Deck 27: Plants Without Seeds: From Water to Land
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/251
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Plants Without Seeds: From Water to Land
1
Refer to the figure. 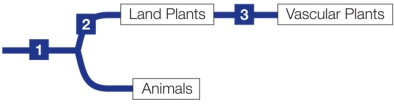 Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "vascular plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer. A.Angiosperms
Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "vascular plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer. A.Angiosperms
B)Horsetails
C)Bryophytes
D)Gymnosperms
E)Hornworts
F)Lycophytes
G)Monilophytes
H)Stoneworts
A) A, B, D, F, G
B) B, C, E, H
C) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
D) F, G, H
E) A, B, C, D, E, F, G
 Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "vascular plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer. A.Angiosperms
Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "vascular plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer. A.AngiospermsB)Horsetails
C)Bryophytes
D)Gymnosperms
E)Hornworts
F)Lycophytes
G)Monilophytes
H)Stoneworts
A) A, B, D, F, G
B) B, C, E, H
C) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
D) F, G, H
E) A, B, C, D, E, F, G
A
2
Which clade is not considered a member of the "green plants"?
A) Embryophytes
B) Stoneworts
C) Chlorophytes
D) Glaucophytes
E) Coleochaetophytes
A) Embryophytes
B) Stoneworts
C) Chlorophytes
D) Glaucophytes
E) Coleochaetophytes
D
3
While scuba diving, you recover several samples of a red alga that appear almost crimson in color.When you return to your lab and attempt to grow the alga in your saltwater fish tank, new growth of the alga appears bright green.What best explains this phenomenon?
A) The intensity of light has changed, affecting pigment composition.
B) The composition of the salt water has changed, affecting pigment composition.
C) The alga has engulfed a new cyanobacterial endosymbiont.
D) The alga is missing vital nutrients that allow for the accumulation of phycoerythrin.
E) The alga is stressed and is slowly dying.
A) The intensity of light has changed, affecting pigment composition.
B) The composition of the salt water has changed, affecting pigment composition.
C) The alga has engulfed a new cyanobacterial endosymbiont.
D) The alga is missing vital nutrients that allow for the accumulation of phycoerythrin.
E) The alga is stressed and is slowly dying.
A
4
In which plant group did stomata first appear?
A) Hornworts
B) Mosses
C) Liverworts
D) Club mosses
E) Angiosperms
A) Hornworts
B) Mosses
C) Liverworts
D) Club mosses
E) Angiosperms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Molecular and morphological evidence indicates that _______ are a sister group of land plants.
A) mosses
B) liverworts
C) red algae
D) stoneworts
E) chlorophytes
A) mosses
B) liverworts
C) red algae
D) stoneworts
E) chlorophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which group represents the most ancient surviving land plant lineage?
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Ferns
E) Stoneworts
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Ferns
E) Stoneworts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following are evolutionary adaptations shared by all land plants except
A) waxy protective coverings.
B) support against gravity.
C) a means of taking up water from the soil.
D) protective structures for the young sporophyte.
E) water transport by xylem.
A) waxy protective coverings.
B) support against gravity.
C) a means of taking up water from the soil.
D) protective structures for the young sporophyte.
E) water transport by xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Horsetails share with club mosses all of the following characteristics except
A) large, independent sporophytes.
B) specialized vascular tissue.
C) apical growth.
D) true roots.
E) leaflike microphylls.
A) large, independent sporophytes.
B) specialized vascular tissue.
C) apical growth.
D) true roots.
E) leaflike microphylls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Hornworts form the sister clade of the
A) vascular plants.
B) mosses.
C) liverworts.
D) horsetails and ferns.
E) nonvascular plants.
A) vascular plants.
B) mosses.
C) liverworts.
D) horsetails and ferns.
E) nonvascular plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The plants classified as embryophytes include which of the following groups?
A) Red algae
B) Chlorophytes
C) Glaucophytes
D) Land plants
E) Coleochaetophytes
A) Red algae
B) Chlorophytes
C) Glaucophytes
D) Land plants
E) Coleochaetophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose you find a new eukaryotic organism with the life cycle shown in the figure. 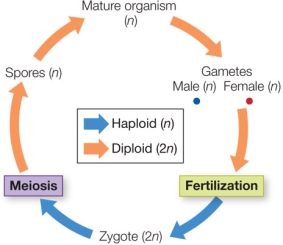 The observation that chloroplasts of this organism have phycoerythrin would lead to the hypothesis that it is related to the
The observation that chloroplasts of this organism have phycoerythrin would lead to the hypothesis that it is related to the
A) coleochaetophytes.
