Deck 10: Photosynthesis: Energy From Sunlight
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/242
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Photosynthesis: Energy From Sunlight
1
Which of the following occurs during the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
A) Water is converted into hydrogen and oxygen.
B) CO2 is converted into sugars.
C) Chlorophyll acts as an enzyme.
D) Nothing occurs; the plant rests in the dark.
E) CO2 is split into carbon and oxygen.
A) Water is converted into hydrogen and oxygen.
B) CO2 is converted into sugars.
C) Chlorophyll acts as an enzyme.
D) Nothing occurs; the plant rests in the dark.
E) CO2 is split into carbon and oxygen.
B
2
Which statement about photosynthesis is false?
A) Land plants take up water from the soil and use it in photosynthesis.
B) CO2 is taken in and water and O2 are released through stomata.
C) Light is necessary for the production of O2 and carbohydrates.
D) Photosynthesis is the reverse of cellular respiration.
E) All the O2 gas produced during photosynthesis comes from water.
A) Land plants take up water from the soil and use it in photosynthesis.
B) CO2 is taken in and water and O2 are released through stomata.
C) Light is necessary for the production of O2 and carbohydrates.
D) Photosynthesis is the reverse of cellular respiration.
E) All the O2 gas produced during photosynthesis comes from water.
D
3
In both oxygenic photosynthesis and anoxygenic photosynthesis,
A) CO2 is the source of carbon for the synthesis of carbohydrates.
B) O2 is a product.
C) H2S is converted to sulfur and water.
D) H2O is the electron donor for photophosphorylation.
E) O2 is derived from H2O.
A) CO2 is the source of carbon for the synthesis of carbohydrates.
B) O2 is a product.
C) H2S is converted to sulfur and water.
D) H2O is the electron donor for photophosphorylation.
E) O2 is derived from H2O.
A
4
Refer to the table below. 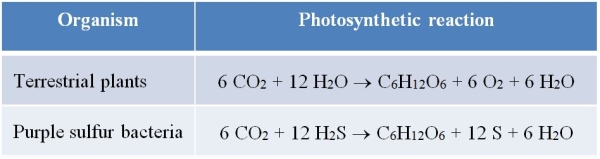 How do these two photosynthetic processes compare?
How do these two photosynthetic processes compare?
A) The electron acceptor in both plants and purple sulfur bacteria is H2O.
B) The electron donor in both plants and purple sulfur bacteria is CO2.
C) The electron acceptor in plants is H2O, and the electron acceptor in purple sulfur bacteria is H2S.
D) The electron donor in plants is H2O, and the electron donor in purple sulfur bacteria is H2S.
E) The electron donor in plants is H2O, and the electron donor in purple sulfur bacteria is CO2.
 How do these two photosynthetic processes compare?
How do these two photosynthetic processes compare?A) The electron acceptor in both plants and purple sulfur bacteria is H2O.
B) The electron donor in both plants and purple sulfur bacteria is CO2.
C) The electron acceptor in plants is H2O, and the electron acceptor in purple sulfur bacteria is H2S.
D) The electron donor in plants is H2O, and the electron donor in purple sulfur bacteria is H2S.
E) The electron donor in plants is H2O, and the electron donor in purple sulfur bacteria is CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The main photosynthetic pigments in plants are _______ and _______.
A) chlorophyll s; chlorophyll a
B) chlorophyll x; chlorophyll y
C) retinal pigment; accessory pigment
D) chlorophyll a; chlorophyll b
E) carotenoids; phycobilins
A) chlorophyll s; chlorophyll a
B) chlorophyll x; chlorophyll y
C) retinal pigment; accessory pigment
D) chlorophyll a; chlorophyll b
E) carotenoids; phycobilins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Examine the following formula: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2.Which statement is true regarding this equation as a representation of the process of oxygenic photosynthesis?
A) It is not balanced.
B) It incorrectly indicates that CO2 is a source of oxygen gas.
C) It does not show that H2O is both a reactant and a product of oxygenic photosynthesis.
D) It does not represent the overall net change that results from oxygenic photosynthesis.
E) It gives a summary of all of the chemical steps involved in oxygenic photosynthesis.
A) It is not balanced.
B) It incorrectly indicates that CO2 is a source of oxygen gas.
C) It does not show that H2O is both a reactant and a product of oxygenic photosynthesis.
D) It does not represent the overall net change that results from oxygenic photosynthesis.
E) It gives a summary of all of the chemical steps involved in oxygenic photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A molecule that has an absorption spectrum showing maximum absorption within the wavelengths of visible light is
A) a pigment.
B) a quantum.
C) a photon.
D) electromagnetic radiation.
E) a reducing agent.
A) a pigment.
B) a quantum.
C) a photon.
D) electromagnetic radiation.
E) a reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How do red and blue light differ from each other?
A) Blue is absorbed by chlorophyll, whereas red is not.
B) They have a different number of photons in each quantum.
C) Their wavelengths are different.
D) They differ in terms of their duration.
E) Red is radiant, whereas blue is electromagnetic.
A) Blue is absorbed by chlorophyll, whereas red is not.
B) They have a different number of photons in each quantum.
C) Their wavelengths are different.
D) They differ in terms of their duration.
E) Red is radiant, whereas blue is electromagnetic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Refer to the table below showing data collected from chloroplasts isolated from spinach leaves.The chloroplasts were incubated with either compound Q or Z, or with no additions in the control.After 30 minutes of incubation, chloroplasts were analyzed for the photosynthetic functions shown in the table. 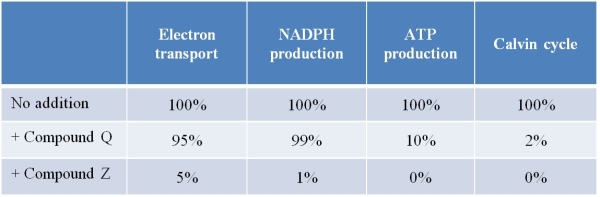 Assume that compounds Q and Z directly affect components involved in the light reactions.What do these data indicate about the relationship between the light reactions and the light-independent reactions?
