Deck 15: Gene Mutation and Molecular Medicine
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/251
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Gene Mutation and Molecular Medicine
1
Suppose that for a certain gene, nearly 100 percent of the normal level of expression is required to produce the normal phenotype.Based on this requirement, one could predict that a _______ mutation would be _______.
A) gain of function; recessive
B) loss of function; dominant
C) loss of function; recessive
D) nonsense; recessive
E) loss of function; a conditional mutation
A) gain of function; recessive
B) loss of function; dominant
C) loss of function; recessive
D) nonsense; recessive
E) loss of function; a conditional mutation
B
2
People are often more concerned about germ line mutations than somatic ones because germ line mutations
A) have phenotypic effects, whereas somatic mutations do not.
B) affect more nucleotides than somatic mutations do.
C) transitions, whereas somatic mutations are transversions.
D) are transmitted to offspring, whereas somatic mutations are not.
E) occur more frequently than somatic mutations.
A) have phenotypic effects, whereas somatic mutations do not.
B) affect more nucleotides than somatic mutations do.
C) transitions, whereas somatic mutations are transversions.
D) are transmitted to offspring, whereas somatic mutations are not.
E) occur more frequently than somatic mutations.
D
3
Gain of function mutations
A) are dominant mutations that are expressed in wild-type cells.
B) are dominant mutations that are expressed in mutant cells.
C) are the cause of continuous division in cancer cells.
D) can be analyzed only under restrictive conditions.
E) are expressed only with the appropriate environmental signals.
A) are dominant mutations that are expressed in wild-type cells.
B) are dominant mutations that are expressed in mutant cells.
C) are the cause of continuous division in cancer cells.
D) can be analyzed only under restrictive conditions.
E) are expressed only with the appropriate environmental signals.
B
4
Suppose that in one cell in your skin, chromosome 14 and chromosome 18 exchange genetic materials.This change is inherited by subsequent cells.This is an example of a _______ mutation that is also a(n) _______.
A) germ line; inversion
B) germ line; point mutation
C) germ line; translocation
D) somatic; inversion
E) somatic; translocation
A) germ line; inversion
B) germ line; point mutation
C) germ line; translocation
D) somatic; inversion
E) somatic; translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is usually caused by the oncogene BCR/ABL.This abnormal gene is the product of the fusion of part of a BCR gene with part of an ABL gene.The resulting protein has unregulated tyrosine kinase activity.The BCR and ABL genes are normally found on two different chromosomes, respectively 22 and 9.What type of mutation is required to generate the BCR/ABL fusion gene?
A) Chromosomal inversions
B) Chromosomal deletion
C) Chromosomal transversions
D) Chromosomal transitions
E) Chromosomal translocation
A) Chromosomal inversions
B) Chromosomal deletion
C) Chromosomal transversions
D) Chromosomal transitions
E) Chromosomal translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a mutation has a visible effect at 26°C, but no visible effect at 20°C, then 20°C is the _______ temperature and 26°C is the _______ temperature.
A) permissive; conditional
B) permissive; restrictive
C) restrictive; conditional
D) restrictive; permissive
E) conditional; restrictive
A) permissive; conditional
B) permissive; restrictive
C) restrictive; conditional
D) restrictive; permissive
E) conditional; restrictive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Sequencing of a child's genomic DNA reveals that the child is a heterozygote for a new mutation.This mutation appears in all of the cells tested from a variety of tissues (including skin, blood, and hair).The mutation is not found in either the mother or the father.Most likely, this is a new _______ mutation that occurred in _______.
A) somatic; one of the parents
B) somatic; the child
C) germ line; one of the parents
D) germ line; both of the parents
E) germ line; the child
A) somatic; one of the parents
B) somatic; the child
C) germ line; one of the parents
D) germ line; both of the parents
E) germ line; the child

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the table.  Alkaptonuria is an inborn error of metabolism, caused by defects in an enzyme in the pathway that breaks down tyrosine (see Section 14.1).Humans who are homozygous for one of these mutations make nonfunctional enzyme and accumulate the enzyme's substrate, homogentisic acid, which causes their disease symptoms.In 1996, researchers in Spain cloned and sequenced the gene for the enzyme and characterized several mutant alleles.The table shows the wild-type coding strand sequence for part of the gene and the corresponding region from one of the mutant alleles.What type of mutation is this?
Alkaptonuria is an inborn error of metabolism, caused by defects in an enzyme in the pathway that breaks down tyrosine (see Section 14.1).Humans who are homozygous for one of these mutations make nonfunctional enzyme and accumulate the enzyme's substrate, homogentisic acid, which causes their disease symptoms.In 1996, researchers in Spain cloned and sequenced the gene for the enzyme and characterized several mutant alleles.The table shows the wild-type coding strand sequence for part of the gene and the corresponding region from one of the mutant alleles.What type of mutation is this?
A) Silent
B) Nonsense
C) Frame-shift
D) Missense
E) Reversion
 Alkaptonuria is an inborn error of metabolism, caused by defects in an enzyme in the pathway that breaks down tyrosine (see Section 14.1).Humans who are homozygous for one of these mutations make nonfunctional enzyme and accumulate the enzyme's substrate, homogentisic acid, which causes their disease symptoms.In 1996, researchers in Spain cloned and sequenced the gene for the enzyme and characterized several mutant alleles.The table shows the wild-type coding strand sequence for part of the gene and the corresponding region from one of the mutant alleles.What type of mutation is this?