B) red algae.
C) glaucophytes.
D) bryophytes.
E) cyanobacteria.
 The observation that chloroplasts of this organism have phycoerythrin would lead to the hypothesis that it is related to the
The observation that chloroplasts of this organism have phycoerythrin would lead to the hypothesis that it is related to theA) coleochaetophytes.
B) red algae.
C) glaucophytes.
D) bryophytes.
E) cyanobacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which synapomorphy of the plant clade is shared by coleochaetophytes (a group of green algae) and glaucophytes (the group most similar to the unicellular ancestor of Plantae)?
A) Chlorophyll b
B) Chloroplasts
C) Multicellular sporophyte
D) Retention of the egg in the parental organism
E) Branched apical growth
A) Chlorophyll b
B) Chloroplasts
C) Multicellular sporophyte
D) Retention of the egg in the parental organism
E) Branched apical growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Refer to the figure. 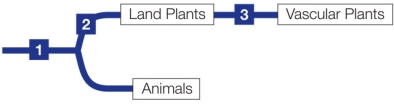 What are the shared derived characteristics indicated on the phylogeny?
What are the shared derived characteristics indicated on the phylogeny?
A) 1: tracheids; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: seeds
B) 1: chloroplasts; 2: spores and protected embryos; 3: tracheids
C) 1: tracheids; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: spores
D) 1: eukaryotic cells; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: tracheids
E) 1: eukaryotic cells; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: spores
 What are the shared derived characteristics indicated on the phylogeny?
What are the shared derived characteristics indicated on the phylogeny?A) 1: tracheids; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: seeds
B) 1: chloroplasts; 2: spores and protected embryos; 3: tracheids
C) 1: tracheids; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: spores
D) 1: eukaryotic cells; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: tracheids
E) 1: eukaryotic cells; 2: chloroplasts and protected embryos; 3: spores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the figure. 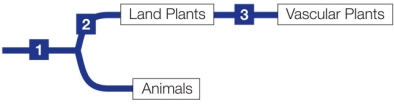 Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "land plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer.
Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "land plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer.
A.Angiosperms
B.Horsetails
C.Bryophytes
D.Gymnosperms
E.Hornworts
F.Lycophytes
G.Monilophytes
H.Stoneworts
A) A, B, D, F, G
B) B, C, E, H
C) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
D) F, G, H
E) A, B, C, D, E, F, G
 Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "land plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer.
Which of the taxa listed below fit the criteria of "land plants" in the diagram? Be sure to include all possible taxa in your answer. A.Angiosperms
B.Horsetails
C.Bryophytes
D.Gymnosperms
E.Hornworts
F.Lycophytes
G.Monilophytes
H.Stoneworts
A) A, B, D, F, G
B) B, C, E, H
C) A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
D) F, G, H
E) A, B, C, D, E, F, G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which characteristic represents an evolutionary link between the "green algae" and the land plants?
A) Use of chlorophylls a and b
B) Active stomata
C) Protected embryos
D) Tracheids for water transport
E) Branched apical growth
A) Use of chlorophylls a and b
B) Active stomata
C) Protected embryos
D) Tracheids for water transport
E) Branched apical growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
These multicellular green algae retain their eggs in the parental organism, and their growth pattern is both branching and apical.
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a characteristic that is present in all groups of land plants?
A) Development from embryos protected by tissues of the parent plant
B) Cuticle
C) Chloroplasts containing chlorophylls a and b
D) Starch as the storage carbohydrate
E) The accessory pigment phycoerythrin
A) Development from embryos protected by tissues of the parent plant
B) Cuticle
C) Chloroplasts containing chlorophylls a and b
D) Starch as the storage carbohydrate
E) The accessory pigment phycoerythrin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
These multicellular green algae grow in the form of an unbranched thallus and retain their eggs in the parental organism.
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is a synapomorphy specific to stoneworts and land plants?
