Deck 14: From Dna to Protein: Gene Expression
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/252
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: From Dna to Protein: Gene Expression
1
In eukaryotic cells, translation occurs in the _______ and transcription occurs _______.
A) nucleus; in the nucleus
B) nucleus; in the cytoplasm
C) cytoplasm; in the nucleus
D) nucleus; outside of the cell
E) cytoplasm; outside of the cell
A) nucleus; in the nucleus
B) nucleus; in the cytoplasm
C) cytoplasm; in the nucleus
D) nucleus; outside of the cell
E) cytoplasm; outside of the cell
C
2
The gene for the reverse transcriptase enzyme, which is used to reverse transcribe viral RNA into DNA in infected cells, is found in the
A) host cell genome.
B) bacterial plasmid genome.
C) mitochondrial genome.
D) genome of retroviruses.
E) genome of DNA viruses.
A) host cell genome.
B) bacterial plasmid genome.
C) mitochondrial genome.
D) genome of retroviruses.
E) genome of DNA viruses.
D
3
The transfer of information from DNA to RNA occurs during _______, while the transfer of information from RNA to protein occurs during _______.
A) translation; transcription
B) translation; elongation
C) translation; transfection
D) transcription; translation
E) transcription; transfection
A) translation; transcription
B) translation; elongation
C) translation; transfection
D) transcription; translation
E) transcription; transfection
D
4
Which statement does not support Garrod's hypothesis that inborn errors of metabolism cause disease?
A) The disease PKU is due to failure to produce a functional variant of an enzyme.
B) A blood disease is due to a recessive allele in a single gene.
C) A neurological disease is due to a dominant allele in a single gene.
D) Multiple genes contribute to the likelihood that a person will develop coronary heart disease.
E) Supplying a patient with a missing enzyme can alleviate the symptoms of a metabolic disease.
A) The disease PKU is due to failure to produce a functional variant of an enzyme.
B) A blood disease is due to a recessive allele in a single gene.
C) A neurological disease is due to a dominant allele in a single gene.
D) Multiple genes contribute to the likelihood that a person will develop coronary heart disease.
E) Supplying a patient with a missing enzyme can alleviate the symptoms of a metabolic disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
People with alkaptonuria are usually placed on diets limited in tyrosine because
A) they lack the enzyme that breaks down tyrosine.
B) they lack the enzyme that breaks down a by-product of tyrosine metabolism.
C) due to a difference in one of their enzymes, they produce too much tyrosine.
D) tyrosine alters their enzymes, causing them not to be able to break down homogentisic acid.
E) tyrosine alters their enzymes, causing them to produce too little homogentisic acid.
A) they lack the enzyme that breaks down tyrosine.
B) they lack the enzyme that breaks down a by-product of tyrosine metabolism.
C) due to a difference in one of their enzymes, they produce too much tyrosine.
D) tyrosine alters their enzymes, causing them not to be able to break down homogentisic acid.
E) tyrosine alters their enzymes, causing them to produce too little homogentisic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that a certain wild-type bacteria can synthesize substance D, but various mutant strains cannot.We know that substance D is synthesized from substance X in a pathway that involves three intermediate substances (A, B, and C), but we do not know the order of the steps in the pathway.The table shows four different mutant strains that have been tested for their ability to grow on the various substances.The "+" means that the strain can grow on that substance.The "‒" means that the strain cannot grow on that substance. 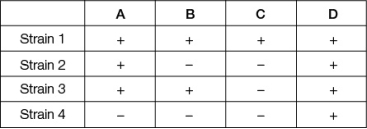 If another strain (say, strain 5) grows on substance B but does not grow on substance C, we can infer that it
If another strain (say, strain 5) grows on substance B but does not grow on substance C, we can infer that it
A) can grow on substance A.
B) cannot grow on substance A.
C) has a defect in the enzyme that converts substance B into substance C.
D) cannot grow on substance D.
E) has a defect in the enzyme that converts substance D into substance B.
 If another strain (say, strain 5) grows on substance B but does not grow on substance C, we can infer that it
If another strain (say, strain 5) grows on substance B but does not grow on substance C, we can infer that itA) can grow on substance A.
B) cannot grow on substance A.
C) has a defect in the enzyme that converts substance B into substance C.
D) cannot grow on substance D.
E) has a defect in the enzyme that converts substance D into substance B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The adaptor between mRNA and a protein is
A) tRNA.
B) a promoter.
C) RNA polymerase.
D) DNA polymerase.
E) DNA.
A) tRNA.
B) a promoter.
C) RNA polymerase.
D) DNA polymerase.
E) DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Beadle and Tatum experiment used X rays
A) to identify mutant genes.
B) as an energy source.
C) to generate mutations.
D) to accelerate metabolism.
E) as a substitute for enzymes.
A) to identify mutant genes.
B) as an energy source.
C) to generate mutations.
D) to accelerate metabolism.
E) as a substitute for enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Alkaptonuria results from a(n) _______ of _______.