Assume that compounds Q and Z directly affect components involved in the light reactions.What do these data indicate about the relationship between the light reactions and the light-independent reactions?
A) The light-independent reactions can occur even if the light reactions are inhibited by chemical agents.
B) If a subset of the light reactions is functional, that is sufficient for the light-independent reactions to also be functional.
C) At least one of the products of the light reactions is essential in enabling the light-independent reactions to run.
D) Chemical agents can reverse the sequence of the light reactions and the light-independent reactions.
E) Light reactions and light-independent reactions can be induced to reverse their dependency on light by the actions of chemical agents.
 Assume that compounds Q and Z directly affect components involved in the light reactions.What do these data indicate about the relationship between the light reactions and the light-independent reactions?
Assume that compounds Q and Z directly affect components involved in the light reactions.What do these data indicate about the relationship between the light reactions and the light-independent reactions?A) The light-independent reactions can occur even if the light reactions are inhibited by chemical agents.
B) If a subset of the light reactions is functional, that is sufficient for the light-independent reactions to also be functional.
C) At least one of the products of the light reactions is essential in enabling the light-independent reactions to run.
D) Chemical agents can reverse the sequence of the light reactions and the light-independent reactions.
E) Light reactions and light-independent reactions can be induced to reverse their dependency on light by the actions of chemical agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which graph illustrates how energy is involved in photosynthesis?
A)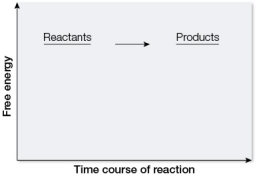
B)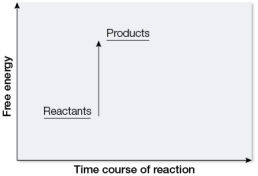
C)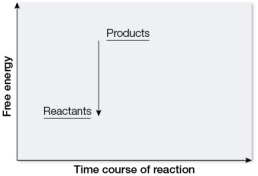
D)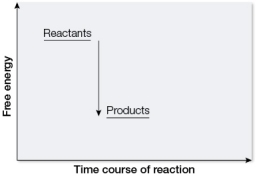
E)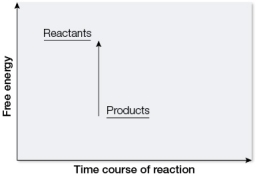
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refer to the diagram below showing the 1941 experiments of Samuel Ruben and Martin Kamen that traced isotopes of oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. 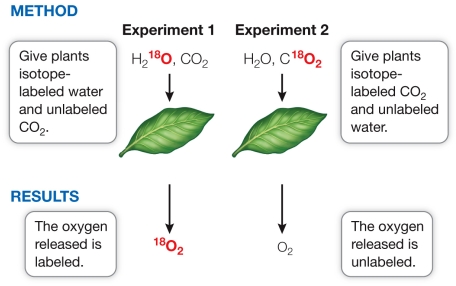 The Ruben and Kamen experiments demonstrated that
The Ruben and Kamen experiments demonstrated that
A) all the oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis comes from water.
B) CO2 is the source of the oxygen released during photosynthesis.
C) the oxygen released by water is incorporated into sugars.
D) oxygen is needed to make rubisco.
E) NADPH is made during the Calvin cycle.
 The Ruben and Kamen experiments demonstrated that
The Ruben and Kamen experiments demonstrated thatA) all the oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis comes from water.
B) CO2 is the source of the oxygen released during photosynthesis.
C) the oxygen released by water is incorporated into sugars.
D) oxygen is needed to make rubisco.
E) NADPH is made during the Calvin cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the first phase of photosynthesis, a series of reactions converts light energy into ATP and NADPH.These reactions are referred to as
A) reduction.
B) dark reactions.
C) carbon fixation.
D) light reactions.
E) ATP/NADPH synthesis.
A) reduction.
B) dark reactions.
C) carbon fixation.
D) light reactions.
E) ATP/NADPH synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which is the complete balanced equation for the generation of hexose from sunlight, water, and oxygen?
A) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + O2
B) 6 CO2 + 12 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
C) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2
D) 12 CO2 + 12 H2O 2 C6H12O6 + 2 O2
E) 6 CO2 + 12 H2O C6H12O6 + 12 O2
A) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + O2
B) 6 CO2 + 12 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
C) 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2
D) 12 CO2 + 12 H2O 2 C6H12O6 + 2 O2
E) 6 CO2 + 12 H2O C6H12O6 + 12 O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll a absorbs
A) infrared light.
B) red and blue light.
C) X rays.
D) gamma rays.
E) green light.
A) infrared light.
B) red and blue light.
C) X rays.
D) gamma rays.
E) green light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The O2 gas produced during photosynthesis is derived from
A) carbon dioxide.
B) sugar.
C) water.
D) ATP.
E) bicarbonate ions.
A) carbon dioxide.
B) sugar.
C) water.
D) ATP.
E) bicarbonate ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Plants are green because
A) chlorophylls absorb green light.
B) chloroplasts transmit all colors except green.
C) energized chlorophyll a emits green light.
D) plants do not possess green pigment.
E) chlorophylls do not absorb green light.
A) chlorophylls absorb green light.
B) chloroplasts transmit all colors except green.
C) energized chlorophyll a emits green light.
D) plants do not possess green pigment.
E) chlorophylls do not absorb green light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When white light strikes a blue pigment, blue light is
A) reduced.
B) absorbed.
C) converted to chemical energy.
D) reflected.
E) used to synthesize ATP.
A) reduced.
B) absorbed.
C) converted to chemical energy.
D) reflected.