Alkaptonuria is an inborn error of metabolism, caused by defects in an enzyme in the pathway that breaks down tyrosine (see Section 14.1).Humans who are homozygous for one of these mutations make nonfunctional enzyme and accumulate the enzyme's substrate, homogentisic acid, which causes their disease symptoms.In 1996, researchers in Spain cloned and sequenced the gene for the enzyme and characterized several mutant alleles.The table shows the wild-type coding strand sequence for part of the gene and the corresponding region from one of the mutant alleles.What type of mutation is this?A) Silent
B) Nonsense
C) Frame-shift
D) Missense
E) Reversion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Because of the redundancy in the genetic code, many mutations in the coding regions of genes are
A) transitions.
B) transversions.
C) inversions.
D) somatic mutations.
E) silent mutations.
A) transitions.
B) transversions.
C) inversions.
D) somatic mutations.
E) silent mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the following image. 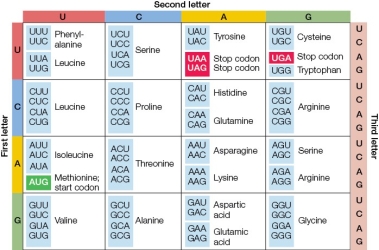 Given the codon UCA in the first exon of a gene, which change is most likely to result in a nonsense mutation?
Given the codon UCA in the first exon of a gene, which change is most likely to result in a nonsense mutation?
A) Change of nucleotide in the first position
B) Change of nucleotide in the second position
C) Change of nucleotide in the third position
D) A transversion of A to U
E) A transition of A to G
 Given the codon UCA in the first exon of a gene, which change is most likely to result in a nonsense mutation?
Given the codon UCA in the first exon of a gene, which change is most likely to result in a nonsense mutation?A) Change of nucleotide in the first position
B) Change of nucleotide in the second position
C) Change of nucleotide in the third position
D) A transversion of A to U
E) A transition of A to G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In wild type Drosophila melanogaster, the order of genes on a chromosome is yellow, vermillion, forked, and Bobbed.Some of the flies have a different gene order: yellow, Bobbed, forked, and vermillion.The flies with the altered gene order most likely have a
A) missense mutation.
B) nonsense mutation.
C) reciprocal translocation.
D) frame-shift mutation.
E) chromosomal inversion.
A) missense mutation.
B) nonsense mutation.
C) reciprocal translocation.
D) frame-shift mutation.
E) chromosomal inversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Analysis of the abnormal white blood cells of a patient with leukemia, a type of cancer, reveals that a protein, termed LP, is always functionally active.In normal white blood cells this protein is found to be only functionally active in response to growth stimuli that induce cell division.Surprisingly, sequencing of leukemic cell DNA shows that both LP alleles in the patient's leukemic cells are normal.However, the DNA sequencing also reveals that both alleles of protein ILP, which normally inhibits LP activity in the absence of growth stimuli, have each acquired a mutation.Further research proves that these _______ mutations in both ILP alleles are the reason why LP is always active and, consequently, induces the leukemic cells to constantly undergo cell division.
A) loss-of-function
B) gain-of-function
C) silent
D) reversion
E) conditional
A) loss-of-function
B) gain-of-function
C) silent
D) reversion
E) conditional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A bacterial cell has been exposed to a powerful mutagen.The chromosomal sequences of the ancestral cell and the descendant cell are shown.(The ellipses represent intervening sequences that are identical.)  Based on this information, there have been _______ transitions and _______ transversions.
Based on this information, there have been _______ transitions and _______ transversions.
A) 0; 5
B) 2; 3
C) 2; 5
D) 3; 2
E) 3; 3
 Based on this information, there have been _______ transitions and _______ transversions.
Based on this information, there have been _______ transitions and _______ transversions.A) 0; 5
B) 2; 3
C) 2; 5
D) 3; 2
E) 3; 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One son of Great Britain's Queen Victoria was born with the X-linked disease hemophilia, and two of her daughters were carriers, as some of their male children were born with hemophilia.King Albert did not have hemophilia, nor did any of Queen Victoria's relatives on her mother's side.Based on this information, the hemophilia mutation most likely originated
A) as a somatic mutation in Queen Victoria.
B) in a sperm cell from King Albert.
C) as a somatic mutation in King Albert.
D) in the egg from Queen Victoria's mother.
E) in the egg from King Albert's mother.
A) as a somatic mutation in Queen Victoria.
B) in a sperm cell from King Albert.
C) as a somatic mutation in King Albert.
D) in the egg from Queen Victoria's mother.
E) in the egg from King Albert's mother.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The isoenzyme hexosaminidase A (HEXA), composed of subunits α and β, breaks down molecules containing terminal N-acetyl hexosamines.Tay-Sachs disease is caused by a recessively inherited mutation in the gene coding for the α subunit, which is the subunit that hydrolyzes the lipid GM2 ganglioside.Accumulation of this lipid in the brain leads to progressive deterioration of the nervous system and death, usually by age 4.A child born homozygous for the loss-of-function α subunit allele nevertheless does not develop Tay-Sachs disease.Sequence analysis of the β subunit alleles reveals that one allele has a mutation that makes it able to hydrolyze GM2 ganglioside.This is a _______-of-function mutation, which is most likely _______.