A) excess; homogentisic acid
B) deficiency; homogentisic acid
C) excess; biotin
D) deficiency; biotin
E) excess; glucose
A) excess; homogentisic acid
B) deficiency; homogentisic acid
C) excess; biotin
D) deficiency; biotin
E) excess; glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which statement about the flow of genetic information is true?
A) Proteins encode information that is used to produce other proteins of the same amino acid sequence.
B) RNA encodes information that is transcribed into DNA, and DNA encodes information that is translated into proteins.
C) Proteins encode information that can be translated into RNA, and RNA encodes information that can be transcribed into DNA.
D) DNA encodes information that is transcribed into RNA, and RNA encodes information that is translated into proteins.
E) DNA encodes information that is translated directly to proteins, without any intermediaries.
A) Proteins encode information that is used to produce other proteins of the same amino acid sequence.
B) RNA encodes information that is transcribed into DNA, and DNA encodes information that is translated into proteins.
C) Proteins encode information that can be translated into RNA, and RNA encodes information that can be transcribed into DNA.
D) DNA encodes information that is transcribed into RNA, and RNA encodes information that is translated into proteins.
E) DNA encodes information that is translated directly to proteins, without any intermediaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement about RNA is false?
A) Transfer RNA functions in translation.
B) Ribosomal RNA functions in translation.
C) RNAs are produced by transcription.
D) Messenger RNAs are produced on ribosomes.
E) DNA codes for mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
A) Transfer RNA functions in translation.
B) Ribosomal RNA functions in translation.
C) RNAs are produced by transcription.
D) Messenger RNAs are produced on ribosomes.
E) DNA codes for mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The study of Neurospora mutants grown on various supplemented media supported the hypothesis that
A) arginine is a nonessential amino acid.
B) one gene encodes one enzyme.
C) genes are "on" chromosomes.
D) DNA polymerases allow mutations.
E) Neurospora is exceptionally sensitive to X rays.
A) arginine is a nonessential amino acid.
B) one gene encodes one enzyme.
C) genes are "on" chromosomes.
D) DNA polymerases allow mutations.
E) Neurospora is exceptionally sensitive to X rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Mapping studies have showed that within a group of mutants with the same growth requirements (i.e., the same overt phenotype), individual mutations are on different chromosomes.This indicates that
A) the same gene governs all the steps in a particular biological pathway.
B) different genes can govern different individual steps in the same biological pathway.
C) different genes govern the same step in a particular biological pathway.
D) all biological pathways are governed by different genes.
E) genes do not govern steps in biological pathways, but proteins do.
A) the same gene governs all the steps in a particular biological pathway.
B) different genes can govern different individual steps in the same biological pathway.
C) different genes govern the same step in a particular biological pathway.
D) all biological pathways are governed by different genes.
E) genes do not govern steps in biological pathways, but proteins do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The "central dogma of molecular biology" states that
A) information flow between DNA, RNA, and protein is reversible.
B) information flow in a cell is unidirectional, from protein to DNA.
C) information flow in a cell is unidirectional, from DNA to protein.
D) the DNA sequence of a gene can be predicted if we know the amino acid sequence of the protein it encodes.
E) the genetic code is ambiguous but not degenerate.
A) information flow between DNA, RNA, and protein is reversible.
B) information flow in a cell is unidirectional, from protein to DNA.
C) information flow in a cell is unidirectional, from DNA to protein.
D) the DNA sequence of a gene can be predicted if we know the amino acid sequence of the protein it encodes.
E) the genetic code is ambiguous but not degenerate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The study of Neurospora mutants grown on various supplemented media enabled researchers to identify single genes involved in the arginine synthesis pathway.Why was Neurospora a better model organism than a human cell line for this study?
A) Neurospora DNA is more sensitive to X rays than human DNA.
B) The arginine synthesis pathway is less complex in Neurospora.
C) Arginine is an essential amino acid in human cells.
D) All human alleles are expressed phenotypically.
E) All Neurospora alleles are expressed phenotypically.
A) Neurospora DNA is more sensitive to X rays than human DNA.
B) The arginine synthesis pathway is less complex in Neurospora.
C) Arginine is an essential amino acid in human cells.
D) All human alleles are expressed phenotypically.
E) All Neurospora alleles are expressed phenotypically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
One can argue that although the existence of retroviruses represents a complication of Crick's central dogma, it does not contradict it.The replication mechanism of retroviruses does not contradict the essence of the central dogma, because
A) retroviruses convert DNA information into RNA information.
B) retroviruses convert RNA information into RNA information.
C) even in retroviruses, information in proteins is not converted into DNA information.
D) even in retroviruses, DNA information is not converted into protein information.
E) retroviruses do not use tRNA.
A) retroviruses convert DNA information into RNA information.
B) retroviruses convert RNA information into RNA information.
C) even in retroviruses, information in proteins is not converted into DNA information.
D) even in retroviruses, DNA information is not converted into protein information.