E) used to synthesize ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Refer to the table below summarizing data from an experiment conducted using chloroplasts isolated from spinach leaves.The chloroplasts were incubated with either no compound (control) or with compound A or B for 1 hour.Chloroplasts were then tested for the three functions listed at the top of the table. 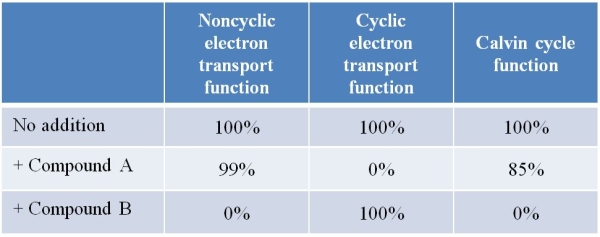 What do these data suggest about the role of NADPH in photosynthesis and why?
What do these data suggest about the role of NADPH in photosynthesis and why?
A) NADPH is required for photosynthesis because Calvin cycle function is blocked when noncyclic electron transport is inhibited.
B) NADPH is required for photosynthesis because Calvin cycle function is not blocked when cyclic electron transport is inhibited.
C) NADPH is required for photosynthesis because cyclic electron transport can function independently of noncyclic electron transport.
D) NADPH is not required for photosynthesis because cyclic electron transport can function even when noncyclic electron transport is inhibited.
E) NADPH is not required for photosynthesis because different chemical agents can inhibit cyclic and noncyclic electron transport separately.
 What do these data suggest about the role of NADPH in photosynthesis and why?
What do these data suggest about the role of NADPH in photosynthesis and why?A) NADPH is required for photosynthesis because Calvin cycle function is blocked when noncyclic electron transport is inhibited.
B) NADPH is required for photosynthesis because Calvin cycle function is not blocked when cyclic electron transport is inhibited.
C) NADPH is required for photosynthesis because cyclic electron transport can function independently of noncyclic electron transport.
D) NADPH is not required for photosynthesis because cyclic electron transport can function even when noncyclic electron transport is inhibited.
E) NADPH is not required for photosynthesis because different chemical agents can inhibit cyclic and noncyclic electron transport separately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Both the light reactions and the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis
A) synthesize ATP.
B) use NADPH.
C) rely on electron transport.
D) occur in the chloroplast.
E) fix CO2.
A) synthesize ATP.
B) use NADPH.
C) rely on electron transport.
D) occur in the chloroplast.
E) fix CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Compared with long-wavelength light, short-wavelength light has
A) an insignificant amount of energy.
B) more energy.
C) energy that is less available to plant cells.
D) a ladder of energy.
E) an equal amount of energy.
A) an insignificant amount of energy.
B) more energy.
C) energy that is less available to plant cells.
D) a ladder of energy.
E) an equal amount of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The precise moment when light energy is transformed into chemical energy is the point at which
A) light shines on chlorophyll.
B) water is hydrolyzed.
C) the P680 chlorophylls are oxidized.
D) chlorophyll is reduced.
E) the CO2 from air is captured in a sugar.
A) light shines on chlorophyll.
B) water is hydrolyzed.
C) the P680 chlorophylls are oxidized.
D) chlorophyll is reduced.
E) the CO2 from air is captured in a sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When a photon is absorbed by a molecule, the photon
A) loses its ability to generate any energy.
B) raises the molecule from a ground state of low energy to an excited state.
C) affects the molecule in ways that are not clearly understood.
D) causes a change in the velocity of the wavelengths.
E) splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
A) loses its ability to generate any energy.
B) raises the molecule from a ground state of low energy to an excited state.
C) affects the molecule in ways that are not clearly understood.
D) causes a change in the velocity of the wavelengths.
E) splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a plant has plenty of NADPH available but is running low on ATP, how does the plant make up the ATP deficit during the daylight hours?
A) It uses photorespiration.
B) It uses noncyclic photophosphorylation.
C) It uses cyclic photophosphorylation.
D) It decreases the rate of chemiosmosis.
E) It increases the rate of the Calvin cycle.
A) It uses photorespiration.
B) It uses noncyclic photophosphorylation.
C) It uses cyclic photophosphorylation.
D) It decreases the rate of chemiosmosis.
E) It increases the rate of the Calvin cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement about NADPH is false?
A) It is synthesized in the stroma of the chloroplast.
B) It is synthesized by cyclic electron transport.
C) It is formed when NADP+ accepts two electrons and one proton.
D) It becomes oxidized to NADP+ during the Calvin cycle.
E) One NADPH is required to reduce one molecule of 3PG to one molecule of G3P.
A) It is synthesized in the stroma of the chloroplast.
B) It is synthesized by cyclic electron transport.
C) It is formed when NADP+ accepts two electrons and one proton.
D) It becomes oxidized to NADP+ during the Calvin cycle.
E) One NADPH is required to reduce one molecule of 3PG to one molecule of G3P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The molecule(s) representing the net energy output of one cycle of photosynthetic cyclic electron transport is/are
A) ATP.
B) ATP and NAD+.
C) NADPH.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) sugar.
A) ATP.
B) ATP and NAD+.
C) NADPH.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The chemiosmotic hypothesis states that the energy for the production of ATP during photosynthesis comes from
A) the release of protons from water.
B) the oxidation of NADP+.
C) a proton gradient set up across the thylakoid membrane.
D) the oxidation of CO2.
E) glycolysis.
A) the release of protons from water.
B) the oxidation of NADP+.
C) a proton gradient set up across the thylakoid membrane.
D) the oxidation of CO2.
E) glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The drug 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) disrupts the proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.If chloroplasts were incubated in a solution of DNP,
A) oxygen would no longer be reduced to water.
B) no ATP would be synthesized as a consequence of the transport of electrons.
C) chloroplasts would show a burst of increased ATP synthesis.
D) the rate of the Calvin cycle would increase.