A) gain; dominant
B) gain; recessive
C) loss; dominant
D) loss; recessive
E) loss; intermediately dominant
A) gain; dominant
B) gain; recessive
C) loss; dominant
D) loss; recessive
E) loss; intermediately dominant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose that a mutation appears in a small population of plants that changes the color of their seeds from yellow to green.This mutation reaches 100 percent frequency in the population.Many generations later, some individuals with yellow seeds are found.We can definitely say that these individuals have acquired a(n)
A) inversion.
B) transition.
C) reversion mutation.
D) conditional mutation.
E) somatic mutation.
A) inversion.
B) transition.
C) reversion mutation.
D) conditional mutation.
E) somatic mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement about mutations is true?
A) All point mutations are transitions.
B) All transitions are point mutations.
C) All point mutations are base substitutions.
D) All point mutations are nonsense mutations.
E) All point mutations are missense mutations.
A) All point mutations are transitions.
B) All transitions are point mutations.
C) All point mutations are base substitutions.
D) All point mutations are nonsense mutations.
E) All point mutations are missense mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which mutation is least likely to be a frame-shift mutation?
A) An insertion of six nucleotides
B) A deletion of four nucleotides
C) An insertion of two nucleotides
D) A deletion of eight nucleotides
E) An insertion of ten nucleotides
A) An insertion of six nucleotides
B) A deletion of four nucleotides
C) An insertion of two nucleotides
D) A deletion of eight nucleotides
E) An insertion of ten nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The functional activity of the KRAS protein promotes cell proliferation and is often mutated in leukemia (cancer of a type of blood cell).In a B cell leukemia, a clinical researcher identifies a G → A transition at the second base of codon 12, resulting in a glycine → aspartic acid substitution in the protein.In normal cells, KRAS protein function can be activated and suppressed by the activity of other proteins.In contrast, in the leukemic cells, KRAS protein function is resistant to suppression.This is an example of a _______ mutation generating a_______-of-function mutation.
A) nonsense; gain
B) nonsense; loss
C) missense; gain
D) missense; loss
E) silent; gain
A) nonsense; gain
B) nonsense; loss
C) missense; gain
D) missense; loss
E) silent; gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Drosophila melanogaster flies that have the Shaker mutation appear normal at room temperature.If you hold a vial of flies with this mutation for a few minutes (i.e., warm the vial to body temperature, or 37oC), the flies become uncoordinated because of the warmth of your hand.If you remove your hand, the flies soon recover.Based on this information, which statement about the Shaker mutation must be true?
A) It is permissive at 37oC.
B) It is a reversion mutation.
C) It improves flight at temperatures lower than 37oC.
D) It is a recessive mutation.
E) It is restrictive at 37oC.
A) It is permissive at 37oC.
B) It is a reversion mutation.
C) It improves flight at temperatures lower than 37oC.
D) It is a recessive mutation.
E) It is restrictive at 37oC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which disease involves an expanding triplet repeat?
A) Sickle-cell disease
B) Huntington's disease
C) Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D) Most cancers
E) PKU
A) Sickle-cell disease
B) Huntington's disease
C) Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D) Most cancers
E) PKU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A medical researcher finds a high incidence of covalent bonds between thymine and other nucleotides in the DNA of skin cells of a patient.The most likely cause is
A) exposure to cigarette smoke.
B) a defective DNA polymerase.
C) nitrous oxide exposure.
D) exposure to UV radiation.
E) unknown; these bonds likely formed spontaneously.
A) exposure to cigarette smoke.
B) a defective DNA polymerase.
C) nitrous oxide exposure.
D) exposure to UV radiation.
E) unknown; these bonds likely formed spontaneously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Fragile-X syndrome
A) is an example of aneuploidy.
B) always results in mental retardation.
C) only affects males.
D) involves repeats of a codon.
E) is an example of a translocation.
A) is an example of aneuploidy.
B) always results in mental retardation.
C) only affects males.
D) involves repeats of a codon.
E) is an example of a translocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Mutational "hot spots" often occur when a methyl group has been added to
A) adenine.
B) cytosine.
C) guanine.
D) thymine.
E) uracil.
A) adenine.
B) cytosine.
C) guanine.
D) thymine.
E) uracil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which disease is caused by interactions of multiple genes and the environment?
A) Sickle-cell disease
B) Huntington's disease
C) Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D) Colon cancer
E) PKU
A) Sickle-cell disease
B) Huntington's disease
C) Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D) Colon cancer
E) PKU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Changes in the tautomer state of nucleotides will most often lead to
A) inversions.
B) reciprocal translocations.
C) point mutations.
D) duplications.
E) deletions.
A) inversions.
B) reciprocal translocations.
C) point mutations.
D) duplications.
E) deletions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Erythropoietin is a growth factor important for the generation of red blood cells (RBCs).In the bone marrow, the cells that will differentiate and proliferate to produce RBCs express a cell surface receptor that is activated by erythropoietin (EpoR).Eero Antero Mäntyranta from Finland was an Olympic skier who was accused of "blood doping" when drug testing revealed that he had abnormally high numbers of RBCs.However, this was a known condition in his family for many generations.A researcher who was studying this family trait discovered that the phenotype was the result of a deletion mutation in the EPOR gene.Mutant EpoR could not be negatively regulated, which resulted in increased production of RBCs.When it comes to competing in competitive sports, this EPOR _______ mutation has proven _______.