E) retroviruses do not use tRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose that a certain wild-type bacteria can synthesize substance D, but various mutant strains cannot.We know that substance D is synthesized from substance X in a pathway that involves three intermediate substances (A, B, and C), but we do not know the order of the steps in the pathway.The table shows four different mutant strains that have been tested for their ability to grow on the various substances.The "+" means that the strain can grow on that substance.The "‒" means that the strain cannot grow on that substance. 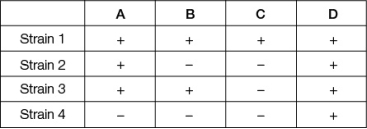 What is the most likely order of the pathway? (For example, A B C D indicates that substance A is converted to substance B, which is converted to substance C, which is converted to substance D.)
What is the most likely order of the pathway? (For example, A B C D indicates that substance A is converted to substance B, which is converted to substance C, which is converted to substance D.)
A) A B C D
B) A C B D
C) B A C D
D) C B A D
E) C A B D
 What is the most likely order of the pathway? (For example, A B C D indicates that substance A is converted to substance B, which is converted to substance C, which is converted to substance D.)
What is the most likely order of the pathway? (For example, A B C D indicates that substance A is converted to substance B, which is converted to substance C, which is converted to substance D.)A) A B C D
B) A C B D
C) B A C D
D) C B A D
E) C A B D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which molecule is used in transcription?
A) GTP
B) dATP
C) Ribosome
D) tRNA
E) DNA polymerase
A) GTP
B) dATP
C) Ribosome
D) tRNA
E) DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Geneticists would expect alkaptonuria to be _______ common when there is mating between relatives, because the condition is inherited as a _______ phenotype.
A) more; dominant
B) more; recessive
C) more; codominant
D) less; dominant
E) less; recessive
A) more; dominant
B) more; recessive
C) more; codominant
D) less; dominant
E) less; recessive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The phenotype of an organism is primarily determined by the activity of _______.
A) proteins
B) tRNA
C) mRNA
D) nucleic acids
E) rRNA
A) proteins
B) tRNA
C) mRNA
D) nucleic acids
E) rRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Humans share the same genetic code with
A) just other vertebrates.
B) just other multicellular animals.
C) just other multicellular animals and plants.
D) just other eukaryotes.
E) all living organisms, with a few exceptions.
A) just other vertebrates.
B) just other multicellular animals.
C) just other multicellular animals and plants.
D) just other eukaryotes.
E) all living organisms, with a few exceptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Compared with DNA replication, transcription is _______ error prone because of differences in _______.
A) more; the number of copies made
B) more; the proofreading system
C) more; excision repair
D) less; the number of copies made
E) less; the proofreading system
A) more; the number of copies made
B) more; the proofreading system
C) more; excision repair
D) less; the number of copies made
E) less; the proofreading system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
DNA is composed of two strands, only one of which is typically used as a template for RNA synthesis.By what mechanism is the correct strand chosen?
A) The promoter acts to direct the RNA polymerase.
B) Only one strand has a start codon.
C) Both strands are tried, and the one that works is remembered.
D) An initiation factor informs the system about which strand to use.
E) The strand chosen randomly.
A) The promoter acts to direct the RNA polymerase.
B) Only one strand has a start codon.
C) Both strands are tried, and the one that works is remembered.
D) An initiation factor informs the system about which strand to use.
E) The strand chosen randomly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If codons were read two bases at a time instead of three bases at a time, how many different possible amino acids could be specified?
A) 16
B) 64
C) 8
D) 32
E) 128
A) 16
B) 64
C) 8
D) 32
E) 128

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Imagine that a novel life-form is found deep within Earth's crust.Although its DNA is composed of the same four nucleotides as other life-forms, its codons are four bases in length.This organism could therefore be composed of _______ different amino acids.
A) 4
B) 16
C) 64
D) 128
E) 256
A) 4
B) 16
C) 64
D) 128
E) 256

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the process of transcription,
A) a DNA molecule is synthesized from an RNA template.
B) ribonucleoside triphosphates are assembled into an RNA molecule in the absence of a template.
C) an RNA molecule is synthesized from a DNA template.
D) a protein is synthesized with the use of information from a messenger RNA.
E) a single-stranded DNA molecule is replicated.
A) a DNA molecule is synthesized from an RNA template.
B) ribonucleoside triphosphates are assembled into an RNA molecule in the absence of a template.
C) an RNA molecule is synthesized from a DNA template.
D) a protein is synthesized with the use of information from a messenger RNA.
E) a single-stranded DNA molecule is replicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
_______ is not required for transcription.
A) A DNA template
B) A primer
C) Ribonucleoside triphosphate
D) RNA polymerase
E) Helicase
A) A DNA template
B) A primer
C) Ribonucleoside triphosphate
D) RNA polymerase
E) Helicase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Aside from using T instead of U, the coding strand of DNA is _______ to the mRNA.
