Deck 16: Regulation of Gene Expression
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/245
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Regulation of Gene Expression
1
In comparison with regulation of the production of enzymes, allosteric regulation of enzyme activity is _______ and _______ energetically efficient.
A) faster; more
B) faster; about as
C) faster; less
D) slower; more
E) slower; less
A) faster; more
B) faster; about as
C) faster; less
D) slower; more
E) slower; less
C
2
In bacterial cells, the concentration of cAMP is _______ correlated with the concentration of glucose; hence, glucose concentrations should _______ correlated with the amount of transcription in the lac operon (assuming that lactose is abundant).
A) positively; be positively
B) positively; be inversely
C) not; not be
D) inversely; be positively
E) inversely; be inversely
A) positively; be positively
B) positively; be inversely
C) not; not be
D) inversely; be positively
E) inversely; be inversely
E
3
In E.coli metabolism, _______ is the preferred energy source because it is _______.
A) lactose; more abundant
B) lactose; easier to metabolize
C) glucose; more abundant
D) glucose; less abundant
E) glucose; easier to metabolize
A) lactose; more abundant
B) lactose; easier to metabolize
C) glucose; more abundant
D) glucose; less abundant
E) glucose; easier to metabolize
E
4
In a particular bacterial cell, β-galactosidase is at high concentrations but -galactoside permease is at very low concentrations.Which is the most likely explanation?
A) Both glucose and lactose are at high concentrations.
B) Both glucose and lactose are at low concentrations.
C) The operator has a mutation.
D) The promoter has a mutation.
E) One of the structural genes has a mutation.
A) Both glucose and lactose are at high concentrations.
B) Both glucose and lactose are at low concentrations.
C) The operator has a mutation.
D) The promoter has a mutation.
E) One of the structural genes has a mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following reflects the order of operon elements, assuming transcription is occurring from left to right?
A) Operator, promoter, structural genes
B) Operator, structural genes, promoter
C) Promoter, operator, structural genes
D) Promoter, structural genes, operator
E) Structural genes, promoter, operator
A) Operator, promoter, structural genes
B) Operator, structural genes, promoter
C) Promoter, operator, structural genes
D) Promoter, structural genes, operator
E) Structural genes, promoter, operator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A certain operon has structural genes that encode enzymes involved in the synthesis of a glycopeptide.This system is likely to be _______, and _______ will most likely bind to the operator.
A) inducible; the glycopeptide
B) inducible; one or more molecules used in the production of the glycopeptide
C) repressible; the glycopeptide
D) repressible; one or more molecules used in the production of the glycopeptide
E) repressible; no molecules
A) inducible; the glycopeptide
B) inducible; one or more molecules used in the production of the glycopeptide
C) repressible; the glycopeptide
D) repressible; one or more molecules used in the production of the glycopeptide
E) repressible; no molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To be activated, the CRP must first bind
A) the repressor molecule.
B) the repressor protein.
C) the activator protein.
D) the co-repressor molecule.
E) cAMP.
A) the repressor molecule.
B) the repressor protein.
C) the activator protein.
D) the co-repressor molecule.
E) cAMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In comparison with structural genes in bacterial operons, genes that encode for stress responses in plants
A) are located closer together on the chromosome.
B) are located farther apart on the chromosome.
C) are not coordinately regulated.
D) do not alter their expression levels in response to transcription factor binding.
E) do not respond to changes in environmental conditions.
A) are located closer together on the chromosome.
B) are located farther apart on the chromosome.
C) are not coordinately regulated.
D) do not alter their expression levels in response to transcription factor binding.
E) do not respond to changes in environmental conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A mutagenesis screen uncovers two discrete mutations, each for a single gene of a given operon that contains the genes that control a biosynthetic pathway.Which phenomenon would likely be observed in an organism that carries both of these mutations?
A) Partial linkage
B) Complete linkage
C) Epistasis
D) Recessive lethality
E) Complete dominance/recessiveness
A) Partial linkage
B) Complete linkage
C) Epistasis
D) Recessive lethality
E) Complete dominance/recessiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Actin, which is part of many cellular structures and has several functions, is produced at constant levels in nearly all cells.It is best described as a(n) _______ protein.
A) inducible
B) repressible
C) conditional
D) constitutive
E) regulated
A) inducible
B) repressible
C) conditional
D) constitutive
E) regulated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a carrier protein?
A) Lactose
B) β-galactoside
C) β-galactoside permease
D) β-galactoside transacetylase
E) Glucose
A) Lactose
B) β-galactoside
C) β-galactoside permease
D) β-galactoside transacetylase
E) Glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the figure showing the potential points for the regulation of gene expression. 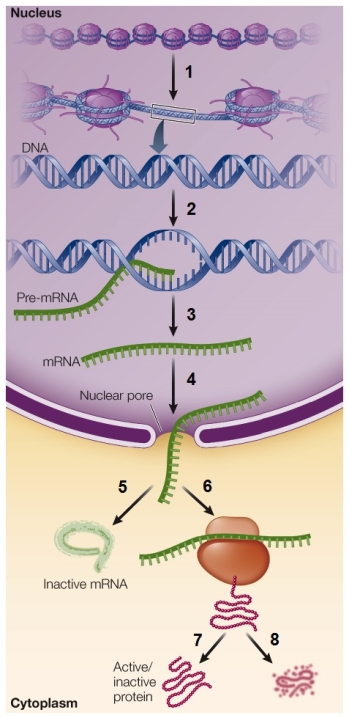 Which point would be considered posttranslational control?
