactions are most likely to be coupled to ATP hydrolysis in a cell.
A) Reactions 1 and 4
B) Reactions 2 and 3
C) Reactions 1 and 2
D) Reactions 2, 3, and 4
E) Reactions 1, 2, and 4
 Predict which reactions are most likely to be coupled to ATP hydrolysis in a cell.
Predict which reactions are most likely to be coupled to ATP hydrolysis in a cell.A) Reactions 1 and 4
B) Reactions 2 and 3
C) Reactions 1 and 2
D) Reactions 2, 3, and 4
E) Reactions 1, 2, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
You are given a solution in which a biochemical reaction is occurring, and you are unsure whether G is positive or negative.You suspect that the reaction might make use of the ATP to ADP + Pi energy-coupling system.To test whether it uses this system, and to determine whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic, you would add _______.If the reaction _______, you would conclude that it is _______.
A) ATP; lit up; exergonic
B) ATP; made more product; endergonic
C) ADP; made more product; exergonic
D) ADP; made phosphate ions; endergonic
E) ATP; produced a decrease in temperature; exergonic
A) ATP; lit up; exergonic
B) ATP; made more product; endergonic
C) ADP; made more product; exergonic
D) ADP; made phosphate ions; endergonic
E) ATP; produced a decrease in temperature; exergonic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Fireflies
A) release a considerable amount of energy as heat.
B) light up to signal danger.
C) use ATP to drive luciferin oxidation.
D) are constantly converting light energy into chemical energy.
E) have a short life cycle because of rapid depletion of ATP.
A) release a considerable amount of energy as heat.
B) light up to signal danger.
C) use ATP to drive luciferin oxidation.
D) are constantly converting light energy into chemical energy.
E) have a short life cycle because of rapid depletion of ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When ADP gains a phosphate to form ATP,
A) free energy is released by the loss of a phosphate.
B) the reaction ends.
C) energy is absorbed.
D) chemical energy is converted to light energy.
E) ribose loses an oxygen to become deoxyribose.
A) free energy is released by the loss of a phosphate.
B) the reaction ends.
C) energy is absorbed.
D) chemical energy is converted to light energy.
E) ribose loses an oxygen to become deoxyribose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
ATP can phosphorylate many different molecules.This means that ATP can
A) receive phosphate groups.
B) donate phosphate groups.
C) convert molecules to nucleic acids.
D) release a large amount of energy when hydrolyzed.
E) waste usable energy available in its phosphate bonds.
A) receive phosphate groups.
B) donate phosphate groups.
C) convert molecules to nucleic acids.
D) release a large amount of energy when hydrolyzed.
E) waste usable energy available in its phosphate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the order in which the following molecules would be produced if phosphate ions were removed from ATP one at a time?
A) ATP, ADP, AMP, adenosine
B) AMP, ADP, ATP, adenosine
C) Adenosine, ATP, AMP, ADP
D) ATP, AMP, ADP, adenosine
E) ADP, adenosine, AMP, ATP
A) ATP, ADP, AMP, adenosine
B) AMP, ADP, ATP, adenosine
C) Adenosine, ATP, AMP, ADP
D) ATP, AMP, ADP, adenosine
E) ADP, adenosine, AMP, ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate has a G of +4.0 kcal/mol.If hexokinase is added to speed up the rate of this reaction, the G will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) increase, but only with an increase in enzyme amount.
E) decrease, but only with a decrease in enzyme amount.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) increase, but only with an increase in enzyme amount.
E) decrease, but only with a decrease in enzyme amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The reaction below takes place in cells and is catalyzed by the enzyme phosphoglucoisomerase. 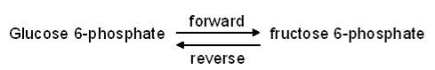 At equilibrium, the ratio of fructose 6-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate is 0.30:1.What will happen if the concentration of glucose 6-phosphate reaches 0.5 nM and the concentration of fructose 6-phosphate reaches 0.8 nM at a particular instant in the cell?