A) Chloroplasts
B) Chlorophyll b
C) Multicellular sporophyte
D) Retention of the egg in the parental organism
E) Branched apical growth
A) Chloroplasts
B) Chlorophyll b
C) Multicellular sporophyte
D) Retention of the egg in the parental organism
E) Branched apical growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which trait shared by coleochaetophytes, stoneworts, and land plants is most likely to have aided with successful colonization on land?
A) The ability to retain eggs in the parental organism
B) Cytoplasmic connections for cell-cell communication
C) Specialized vascular cells
D) A dominant sporophyte generation
E) Presence of stomata
A) The ability to retain eggs in the parental organism
B) Cytoplasmic connections for cell-cell communication
C) Specialized vascular cells
D) A dominant sporophyte generation
E) Presence of stomata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
During the Carboniferous period, forests of large plants dominated the landscape.Which of the following were not among them?
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Lycophytes
E) Mosses
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Lycophytes
E) Mosses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How does the alternation of generations of plants differ from the typical animal life cycle?
A) In plants, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by mitosis rather than meiosis.
B) In plants, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by meiosis rather than mitosis.
C) In plants, only the diploid stage of the life cycle includes multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by meiosis rather than mitosis.
D) In animals, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by mitosis rather than meiosis.
E) In animals, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by meiosis rather than mitosis.
A) In plants, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by mitosis rather than meiosis.
B) In plants, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by meiosis rather than mitosis.
C) In plants, only the diploid stage of the life cycle includes multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by meiosis rather than mitosis.
D) In animals, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by mitosis rather than meiosis.
E) In animals, the diploid and haploid stages of the life cycle both include multicellular individuals, and gametes are produced by meiosis rather than mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The nonvascular plants have a number of structures or characteristics that allow them to obtain water and minerals in the absence of a vascular system.These include all of the following except
A) growth in dense masses through which water can move by capillary action.
B) leaflike structures that catch and hold water.
C) small size, which allows minerals to be distributed evenly by diffusion.
D) an extensive root system to take up water from soil.
E) mycorrhizae, a mutualistic association with a fungus.
A) growth in dense masses through which water can move by capillary action.
B) leaflike structures that catch and hold water.
C) small size, which allows minerals to be distributed evenly by diffusion.
D) an extensive root system to take up water from soil.
E) mycorrhizae, a mutualistic association with a fungus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Within vascular plants, the prominent generation is the _______; in nonvascular plants, it is the _______.
A) gametophyte; sporophyte
B) sporophyte; gametophyte
C) gametophyte; gametophyte
D) sporophyte; sporophyte
E) sporangium; gametophyte
A) gametophyte; sporophyte
B) sporophyte; gametophyte
C) gametophyte; gametophyte
D) sporophyte; sporophyte
E) sporangium; gametophyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose you find a new eukaryotic organism with the life cycle shown in the figure. 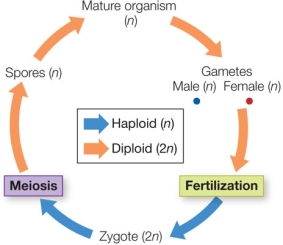 What evidence would lead to the conclusion that it does not belong in the plant clade?
What evidence would lead to the conclusion that it does not belong in the plant clade?
A) It lacks a multicellular diploid generation.
B) It has both gametes and spores.
C) Both the male and female gametes are haploid.
D) It has a multicellular haploid generation.
E) It is homosporous.
 What evidence would lead to the conclusion that it does not belong in the plant clade?
What evidence would lead to the conclusion that it does not belong in the plant clade?A) It lacks a multicellular diploid generation.
B) It has both gametes and spores.
C) Both the male and female gametes are haploid.
D) It has a multicellular haploid generation.
E) It is homosporous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure, which shows alternation of generations in the life cycle of a land plant. 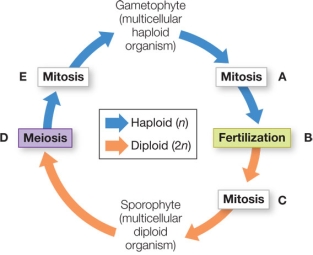 At which step in the diagram are gametes being formed?
At which step in the diagram are gametes being formed?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 At which step in the diagram are gametes being formed?