Which point would be considered posttranslational control?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 7
 Which point would be considered posttranslational control?
Which point would be considered posttranslational control?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement is false?
A) Operons involved in catabolism are typically inducible.
B) Operons involved in anabolism are typically repressible.
C) Constitutively expressed genes are generally unregulated.
D) Regulation of gene expression only involves control of transcription.
E) The lac repressor gene is expressed constitutively.
A) Operons involved in catabolism are typically inducible.
B) Operons involved in anabolism are typically repressible.
C) Constitutively expressed genes are generally unregulated.
D) Regulation of gene expression only involves control of transcription.
E) The lac repressor gene is expressed constitutively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the gene encoding the lac repressor is mutated such that the repressor can no longer bind the operator, will transcription of that operon occur?
A) Yes, because the repressor transcriptionally activates the lac genes.
B) Yes, but only when lactose is present.
C) No, because RNA polymerase is needed to transcribe the genes.
D) Yes, because RNA polymerase will be able to bind the promoter and transcribe the operon.
E) No, because cAMP levels are low when the repressor is nonfunctional.
A) Yes, because the repressor transcriptionally activates the lac genes.
B) Yes, but only when lactose is present.
C) No, because RNA polymerase is needed to transcribe the genes.
D) Yes, because RNA polymerase will be able to bind the promoter and transcribe the operon.
E) No, because cAMP levels are low when the repressor is nonfunctional.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An inducer
A) inhibits the synthesis of needed enzyme(s).
B) stimulates the synthesis of needed enzyme(s).
C) binds to the promoter and prevents the repressor from binding to the operator.
D) binds to the operator and prevents the repressor from binding at this site.
E) is the same as a promoter.
A) inhibits the synthesis of needed enzyme(s).
B) stimulates the synthesis of needed enzyme(s).
C) binds to the promoter and prevents the repressor from binding to the operator.
D) binds to the operator and prevents the repressor from binding at this site.
E) is the same as a promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which is least likely to occur in a non-mutant bacterial cell?
A) -galactoside transacetylase is present at a high concentration when -galactoside is present at a low concentration.
B) -galactoside transacetylase is produced at very low levels in the absence of lactose.
C) -galactoside transacetylase is produced at very low levels when glucose is abundant.
D) -galactoside transacetylase is produced at high levels when lactose is at a high concentration and glucose is not available.
E) -galactoside transacetylase and β-galactoside are both present in very low concentrations.
A) -galactoside transacetylase is present at a high concentration when -galactoside is present at a low concentration.
B) -galactoside transacetylase is produced at very low levels in the absence of lactose.
C) -galactoside transacetylase is produced at very low levels when glucose is abundant.
D) -galactoside transacetylase is produced at high levels when lactose is at a high concentration and glucose is not available.
E) -galactoside transacetylase and β-galactoside are both present in very low concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
-galactoside transacetylase is
A) a promoter.
B) encoded by a structural gene.
C) a constitutive protein.
D) usually produced at high levels when -galactoside is produced at low levels.
E) usually produced at low levels when -galactoside is produced at high levels.
A) a promoter.
B) encoded by a structural gene.
C) a constitutive protein.
D) usually produced at high levels when -galactoside is produced at low levels.
E) usually produced at low levels when -galactoside is produced at high levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Bacterial promoters of different housekeeping genes
A) are nearly identical throughout their sequence.
B) can vary in sequence but share consensus sequences at which they are very similar.
C) can vary in sequence but share sigma factors at which they are very similar.
D) can vary in sequence but share regulatory sequences at which they are very similar.
E) can vary in sequence and share no common motifs.
A) are nearly identical throughout their sequence.
B) can vary in sequence but share consensus sequences at which they are very similar.
C) can vary in sequence but share sigma factors at which they are very similar.
D) can vary in sequence but share regulatory sequences at which they are very similar.
E) can vary in sequence and share no common motifs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The earlier the cell intervenes in the process of protein synthesis, the _______ energy it wastes.Thus, cells will tend to regulate protein synthesis _______.
A) more; at the earliest possible stage
B) more; at all stages
C) more; at the latest possible stage
D) less; at the earliest possible stage
E) less; at the latest possible stage
A) more; at the earliest possible stage
B) more; at all stages
C) more; at the latest possible stage
D) less; at the earliest possible stage
E) less; at the latest possible stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which event would lead to a reduction in gene expression?
A) Mutation of the DNA-binding domain of an activator, changing its shape
B) Mutation of the binding site of a co-repressor molecule within a repressor protein
C) Removal of all methylation marks from a region of DNA
D) Remodeling of the chromatin environment, resulting in removal of histone octamers from a gene's promoter region
E) Mutation of a TATA box to create a tighter binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA
A) Mutation of the DNA-binding domain of an activator, changing its shape
B) Mutation of the binding site of a co-repressor molecule within a repressor protein
C) Removal of all methylation marks from a region of DNA
D) Remodeling of the chromatin environment, resulting in removal of histone octamers from a gene's promoter region
E) Mutation of a TATA box to create a tighter binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Sigma factors bind to
A) promoters with no specificity.
B) specific types of promoters.
C) repressors.
D) co-repressors.
E) RNA polymerases.
A) promoters with no specificity.
B) specific types of promoters.
C) repressors.
D) co-repressors.
E) RNA polymerases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Inducible and repressible systems are similar in that
A) in both systems the regulatory molecules function by binding to the operator.
B) both systems usually control biosynthetic pathways.