A) identical in sequence
B) identical in sequence but antiparallel
C) complementary and parallel
D) complementary and antiparallel
E) in a random order and complementary
A) identical in sequence
B) identical in sequence but antiparallel
C) complementary and parallel
D) complementary and antiparallel
E) in a random order and complementary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The promoter region of a gene has undergone an inversion with the 3′ end break point within the initiation site.This will affect the transcription of this gene in all of the following ways except
A) the determination of the coding strand.
B) the orientation of the RNA polymerase.
C) the binding of RNA polymerase to the initiation site.
D) the separation of the double-stranded DNA.
E) the process of elongation.
A) the determination of the coding strand.
B) the orientation of the RNA polymerase.
C) the binding of RNA polymerase to the initiation site.
D) the separation of the double-stranded DNA.
E) the process of elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ coding strand of DNA is GTCTATGCATTA. Which sequence represents the resulting transcribed RNA?
A) 5ʹ-GTCTATGCATTA-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-GUCUAUGCAUUA-3ʹ
C) 5ʹ-CAGATACGTAAT-3ʹ
D) 5ʹ-CAGAUACGUAAU-3ʹ
E) 3ʹ-GUCUAUGCAUUA-5ʹ
A) 5ʹ-GTCTATGCATTA-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-GUCUAUGCAUUA-3ʹ
C) 5ʹ-CAGATACGTAAT-3ʹ
D) 5ʹ-CAGAUACGUAAU-3ʹ
E) 3ʹ-GUCUAUGCAUUA-5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A codon is _______ nucleotides long, and there are _______ different possible codons in total.
A) 2; 16
B) 2; 64
C) 3; 16
D) 3; 64
E) 4; 64
A) 2; 16
B) 2; 64
C) 3; 16
D) 3; 64
E) 4; 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If there were only three kinds of nucleotides, how many different types of codons would a genetic code have? (Assume that the codons are three nucleotides long.)
A) 9
B) 16
C) 27
D) 32
E) 64
A) 9
B) 16
C) 27
D) 32
E) 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An mRNA has the sequence 5'-AUGAAAUCCUAG-3'.What is the template DNA strand for this sequence?
A) 5'-TACTTTAGGATC-3'
B) 5'-ATGAAATCCTAG-3'
C) 5'-GATCCTAAAGTA-3'
D) 5'-TACAAATCCTAG-3'
E) 5'-CTAGGATTTCAT-3'
A) 5'-TACTTTAGGATC-3'
B) 5'-ATGAAATCCTAG-3'
C) 5'-GATCCTAAAGTA-3'
D) 5'-TACAAATCCTAG-3'
E) 5'-CTAGGATTTCAT-3'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The stop codons code for
A) no amino acid.
B) methionine.
C) glycine.
D) halt enzyme.
E) DNA binding protein.
A) no amino acid.
B) methionine.
C) glycine.
D) halt enzyme.
E) DNA binding protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose the 5ʹ-to-3ʹ coding strand of DNA is GTCTATGCATTA. What is the template DNA strand that would be used for transcription?
A) 5ʹ-GTCTATGCATTA-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-CAGATACGTAAT-3ʹ
C) 3ʹ-GTCTATGCATTA-5ʹ
D) 3ʹ-CAGATACGTAAT-5ʹ
E) 5ʹ-GUCUAUGCAUUA-3ʹ
A) 5ʹ-GTCTATGCATTA-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-CAGATACGTAAT-3ʹ
C) 3ʹ-GTCTATGCATTA-5ʹ
D) 3ʹ-CAGATACGTAAT-5ʹ
E) 5ʹ-GUCUAUGCAUUA-3ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The amino acids in proteins are encoded by _______ different codons.
A) 20
B) 23
C) 42
D) 61
E) 64
A) 20
B) 23
C) 42
D) 61
E) 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The direction of synthesis for a new mRNA molecule is _______ from a _______ template strand.
A) 5ʹ to 3ʹ; 5ʹ-to-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ to 3ʹ; 3ʹ-to-5ʹ
C) 3ʹ to 5ʹ; 5ʹ-to-3ʹ
D) 3ʹ to 5ʹ; 3ʹ-to-5ʹ
E) 5ʹ to 5ʹ; 3ʹ-to-5ʹ
A) 5ʹ to 3ʹ; 5ʹ-to-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ to 3ʹ; 3ʹ-to-5ʹ
C) 3ʹ to 5ʹ; 5ʹ-to-3ʹ
D) 3ʹ to 5ʹ; 3ʹ-to-5ʹ
E) 5ʹ to 5ʹ; 3ʹ-to-5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In prokaryotes, the region of DNA to which RNA polymerase binds most tightly is the
A) promoter.
B) poly C center.
C) enhancer.
D) operator site.
E) minor groove.
A) promoter.
B) poly C center.
C) enhancer.
D) operator site.
E) minor groove.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Greater numbers of base changes are found in mRNA than in replicated DNA from the same gene sequence, because RNA polymerase
A) does not proofread.
B) uses UTP instead of thymidine triphosphate (TTP).
C) uses only one strand as its template.
D) is not processive.
E) catalyzes the addition of nucleotides in the 3′-to-5′ direction.
A) does not proofread.