A) gain-of-function; harmful
B) loss-of-function; harmful
C) induced; beneficial
D) loss-of-function; beneficial
E) gain-of-function; beneficial
A) gain-of-function; harmful
B) loss-of-function; harmful
C) induced; beneficial
D) loss-of-function; beneficial
E) gain-of-function; beneficial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Benzopyrene, a component of cigarette smoke, can induce DNA mutations by
A) converting cytosine to uracil by deamination.
B) converting an amino group on cytosine into a keto group.
C) adding a chemical to guanine, making it unavailable for base pairing.
D) changing bases to forms that are unrecognizable by DNA polymerase.
E) breaking the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA.
A) converting cytosine to uracil by deamination.
B) converting an amino group on cytosine into a keto group.
C) adding a chemical to guanine, making it unavailable for base pairing.
D) changing bases to forms that are unrecognizable by DNA polymerase.
E) breaking the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During the winter months at a farm in a warm climate, wild geese commonly feed on the peanuts, corn kernels, and grains that are scattered across the fields.During one unusually wet hunting season, some game hunters are alarmed to find that the livers of some of the harvested geese are abnormally lumpy.A veterinarian diagnoses the lumps as tumors, most likely the consequence of _______ poisoning through their ingestion of moldy peanuts.
A) ionizing radiation
B) aflatoxin
C) benzopyrene
D) free radical
E) 5-methylcytosine
A) ionizing radiation
B) aflatoxin
C) benzopyrene
D) free radical
E) 5-methylcytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
People with sickle-cell disease have abnormal
A) phenylalanine hydrolase activity.
B) tumor suppressor function.
C) cholesterol transport function.
D) hemoglobin function.
E) glucose metabolism.
A) phenylalanine hydrolase activity.
B) tumor suppressor function.
C) cholesterol transport function.
D) hemoglobin function.
E) glucose metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A researcher studying multi-coloration of Zea mays (maize) kernels compares the genomes of kernels that are red with those of kernels that are purple on the same corncob.The researcher examines the gene Zmf3′h1, whose functional expression results in red color instead of purple color.In the purple kernels, there is an insertion a few hundred base pairs long within this gene.When the researcher repeats this analysis of purple kernels on other corncobs, she sees the same phenomenon.However, the insertions occur at different points within the Zmf3′h1 gene.What genetic phenomenon has the researcher most likely found evidence of?
A) Chromosomal inversions
B) Reciprocal translocation
C) Duplication
D) Transposons
E) Chromosomal deletions
A) Chromosomal inversions
B) Reciprocal translocation
C) Duplication
D) Transposons
E) Chromosomal deletions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The primary consequence of untreated phenylketonuria is
A) muscle atrophy.
B) kidney failure.
C) mental retardation.
D) skeletal defects.
E) circulatory diseases.
A) muscle atrophy.
B) kidney failure.
C) mental retardation.
D) skeletal defects.
E) circulatory diseases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Mutations that are not due to the presence or activity of a mutagen are referred to as _______ mutations.
A) spontaneous
B) induced
C) nonsense
D) silent
E) conditional
A) spontaneous
B) induced
C) nonsense
D) silent
E) conditional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which disease would be most difficult to detect with standard pedigree analysis?
A) A multifactorial disease
B) A disease caused by a recessive loss-of-function point mutation
C) A disease caused by a missense mutation
D) A disease caused by a dominant gain-of-function point mutation
E) A disease caused by a base deletion
A) A multifactorial disease
B) A disease caused by a recessive loss-of-function point mutation
C) A disease caused by a missense mutation
D) A disease caused by a dominant gain-of-function point mutation
E) A disease caused by a base deletion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Nitrites, a human-made preservative for meats, and aflatoxin, a natural product produced by the mold Aspergillus, are similar in that
A) they are converted by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum into a mutagenic substance.
B) they readily lose an amine group to form a unique nitrogenous base.
C) their unmethylated cytosine loses its amino group to form uracil.
D) their thymine bases form covalent bonds with adjacent bases.
E) ultraviolet light distorts their DNA double helix, which interferes with replication.
A) they are converted by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum into a mutagenic substance.
B) they readily lose an amine group to form a unique nitrogenous base.
C) their unmethylated cytosine loses its amino group to form uracil.
D) their thymine bases form covalent bonds with adjacent bases.
E) ultraviolet light distorts their DNA double helix, which interferes with replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A disease that manifests itself in symptoms of neurodegeneration is passed down from generation to generation in a manner consistent with an autosomal dominant mutation.The symptoms tend to get worse in subsequent generations, with individuals showing symptoms at progressively earlier ages than their afflicted parents.What is the most reasonable hypothesis consistent with all of these facts?
A) The mutation is due to a reciprocal translocation.
B) The disease is due to many different mutations.
C) The mutated gene contains an expanding triplet repeat.
D) The mutated gene is a dominant loss-of-function mutation.
E) The mutation is due to an insertion of a transposon.
A) The mutation is due to a reciprocal translocation.
B) The disease is due to many different mutations.
C) The mutated gene contains an expanding triplet repeat.
D) The mutated gene is a dominant loss-of-function mutation.
E) The mutation is due to an insertion of a transposon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Individuals with PKU tend to have high levels of _______ in their blood because they have an inactive variant of an _______.