E) photosystem II would become overly reduced and would no longer absorb photons of light.
A) oxygen would no longer be reduced to water.
B) no ATP would be synthesized as a consequence of the transport of electrons.
C) chloroplasts would show a burst of increased ATP synthesis.
D) the rate of the Calvin cycle would increase.
E) photosystem II would become overly reduced and would no longer absorb photons of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
One reason the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a is not identical to the action spectrum of photosynthesis is that
A) accessory pigments also absorb energy to drive photosynthesis.
B) chlorophyll a absorbs both red light and blue light.
C) chlorophyll a reflects green light.
D) different wavelengths of light have different energies.
E) chlorophyll a can be activated by absorbing a photon of light.
A) accessory pigments also absorb energy to drive photosynthesis.
B) chlorophyll a absorbs both red light and blue light.
C) chlorophyll a reflects green light.
D) different wavelengths of light have different energies.
E) chlorophyll a can be activated by absorbing a photon of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A researcher exposes a suspension of green algae to different light sources with different combinations of wavelengths.Compared with a suspension of algae that is receiving white light (source C), the algae suspension exposed to artificial light from source A remains healthy but produces less oxygen and has a slower growth rate.The algae suspension exposed to artificial light from source B ceases to produce oxygen, and its growth is halted.Which of the following statements about light sources is correct?
A) Light source A provides only infrared light.
B) Light source B provides only red light.
C) Light source A provides either blue or red light but not both.
D) Light source B provides only blue light.
E) Light source A provides only green light.
A) Light source A provides only infrared light.
B) Light source B provides only red light.
C) Light source A provides either blue or red light but not both.
D) Light source B provides only blue light.
E) Light source A provides only green light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In both photosynthesis and respiration, protons are pumped across a membrane during
A) reduction of O2.
B) ATP hydrolysis.
C) CO2 fixation.
D) electron transport.
E) glycolysis.
A) reduction of O2.
B) ATP hydrolysis.
C) CO2 fixation.
D) electron transport.
E) glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If two plants have different-colored leaves,
A) their absorption spectra will match, but their action spectra may differ.
B) their action spectra may match, but their absorption spectra will differ.
C) their absorption spectra and their action spectra will differ.
D) their absorption spectra and their action spectra will be the same.
E) the outcome is unpredictable because a plant's action spectra cannot be reliably determined.
A) their absorption spectra will match, but their action spectra may differ.
B) their action spectra may match, but their absorption spectra will differ.
C) their absorption spectra and their action spectra will differ.
D) their absorption spectra and their action spectra will be the same.
E) the outcome is unpredictable because a plant's action spectra cannot be reliably determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the hydrolysis of H2O to protons and oxygen during photosynthesis, electrons are transferred to P680.This reaction is an example of
A) a redox reaction.
B) a metabolic pathway.
C) oxidative phosphorylation.
D) the creation of a proton gradient.
E) an aerobic reaction.
A) a redox reaction.
B) a metabolic pathway.
C) oxidative phosphorylation.
D) the creation of a proton gradient.
E) an aerobic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The enzyme ATP synthase couples the synthesis of ATP to
A) the reduction of NADP+.
B) the excitation of chlorophyll.
C) the reduction of chlorophyll.
D) CO2 fixation.
E) the diffusion of protons.
A) the reduction of NADP+.
B) the excitation of chlorophyll.
C) the reduction of chlorophyll.
D) CO2 fixation.
E) the diffusion of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
During photophosphorylation, the energy to produce ATP is provided by
A) heat.
B) NADPH.
C) ground-state chlorophyll.
D) the pH gradient generated during electron transport.
E) NADP+ reductase.
A) heat.
B) NADPH.
C) ground-state chlorophyll.
D) the pH gradient generated during electron transport.
E) NADP+ reductase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Accessory pigments
A) play no specific role in photosynthesis.
B) transfer energy from chlorophyll to the electron transport chain.
C) absorb only red wavelengths of light.
D) broaden the range of wavelengths plants can use for photosynthesis.
E) transfer electrons to NADP+.
A) play no specific role in photosynthesis.
B) transfer energy from chlorophyll to the electron transport chain.
C) absorb only red wavelengths of light.
D) broaden the range of wavelengths plants can use for photosynthesis.
E) transfer electrons to NADP+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A graph that plots the rate at which CO2 is converted to sugar versus the wavelength of light illuminating a leaf is called
A) a Planck equation plot.
B) an absorption spectrum.
C) an enzyme kinetics plot.
D) an electromagnetic spectrum.
E) an action spectrum.
A) a Planck equation plot.
B) an absorption spectrum.
C) an enzyme kinetics plot.
D) an electromagnetic spectrum.
E) an action spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In photosynthetic noncyclic electron transport, water is used for the
A) hydrolysis of ATP.
B) excitation of chlorophyll.
C) reduction of the P680 chlorophylls.
D) oxidation of NADPH.
E) synthesis of chlorophyll.
A) hydrolysis of ATP.
B) excitation of chlorophyll.
C) reduction of the P680 chlorophylls.
D) oxidation of NADPH.
E) synthesis of chlorophyll.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In water, red light is fully absorbed at about 15 meters, orange light is fully absorbed at about 30 meters, yellow light is fully absorbed at about 50 meters, and blue light is fully absorbed at about 100 meters.Based on this information, one can predict that photosynthetic organisms can survive at a depth of up to almost _______ meters.
A) 10
B) 15
C) 30
D) 50
E) 100
A) 10
B) 15
C) 30
D) 50
E) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The carbon-fixation reactions of photosynthesis require more ATP than NADPH.The additional ATP is provided by
A) the splitting of water.
B) the reduction of oxygen.
C) the oxidation of sugars.
D) cyclic electron transport.
E) noncyclic electron transport.
A) the splitting of water.
B) the reduction of oxygen.
C) the oxidation of sugars.