B) uses UTP instead of thymidine triphosphate (TTP).
C) uses only one strand as its template.
D) is not processive.
E) catalyzes the addition of nucleotides in the 3′-to-5′ direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An example of an ambiguous genetic code is one
A) with 61 codons for 20 amino acids.
B) in which UUU and UUA both code for phenylalanine.
C) in which CCU could code for either alanine or leucine.
D) in which some codons do not code for amino acids.
E) in which CCU and UUA both code for phenylalanine.
A) with 61 codons for 20 amino acids.
B) in which UUU and UUA both code for phenylalanine.
C) in which CCU could code for either alanine or leucine.
D) in which some codons do not code for amino acids.
E) in which CCU and UUA both code for phenylalanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The binding of snRNPs to consensus sequences is necessary for
A) gene duplication.
B) the addition of a poly A tail.
C) the capping of mRNA.
D) transcription.
E) RNA splicing.
A) gene duplication.
B) the addition of a poly A tail.
C) the capping of mRNA.
D) transcription.
E) RNA splicing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose the DNA of a gene contains five regions-A, B, C, D, and E, in that order.Regions A, B, and D are located in introns, while regions C and E are located in exons.What is the order of the regions in the mature mRNA transcribed from that sequence?
A) CE
B) ABD
C) BAD
D) ABDCE
E) ABCDE
A) CE
B) ABD
C) BAD
D) ABDCE
E) ABCDE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a mutation occurs such that splicing does not remove one of the introns in a gene, what effect will this have on the protein encoded by that gene?
A) It will have no effect; the gene will be transcribed and translated into protein.
B) Transcription will terminate early, and the protein will not be made.
C) Transcription will continue, but translation will stop at the site where the intron remains.
D) Translation will continue, but it is likely that a nonfunctional or aberrant protein will be made.
E) Translation will and will skip the intron sequence.
A) It will have no effect; the gene will be transcribed and translated into protein.
B) Transcription will terminate early, and the protein will not be made.
C) Transcription will continue, but translation will stop at the site where the intron remains.
D) Translation will continue, but it is likely that a nonfunctional or aberrant protein will be made.
E) Translation will and will skip the intron sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Exons are
A) spliced out of the original transcript.
B) spliced together from the original transcript.
C) spliced to introns to form the final transcript.
D) much larger than introns.
E) larger than the original coding region.
A) spliced out of the original transcript.
B) spliced together from the original transcript.
C) spliced to introns to form the final transcript.
D) much larger than introns.
E) larger than the original coding region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose that the coding region of a gene contains 1,800 base pairs, with 570 in exon 1, with 420 in exon 2, and with 810 in exon 3 (not counting the stop codon).A protein in a splice variant of this gene in which exon 2 was spliced out would be composed of _______ amino acids.
A) 149
B) 190
C) 457
D) 463
E) 1,380
A) 149
B) 190
C) 457
D) 463
E) 1,380

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which event must occur before eukaryotic mRNA is transcribed?
A) Binding of a transcription factor to the promoter
B) Capping of the 5' end
C) Addition of a poly A tail to the 3'end
D) Splicing out of the introns
E) Transport to the cytosol
A) Binding of a transcription factor to the promoter
B) Capping of the 5' end
C) Addition of a poly A tail to the 3'end
D) Splicing out of the introns
E) Transport to the cytosol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose that nucleic acid hybridization experiments revealed that the mRNA-DNA complexes form different loop patterns depending on which cell type is the source of the mRNA.Such data would support
A) the one-gene, one-polypeptide hypothesis.
B) the conclusion that the genetic code is redundant but not ambiguous.
C) the conclusion that the genetic code is ambiguous but not redundant.
D) the existence of alternative splicing.
E) the conclusion that the genetic code is not universal.
A) the one-gene, one-polypeptide hypothesis.
B) the conclusion that the genetic code is redundant but not ambiguous.
C) the conclusion that the genetic code is ambiguous but not redundant.
D) the existence of alternative splicing.
E) the conclusion that the genetic code is not universal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the figure. 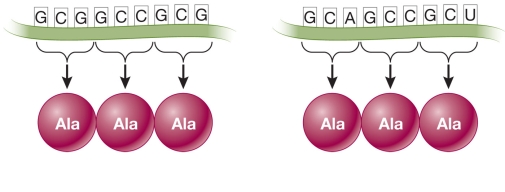 If the base inosine is available, the smallest number of hypothetically possible tRNAs that could be used to translate these two sequences would be
If the base inosine is available, the smallest number of hypothetically possible tRNAs that could be used to translate these two sequences would be
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.
 If the base inosine is available, the smallest number of hypothetically possible tRNAs that could be used to translate these two sequences would be
If the base inosine is available, the smallest number of hypothetically possible tRNAs that could be used to translate these two sequences would beA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The regions of DNA in a eukaryotic gene that contain noncoding base sequences are called
A) enhancers.
B) mRNAs.
C) hnRNAs.
D) leader sequences.
E) introns.