A) tyrosine; enzyme
B) tyrosine; oxygen transport protein
C) phenylpyruvic acid; enzyme
D) phenylpyruvic acid; oxygen transport protein
E) hemoglobin; oxygen transport protein
A) tyrosine; enzyme
B) tyrosine; oxygen transport protein
C) phenylpyruvic acid; enzyme
D) phenylpyruvic acid; oxygen transport protein
E) hemoglobin; oxygen transport protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The phenotypic effects of Duchenne muscle dystrophy vary considerably.This variation is explained largely by
A) how much of the dystrophin gene is deleted.
B) how much of the dystrophin gene is duplicated.
C) which chromosome the dystrophin gene is translocated to.
D) which point mutation is involved.
E) how many trinucleotide repeats are in the mutated gene.
A) how much of the dystrophin gene is deleted.
B) how much of the dystrophin gene is duplicated.
C) which chromosome the dystrophin gene is translocated to.
D) which point mutation is involved.
E) how many trinucleotide repeats are in the mutated gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which condition most likely leads to mutations that can be observed in a karyotype (a direct examination of an individual's chromosomes)?
A) Errors caused by DNA polymerase
B) Tautomer changes of nucleotides
C) Deamination of nucleotides
D) Nondisjunction
E) Modifications of nucleotides
A) Errors caused by DNA polymerase
B) Tautomer changes of nucleotides
C) Deamination of nucleotides
D) Nondisjunction
E) Modifications of nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which type of mutation involves two different nonhomologous chromosomes?
A) Inversions
B) Translocations
C) Duplications
D) Reversions
E) Transversions
A) Inversions
B) Translocations
C) Duplications
D) Reversions
E) Transversions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which type of variation would be most detectable by gel electrophoresis if the differences in the DNA were between two recognition sites for a restriction enzyme?
A) SNPs
B) PCRs
C) HMRs
D) STRs
E) Transitions
A) SNPs
B) PCRs
C) HMRs
D) STRs
E) Transitions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose restriction enzyme A makes two cuts in a linear DNA fragment and restriction enzyme B makes one cut in that same DNA.The cuts are not in the same place, and no two of the cut fragments is exactly the same size.The digested samples are run in an electrophoresis gel.How many bands should the gel pick up if only enzyme A is used in the restriction digest?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
E) Six
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
E) Six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the figure. 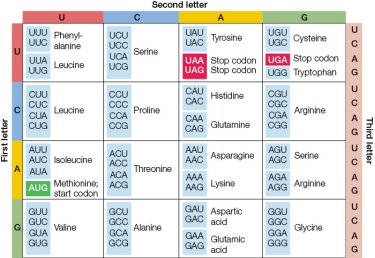 The restriction enzyme EcoR1 recognizes the palindromic sequence of GAATTC.You know the sequence of a protein but not the DNA sequence.You would like to have an idea about where in the gene there could be EcoR1 active sites.Which two consecutive amino acids could have nucleotide codons that would generate an EcoR1 active site in the DNA sequence?
The restriction enzyme EcoR1 recognizes the palindromic sequence of GAATTC.You know the sequence of a protein but not the DNA sequence.You would like to have an idea about where in the gene there could be EcoR1 active sites.Which two consecutive amino acids could have nucleotide codons that would generate an EcoR1 active site in the DNA sequence?
A) Alanine and aspartic acid
B) Glutamic acid and phenylalanine
C) Aspartic acid and phenylalanine
D) Leucine and lysine
E) Lysine and leucine
 The restriction enzyme EcoR1 recognizes the palindromic sequence of GAATTC.You know the sequence of a protein but not the DNA sequence.You would like to have an idea about where in the gene there could be EcoR1 active sites.Which two consecutive amino acids could have nucleotide codons that would generate an EcoR1 active site in the DNA sequence?
The restriction enzyme EcoR1 recognizes the palindromic sequence of GAATTC.You know the sequence of a protein but not the DNA sequence.You would like to have an idea about where in the gene there could be EcoR1 active sites.Which two consecutive amino acids could have nucleotide codons that would generate an EcoR1 active site in the DNA sequence?A) Alanine and aspartic acid
B) Glutamic acid and phenylalanine
C) Aspartic acid and phenylalanine
D) Leucine and lysine
E) Lysine and leucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement regarding short tandem repeats (STRs) is false?
A) STRs are inherited.
B) STRs are usually the result of a single nucleotide base mutation.
C) The FBI uses STR loci in its database to solve crimes.
D) STRs were used to confirm the identity of Osama bin Laden.
E) DNA fingerprinting in the United States usually involves STR analysis.
A) STRs are inherited.
B) STRs are usually the result of a single nucleotide base mutation.
C) The FBI uses STR loci in its database to solve crimes.
D) STRs were used to confirm the identity of Osama bin Laden.
E) DNA fingerprinting in the United States usually involves STR analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a gel electrophoresis experiment, researchers notice that one DNA band on the gel appears much darker than the others.The DNA fragment forming the band is most likely _______ than the others.
A) a shorter fragment
B) a longer fragment
C) more negatively charged
D) less negatively charged
E) more abundant
A) a shorter fragment
B) a longer fragment
C) more negatively charged
D) less negatively charged
E) more abundant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The "P" in SNP stands for
A) protein.
B) particle.
C) piece.
D) precipitate.
E) polymorphism.
A) protein.
B) particle.
C) piece.