C) both systems usually control catabolic pathways.
D) both systems block transcription through the presence of a regulatory protein.
E) both systems are unique to prokaryotes.
A) in both systems the regulatory molecules function by binding to the operator.
B) both systems usually control biosynthetic pathways.
C) both systems usually control catabolic pathways.
D) both systems block transcription through the presence of a regulatory protein.
E) both systems are unique to prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a repressible operon, the repressor molecule
A) is the substrate of the metabolic pathway.
B) can repress the transcription of the operon on its own.
C) is a molecule made from the operon.
D) binds to the mRNA.
E) must be activated by a co-repressor.
A) is the substrate of the metabolic pathway.
B) can repress the transcription of the operon on its own.
C) is a molecule made from the operon.
D) binds to the mRNA.
E) must be activated by a co-repressor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Catabolite repression would least likely be found in a metabolic network
A) involved in breaking down sugars.
B) involved in breaking down lipids.
C) involved in the production of an enzyme.
D) in Gram-positive bacteria.
E) in Gram-negative bacteria.
A) involved in breaking down sugars.
B) involved in breaking down lipids.
C) involved in the production of an enzyme.
D) in Gram-positive bacteria.
E) in Gram-negative bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The TATA box is a(n)
A) sequence in the promoter region of many genes.
B) square-shaped sequence.
C) enhancer consensus sequence.
D) activator sequence necessary for proper translation.
E) transcription factor.
A) sequence in the promoter region of many genes.
B) square-shaped sequence.
C) enhancer consensus sequence.
D) activator sequence necessary for proper translation.
E) transcription factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure showing the initiation of transcription in eukaryotes. 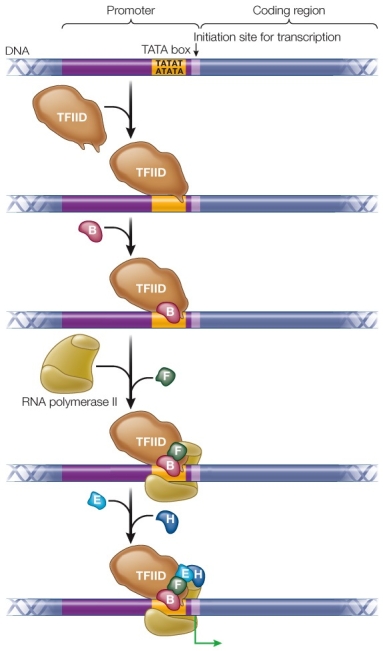 Which represents the regulatory sequence of the DNA?
Which represents the regulatory sequence of the DNA?
A) TATAT
B) ATATA
C) TFIID
D) BFEH
E) TFIID + B
 Which represents the regulatory sequence of the DNA?
Which represents the regulatory sequence of the DNA?A) TATAT
B) ATATA
C) TFIID
D) BFEH
E) TFIID + B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is an example of regulation of eukaryotic transcription?
A) Iron binding the repressor protein for the ferritin mRNA and increasing ferritin expression
B) Proteasome breakdown of protein-polyubiquitin complexes
C) MicroRNAs binding their target mRNA and causing its degradation
D) Alternative splicing of an mRNA transcript
E) Activator proteins binding an enhancer
A) Iron binding the repressor protein for the ferritin mRNA and increasing ferritin expression
B) Proteasome breakdown of protein-polyubiquitin complexes
C) MicroRNAs binding their target mRNA and causing its degradation
D) Alternative splicing of an mRNA transcript
E) Activator proteins binding an enhancer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the gene encoding the trp repressor is mutated such that the repressor can no longer bind tryptophan but can still bind the operon, will transcription of the trp operon occur?
A) Yes, because the trp repressor can bind the trp operon and block transcription only when it is bound to tryptophan.
B) No, because this mutation does not affect the part of the repressor that can bind the operator.
C) No, because the trp operon is repressed only when tryptophan levels are high.
D) Yes, because the trp operon can allosterically regulate the enzymes needed to synthesize the amino acid tryptophan.
E) No, because the repressor will be continuously bound to the operator.
A) Yes, because the trp repressor can bind the trp operon and block transcription only when it is bound to tryptophan.
B) No, because this mutation does not affect the part of the repressor that can bind the operator.
C) No, because the trp operon is repressed only when tryptophan levels are high.
D) Yes, because the trp operon can allosterically regulate the enzymes needed to synthesize the amino acid tryptophan.
E) No, because the repressor will be continuously bound to the operator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure showing the initiation of transcription in eukaryotes. 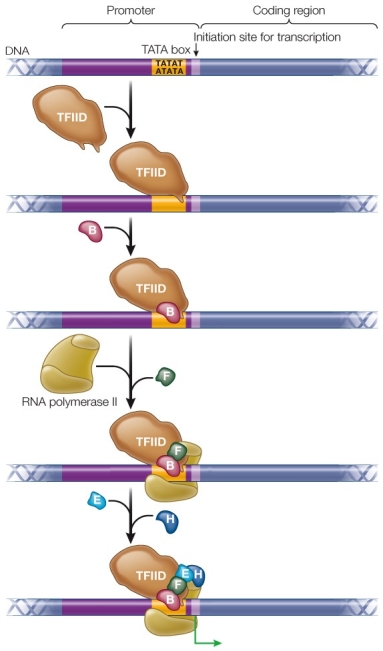 Which transcription factor(s) bind(s) directly to DNA?
Which transcription factor(s) bind(s) directly to DNA?