At which step in the diagram are gametes being formed?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the figure, which shows alternation of generations in plants. 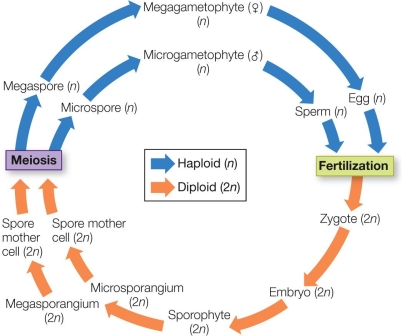 In a plant with this type of alternation of generations, the zygote develops on a
In a plant with this type of alternation of generations, the zygote develops on a
A) microgametophyte.
B) megagametophyte.
C) microphyll.
D) megaphyll.
E) microsporangium.
 In a plant with this type of alternation of generations, the zygote develops on a
In a plant with this type of alternation of generations, the zygote develops on aA) microgametophyte.
B) megagametophyte.
C) microphyll.
D) megaphyll.
E) microsporangium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In order to thrive on land and colonize drier habitats, plants had to develop
A) photosynthetic pigments and mechanisms for transporting water and minerals to aerial parts.
B) starch for carbohydrate storage and mechanisms for transporting water and minerals to aerial parts.
C) physical support structures and mechanisms for gamete dispersal.
D) photosynthetic pigments that are not dependent on an aqueous environment, and starch for carbohydrate storage.
E) alternation of generations and physical support structures.
A) photosynthetic pigments and mechanisms for transporting water and minerals to aerial parts.
B) starch for carbohydrate storage and mechanisms for transporting water and minerals to aerial parts.
C) physical support structures and mechanisms for gamete dispersal.
D) photosynthetic pigments that are not dependent on an aqueous environment, and starch for carbohydrate storage.
E) alternation of generations and physical support structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
All land plants produce _______ by mitosis and _______ by meiosis.
A) spores; gametes
B) gametes; gametes
C) gametes; spores
D) spores; spores
E) spores; gametes and spores
A) spores; gametes
B) gametes; gametes
C) gametes; spores
D) spores; spores
E) spores; gametes and spores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the figure, which shows alternation of generations in the life cycle of a land plant. 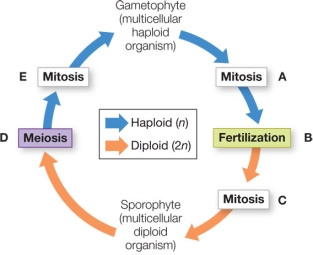 In the life cycle of a plant, the spores are _______, the gametes are _______, and the zygote is _______.
In the life cycle of a plant, the spores are _______, the gametes are _______, and the zygote is _______.
A) haploid; diploid; haploid
B) haploid; haploid; diploid
C) diploid; haploid; diploid
D) haploid; diploid; diploid
E) diploid; diploid; haploid
 In the life cycle of a plant, the spores are _______, the gametes are _______, and the zygote is _______.
In the life cycle of a plant, the spores are _______, the gametes are _______, and the zygote is _______.A) haploid; diploid; haploid
B) haploid; haploid; diploid
C) diploid; haploid; diploid
D) haploid; diploid; diploid
E) diploid; diploid; haploid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How can nonvascular plants survive on land without true leaves, stems, and roots?
A) They are small enough to allow minerals to diffuse throughout their bodies.
B) They live in dry habitats.
C) They have a thick cuticle to prevent water loss.
D) Their spores are dispersed by wind.
E) Their sporophytes are nutritionally independent and provide carbohydrates to the rest of the plant.
A) They are small enough to allow minerals to diffuse throughout their bodies.
B) They live in dry habitats.
C) They have a thick cuticle to prevent water loss.
D) Their spores are dispersed by wind.
E) Their sporophytes are nutritionally independent and provide carbohydrates to the rest of the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the figure, which shows alternation of generations in the life cycle of a land plant. 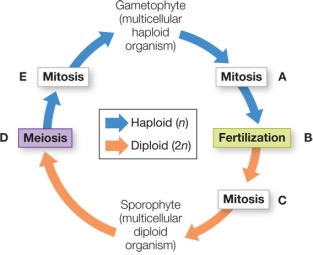 In a nonvascular land plant, the structure being formed at step E in the diagram would be
In a nonvascular land plant, the structure being formed at step E in the diagram would be
A) inconspicuous and lack chloroplasts.
B) conspicuous and lack chloroplasts.
C) conspicuous and nutritionally independent.
D) conspicuous and nutritionally dependent on the sporophyte.