At equilibrium, the ratio of fructose 6-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate is 0.30:1.What will happen if the concentration of glucose 6-phosphate reaches 0.5 nM and the concentration of fructose 6-phosphate reaches 0.8 nM at a particular instant in the cell?
A) Only the forward reaction will occur.
B) Only the reverse reaction will occur.
C) The rate of the forward reaction will be greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
D) The rate of the reverse reaction will be greater than the rate of the forward reaction.
E) The rate of the forward reaction will be the same as the rate of the reverse reaction.
 At equilibrium, the ratio of fructose 6-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate is 0.30:1.What will happen if the concentration of glucose 6-phosphate reaches 0.5 nM and the concentration of fructose 6-phosphate reaches 0.8 nM at a particular instant in the cell?
At equilibrium, the ratio of fructose 6-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate is 0.30:1.What will happen if the concentration of glucose 6-phosphate reaches 0.5 nM and the concentration of fructose 6-phosphate reaches 0.8 nM at a particular instant in the cell?A) Only the forward reaction will occur.
B) Only the reverse reaction will occur.
C) The rate of the forward reaction will be greater than the rate of the reverse reaction.
D) The rate of the reverse reaction will be greater than the rate of the forward reaction.
E) The rate of the forward reaction will be the same as the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a chemical reaction, transition-state intermediates have free energies that are
A) lower than those of either the reactants or the products.
B) lower than those of the reactants, but higher than those of the products.
C) higher than those of either the reactants or the products.
D) higher than those of the reactants, but lower than those of the products.
E) lower than those of the reactants, but the same as those of the products.
A) lower than those of either the reactants or the products.
B) lower than those of the reactants, but higher than those of the products.
C) higher than those of either the reactants or the products.
D) higher than those of the reactants, but lower than those of the products.
E) lower than those of the reactants, but the same as those of the products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In glycolysis, the exergonic reaction 1,3-diphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate is coupled to the reaction ADP + Pi ATP.Based on this information, which statement is most likely to be true about the reaction
ADP + Pi ATP?
A) The reaction never reaches equilibrium.
B) The reaction is spontaneous.
C) There is a large decrease in free energy.
D) The reaction is endergonic.
E) Temperature will not affect the rate constant of the reaction.
ADP + Pi ATP?
A) The reaction never reaches equilibrium.
B) The reaction is spontaneous.
C) There is a large decrease in free energy.
D) The reaction is endergonic.
E) Temperature will not affect the rate constant of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the table below. 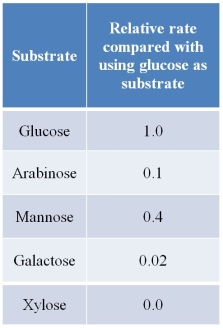 Hexokinase catalyzes the reaction between glucose and ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate and ADP.The table summarizes results of experiments using purified hexokinase.In the experiments, different sugars were substituted for glucose, and the rate of each catalytic reaction was measured and divided by the rate of reaction using glucose as substrate.These data provide evidence for which general statement that has been made about enzymes?
Hexokinase catalyzes the reaction between glucose and ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate and ADP.The table summarizes results of experiments using purified hexokinase.In the experiments, different sugars were substituted for glucose, and the rate of each catalytic reaction was measured and divided by the rate of reaction using glucose as substrate.These data provide evidence for which general statement that has been made about enzymes?
A) Enzymes are able to speed up a reaction by lowering its activation energy.
B) Enzymes display high specificity with respect to their substrates.
C) Enzymes often require cofactors and/or coenzymes in addition to their substrates.
D) Enzymes bind substrates at their active sites using noncovalent forces of attraction.
E) Enzymes lower activation energy of a reaction by stabilizing the substrate's transition state.
 Hexokinase catalyzes the reaction between glucose and ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate and ADP.The table summarizes results of experiments using purified hexokinase.In the experiments, different sugars were substituted for glucose, and the rate of each catalytic reaction was measured and divided by the rate of reaction using glucose as substrate.These data provide evidence for which general statement that has been made about enzymes?