A) B
B) F
C) E and H
D) TFIID
E) B and H
 Which transcription factor(s) bind(s) directly to DNA?
Which transcription factor(s) bind(s) directly to DNA?A) B
B) F
C) E and H
D) TFIID
E) B and H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A DNA sequence is several thousands of nucleotides distant from the promoter.When this sequence is bound by a protein, transcription rates increase greatly.This sequence is most likely a(n)
A) TATA box.
B) enhancer.
C) operon.
D) promoter.
E) consensus sequence.
A) TATA box.
B) enhancer.
C) operon.
D) promoter.
E) consensus sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the main difference between general and specific transcription factors?
A) Specific transcription factors are found only in multicellular animals, whereas general transcription factors are found in most eukaryotes.
B) Specific transcription factors are found only in multicellular plants, whereas general transcription factors are found in most eukaryotes.
C) Specific transcription factors bind to regulatory sequences of fewer genes than general transcription factors do.
D) Specific transcription factors bind regulatory sequences more tightly than general transcription factors do.
E) Specific transcription factors bind regulatory sequences less tightly than general transcription factors do.
A) Specific transcription factors are found only in multicellular animals, whereas general transcription factors are found in most eukaryotes.
B) Specific transcription factors are found only in multicellular plants, whereas general transcription factors are found in most eukaryotes.
C) Specific transcription factors bind to regulatory sequences of fewer genes than general transcription factors do.
D) Specific transcription factors bind regulatory sequences more tightly than general transcription factors do.
E) Specific transcription factors bind regulatory sequences less tightly than general transcription factors do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the figure showing the initiation of transcription in eukaryotes. 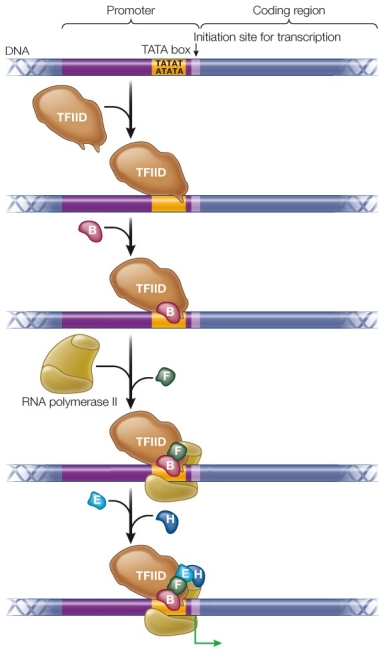 From the figure it can be concluded that
From the figure it can be concluded that
A) all transcription factors work alone to initiate transcription.
B) some transcription factors bind directly to DNA.
C) TFIID binds to the promoter at the TATA box after transcription factors B and F have altered its shape.
D) protein-coding genes contain noncoding sequences.
E) RNA polymerase II independently binds to the promoter and initiates transcription.
 From the figure it can be concluded that
From the figure it can be concluded thatA) all transcription factors work alone to initiate transcription.
B) some transcription factors bind directly to DNA.
C) TFIID binds to the promoter at the TATA box after transcription factors B and F have altered its shape.
D) protein-coding genes contain noncoding sequences.
E) RNA polymerase II independently binds to the promoter and initiates transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When an enhancer is bound, it
A) increases the stability of a specific mRNA.
B) stimulates transcription of a specific gene.
C) stimulates transcription of nearly all genes.
D) stimulates splicing of a specific mRNA.
E) stimulates splicing of nearly all mRNAs.
A) increases the stability of a specific mRNA.
B) stimulates transcription of a specific gene.
C) stimulates transcription of nearly all genes.
D) stimulates splicing of a specific mRNA.
E) stimulates splicing of nearly all mRNAs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A certain enzyme is synthesized whenever the solution in which some cells are growing lacks substance X.This phenomenon is most likely an example of a(n) _______ system.
A) inducible
B) positive
C) negative
D) repressible
E) positive-negative
A) inducible
B) positive
C) negative
D) repressible
E) positive-negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a mutation in a silencer makes it much harder for proteins to bind to it, which is most likely to occur?
A) A specific gene near the silencer will be transcribed all the time, even when not needed.
B) There will be a large decrease in transcription rates for most genes.
C) There will be a large increase in transcription rates for most genes.
D) The rate of transcription of a specific gene located near the silencer will be reduced, even when it is needed the most.
E) Transcription will be terminated prematurely.
A) A specific gene near the silencer will be transcribed all the time, even when not needed.
B) There will be a large decrease in transcription rates for most genes.
C) There will be a large increase in transcription rates for most genes.
D) The rate of transcription of a specific gene located near the silencer will be reduced, even when it is needed the most.
E) Transcription will be terminated prematurely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The trp operon
A) codes for proteins needed for tryptophan synthesis.
B) codes for proteins needed to metabolize tryptophan.
C) is activated by the presence of tryptophan.
D) is inducible by tryptophan.
E) is inducible by lactose (or allolactose).
A) codes for proteins needed for tryptophan synthesis.
B) codes for proteins needed to metabolize tryptophan.
C) is activated by the presence of tryptophan.
D) is inducible by tryptophan.
E) is inducible by lactose (or allolactose).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How do negative regulation and positive regulation in bacteria differ?
A) Only negative regulation involves promoters.
B) Only positive regulation involves promoters.
C) Only in negative regulation is transcription reduced when the regulatory complex binds to the promoter.
D) Only in positive regulation is transcription reduced when the regulatory complex binds to the promoter.
E) Positive regulation must occur at an earlier stage than negative regulation.