A) enhancers.
B) mRNAs.
C) hnRNAs.
D) leader sequences.
E) introns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a nucleic acid hybridization experiment performed to detect exons, an appropriate probe would be
A) single-stranded DNA.
B) double-stranded DNA.
C) triple-stranded DNA.
D) single-stranded RNA.
E) double-stranded RNA.
A) single-stranded DNA.
B) double-stranded DNA.
C) triple-stranded DNA.
D) single-stranded RNA.
E) double-stranded RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The guanosine triphosphate (GTP) cap that is added to the 5ʹ end of primary mRNA
A) contains all the coding and noncoding sequences of the DNA template.
B) provides the mRNA molecule with a poly A tail.
C) helps transfer amino acids to the ribosomes.
D) forms hydrogen bonds with the polymerase.
E) facilitates the binding of mRNA to ribosomes.
A) contains all the coding and noncoding sequences of the DNA template.
B) provides the mRNA molecule with a poly A tail.
C) helps transfer amino acids to the ribosomes.
D) forms hydrogen bonds with the polymerase.
E) facilitates the binding of mRNA to ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The difference between mRNA and tRNA is that
A) tRNA has a more elaborate three-dimensional structure.
B) tRNA is usually much larger than mRNA.
C) mRNA is composed from only one strand of RNA.
D) tRNA is located in the cytoplasm.
E) mRNA is composed of ribonucleic acids.
A) tRNA has a more elaborate three-dimensional structure.
B) tRNA is usually much larger than mRNA.
C) mRNA is composed from only one strand of RNA.
D) tRNA is located in the cytoplasm.
E) mRNA is composed of ribonucleic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose that the coding region of a gene contains 1,800 base pairs, with 570 in exon 1, with 420 in exon 2, and with 810 in exon 3 (not counting the stop codon).The protein translated from this gene will consist of _______ amino acids.
A) 190
B) 597
C) 600
D) 819
E) 1,800
A) 190
B) 597
C) 600
D) 819
E) 1,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the DNA of a gene contains five regions-A, B, C, D, and E, in that order.Regions A, B, and D are located in introns, while regions C and E are located in exons.What is the order of the regions in the pre-mRNA transcribed from that sequence?
A) CE
B) ABD
C) BAD
D) ABDCE
E) ABCDE
A) CE
B) ABD
C) BAD
D) ABDCE
E) ABCDE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a strand of mRNA has the sequence 5ʹ-CUGUCA...ACUC-3ʹ (with […] representing the intervening sequence), what was the template strand of DNA used to produce this mRNA?
A) 5ʹ-CUGUCA...ACUC-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-CTGTCA...ACTC-3ʹ
C) 3ʹ-CTGTCA...ACTC-5ʹ
D) 3ʹ-GACAGU...UGAG-5ʹ
E) 3ʹ-GACAGT...TGAG-5ʹ
A) 5ʹ-CUGUCA...ACUC-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-CTGTCA...ACTC-3ʹ
C) 3ʹ-CTGTCA...ACTC-5ʹ
D) 3ʹ-GACAGU...UGAG-5ʹ
E) 3ʹ-GACAGT...TGAG-5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An individual has a metabolic disease that is traced to one nonfunctional enzyme.Protein analysis reveals that the protein is larger than normal and fails to assemble into the proper tertiary structure.Analysis of the gene sequence will most likely reveal that the mutation
A) disrupts the signal sequence.
B) disrupts the initiation site.
C) disrupts a splice site.
D) is within an intron.
E) is silent.
A) disrupts the signal sequence.
B) disrupts the initiation site.
C) disrupts a splice site.
D) is within an intron.
E) is silent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The poly A tail added to pre-mRNA
A) is coded for by DNA.
B) increases mRNA stability.
C) reduces mRNA stability.
D) is attached to its 5ʹ end.
E) allows it to be reverse transcribed.
A) is coded for by DNA.
B) increases mRNA stability.
C) reduces mRNA stability.
D) is attached to its 5ʹ end.
E) allows it to be reverse transcribed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the following synthetic RNA were added to a test tube containing all the components necessary for protein translation to occur, what would the amino acid sequence be? 5'-AUAUAUAUAUAU-3'
A) Polyphenylalanine
B) Isoleucine-tyrosine-isoleucine-tyrosine
C) Isoleucine-isoleucine-isoleucine-isoleucine
D) Tyrosine-tyrosine-tyrosine-tyrosine
E) Asparagine-asparagine-asparagine-asparagine
A) Polyphenylalanine
B) Isoleucine-tyrosine-isoleucine-tyrosine
C) Isoleucine-isoleucine-isoleucine-isoleucine
D) Tyrosine-tyrosine-tyrosine-tyrosine
E) Asparagine-asparagine-asparagine-asparagine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consensus sequences (short segments of DNA) appear in the boundaries between introns and exons of various genes.These sequences appear to be involved in
A) directing the polymerases to the appropriate place on the DNA for transcription to begin.
B) the splicing of introns out of the RNA.