Hexokinase catalyzes the reaction between glucose and ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate and ADP.The table summarizes results of experiments using purified hexokinase.In the experiments, different sugars were substituted for glucose, and the rate of each catalytic reaction was measured and divided by the rate of reaction using glucose as substrate.These data provide evidence for which general statement that has been made about enzymes?A) Enzymes are able to speed up a reaction by lowering its activation energy.
B) Enzymes display high specificity with respect to their substrates.
C) Enzymes often require cofactors and/or coenzymes in addition to their substrates.
D) Enzymes bind substrates at their active sites using noncovalent forces of attraction.
E) Enzymes lower activation energy of a reaction by stabilizing the substrate's transition state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The molecules that are acted on by an enzyme are called
A) products.
B) substrates.
C) carriers.
D) prosthetics.
E) effectors.
A) products.
B) substrates.
C) carriers.
D) prosthetics.
E) effectors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement about enzymes is false?
A) Enzymes do not affect the equilibrium point of a reaction.
B) Enzymes lower activation energy.
C) Enzymes are highly specific.
D) Enzymes can convert an endergonic to an exergonic reaction.
E) Enzymes undergo no net chemical change during catalysis.
A) Enzymes do not affect the equilibrium point of a reaction.
B) Enzymes lower activation energy.
C) Enzymes are highly specific.
D) Enzymes can convert an endergonic to an exergonic reaction.
E) Enzymes undergo no net chemical change during catalysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In some cases, a substrate-enzyme complex is stabilized by
A) peptide bonds.
B) disulfide bonds.
C) ester bonds.
D) hydrogen bonds.
E) phosphate bonds.
A) peptide bonds.
B) disulfide bonds.
C) ester bonds.
D) hydrogen bonds.
E) phosphate bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The statement "enzymes are highly specific" means that specific
A) enzymes are found in specific cells.
B) reactions involving specific substrates are catalyzed by specific enzymes.
C) enzymes require specific concentrations of substrates.
D) reactions with specific activation energies are catalyzed by specific enzymes.
E) concentrations of substrates work with specific enzymes.
A) enzymes are found in specific cells.
B) reactions involving specific substrates are catalyzed by specific enzymes.
C) enzymes require specific concentrations of substrates.
D) reactions with specific activation energies are catalyzed by specific enzymes.
E) concentrations of substrates work with specific enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An RNA molecule that has enzyme activity is called
A) RNAse.
B) ribonuclease.
C) an allosteric enzyme.
D) a regulatory enzyme.
E) a ribozyme.
A) RNAse.
B) ribonuclease.
C) an allosteric enzyme.
D) a regulatory enzyme.
E) a ribozyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following affects the rate of a reaction?
A) S
B) G
C) H
D) The activation energy
E) The overall change in free energy
A) S
B) G
C) H
D) The activation energy
E) The overall change in free energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Enzymes of the acid-base catalysis type contain
A) a metal ion bound to a side chain.
B) a prosthetic group.
C) a coenzyme.
D) acidic or basic amino acid side chains (R groups) in the active site.
E) a covalently activated active site.
A) a metal ion bound to a side chain.
B) a prosthetic group.
C) a coenzyme.
D) acidic or basic amino acid side chains (R groups) in the active site.
E) a covalently activated active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The five reactions listed are catalyzed by enzymes in a cell.Which reaction is catalyzed by an oxidoreductase?
A) Glucose + ATP glucose 6-phosphate + ADP
B) Sucrose + H2O glucose + fructose
C) Ethanol + NAD+ acetaldehyde + NADH
D) ATP cAMP + Pi
E) Maltose + H2O 2 glucose
A) Glucose + ATP glucose 6-phosphate + ADP
B) Sucrose + H2O glucose + fructose
C) Ethanol + NAD+ acetaldehyde + NADH
D) ATP cAMP + Pi
E) Maltose + H2O 2 glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An active site is the
A) part of the substrate that binds with an enzyme.