D) cyclic electron transport.
E) noncyclic electron transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The energy difference between an electron excited by a photon and the electron in its ground state is
A) less than the energy of the photon.
B) greater than the energy of the photon.
C) equal to the energy of the photon.
D) highly variable.
E) not possible to quantify.
A) less than the energy of the photon.
B) greater than the energy of the photon.
C) equal to the energy of the photon.
D) highly variable.
E) not possible to quantify.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When CO2 is added to RuBP, the first stable product synthesized is
A) pyruvate.
B) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
C) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG).
D) ATP.
E) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P).
A) pyruvate.
B) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
C) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG).
D) ATP.
E) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the table below, which contains data collected using the same techniques that Calvin and his colleagues used to determine the pathway of carbon atoms during photosynthesis.In this experiment, the starting material was a synthesized compound that contained carbon-14.This 14C-labeled compound was supplied to a living culture of algae at time zero.Then, at 5-second intervals, samples of the culture were harvested and extracted.The extracts were subjected to two-dimensional chromatography, and the resulting spots were numbered and measured for radioactivity.A "0" indicates negligible radioactivity, while a "+" indicates measurable radioactivity; the greater the number of "+" symbols, the greater the radioactivity detected. 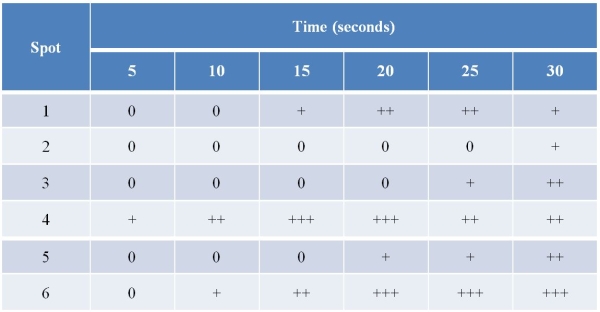 Based on these results, what is the sequence of compounds in the metabolic pathway?
Based on these results, what is the sequence of compounds in the metabolic pathway?
A) 3 5 2 4 1 6
B) 4 6 1 5 3 2
C) 1 4 6 3 5 2
D) 2 3 5 1 6 4
E) 4 1 5 2 6 3
 Based on these results, what is the sequence of compounds in the metabolic pathway?
Based on these results, what is the sequence of compounds in the metabolic pathway?A) 3 5 2 4 1 6
B) 4 6 1 5 3 2
C) 1 4 6 3 5 2
D) 2 3 5 1 6 4
E) 4 1 5 2 6 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Electron transport and photophosphorylation provide the Calvin cycle with
A) protons and electrons.
B) ATP and NADPH.
C) water and photons.
D) light and chlorophyll.
E) CO2 and sugars.
A) protons and electrons.
B) ATP and NADPH.
C) water and photons.
D) light and chlorophyll.
E) CO2 and sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
After one turn of the Calvin cycle,
A) all G3P molecules are converted into sugars.
B) one-third of the G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP.
C) about one-sixth of the G3P molecules are converted into sugars.
D) the G3P is metabolized using photorespiration.
E) the G3P feedback inhibits the activity of rubisco.
A) all G3P molecules are converted into sugars.
B) one-third of the G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP.
C) about one-sixth of the G3P molecules are converted into sugars.
D) the G3P is metabolized using photorespiration.
E) the G3P feedback inhibits the activity of rubisco.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The activity of the Calvin cycle is linked to the light reactions of photosynthesis through the
A) production of ATP and NADPH.
B) synthesis of H2O.
C) uptake of CO2.
D) release of O2.
E) regeneration of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
A) production of ATP and NADPH.
B) synthesis of H2O.
C) uptake of CO2.
D) release of O2.
E) regeneration of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement regarding the electron transport chain between photosystem II and photosystem I is true?
A) Its terminal electron acceptor is oxygen.
B) Its terminal electron acceptor is P680.
C) Most of its components are found in the lumen of the thylakoid.
D) It generates a pH gradient that supplies the energy for ATP synthesis.
E) It generates NADPH.
A) Its terminal electron acceptor is oxygen.
B) Its terminal electron acceptor is P680.
C) Most of its components are found in the lumen of the thylakoid.
D) It generates a pH gradient that supplies the energy for ATP synthesis.
E) It generates NADPH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How many moles of CO2 must enter the Calvin cycle for the synthesis of one mole of hexose to be synthesized?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 12
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The NADPH required for the reduction of 3PG to G3P comes from
A) the light-independent reactions.
B) the light reactions.
C) the synthesis of ATP.
D) the Calvin cycle.
E) oxidative phosphorylation.
A) the light-independent reactions.
B) the light reactions.
C) the synthesis of ATP.
D) the Calvin cycle.
E) oxidative phosphorylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
During photophosphorylation, free energy is released
A) by the formation of ATP.
B) during the excitation of chlorophyll in photosystem I.
C) during the oxidation of chlorophyll.
D) during the excitation of chlorophyll in photosystem II.
E) during each of the redox reactions of the electron transport chain.
A) by the formation of ATP.
B) during the excitation of chlorophyll in photosystem I.
C) during the oxidation of chlorophyll.
D) during the excitation of chlorophyll in photosystem II.
E) during each of the redox reactions of the electron transport chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a suspension of algae is incubated in a flask in the presence of light and CO2 and then transferred to the dark, the reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate slows and then stops.This happens because
A) the reaction requires CO2.
B) the reaction is exergonic.
C) the reaction requires ATP and NADPH.
D) the reaction requires O2.
E) chlorophyll is not synthesized in the dark.
A) the reaction requires CO2.
B) the reaction is exergonic.
C) the reaction requires ATP and NADPH.
D) the reaction requires O2.
E) chlorophyll is not synthesized in the dark.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which sequence gives a correct order of steps taking place during the light reactions?