C) allowing the transcription to stop at the appropriate spot.
D) catalyzing the synthesis of a protein.
E) a proofreading mechanism that minimizes errors.
A) directing the polymerases to the appropriate place on the DNA for transcription to begin.
B) the splicing of introns out of the RNA.
C) allowing the transcription to stop at the appropriate spot.
D) catalyzing the synthesis of a protein.
E) a proofreading mechanism that minimizes errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When eukaryotic DNA is hybridized with mRNA, the hybrid molecules contain loops of DNA, which are
A) retroviruses.
B) introns.
C) exons.
D) transcripts.
E) puffs.
A) retroviruses.
B) introns.
C) exons.
D) transcripts.
E) puffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A charged tRNA travels across a ribosome from the _______ site, to the _______ site, and then to the _______ site.
A) A; E; P
B) A; P; E
C) E; P; A
D) P; E; A
E) P; A; E
A) A; E; P
B) A; P; E
C) E; P; A
D) P; E; A
E) P; A; E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Peptidyl transferase activity in ribosomes is catalyzed by
A) protein.
B) mRNA.
C) tRNA.
D) rRNA.
E) elongation factors.
A) protein.
B) mRNA.
C) tRNA.
D) rRNA.
E) elongation factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A charged tRNA has _______ attached.
A) a phosphate group
B) one or more sugar groups
C) an amino acid
D) an mRNA molecule
E) an rRNA molecule
A) a phosphate group
B) one or more sugar groups
C) an amino acid
D) an mRNA molecule
E) an rRNA molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Translation of messenger RNA into protein occurs in mRNA in a _______ direction, and the protein is built from _______ terminus to _______ terminus.
A) 3'-to-5'; N; C
B) 5'-to-3'; N; C
C) 3'-to-5'; C; N
D) 5'-to-3'; C; N
E) 3'-to-5'; C; C
A) 3'-to-5'; N; C
B) 5'-to-3'; N; C
C) 3'-to-5'; C; N
D) 5'-to-3'; C; N
E) 3'-to-5'; C; C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
At which sites on the ribosome is the tRNA never charged?
A) At the A site
B) At the P site
C) At the E site
D) At both the A and P sites
E) None of the above; the tRNA is always charged when it interacts with the ribosome.
A) At the A site
B) At the P site
C) At the E site
D) At both the A and P sites
E) None of the above; the tRNA is always charged when it interacts with the ribosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which statement about codons and anticodons is true?
A) The codon bonds covalently with the anticodon.
B) They have the same base sequences.
C) There are 64 codons and 61 anticodons.
D) Activating enzymes link codons and anticodons.
E) At contact, the codon and the anticodon are antiparallel to each other.
A) The codon bonds covalently with the anticodon.
B) They have the same base sequences.
C) There are 64 codons and 61 anticodons.
D) Activating enzymes link codons and anticodons.
E) At contact, the codon and the anticodon are antiparallel to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
tRNAs are "charged" by
A) mRNAs.
B) amino acids.
C) tRNA polymerases.
D) proteases.
E) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
A) mRNAs.
B) amino acids.
C) tRNA polymerases.
D) proteases.
E) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Ribosomes are a collection of _______ that are needed for _______.
A) small proteins; translation
B) proteins and rRNAs; translation
C) proteins and tRNAs; transcription
D) proteins and mRNAs; translation
E) mRNAs and tRNAs; translation
A) small proteins; translation
B) proteins and rRNAs; translation
C) proteins and tRNAs; transcription
D) proteins and mRNAs; translation
E) mRNAs and tRNAs; translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Based on the complexity of tRNA's function, one might conclude that the number of different tRNA molecules that exist is surprisingly small.This discrepancy is possible because
A) the third position of the codon can pair with unusual bases in the anticodon.
B) the second position of the codon can pair with unusual bases in the anticodon.
C) the third position of the codon contains unusual bases.
D) there are fewer amino acids than there are possible codons.
E) the code is ambiguous.
A) the third position of the codon can pair with unusual bases in the anticodon.
B) the second position of the codon can pair with unusual bases in the anticodon.
C) the third position of the codon contains unusual bases.
D) there are fewer amino acids than there are possible codons.
E) the code is ambiguous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the experiments by Benzer and colleagues, the cysteine in a cys-tRNA molecule was converted into alanine.Suppose, instead, that the cysteine had appeared in the synthesized protein where it normally does.The most likely conclusion would have been that the protein synthesis system
A) recognized tRNAs.
B) recognized amino acids.
C) recognized mRNAs.
D) was redundant but not ambiguous.
E) was ambiguous but not redundant.
A) recognized tRNAs.
B) recognized amino acids.
C) recognized mRNAs.
D) was redundant but not ambiguous.
E) was ambiguous but not redundant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The wobble phenomenon occurs at _______end of the anticodon and helps explain why the _______ end of the codon shows the most redundancy.