B) site where enzymes are found in cells.
C) site where energy is added to an enzyme catalyst.
D) part of the enzyme that binds with a substrate.
E) part of the enzyme that binds with an allosteric activator or inhibitor.
A) part of the substrate that binds with an enzyme.
B) site where enzymes are found in cells.
C) site where energy is added to an enzyme catalyst.
D) part of the enzyme that binds with a substrate.
E) part of the enzyme that binds with an allosteric activator or inhibitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The hydrolysis of sucrose to glucose and fructose is exergonic.However, if sucrose is dissolved in water and the solution is kept overnight at room temperature, there is no detectable conversion to glucose and fructose.Why?
A) The change in free energy of the reaction is positive.
B) The activation energy of the reaction is high.
C) The change in free energy of the reaction is negative.
D) This is a hydrolysis reaction, so it requires an input of energy.
E) The free energy of the products is higher than the free energy of the reactants.
A) The change in free energy of the reaction is positive.
B) The activation energy of the reaction is high.
C) The change in free energy of the reaction is negative.
D) This is a hydrolysis reaction, so it requires an input of energy.
E) The free energy of the products is higher than the free energy of the reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which will not increase the rate of conversion of reactant A to product B in the presence of enzyme C?
A) An increase in enzyme concentration
B) An increase in temperature to the optimum for the reaction
C) An increase in substrate concentration
D) The addition of a nonbiological molecule that can catalyze the same reaction
E) The addition of D that can compete with A for binding at the active site of C
A) An increase in enzyme concentration
B) An increase in temperature to the optimum for the reaction
C) An increase in substrate concentration
D) The addition of a nonbiological molecule that can catalyze the same reaction
E) The addition of D that can compete with A for binding at the active site of C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Trypsin and elastase are both enzymes that catalyze hydrolysis of peptide bonds.However, trypsin only hydrolyzes peptide bonds next to lysine, and elastase only hydrolyzes peptide bonds next to alanine.Why?
A) Trypsin is a protein, and elastase is not.
B) The Gs for the two reactions are different.
C) The shapes of the active sites for the two enzymes are different.
D) One of the reactions is endergonic and the other is exergonic.
E) Hydrolysis of lysine bonds requires water; hydrolysis of alanine bonds does not.
A) Trypsin is a protein, and elastase is not.
B) The Gs for the two reactions are different.
C) The shapes of the active sites for the two enzymes are different.
D) One of the reactions is endergonic and the other is exergonic.
E) Hydrolysis of lysine bonds requires water; hydrolysis of alanine bonds does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The presence of a catalyst affects the
A) position of equilibrium of the reaction.
B) overall energy change, or G.
C) energy of the reactants.
D) energy of the products.
E) free energy of the transition state.
A) position of equilibrium of the reaction.
B) overall energy change, or G.
C) energy of the reactants.
D) energy of the products.
E) free energy of the transition state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The enzyme -amylase increases the rate at which starch is broken down into smaller oligosaccharides by _______ of the reaction.
A) decreasing the equilibrium constant
B) increasing the change in free energy
C) decreasing the change in free energy
D) increasing the change in entropy
E) lowering the activation energy
A) decreasing the equilibrium constant
B) increasing the change in free energy
C) decreasing the change in free energy
D) increasing the change in entropy
E) lowering the activation energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Mechanisms used by enzymes to catalyze reactions are similar in that they all
A) involve transient chemical change in the enzyme.
B) involve permanent chemical change in the enzyme.
C) lead to stabilization of the transition state of the substrate.
D) require the involvement of cofactors or coenzymes.
E) work individually in any one enzyme and not in conjunction with one another.
A) involve transient chemical change in the enzyme.
B) involve permanent chemical change in the enzyme.
C) lead to stabilization of the transition state of the substrate.
D) require the involvement of cofactors or coenzymes.
E) work individually in any one enzyme and not in conjunction with one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 1,3-diphosphoglycerate.The binding of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to the enzyme creates a(n)
A) transition state.