A) Light energy excited electron pH gradient ATP synthesis electron transport
B) Excited electron light energy ATP synthesis electron transport pH gradient
C) pH gradient light energy excited electron electron transport ATP synthesis
D) Light energy excited electron electron transport pH gradient ATP synthesis
E) ATP synthesis light energy excited electron electron transport pH gradient
A) Light energy excited electron pH gradient ATP synthesis electron transport
B) Excited electron light energy ATP synthesis electron transport pH gradient
C) pH gradient light energy excited electron electron transport ATP synthesis
D) Light energy excited electron electron transport pH gradient ATP synthesis
E) ATP synthesis light energy excited electron electron transport pH gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In noncyclic electron transport, electrons from _______ replenish chlorophyll molecules that have given up electrons.
A) CO2
B) H2O
C) NADPH + H+
D) O2 gas
E) ATP
A) CO2
B) H2O
C) NADPH + H+
D) O2 gas
E) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
During CO2 fixation, CO2 combines with
A) NADPH.
B) 3PG.
C) G3P.
D) Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
E) water.
A) NADPH.
B) 3PG.
C) G3P.
D) Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
E) water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Calvin cycle uses all of the following except _______ to produce glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P).
A) CO2
B) ATP
C) NADPH
D) rubisco
E) oxygen
A) CO2
B) ATP
C) NADPH
D) rubisco
E) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The light reactions
A) require light of any wavelength.
B) result in the hydrolysis of ATP.
C) produce NADPH used in the Calvin cycle.
D) occur in C4 plants only.
E) take place in the stroma.
A) require light of any wavelength.
B) result in the hydrolysis of ATP.
C) produce NADPH used in the Calvin cycle.
D) occur in C4 plants only.
E) take place in the stroma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which scientific tools helped researchers "crack" the Calvin cycle?
A) Electron microscopy and radioisotopes
B) Paper chromatography and crystallography
C) Crystallography and centrifugation
D) Centrifugation and electron microscopy
E) Radioisotopes and paper chromatography
A) Electron microscopy and radioisotopes
B) Paper chromatography and crystallography
C) Crystallography and centrifugation
D) Centrifugation and electron microscopy
E) Radioisotopes and paper chromatography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the graph below, which shows the amount of carbon present as starch, sucrose, and hexose sugars at various times over a 24-hour period in the chloroplasts of leaf cells from a living green plant.Dawn marks the zero time point, and dusk marks the 14-hour time point. 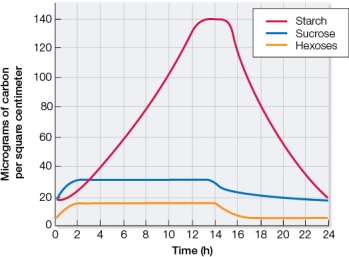 These data provide evidence in support of which statement about chloroplasts?
These data provide evidence in support of which statement about chloroplasts?
A) The plant uses the carbohydrates produced in chloroplasts to make amino acids, lipids, and the building blocks of nucleic acids.
B) Chloroplasts are found in organisms called autotrophs that are able to carry out photosynthesis; chloroplasts are not found in organisms called heterotrophs that do not carry out photosynthesis.
C) Sugars accumulate in the chloroplasts as the result of photosynthesis and are stored in polysaccharide form until needed during the night, when photosynthesis stops.
D) Photophosphorylation occurs in the chloroplast, where electron transport is coupled to proton transport across a membrane.
E) The thylakoid membranes of a chloroplast contain light-harvesting complexes and electron transport proteins, while the stroma contains Calvin cycle enzymes.
 These data provide evidence in support of which statement about chloroplasts?
These data provide evidence in support of which statement about chloroplasts?A) The plant uses the carbohydrates produced in chloroplasts to make amino acids, lipids, and the building blocks of nucleic acids.
B) Chloroplasts are found in organisms called autotrophs that are able to carry out photosynthesis; chloroplasts are not found in organisms called heterotrophs that do not carry out photosynthesis.
C) Sugars accumulate in the chloroplasts as the result of photosynthesis and are stored in polysaccharide form until needed during the night, when photosynthesis stops.
D) Photophosphorylation occurs in the chloroplast, where electron transport is coupled to proton transport across a membrane.
E) The thylakoid membranes of a chloroplast contain light-harvesting complexes and electron transport proteins, while the stroma contains Calvin cycle enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In noncyclic photophosphorylation, oxidized chlorophyll in photosystem I returns to its reduced state by
A) splitting water.
B) accepting electrons from photosystem II through the electron transport chain.
C) absorbing two photons of light.
D) taking electrons from NADPH.
E) hydrolyzing ATP.
A) splitting water.
B) accepting electrons from photosystem II through the electron transport chain.
C) absorbing two photons of light.
D) taking electrons from NADPH.
E) hydrolyzing ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the figure below. 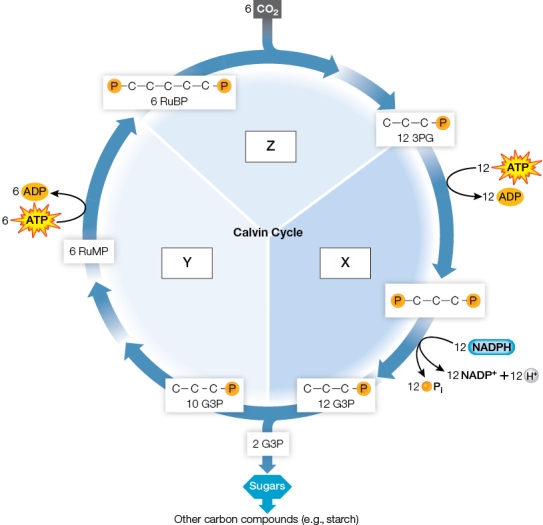 In the figure, how should boxes X, Y, and Z be labeled?
In the figure, how should boxes X, Y, and Z be labeled?