A) Only negative regulation involves promoters.
B) Only positive regulation involves promoters.
C) Only in negative regulation is transcription reduced when the regulatory complex binds to the promoter.
D) Only in positive regulation is transcription reduced when the regulatory complex binds to the promoter.
E) Positive regulation must occur at an earlier stage than negative regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Helix-turn-helix is a _______ found in a _______.
A) structural motif; promoter
B) structural motif; transcription factor
C) consensus sequence; promoter
D) consensus sequence; enhancer
E) consensus sequence; transcription factor
A) structural motif; promoter
B) structural motif; transcription factor
C) consensus sequence; promoter
D) consensus sequence; enhancer
E) consensus sequence; transcription factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement about TFIID is false?
A) It is the first transcription factor to bind to the TATA box.
B) Its shape changes after it binds to the TATA box.
C) It attracts other transcription factors to the transcription initiation complex.
D) It is a specific transcription factor.
E) It is not sufficient to activate RNA polymerase II by itself.
A) It is the first transcription factor to bind to the TATA box.
B) Its shape changes after it binds to the TATA box.
C) It attracts other transcription factors to the transcription initiation complex.
D) It is a specific transcription factor.
E) It is not sufficient to activate RNA polymerase II by itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a fruit fly, the transcription rates of a gene that codes for an enzyme vary tremendously among different cell types.The most likely reason for these differences is that different cell types have different
A) promoters.
B) inducers.
C) transcription factors present.
D) silencers.
E) enhancers.
A) promoters.
B) inducers.
C) transcription factors present.
D) silencers.
E) enhancers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a loss-of-function mutation occurs in one of the early genes in a lytic bacteriophage, which change is most likely to occur?
A) Late genes will be turned on.
B) The host genes will remain turned on.
C) The viral genome will be replicated.
D) New viral capsid proteins will be produced.
E) Proteins that lyse the host cell will be produced.
A) Late genes will be turned on.
B) The host genes will remain turned on.
C) The viral genome will be replicated.
D) New viral capsid proteins will be produced.
E) Proteins that lyse the host cell will be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Cro is a bacteriophage λ protein that represses transcription of cI but promotes expression of genes that encourage the lytic cycle.cI protein represses Cro transcription but promotes expression of genes that encourage lysogeny.If the environment experienced by bacteriophage λ deteriorates, the change will most likely _______ the lifespan of cI protein.This result will have the effect of _______.
A) increase; maintaining lysogeny
B) increase; increasing the production of capsid proteins
C) increase; making entry into the lytic phase more likely
D) decrease; maintaining lysogeny
E) decrease; making entry into the lytic phase more likely
A) increase; maintaining lysogeny
B) increase; increasing the production of capsid proteins
C) increase; making entry into the lytic phase more likely
D) decrease; maintaining lysogeny
E) decrease; making entry into the lytic phase more likely

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Eukaryotic gene regulation differs from prokaryotic gene regulation in that
A) there is no negative control in eukaryotes.
B) there is no positive control in prokaryotes.
C) there is no negative control in prokaryotes.
D) transcription and translation occur at the same location in eukaryotes, but at different locations in prokaryotes.
E) transcription and translation occur at the same location in prokaryotes, but at different locations in eukaryotes.
A) there is no negative control in eukaryotes.
B) there is no positive control in prokaryotes.
C) there is no negative control in prokaryotes.
D) transcription and translation occur at the same location in eukaryotes, but at different locations in prokaryotes.
E) transcription and translation occur at the same location in prokaryotes, but at different locations in eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How does regulation of stress response proteins in plants differ from regulation of enzymes produced from a bacterial operon?
A) Expression of stress response proteins is coordinately regulated; expression of bacterial operon genes is not.
B) Expression of bacterial operon genes is coordinately regulated; expression of stress response proteins is not.
C) Regulation of stress response proteins involves DNA-protein interactions; regulation of bacterial operon genes does not.
D) Regulation of bacterial operon genes involves DNA-protein interactions; regulation of stress response proteins does not.
E) Stress response genes are found in various locations throughout the plant genome; bacterial operon genes are found in one unit.
A) Expression of stress response proteins is coordinately regulated; expression of bacterial operon genes is not.
B) Expression of bacterial operon genes is coordinately regulated; expression of stress response proteins is not.
C) Regulation of stress response proteins involves DNA-protein interactions; regulation of bacterial operon genes does not.
D) Regulation of bacterial operon genes involves DNA-protein interactions; regulation of stress response proteins does not.
E) Stress response genes are found in various locations throughout the plant genome; bacterial operon genes are found in one unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a bacteriophage undergoing a lytic phase, the early gene products _______ the host genes and _______ the late genes.
A) stimulate; stimulate
B) stimulate; have no effect on
C) stimulate; inhibit
D) inhibit; stimulate
E) inhibit; inhibit
A) stimulate; stimulate
B) stimulate; have no effect on
C) stimulate; inhibit
D) inhibit; stimulate
E) inhibit; inhibit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If you wanted to build a complex organism with differentiated cells, which type of molecule would not help achieve that goal?
A) General transcription factors
B) Varied RNA polymerases
C) Nuclear envelopes
D) Operons
E) Specific transcription factors
A) General transcription factors
B) Varied RNA polymerases
C) Nuclear envelopes
D) Operons
E) Specific transcription factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The TATA box in eukaryotes is most similar to _______ in prokaryotes.