B) activation groove.
C) catalyst.
D) enzyme-substrate complex.
E) energy barrier.
A) transition state.
B) activation groove.
C) catalyst.
D) enzyme-substrate complex.
E) energy barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the figure below. 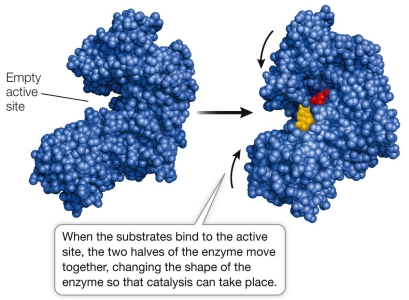 Which type of mechanism used by an enzyme to catalyze a reaction is illustrated in the figure?
Which type of mechanism used by an enzyme to catalyze a reaction is illustrated in the figure?
A) Covalent catalysis
B) Acid-base catalysis
C) Metal ion catalysis
D) Induced fit
E) Induced strain
 Which type of mechanism used by an enzyme to catalyze a reaction is illustrated in the figure?
Which type of mechanism used by an enzyme to catalyze a reaction is illustrated in the figure?A) Covalent catalysis
B) Acid-base catalysis
C) Metal ion catalysis
D) Induced fit
E) Induced strain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The enzyme glucose oxidase binds the six-carbon sugar glucose and catalyzes its conversion to glucono-1,5-lactone.Mannose is also a six-carbon sugar, but glucose oxidase cannot bind mannose.The specificity of glucose oxidase is based on the
A) free energy of the transition state.
B) activation energy of the reaction.
C) change in free energy of the reaction.
D) three-dimensional shape and structure of the active site.
E) rate constant of the reaction.
A) free energy of the transition state.
B) activation energy of the reaction.
C) change in free energy of the reaction.
D) three-dimensional shape and structure of the active site.
E) rate constant of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The enzyme sucrase increases the rate at which sucrose is broken down into glucose and fructose.Sucrase works by
A) increasing the amount of free energy of the reaction.
B) lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
C) decreasing the equilibrium constant of the reaction.
D) supplying energy to speed up the reaction.
E) changing the shape of the active site.
A) increasing the amount of free energy of the reaction.
B) lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
C) decreasing the equilibrium constant of the reaction.
D) supplying energy to speed up the reaction.
E) changing the shape of the active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the reaction between ATP and glucose to form glucose 6-phosphate and ADP.In order to determine the efficiency of hexokinase, you wish to conduct an experiment to calculate its turnover number.To do so, you would set up
A) a reaction with a maximum amount of hexokinase at optimal pH and temperature.
B) a reaction with a known amount of enzyme and saturating levels of glucose 6-phosphate at optimal pH and temperature.
C) a reaction with a known amount of enzyme and saturating levels of glucose and ATP at optimal pH and temperature.
D) multiple reactions at varying pH levels but with a constant amount of glucose, a constant temperature, and a known amount of enzyme.
E) multiple reactions with varying temperatures but a constant amount of glucose, constant pH levels, and a known amount of enzyme.
A) a reaction with a maximum amount of hexokinase at optimal pH and temperature.
B) a reaction with a known amount of enzyme and saturating levels of glucose 6-phosphate at optimal pH and temperature.
C) a reaction with a known amount of enzyme and saturating levels of glucose and ATP at optimal pH and temperature.
D) multiple reactions at varying pH levels but with a constant amount of glucose, a constant temperature, and a known amount of enzyme.
E) multiple reactions with varying temperatures but a constant amount of glucose, constant pH levels, and a known amount of enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the expression below.  The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes this reaction in cells.The enzyme uses the coenzyme NAD+ in the reaction.Not shown are details about the active site, which contains a zinc ion that functions as a cofactor.How do the roles of cofactor and coenzyme compare in this particular case?