D) precipitate.
E) polymorphism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which DNA sequence forms a palindromic sequence?
A) GTCCCG
B) GTACGC
C) TACG
D) TACT
E) ACGT
A) GTCCCG
B) GTACGC
C) TACG
D) TACT
E) ACGT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which statement is not one of the reasons that STRs can be used for DNA fingerprinting?
A) There are many alleles per locus.
B) Many loci can be tested.
C) STR analysis methods can take advantage of PCR technology.
D) Variants of STR loci can be easily analyzed with gel electrophoresis.
E) All of the above make STRs an effective method of DNA fingerprinting.
A) There are many alleles per locus.
B) Many loci can be tested.
C) STR analysis methods can take advantage of PCR technology.
D) Variants of STR loci can be easily analyzed with gel electrophoresis.
E) All of the above make STRs an effective method of DNA fingerprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which mutation would result in a SNP?
A) A transition
B) A deletion
C) An inversion
D) A duplication
E) A translocation
A) A transition
B) A deletion
C) An inversion
D) A duplication
E) A translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A restriction enzyme cuts a 25,700 bp segment of DNA into three fragments: fragment A is 5,800 bp; fragment B is 6,600 bp; and fragment C is _______ bp.Fragment _______ will move the farthest in an electrophoresis gel.
A) 12,400; A
B) 12,400; C
C) 13,300; A
D) 13,300; C
E) 19,900; C
A) 12,400; A
B) 12,400; C
C) 13,300; A
D) 13,300; C
E) 19,900; C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Multifactorial (complex) diseases
A) are less common than single-gene diseases.
B) involve the interaction of many genes with the environment.
C) affect less than 1 percent of humans.
D) involve the interactions of several mRNAs.
E) are exemplified by sickle-cell disease.
A) are less common than single-gene diseases.
B) involve the interaction of many genes with the environment.
C) affect less than 1 percent of humans.
D) involve the interactions of several mRNAs.
E) are exemplified by sickle-cell disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Bacteria add _______ to their DNA to protect it from their own restriction enzymes.
A) phenyl groups
B) carboxyl groups
C) methyl groups
D) uracil
E) enzymes
A) phenyl groups
B) carboxyl groups
C) methyl groups
D) uracil
E) enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Because DNA has a _______ charge, it moves to the _______ end of the field in gel electrophoresis.The _______ DNA molecules migrate the most quickly.
A) positive; positive; smaller
B) positive; positive; larger
C) positive; negative; smaller
D) negative; positive; larger
E) negative; positive; smaller
A) positive; positive; smaller
B) positive; positive; larger
C) positive; negative; smaller
D) negative; positive; larger
E) negative; positive; smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose restriction enzyme A makes two cuts in a linear DNA fragment and restriction enzyme B makes one cut in that same DNA.The cuts are not in the same place, and no two of the cut fragments is exactly the same size.The digested samples are run in an electrophoresis gel.How many bands should the gel pick up if both enzymes A and B are used in the restriction digest?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
E) Six
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
E) Six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a DNA electrophoresis procedure, a geneticist will most likely use a longer-than-usual gel matrix and allow the procedure to proceed for a longer length of time than usual when
A) there is very little genetic material.
B) the DNA is negatively charged.
C) the DNA is positively charged.
D) the fragments are fairly similar in size.
E) the DNA has been cut by restriction enzymes.
A) there is very little genetic material.
B) the DNA is negatively charged.
C) the DNA is positively charged.
D) the fragments are fairly similar in size.
E) the DNA has been cut by restriction enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which DNA sequence would most likely be recognized by a restriction enzyme? (Note: Only the coding strand is shown.)
A) AGTCGA
B) GTCTGA
C) TAAGGT
D) TAGCTA
E) TCGTGGA
A) AGTCGA
B) GTCTGA
C) TAAGGT
D) TAGCTA
E) TCGTGGA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which enzyme is used by bacteria as a defense against bacteriophage?
A) Restriction enzyme (or restriction endonuclease)
B) Reverse transcriptase
C) Phosphofructokinase
D) DNA polymerase
E) DNA ligase
A) Restriction enzyme (or restriction endonuclease)
B) Reverse transcriptase
C) Phosphofructokinase
D) DNA polymerase
E) DNA ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a gel electrophoresis experiment, researchers notice that one band has migrated much farther on the gel than the others.They conclude that it is _______ than the others.
A) a shorter fragment
B) a longer fragment
C) more negatively charged
D) less negatively charged
E) more abundant
A) a shorter fragment
B) a longer fragment
C) more negatively charged
D) less negatively charged
E) more abundant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which technique usually requires pedigree information?
A) DNA fingerprinting
B) DNA linkage analysis
C) DNA sequencing
D) Gel electrophoresis
E) Genetic screening
A) DNA fingerprinting
B) DNA linkage analysis
C) DNA sequencing
D) Gel electrophoresis
E) Genetic screening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The research area of molecular genetics is bolstered by DNA sequencing for all of the following reasons except
A) DNA sequencing technologies are continually improving.
B) the entire genomes of many organisms have been sequenced.
C) the genomes of closely related organisms have been sequenced.
D) it is now routinely used in medical diagnosis.
E) it can identify DNA changes that affect a protein's function.
A) DNA sequencing technologies are continually improving.
B) the entire genomes of many organisms have been sequenced.