A) sigma factors
B) the entire promoter
C) a consensus sequence in the promoter
D) an operator
E) an inducer
A) sigma factors
B) the entire promoter
C) a consensus sequence in the promoter
D) an operator
E) an inducer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Viruses are
A) cells containing DNA and protein.
B) larger than most bacteria.
C) acellular.
D) able to take in nutrients and expel wastes.
E) mutated forms of DNA.
A) cells containing DNA and protein.
B) larger than most bacteria.
C) acellular.
D) able to take in nutrients and expel wastes.
E) mutated forms of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
With respect to bacteria, the term "lysogeny" refers to
A) the stable integration of bacteriophage DNA into the bacterial chromosome.
B) the excision of bacteriophage DNA from the bacterial chromosome.
C) the lysing of a bacterium by a bacteriophage.
D) mutation induced by a bacteriophage.
E) the reciprocal exchange of genetic material between a bacteriophage and a bacterium.
A) the stable integration of bacteriophage DNA into the bacterial chromosome.
B) the excision of bacteriophage DNA from the bacterial chromosome.
C) the lysing of a bacterium by a bacteriophage.
D) mutation induced by a bacteriophage.
E) the reciprocal exchange of genetic material between a bacteriophage and a bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which is an anti-HIV treatment that works by preventing the formation of provirus?
A) Integrase inhibitors
B) Protease inhibitors
C) Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
D) Tat
E) Capsid
A) Integrase inhibitors
B) Protease inhibitors
C) Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
D) Tat
E) Capsid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the difference between a prophage and a provirus, based on what you know about HIV and bacteriophage ?
A) The host of a prophage is a bacterium, whereas the host of a provirus is a eukaryote.
B) A provirus is in lysogeny, whereas a prophage is the provirus after a return to the lytic phase.
C) A prophage is in lysogeny, whereas a provirus is the prophage after a return to the lytic phase.
D) The host of a prophage is a eukaryote, whereas the host of a provirus is a bacterium.
E) A prophage is regulated by early genes, whereas a provirus is regulated by late genes.
A) The host of a prophage is a bacterium, whereas the host of a provirus is a eukaryote.
B) A provirus is in lysogeny, whereas a prophage is the provirus after a return to the lytic phase.
C) A prophage is in lysogeny, whereas a provirus is the prophage after a return to the lytic phase.
D) The host of a prophage is a eukaryote, whereas the host of a provirus is a bacterium.
E) A prophage is regulated by early genes, whereas a provirus is regulated by late genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which item is not used by a bacteriophage to generate new viral particles?
A) A promoter sequence that is compatible with the host RNA polymerase
B) Genes for proteins that inhibit host transcription
C) Genes for capsid proteins
D) Nucleases
E) Genes for viral RNA polymerase
A) A promoter sequence that is compatible with the host RNA polymerase
B) Genes for proteins that inhibit host transcription
C) Genes for capsid proteins
D) Nucleases
E) Genes for viral RNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The stress response elements in plants are
A) transcription factors.
B) inducers.
C) RNA sequences.
D) enzymes.
E) DNA sequences.
A) transcription factors.
B) inducers.
C) RNA sequences.
D) enzymes.
E) DNA sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cro is a phage protein that represses transcription of cI but promotes expression of genes that encourage the lytic cycle.cI protein represses Cro transcription but promotes expression of genes that encourage lysogeny.A mutation in Cro decreases its expression.This mutation would make entering lysogeny _______ likely.A mutation that decreases the expression of cI would have _______ effect on the likelihood of the virus entering lysogeny.
A) more; a similar
B) more; no
C) more; the opposite
D) less; a similar
E) less; the opposite
A) more; a similar
B) more; no
C) more; the opposite
D) less; a similar
E) less; the opposite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which action would not affect gene expression in a eukaryotic cell?
A) Deletion of a promoter
B) Deletion of an enhancer
C) Lack of modification of the cap structure on mRNA
D) Inability of a transcription factor to bind the promoter
E) Deletion of a DNA ori site
A) Deletion of a promoter
B) Deletion of an enhancer
C) Lack of modification of the cap structure on mRNA
D) Inability of a transcription factor to bind the promoter
E) Deletion of a DNA ori site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Gene regulation by tat in HIV occurs at the level of
A) transcription initiation.
B) transcription elongation.
C) mRNA stability.
D) translation initiation.
E) translation elongation.
A) transcription initiation.
B) transcription elongation.
C) mRNA stability.
D) translation initiation.
E) translation elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is a strategy that a virus could use in order to ensure viral reproduction in the host cell?
A) Production of tat protein, which allows viral mRNA elongation
B) Production of protease inhibitors, which block posttranslational processing
C) Use of integrase inhibitors, which prevent the viral genome from inserting into the host genome
D) Use of reverse transcriptase inhibitors, which block viral DNA synthesis from RNA
E) Carrying ribosomes for quick viral RNA translation
A) Production of tat protein, which allows viral mRNA elongation
B) Production of protease inhibitors, which block posttranslational processing
C) Use of integrase inhibitors, which prevent the viral genome from inserting into the host genome
D) Use of reverse transcriptase inhibitors, which block viral DNA synthesis from RNA
E) Carrying ribosomes for quick viral RNA translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Early genes of a lytic bacteriophage are transcribed by
A) late genes.
B) viral RNA polymerase from earlier lytic cycles.
C) host DNA polymerase.
D) host RNA polymerase.
E) reverse transcriptase.
A) late genes.
B) viral RNA polymerase from earlier lytic cycles.
C) host DNA polymerase.