The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes this reaction in cells.The enzyme uses the coenzyme NAD+ in the reaction.Not shown are details about the active site, which contains a zinc ion that functions as a cofactor.How do the roles of cofactor and coenzyme compare in this particular case?
A) Both function in the catalytic mechanism and do not undergo net chemical change themselves as a result of the reaction.
B) Both function as substrates and undergo net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
C) The coenzyme functions in the catalytic mechanism, changing only transiently, whereas the cofactor functions as a substrate and undergoes net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
D) The cofactor functions in the catalytic mechanism, changing only transiently, whereas the coenzyme functions as a substrate and undergoes net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
E) The cofactor functions as a substrate, changing only transiently, whereas the coenzyme functions in the catalytic mechanism and undergoes net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
 The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes this reaction in cells.The enzyme uses the coenzyme NAD+ in the reaction.Not shown are details about the active site, which contains a zinc ion that functions as a cofactor.How do the roles of cofactor and coenzyme compare in this particular case?
The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes this reaction in cells.The enzyme uses the coenzyme NAD+ in the reaction.Not shown are details about the active site, which contains a zinc ion that functions as a cofactor.How do the roles of cofactor and coenzyme compare in this particular case?A) Both function in the catalytic mechanism and do not undergo net chemical change themselves as a result of the reaction.
B) Both function as substrates and undergo net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
C) The coenzyme functions in the catalytic mechanism, changing only transiently, whereas the cofactor functions as a substrate and undergoes net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
D) The cofactor functions in the catalytic mechanism, changing only transiently, whereas the coenzyme functions as a substrate and undergoes net chemical change as a result of the reaction.
E) The cofactor functions as a substrate, changing only transiently, whereas the coenzyme functions in the catalytic mechanism and undergoes net chemical change as a result of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the presence of alcohol dehydrogenase, the rate of reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol increases as the concentration of acetaldehyde increases.Eventually, the rate of the reaction reaches a maximum, at which point further increases in the concentration of acetaldehyde have no effect.Why?
A) All the alcohol dehydrogenase molecules are bound to acetaldehyde molecules.
B) At high concentrations of acetaldehyde, the activation energy of the reaction increases.
C) At high concentrations of acetaldehyde, the activation energy of the reaction decreases.
D) The enzyme is no longer specific for acetaldehyde.
E) At high concentrations of acetaldehyde, the change in free energy of the reaction decreases.
A) All the alcohol dehydrogenase molecules are bound to acetaldehyde molecules.
B) At high concentrations of acetaldehyde, the activation energy of the reaction increases.
C) At high concentrations of acetaldehyde, the activation energy of the reaction decreases.
D) The enzyme is no longer specific for acetaldehyde.
E) At high concentrations of acetaldehyde, the change in free energy of the reaction decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Enzymatic reactions can become saturated as substrate concentration increases because
A) enzymes have the highest possible number of hydrogen atoms attached to them.
B) the concentration of substrate reaches a point at which it cannot increase any further.
C) substrates are inhibitors of enzymes at high concentrations.
D) the activation energy of the reaction reaches a point at which it cannot be lowered further.
E) a limited number of enzyme molecules are present.
A) enzymes have the highest possible number of hydrogen atoms attached to them.
B) the concentration of substrate reaches a point at which it cannot increase any further.
C) substrates are inhibitors of enzymes at high concentrations.
D) the activation energy of the reaction reaches a point at which it cannot be lowered further.
E) a limited number of enzyme molecules are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Many enzymes require small nonprotein molecules for a reaction to occur.These molecules temporarily bind to and then are released from the substrate before participating in other reactions.These types of molecules are called
A) side chains.
B) coenzymes.
C) substrates.
D) prosthetic groups.
E) cofactors.
A) side chains.
B) coenzymes.
C) substrates.
D) prosthetic groups.
E) cofactors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In order to determine whether a reaction is at "saturation," you can add _______ and determine whether the reaction rate _______.