C) the genomes of closely related organisms have been sequenced.
D) it is now routinely used in medical diagnosis.
E) it can identify DNA changes that affect a protein's function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The standard test for PKU examines the _______ in the blood of newborns.
A) concentration of phenylalanine
B) concentration of tyrosine
C) presence of the enzyme PAH
D) presence of ketones
E) presence of antibodies
A) concentration of phenylalanine
B) concentration of tyrosine
C) presence of the enzyme PAH
D) presence of ketones
E) presence of antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Abnormal genes are detected most accurately by examining
A) enzymes.
B) the substrate levels of enzymes.
C) the levels of enzyme products.
D) mRNA concentrations.
E) DNA.
A) enzymes.
B) the substrate levels of enzymes.
C) the levels of enzyme products.
D) mRNA concentrations.
E) DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One parent is heterozygous for a certain known disease and is unaffected.The other parent is homozygous normal.Under which circumstance would DNA testing be of value for their newborn son to ensure he does not suffer complications due to the disease?
A) The disease is PKU.
B) The disease is metabolic.
C) The disease is neurological.
D) The disease is X-linked.
E) The disease is autosomal.
A) The disease is PKU.
B) The disease is metabolic.
C) The disease is neurological.
D) The disease is X-linked.
E) The disease is autosomal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A child complains of dizziness and sporadic pain in his joints.Because sickle-cell anemia runs in the family, his doctor tests for the _______ of the disorder via a blood smear, which reveals a low red blood cell count and fragmented red blood cells.To confirm the _______ of the disorder, the doctor orders a DNA sequencing test of hemoglobin.
A) genotype; metabolism
B) phenotype; genotype
C) metabolism; phenotype
D) genotype; severity
E) phenotype; severity
A) genotype; metabolism
B) phenotype; genotype
C) metabolism; phenotype
D) genotype; severity
E) phenotype; severity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Genetic diagnosis by DNA fingerprinting
A) detects only mutant and abnormal alleles.
B) can be done only on eggs or sperm.
C) involves hybridization to rRNA.
D) uses restriction enzymes and a polymorphic restriction site.
E) cannot be done with PCR.
A) detects only mutant and abnormal alleles.
B) can be done only on eggs or sperm.
C) involves hybridization to rRNA.
D) uses restriction enzymes and a polymorphic restriction site.
E) cannot be done with PCR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following techniques involves the manipulation of single-stranded DNA?
A) Restriction digestion
B) Allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization
C) Gel electrophoresis
D) PCR amplification
E) DNA linkage analysis
A) Restriction digestion
B) Allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization
C) Gel electrophoresis
D) PCR amplification
E) DNA linkage analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
To test an individual's genotype for the sickle-cell mutation, a _______ test would use a probe for normal hemoglobin and a probe for the sickle-cell mutation.
A) linkage analysis
B) PCR amplification
C) allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization
D) genetic marker
E) DNA fingerprinting
A) linkage analysis
B) PCR amplification
C) allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization
D) genetic marker
E) DNA fingerprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following treatments involves restricting the substrate?
A) Use of statin drugs to reduce cholesterol
B) Giving children with PKU Lofenalac instead of formula
C) Germ line gene therapy
D) Somatic cell gene therapy
E) Providing individuals with glutamate decarboxylase
A) Use of statin drugs to reduce cholesterol
B) Giving children with PKU Lofenalac instead of formula
C) Germ line gene therapy
D) Somatic cell gene therapy
E) Providing individuals with glutamate decarboxylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Ingesting which of the following foods would be dangerous for a child with PKU?
A) Fruit
B) Vegetables
C) Cane sugar
D) Chicken
E) Berries
A) Fruit
B) Vegetables
C) Cane sugar
D) Chicken
E) Berries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Prenatal screening for PKU usually involves examining
A) RNA.
B) an enzyme substrate.
C) the product of an enzyme.
D) DNA.
E) an enzyme.
A) RNA.
B) an enzyme substrate.
C) the product of an enzyme.
D) DNA.
E) an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Phenylketonuria (PKU) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are both molecular diseases that are caused by mutations in particular genes, yet PKU is easier to treat than muscular dystrophy.Why?
A) PKU can be treated through ingesting the substrate.
B) PKU is a mild condition.
C) DMD is caused by a dysfunctional enzyme.
D) DMD is caused by a somatic mutation.
E) PKU can be treated by restriction of the substrate.
A) PKU can be treated through ingesting the substrate.
B) PKU is a mild condition.
C) DMD is caused by a dysfunctional enzyme.
D) DMD is caused by a somatic mutation.
E) PKU can be treated by restriction of the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure. 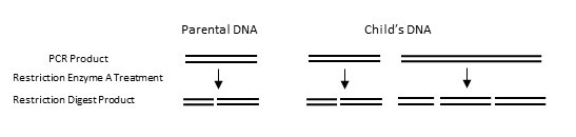 Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.From this information one can infer that one of the child's alleles probably has one or more _______ mutation(s).
Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.From this information one can infer that one of the child's alleles probably has one or more _______ mutation(s).
A) nonsense
B) missense
C) deletion
D) duplication
E) reversion
 Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.From this information one can infer that one of the child's alleles probably has one or more _______ mutation(s).
Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.From this information one can infer that one of the child's alleles probably has one or more _______ mutation(s).A) nonsense
B) missense
C) deletion
D) duplication
E) reversion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Inborn errors of metabolism are more frequently encountered in highly consanguineous populations.To identify all mutations in the known genes responsible for a group of metabolic disorders that were common in such a population, researchers first established a pedigree of afflicted families, _______ the genes involved, then sequenced the products.
A) linkage analyzed
B) DNA fingerprinted
C) gel electrophoresed
D) annealed
E) PCR amplified
A) linkage analyzed
B) DNA fingerprinted
C) gel electrophoresed
D) annealed
E) PCR amplified

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A woman whose mother has Huntington's disease is concerned that she may also have the disease, even though she is currently asymptomatic.She can get this information from
A) DNA fingerprinting.
B) linkage analysis.
C) SNP analysis.
D) genetic screening.
E) pedigree analysis.
A) DNA fingerprinting.
B) linkage analysis.
C) SNP analysis.
D) genetic screening.
E) pedigree analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that the DNA change associated with a cholesterol metabolism disease is discovered and this discovery leads to the identification of the causative enzyme.This process would be an example of
A) linkage analysis.
B) genetic screening.
C) DNA analysis.
D) DNA fingerprinting.
E) protein fingerprinting.
A) linkage analysis.
B) genetic screening.
C) DNA analysis.
D) DNA fingerprinting.
E) protein fingerprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fetuses with PKU usually are _______ because the mother's blood _______.
A) symptom free; has the enzyme to metabolize phenylalanine
B) afflicted with the disease; is lacking in tyrosine
C) afflicted with the disease; has the enzyme to metabolize phenylalanine
D) symptom-free; is rich in phenylalanine
E) afflicted with the disease; is rich in phenylalanine
A) symptom free; has the enzyme to metabolize phenylalanine
B) afflicted with the disease; is lacking in tyrosine
C) afflicted with the disease; has the enzyme to metabolize phenylalanine
D) symptom-free; is rich in phenylalanine
E) afflicted with the disease; is rich in phenylalanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A child born of parents heterozygous for sickle-cell disease is screened at birth for the disease and is diagnosed as heterozygous by allele-specific oligonucleotide screening based on the genotypes of the parents.Thus, it is an unpleasant surprise when the child exhibits the symptoms of a homozygous individual.The doctor concludes that the screening test failed to pick up the second abnormal HBB allele due to a _______ mutation.DNA sequencing later reveals a de novo loss-of-function mutation elsewhere in the HBB gene.
A) somatic
B) point
C) silent
D) reversion
E) induced
A) somatic
B) point
C) silent
D) reversion
E) induced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A child is diagnosed with a novel metabolic disease.In an interview with the parents, the clinician learns that the symptoms exhibited by the child are commonly found within the extended family.The clinician is able to obtain blood samples from all of the afflicted members of the extended family, as well as multiple unafflicted members.Which technique would be most appropriate to identify the gene of interest?
A) Linkage analysis
B) Genetic screening
C) DNA sequencing
D) DNA fingerprinting
E) Protein fingerprinting
A) Linkage analysis
B) Genetic screening
C) DNA sequencing
D) DNA fingerprinting
E) Protein fingerprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A couple plans to have children.Since breast cancer has occurred on both sides of the family, they are concerned about their BRCA1 status and decide to have their genomes sequenced.With the guidance of a genetic counselor, they evaluate the results and are relieved to find that neither carries a BRCA1 allele associated with increased incidence of breast and ovarian cancer.However, they are upset to discover that they are both heterozygous for the gene that causes tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) deficiency, also known as hypophosphatasia.This disease affects osteoblasts and chondrocytes and results in impaired bone mineralization.One of the prospective parents carries a mutation associated with the severe form, which results in fatality not long after birth.Which test could ensure that the mother does not become pregnant with a fetus homozygous for hypophosphatasia?
A) Prenatal screening
B) Postnatal screening
C) Amniocentesis
D) Chorionic villus sampling
E) Preimplantation screening
A) Prenatal screening
B) Postnatal screening
C) Amniocentesis
D) Chorionic villus sampling
E) Preimplantation screening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the figure. 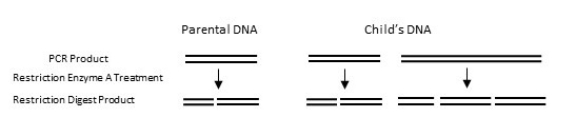 Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.What technique should the researcher next use to identify the nature of the mutation with certainty?
Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.What technique should the researcher next use to identify the nature of the mutation with certainty?
A) DNA fingerprinting
B) DNA linkage analysis
C) DNA sequencing
D) Gel electrophoresis
E) Genetic screening
 Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.What technique should the researcher next use to identify the nature of the mutation with certainty?
Through the use of linkage analysis, a researcher has identified a candidate gene responsible for a novel neurological disease.To obtain enough sample for DNA fingerprinting, the researcher uses PCR to amplify the gene.From the parent's DNA, PCR amplifies one band.From the child's DNA, the same size band plus a second larger band is amplified.Based on the published sequence of the gene, the researcher knows that restriction enzyme A will cut the wild-type allele into two fragments.The fragment sizes identified by DNA gel electrophoresis are shown in the figure.What technique should the researcher next use to identify the nature of the mutation with certainty?A) DNA fingerprinting
B) DNA linkage analysis
C) DNA sequencing
D) Gel electrophoresis
E) Genetic screening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