D) host RNA polymerase.
E) reverse transcriptase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How does gene regulation differ between prokaryotes and multicellular eukaryotes?
A) Different cells vary in the types and number of genes they express in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes.
B) Protein-DNA interactions occur only in eukaryotes.
C) Protein-DNA interactions occur only in prokaryotes.
D) Cell-specific gene expression and protein-DNA interactions both occur only in eukaryotes.
E) Cell-specific gene expression and protein-DNA interactions both occur only in prokaryotes.
A) Different cells vary in the types and number of genes they express in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes.
B) Protein-DNA interactions occur only in eukaryotes.
C) Protein-DNA interactions occur only in prokaryotes.
D) Cell-specific gene expression and protein-DNA interactions both occur only in eukaryotes.
E) Cell-specific gene expression and protein-DNA interactions both occur only in prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If HIV is mutated such that its tat protein is less able to bind to mRNA, the most likely result will be
A) more initiation of transcription.
B) less initiation of transcription.
C) the termination of more partial transcripts, and thus the making of fewer complete transcripts.
D) the termination of fewer partial transcripts, and thus the making of more complete transcripts.
E) a reduction in the stability of complete transcripts.
A) more initiation of transcription.
B) less initiation of transcription.
C) the termination of more partial transcripts, and thus the making of fewer complete transcripts.
D) the termination of fewer partial transcripts, and thus the making of more complete transcripts.
E) a reduction in the stability of complete transcripts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Methylation most often occurs to _______ that are next to _______.
A) adenines; cytosines
B) adenines; guanines
C) cytosines; adenines
D) cytosines; guanines
E) guanines; adenines
A) adenines; cytosines
B) adenines; guanines
C) cytosines; adenines
D) cytosines; guanines
E) guanines; adenines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Imagine that the promoter for gene X becomes highly methylated.How will this affect the expression of gene X?
A) There will be no effect.
B) Gene X will be transcribed but not translated.
C) Gene X will be transcribed if the transcription factors receive the appropriate environmental signal.
D) Gene X will not be transcribed or translated.
E) Gene X will be transcribed if the histones become acetylated.
A) There will be no effect.
B) Gene X will be transcribed but not translated.
C) Gene X will be transcribed if the transcription factors receive the appropriate environmental signal.
D) Gene X will not be transcribed or translated.
E) Gene X will be transcribed if the histones become acetylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a mutation causes a decrease in the activity of histone acetyltransferases, histones will most likely have a _______ affinity for DNA, and there will be _______ in transcription rates.
A) greater; an increase
B) greater; a decrease
C) reduced; an increase
D) reduced; no change
E) reduced; a decrease
A) greater; an increase
B) greater; a decrease
C) reduced; an increase
D) reduced; no change
E) reduced; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Heterochromatin stains _______ than euchromatin and is _______ transcriptionally active.
A) darker; more
B) darker; just as
C) darker; less
D) lighter; more
E) lighter; less
A) darker; more
B) darker; just as
C) darker; less
D) lighter; more
E) lighter; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a mutation causes a reduction in the production of demethylase, the expected effect will be _______ in the amount of overall methylation and therefore _______ in overall gene expression.
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) no change; an increase
D) a decrease; an increase
E) a decrease; a decrease
A) an increase; an increase
B) an increase; a decrease
C) no change; an increase
D) a decrease; an increase
E) a decrease; a decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If each interphase nucleus in 100 epithelial cells from a rat contains a single Barr body, one can conclude that
A) the cells have an excess of DNA methyltransferase.
B) the cells have a deficiency of DNA methyltransferase.
C) all of the chromatin in these cells is inactive.
D) the cells came from a male rat.
E) the cells came from a female rat.
A) the cells have an excess of DNA methyltransferase.
B) the cells have a deficiency of DNA methyltransferase.
C) all of the chromatin in these cells is inactive.
D) the cells came from a male rat.
E) the cells came from a female rat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
One of the genes that is known to be transcribed from the inactive X chromosome is
A) Xist.
B) ZIST.
C) the gene that encodes inactivation controller protein.
D) the gene that encodes DNA methyltransferase.
E) methyl-X.
A) Xist.
B) ZIST.
C) the gene that encodes inactivation controller protein.
D) the gene that encodes DNA methyltransferase.
E) methyl-X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Nucleosomes disaggregate (or "open") to allow transcription and then reaggregate
A) through alternative splicing.
B) by methylation and demethylation.
C) through alternation of nucleotides.
D) by acetylation and deacetylation.
E) through insertion of nucleotides.
A) through alternative splicing.
B) by methylation and demethylation.
C) through alternation of nucleotides.
D) by acetylation and deacetylation.
E) through insertion of nucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which enzyme allows methylation changes to be passed on after DNA replication?
A) Demethylase
B) DNA methyltransferase
C) Methylheritablase
D) Maintenance methylase
E) CpG
A) Demethylase
B) DNA methyltransferase
C) Methylheritablase
D) Maintenance methylase
E) CpG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Imagine that gene X is in a chromosome region where the histones are highly acetylated.How will this affect its expression?
A) There will be no effect.
B) It will be transcribed but not translated.
C) It will be transcribed if the transcription factors receive the appropriate environmental signal.
D) It will not be transcribed or translated.
E) It will be transcribed if the histones become deacetylated.
A) There will be no effect.
B) It will be transcribed but not translated.
C) It will be transcribed if the transcription factors receive the appropriate environmental signal.
D) It will not be transcribed or translated.