A) ATP; increases
B) more substrate; increases
C) a competitive inhibitor; decreases
D) a downstream product; decreases
E) a noncompetitive inhibitor; decreases
A) ATP; increases
B) more substrate; increases
C) a competitive inhibitor; decreases
D) a downstream product; decreases
E) a noncompetitive inhibitor; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which graph shows changes in the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as substrate concentration is varied?
A)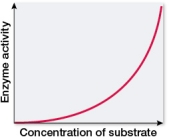
B)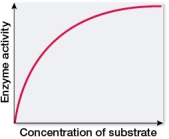
C)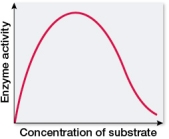
D)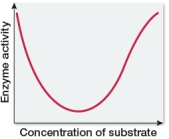
E)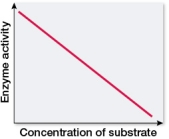
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
You observe an enzymatic reaction that exhibits a standard relationship between reaction rate and substrate concentration as it converts substrate B to product C.When you add compound A, the creation of product C comes to a complete stop.You add large quantities of substrate B but still are unable to create product C in the presence of compound A.Compound A is therefore most likely a
A) noncompetitive inhibitor.
B) competitive inhibitor.
C) coenzyme.
D) cofactor.
E) transcription factor.
A) noncompetitive inhibitor.
B) competitive inhibitor.
C) coenzyme.
D) cofactor.
E) transcription factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Refer to the figure below. 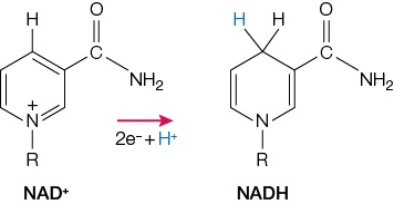 NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions.The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure.It is likely that, in these reactions, NAD+
NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions.The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure.It is likely that, in these reactions, NAD+
A) functions as an electron donor in an oxidation-reduction reaction.
B) functions as an electron acceptor in an oxidation-reduction reaction.
C) forms a covalent intermediate during covalent catalysis.
D) induces strain in other substrates bound at active sites.
E) functions as a base in acid-base catalytic mechanisms.
 NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions.The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure.It is likely that, in these reactions, NAD+
NAD+ functions as a coenzyme in many enzyme-catalyzed reactions.The changes that take place in this coenzyme are the same for all of these reactions and are illustrated in the figure.It is likely that, in these reactions, NAD+A) functions as an electron donor in an oxidation-reduction reaction.
B) functions as an electron acceptor in an oxidation-reduction reaction.
C) forms a covalent intermediate during covalent catalysis.
D) induces strain in other substrates bound at active sites.
E) functions as a base in acid-base catalytic mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Competitive inhibitors of enzymes work by
A) fitting into the active site.
B) fitting into a site other than the active site.
C) altering the shape of the enzyme.
D) changing the enzyme into an inactive form.
E) increasing the activation energy of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
A) fitting into the active site.
B) fitting into a site other than the active site.
C) altering the shape of the enzyme.
D) changing the enzyme into an inactive form.
E) increasing the activation energy of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A noncompetitive inhibitor hinders binding of a substrate to an enzyme by
A) binding to the substrate.
B) binding to the active site.
C) lowering the activation energy.
D) increasing the G of the reaction.
E) changing the shape of the active site.
A) binding to the substrate.
B) binding to the active site.
C) lowering the activation energy.
D) increasing the G of the reaction.
E) changing the shape of the active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The addition of the competitive inhibitor mevinolin slows the reaction
HMG-CoA mevalonate, which is catalyzed by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase.In order to overcome the effects of mevinolin and increase the rate of the reaction, you would
A) add more mevalonate.
B) add more HMG-CoA.
C) lower the temperature of the reaction.
D) add a prosthetic group.
E) lower the rate constant of the reaction.
HMG-CoA mevalonate, which is catalyzed by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase.In order to overcome the effects of mevinolin and increase the rate of the reaction, you would
A) add more mevalonate.
B) add more HMG-CoA.
C) lower the temperature of the reaction.