A) the 5ʹ; 3ʹ
B) the 3ʹ; 5ʹ
C) the 3ʹ; 3ʹ
D) the 5ʹ; 5ʹ
E) either; 5ʹ
A) the 5ʹ; 3ʹ
B) the 3ʹ; 5ʹ
C) the 3ʹ; 3ʹ
D) the 5ʹ; 5ʹ
E) either; 5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During translation elongation, the growing polypeptide chain moves to
A) the tRNA occupying the A site.
B) the tRNA occupying the P site.
C) the ribosomal rRNA.
D) a signal recognition particle.
E) DNA.
A) the tRNA occupying the A site.
B) the tRNA occupying the P site.
C) the ribosomal rRNA.
D) a signal recognition particle.
E) DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The anticodon 3ʹ-UAC-5ʹ will bind to which of the following codons?
A) 5ʹ-ATC-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-AUC-3ʹ
C) 5ʹ-AUG-3ʹ
D) 5ʹ-TAG-3ʹ
E) 3ʹ-AUG-5ʹ
A) 5ʹ-ATC-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-AUC-3ʹ
C) 5ʹ-AUG-3ʹ
D) 5ʹ-TAG-3ʹ
E) 3ʹ-AUG-5ʹ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How is it possible for single-stranded RNA to fold into complex shapes?
A) Phosphodiester linkages form between the phosphate and the sugar ribose.
B) Internal base pairings occur—adenine with uracil, and cytosine with guanine.
C) Uracil's methyl group binds to adenine, coiling the molecule.
D) The single strand "twists" around itself.
E) The RNA binds to proteins, creating a conformation (three-dimensional shape).
A) Phosphodiester linkages form between the phosphate and the sugar ribose.
B) Internal base pairings occur—adenine with uracil, and cytosine with guanine.
C) Uracil's methyl group binds to adenine, coiling the molecule.
D) The single strand "twists" around itself.
E) The RNA binds to proteins, creating a conformation (three-dimensional shape).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
mRNA is synthesized in the _______ direction, which corresponds to the _______ of the protein.
A) 5ʹ-to-3ʹ; N terminus to C terminus
B) 3ʹ-to-5ʹ; C terminus to N terminus
C) 5ʹ-to-3ʹ; C terminus to N terminus
D) 3ʹ-to-5ʹ; N terminus to C terminus
E) Examples of all of the above have been found.
A) 5ʹ-to-3ʹ; N terminus to C terminus
B) 3ʹ-to-5ʹ; C terminus to N terminus
C) 5ʹ-to-3ʹ; C terminus to N terminus
D) 3ʹ-to-5ʹ; N terminus to C terminus
E) Examples of all of the above have been found.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The formation of a peptide bond between an amino acid at the P site and an amino acid at the A site during translation is catalyzed by
A) the large ribosomal subunit.
B) a specialized segment of DNA.
C) a specialized segment of RNA.
D) the initiation complex.
E) initiation factors.
A) the large ribosomal subunit.
B) a specialized segment of DNA.
C) a specialized segment of RNA.
D) the initiation complex.
E) initiation factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Stop codons on mRNA
A) bind with tRNAs to stop translation.
B) code for a specific "stop" amino acid.
C) enter the A site of the ribosome.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) bind with tRNAs to stop translation.
B) code for a specific "stop" amino acid.
C) enter the A site of the ribosome.
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Peptidyl transferase is an
A) enzyme found in the nucleus of the cell that assists in the transfer of mRNA to the cytoplasm.
B) enzyme that adds the amino acid to the 3'end of the tRNA.
C) enzyme found in the large subunit of the ribosome that catalyzes the formation of the peptide bond in the growing polypeptide.
D) RNA molecule that is catalytic.
E) Both c and d
A) enzyme found in the nucleus of the cell that assists in the transfer of mRNA to the cytoplasm.
B) enzyme that adds the amino acid to the 3'end of the tRNA.
C) enzyme found in the large subunit of the ribosome that catalyzes the formation of the peptide bond in the growing polypeptide.
D) RNA molecule that is catalytic.
E) Both c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which statement about translation is false?
A) Translation is RNA-directed polypeptide synthesis.
B) An mRNA molecule can be translated by only one ribosome at a time.
C) The same genetic code operates in almost all organisms and organelles.
D) Energy is used in the formation of the bond between a tRNA and an amino acid.
E) There are both start and stop codons.
A) Translation is RNA-directed polypeptide synthesis.
B) An mRNA molecule can be translated by only one ribosome at a time.
C) The same genetic code operates in almost all organisms and organelles.
D) Energy is used in the formation of the bond between a tRNA and an amino acid.
E) There are both start and stop codons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The anticodon 3ʹ-GCI-5ʹ cannot pair with which of the following codons?
A) 5ʹ-GCA-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-GCC-3ʹ
C) 5ʹ-GCU-3ʹ
D) 5ʹ-GCG-3ʹ
E) All of the above
A) 5ʹ-GCA-3ʹ
B) 5ʹ-GCC-3ʹ
C) 5ʹ-GCU-3ʹ
D) 5ʹ-GCG-3ʹ
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