E) It will be transcribed if the histones become deacetylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Refer to the figure showing the potential points for the regulation of gene expression. 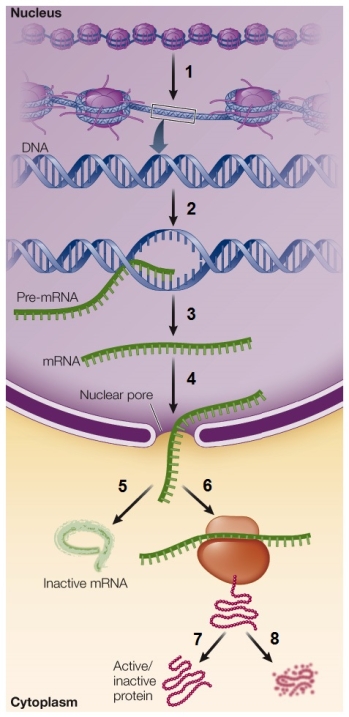 Which point would be considered epigenetic control?
Which point would be considered epigenetic control?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
 Which point would be considered epigenetic control?
Which point would be considered epigenetic control?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Consider the following statement: Histone deacetylases tend to decrease transcription from particular genes.Is it true or false, and for what reason?
A) True, because acetylated histones have higher affinity for DNA
B) True, because acetylated histones have lower affinity for DNA
C) False, because acetylated histones have higher affinity for DNA
D) False, because acetylated histones have lower affinity for DNA
E) False, because acetylation status of histones has no bearing on transcription
A) True, because acetylated histones have higher affinity for DNA
B) True, because acetylated histones have lower affinity for DNA
C) False, because acetylated histones have higher affinity for DNA
D) False, because acetylated histones have lower affinity for DNA
E) False, because acetylation status of histones has no bearing on transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The activity of _______ tends to lead to increased transcription.
A) histone deacetylase
B) histone acetyltransferase
C) DNA methyltransferase
D) maintenance methylase
E) RNA polymerase
A) histone deacetylase
B) histone acetyltransferase
C) DNA methyltransferase
D) maintenance methylase
E) RNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which statement about epigenetics is false?
A) One type of epigenetic change occurs via DNA methylation.
B) One type of epigenetic change occurs via chromosomal protein alterations.
C) Epigenetic changes can lead to gene expression changes.
D) Epigenetic changes do not change the DNA sequence.
E) DNA methylation can prevent binding of repressor proteins, resulting in increased gene expression.
A) One type of epigenetic change occurs via DNA methylation.
B) One type of epigenetic change occurs via chromosomal protein alterations.
C) Epigenetic changes can lead to gene expression changes.
D) Epigenetic changes do not change the DNA sequence.
E) DNA methylation can prevent binding of repressor proteins, resulting in increased gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Barr body indicates
A) X chromosome inactivation.
B) cell death.
C) genomic imprinting.
D) posttranslational control of eukaryotic gene expression.
E) stress response.
A) X chromosome inactivation.
B) cell death.
C) genomic imprinting.
D) posttranslational control of eukaryotic gene expression.
E) stress response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The expression of some genes can be regulated in part by the pattern of RNA splicing.This is an example of
A) DNA methylation.
B) transcriptional regulation.
C) pretranscriptional control.
D) posttranscriptional control.
E) genomic imprinting.
A) DNA methylation.
B) transcriptional regulation.
C) pretranscriptional control.
D) posttranscriptional control.
E) genomic imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The addition of acetyl groups makes histones _______ positively charged, and thus _______ their affinity for DNA.
A) more; increases
B) more; decreases
C) less; increases
D) less; has no effect on
E) less; decreases
A) more; increases
B) more; decreases
C) less; increases
D) less; has no effect on
E) less; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Identical twins show
A) similar methylation patterns throughout their lives.
B) similar methylation patterns as children but divergent patterns as adults.
C) divergent methylation patterns as children but similar patterns as adults.
D) divergent methylation patterns as children, similar patterns as teenagers, and divergent patterns as adults.
E) divergent methylation patterns throughout their lives.
A) similar methylation patterns throughout their lives.
B) similar methylation patterns as children but divergent patterns as adults.
C) divergent methylation patterns as children but similar patterns as adults.
D) divergent methylation patterns as children, similar patterns as teenagers, and divergent patterns as adults.
E) divergent methylation patterns throughout their lives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Two identical twins showed very similar methylation patterns when they were 4 years old, but these patterns diverged considerably by the time they were 40 years old.What is the most likely explanation for this?
A) It is an effect of different genomic imprinting in the twins.
B) It is due to different alternative splicing in the twins.
C) It is due to the twins experiencing different environments as adults.
D) It is due to different levels of histone acetyltransferase in the twins.
E) It is due to differences the twins experienced in utero.
A) It is an effect of different genomic imprinting in the twins.
B) It is due to different alternative splicing in the twins.
C) It is due to the twins experiencing different environments as adults.
D) It is due to different levels of histone acetyltransferase in the twins.
E) It is due to differences the twins experienced in utero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In teenage children of women who suffered physical abuse while pregnant, the glucocorticoid receptor has a promoter region
A) with more methylated bases than are typical.
B) with fewer methylated bases than are typical.
C) without epigenetic changes.
D) with more euchromatin than is typical.
E) with more heterochromatin than is typical.
A) with more methylated bases than are typical.
B) with fewer methylated bases than are typical.
C) without epigenetic changes.
D) with more euchromatin than is typical.
E) with more heterochromatin than is typical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 245 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