D) add a prosthetic group.
E) lower the rate constant of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How do competitive and noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors differ from each other?
A) Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site, whereas noncompetitive inhibitors change the shape of the active site.
B) Competitive inhibitors have a higher energy of activation than noncompetitive inhibitors have.
C) Noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors contain magnesium, whereas competitive inhibitors contain iron.
D) Noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors are reversible, whereas competitive inhibitors are irreversible.
E) They function at different pH values.
A) Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site, whereas noncompetitive inhibitors change the shape of the active site.
B) Competitive inhibitors have a higher energy of activation than noncompetitive inhibitors have.
C) Noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors contain magnesium, whereas competitive inhibitors contain iron.
D) Noncompetitive enzyme inhibitors are reversible, whereas competitive inhibitors are irreversible.
E) They function at different pH values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The inhibition of enzyme activity by noncompetitive inhibitors can be reduced
A) by decreasing the concentration of allosteric enzymes.
B) by decreasing the concentration of substrate.
C) by increasing the concentration of competitive inhibitor.
D) by increasing the concentration of substrate.
E) only when they become unbound.
A) by decreasing the concentration of allosteric enzymes.
B) by decreasing the concentration of substrate.
C) by increasing the concentration of competitive inhibitor.
D) by increasing the concentration of substrate.
E) only when they become unbound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If you wanted to permanently block the function of an enzyme, you could add
A) a molecule that can covalently bind to the active site.
B) more product.
C) a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) an allosteric inhibitor.
E) a competitive inhibitor.
A) a molecule that can covalently bind to the active site.
B) more product.
C) a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) an allosteric inhibitor.
E) a competitive inhibitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which type of inhibitor can be overcome completely by the addition of more substrate?
A) Irreversible
B) Noncompetitive
C) Competitive
D) Prosthetic
E)
A) Irreversible
B) Noncompetitive
C) Competitive
D) Prosthetic
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
You are working with an enzyme and wish to determine its saturation point.You note that the reaction rate increases slowly at first, then increases dramatically over a narrow range of substrate concentrations, and then levels off, creating a sigmoid reaction curve.It is likely that this enzyme is regulated by
A) temperature.
B) pH.
C) an allosteric mechanism.
D) a competitive inhibitor.
E) a coenzyme.
A) temperature.
B) pH.
C) an allosteric mechanism.
D) a competitive inhibitor.
E) a coenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which action would reverse the effects of a competitive inhibitor on an enzyme but not the effects of a noncompetitive or an irreversible inhibitor?
A) Dilute the solution by adding more solvent.
B) Add an allosteric activator.
C) Heat the solution.
D) Add substrate.
E) Remove substrate.
A) Dilute the solution by adding more solvent.
B) Add an allosteric activator.
C) Heat the solution.
D) Add substrate.
E) Remove substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An allosteric inhibitor
A) decreases the concentration of an inactive enzyme.
B) changes the shape of an enzyme.
C) increases the concentration of a product.
D) changes the shape of a substrate.
E) increases the concentration of an enzyme-substrate complex.
A) decreases the concentration of an inactive enzyme.
B) changes the shape of an enzyme.
C) increases the concentration of a product.
D) changes the shape of a substrate.
E) increases the concentration of an enzyme-substrate complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which statement about allosteric regulators is true?
A) The plot of reaction rate versus substrate concentration for allosteric regulators often displays a sigmoid curve.
B) All enzymes can be allosterically regulated.
C) Allosteric regulators affect substrate binding but do not affect enzyme structure.
D) Binding of allosteric regulators is nonspecific.
E) Allosteric regulators bind to the active site, blocking enzyme function.
A) The plot of reaction rate versus substrate concentration for allosteric regulators often displays a sigmoid curve.
B) All enzymes can be allosterically regulated.
C) Allosteric regulators affect substrate binding but do not affect enzyme structure.
D) Binding of allosteric regulators is nonspecific.
E) Allosteric regulators bind to the active site, blocking enzyme function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