A) X = regeneration of RuBP, Y = carbon fixation, Z = reduction and sugar production
B) X = carbon fixation, Y = reduction and sugar production, Z = regeneration of RuBP
C) X = reduction and sugar production, Y = regeneration of RuBP, Z = carbon fixation
D) X = regeneration of RuBP, Y = reduction and sugar production, Z = carbon fixation
E) X = reduction and sugar production, Y = carbon fixation, Z = regeneration of RuBP
 In the figure, how should boxes X, Y, and Z be labeled?
In the figure, how should boxes X, Y, and Z be labeled?A) X = regeneration of RuBP, Y = carbon fixation, Z = reduction and sugar production
B) X = carbon fixation, Y = reduction and sugar production, Z = regeneration of RuBP
C) X = reduction and sugar production, Y = regeneration of RuBP, Z = carbon fixation
D) X = regeneration of RuBP, Y = reduction and sugar production, Z = carbon fixation
E) X = reduction and sugar production, Y = carbon fixation, Z = regeneration of RuBP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Calvin cycle
A) generates ATP and NADPH.
B) is part of photorespiration.
C) uses CO2 to synthesize the sugar phosphate G3P.
D) adds O2 to RuBP.
E) is not always dependent upon photosynthesis for energy.
A) generates ATP and NADPH.
B) is part of photorespiration.
C) uses CO2 to synthesize the sugar phosphate G3P.
D) adds O2 to RuBP.
E) is not always dependent upon photosynthesis for energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Photorespiration reduces the net carbon fixed by the Calvin cycle by _______ percent.
A) 0.02
B) 0.21
C) 2.1
D) 25
E) 70
A) 0.02
B) 0.21
C) 2.1
D) 25
E) 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In sunny, hot weather, corn, which is a C4 plant, has a survival advantage over wheat, which is a C3 plant, because
A) wheat loses water through its stomata and corn does not.
B) wheat is less efficient in its use of ATP than corn is.
C) corn undergoes photorespiration and wheat does not.
D) corn is able to keep its stomata open and wheat cannot.
E) corn keeps CO2 levels high around rubisco even when stomata are closed.
A) wheat loses water through its stomata and corn does not.
B) wheat is less efficient in its use of ATP than corn is.
C) corn undergoes photorespiration and wheat does not.
D) corn is able to keep its stomata open and wheat cannot.
E) corn keeps CO2 levels high around rubisco even when stomata are closed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A suspension of algae is incubated in a flask in the presence of both light and CO2.When it is transferred to the dark, the reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) slows and then stops.At the same time, the concentration of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) declines.Why does the RuBP concentration decline?
A) RuBP is more rapidly metabolized in the dark.
B) RuBP is used up in making more 3PG.
C) Sugar is no longer generated from G3P.
D) The levels of oxygen drop.
E) RuBP needs to be regenerated from G3P.
A) RuBP is more rapidly metabolized in the dark.
B) RuBP is used up in making more 3PG.
C) Sugar is no longer generated from G3P.
D) The levels of oxygen drop.
E) RuBP needs to be regenerated from G3P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The enzyme PEP carboxylase
A) can fix CO2 even at relatively low CO2 concentrations.
B) catalyzes the synthesis of RuBP.
C) catalyzes the synthesis of 3PG.
D) is found in the chloroplasts of bundle sheath cells.
E) couples the synthesis of ATP to the diffusion of protons.
A) can fix CO2 even at relatively low CO2 concentrations.
B) catalyzes the synthesis of RuBP.
C) catalyzes the synthesis of 3PG.
D) is found in the chloroplasts of bundle sheath cells.
E) couples the synthesis of ATP to the diffusion of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure below. 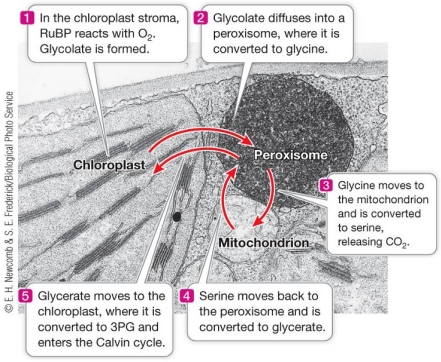 What process is depicted in this figure?
What process is depicted in this figure?
A) The movement of molecules linking the light reactions and the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis
B) The recovery of some of the fixed carbon that is channeled away by photorespiration
C) The fixation of carbon by C4 plants in a location separate from the Calvin cycle
D) The fixation of carbon by CAM plants during the night, when stomata are open
E) The production of hexose sugars, disaccharides, and polysaccharides following Calvin cycle reactions
 What process is depicted in this figure?
What process is depicted in this figure?A) The movement of molecules linking the light reactions and the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis
B) The recovery of some of the fixed carbon that is channeled away by photorespiration
C) The fixation of carbon by C4 plants in a location separate from the Calvin cycle
D) The fixation of carbon by CAM plants during the night, when stomata are open
E) The production of hexose sugars, disaccharides, and polysaccharides following Calvin cycle reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In C4 plants, CO2 is first fixed to form a compound called
A) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
B) glucose.
C) 3-phosphoglycerate.
D) ribulose bisphosphate.
E) oxaloacetate.
A) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
B) glucose.
C) 3-phosphoglycerate.
D) ribulose bisphosphate.
E) oxaloacetate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Photorespiration
A) results in CO2 fixation.
B) replaces cellular respiration.
C) generates a proton gradient.
D) results in stimulated plant growth.
E) occurs when CO2 levels are low.
A) results in CO2 fixation.
B) replaces cellular respiration.
C) generates a proton gradient.
D) results in stimulated plant growth.
E) occurs when CO2 levels are low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The level of atmospheric CO2 has varied considerably over the history of Earth.Currently, the level of atmospheric CO2
A) is greater than it was during the time of the dinosaurs.
B) favors C4 plants under hot conditions.
C) has resulted in maximum CO2 fixation by rubisco.
D) is decreasing.
E) prevents the occurrence of photorespiration.
A) is greater than it was during the time of the dinosaurs.
B) favors C4 plants under hot conditions.
C) has resulted in maximum CO2 fixation by rubisco.
D) is decreasing.
E) prevents the occurrence of photorespiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which occurs during the Calvin cycle and also during photorespiration?
A) Generation of 3PG
B) Formation of NADPH
C) Fixation of CO2
D) Fixation of O2
E) Formation of ATP
A) Generation of 3PG
B) Formation of NADPH
C) Fixation of CO2
D) Fixation of O2
E) Formation of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
During photorespiration, rubisco uses _______ as a substrate.
A) CO2
B) O2
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D) 3-phosphoglycerate
E) NADPH
A) CO2
B) O2
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D) 3-phosphoglycerate
E) NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Photorespiration takes place in
A) C3 plants only.
B) C4 plants only.
C) CAM plants only.
D) C3 and C4 plants.
E) C4 and CAM plants.
A) C3 plants only.
B) C4 plants only.
C) CAM plants only.
D) C3 and C4 plants.
E) C4 and CAM plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
As global atmospheric CO2 levels continue to rise,
A) C4 plants will have an advantage over C3 plants.
B) C3 plants will have an advantage over C4 plants.
C) the growth rates of rice and wheat will decrease.
D) photorespiration will increase.
E) CAM plants will have an advantage over C3 plants.
A) C4 plants will have an advantage over C3 plants.
B) C3 plants will have an advantage over C4 plants.
C) the growth rates of rice and wheat will decrease.
D) photorespiration will increase.
E) CAM plants will have an advantage over C3 plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A plant geneticist would like to engineer a plant with a photosynthetic efficiency that is superior to that of C3 and C4 plants.Such an engineered plant would
A) always keep its stomata open.
B) express rubisco that lacks oxygenase activity.
C) fix CO2 only during the night.
D) fix CO2 only during the day.
E) always perform cyclic electron transfer and never perform noncyclic electron transfer.
A) always keep its stomata open.
B) express rubisco that lacks oxygenase activity.
C) fix CO2 only during the night.
D) fix CO2 only during the day.
E) always perform cyclic electron transfer and never perform noncyclic electron transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In C4 plants, starch grains are found in the chloroplasts of
A) the stems.
B) mesophyll cells.
C) the intercellular region.
D) the epidermis.
E) bundle sheath cells.
A) the stems.
B) mesophyll cells.
C) the intercellular region.
D) the epidermis.
E) bundle sheath cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a C3 plant does not open its stomata on a sunny, hot day,
A) it will synthesize more water from photosynthesis.
B) photorespiration will become favorable.
C) photosynthesis will be more effective.
D) more ATP and NADPH can be synthesized.
E) only ATP can be synthesized.
A) it will synthesize more water from photosynthesis.
B) photorespiration will become favorable.
C) photosynthesis will be more effective.
D) more ATP and NADPH can be synthesized.
E) only ATP can be synthesized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When RuBP reacts with O2,
A) it cannot react with CO2.
B) carbohydrate production increases.
C) plant growth is stimulated.
D) net carbon fixation increases by 25 percent.
E) two carbon molecules combine to form the four-carbon phosphoglycolate.
A) it cannot react with CO2.
B) carbohydrate production increases.
C) plant growth is stimulated.
D) net carbon fixation increases by 25 percent.
E) two carbon molecules combine to form the four-carbon phosphoglycolate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Both C4 plants and C3 plants
A) use rubisco to carboxylate RuBP.
B) use PEP carboxylase to form oxaloacetate.
C) keep CO2 levels high around rubisco.
D) express rubisco in bundle sheath cells.
E) keep PEP carboxylase in the mesophyll cells.
A) use rubisco to carboxylate RuBP.
B) use PEP carboxylase to form oxaloacetate.
C) keep CO2 levels high around rubisco.
D) express rubisco in bundle sheath cells.
E) keep PEP carboxylase in the mesophyll cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
On a very hot summer day, the greatest level of O2 production (photorespiration) by a C3 plant would likely take place
A) 3 hours after nightfall.
B) 3 hours before sunrise.
C) in midafternoon.
D) in midmorning.
E) at midnight.
A) 3 hours after nightfall.
B) 3 hours before sunrise.
C) in midafternoon.
D) in midmorning.
E) at midnight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What determines whether rubisco acts as an oxygenase or a carboxylase?
A) Rubisco has ten times more affinity for O2 than for CO2; therefore, it favors O2 fixation.
B) If O2 is relatively abundant, rubisco acts as a carboxylase.
C) If O2 predominates, rubisco fixes it, and the Calvin cycle occurs.
D) Oxygenase activity is more likely at low temperatures.
E) As the ratio of CO2 to O2 falls in the leaf, the reaction of rubisco with O2 is favored.
A) Rubisco has ten times more affinity for O2 than for CO2; therefore, it favors O2 fixation.
B) If O2 is relatively abundant, rubisco acts as a carboxylase.
C) If O2 predominates, rubisco fixes it, and the Calvin cycle occurs.
D) Oxygenase activity is more likely at low temperatures.
E) As the ratio of CO2 to O2 falls in the leaf, the reaction of rubisco with O2 is favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In C4 plants, the four-carbon compound that is synthesized by carbon fixation in the mesophyll cells
A) reduces NADP+.
B) combines with CO2 to produce sugar.
C) carries CO2 to the bundle sheath cells.
D) drives the synthesis of ATP.
E) closes the stomata.
A) reduces NADP+.
B) combines with CO2 to produce sugar.
C) carries CO2 to the bundle sheath cells.
D) drives the synthesis of ATP.
E) closes the stomata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 242 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