E) inconspicuous and might or might not be nutritionally independent.
 In a nonvascular land plant, the structure being formed at step E in the diagram would be
In a nonvascular land plant, the structure being formed at step E in the diagram would beA) inconspicuous and lack chloroplasts.
B) conspicuous and lack chloroplasts.
C) conspicuous and nutritionally independent.
D) conspicuous and nutritionally dependent on the sporophyte.
E) inconspicuous and might or might not be nutritionally independent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the figure, which shows alternation of generations in the life cycle of a land plant. 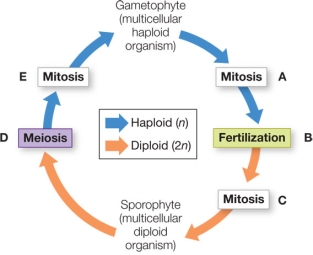 At which step in the diagram are spores being produced?
At which step in the diagram are spores being produced?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
 At which step in the diagram are spores being produced?
At which step in the diagram are spores being produced?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Several important adaptations evolved in the common ancestor of land plants that allowed for successful emergence on land.Which of the following is one of those changes?
A) Evolution of a waxy cuticle
B) Evolution of a carbohydrate energy-storage molecule
C) Evolution of a diploid form that produces haploid gametes
D) Evolution of a mechanism for structural support
E) Evolution of channels for transporting water
A) Evolution of a waxy cuticle
B) Evolution of a carbohydrate energy-storage molecule
C) Evolution of a diploid form that produces haploid gametes
D) Evolution of a mechanism for structural support
E) Evolution of channels for transporting water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The sporophyte of a vascular plant is nutritionally _______; the sporophyte of a nonvascular plant is nutritionally _______.
A) dependent; independent
B) independent; independent
C) haploid; diploid
D) dependent; dependent
E) independent; dependent
A) dependent; independent
B) independent; independent
C) haploid; diploid
D) dependent; dependent
E) independent; dependent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which innovation in land plants addressed the challenges of reproduction rather than mere survival?
A) The cuticle
B) Stomata
C) Gametangia
D) Association with mycorrhizae
E) Protection from UV radiation
A) The cuticle
B) Stomata
C) Gametangia
D) Association with mycorrhizae
E) Protection from UV radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Earth is estimated to be 4.65 billion years old.Although life first appeared about 3.7 billion years ago, land plants did not appear until _______ years ago.
A) 400,000-500,000
B) 3-4 million
C) 40-50 million
D) 400-500 million
E) 3-4 billion
A) 400,000-500,000
B) 3-4 million
C) 40-50 million
D) 400-500 million
E) 3-4 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The first ferns appeared during the _______ period.
A) Permian
B) Carboniferous
C) Silurian
D) Devonian
E) Triassic
A) Permian
B) Carboniferous
C) Silurian
D) Devonian
E) Triassic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Haploid unicellular spores are produced in the sporangia via
A) mitosis.
B) fertilization.
C) conjugation.
D) budding.
E) meiosis.
A) mitosis.
B) fertilization.
C) conjugation.
D) budding.
E) meiosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which feature is universal in the life cycles of land plants?
A) Morphologically identical gametophyte and sporophyte stages
B) Genetically identical gametophyte and sporophyte stages
C) Alteration of generations between haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes
D) Multicellular haploid and diploid gametes
E) A unicellular gametophyte generation
A) Morphologically identical gametophyte and sporophyte stages
B) Genetically identical gametophyte and sporophyte stages
C) Alteration of generations between haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes
D) Multicellular haploid and diploid gametes
E) A unicellular gametophyte generation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The branched filamentous structure of the moss gametophyte that develops after spore germination is the
A) antheridium.
B) capsule.
C) protonema.
D) hydroid.
E) microphyll.
A) antheridium.
B) capsule.
C) protonema.
D) hydroid.
E) microphyll.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Mosses are dependent on external water for sexual reproduction because
A) sperm diffuse to eggs through water.
B) gametogenesis occurs only when the plants are moist.
C) eggs and sperm are released into water and then unite.
D) sperm must swim through water to reach and fertilize eggs.
E) spores are released only after the outer coat of the sporangium dissolves in water.
A) sperm diffuse to eggs through water.
B) gametogenesis occurs only when the plants are moist.
C) eggs and sperm are released into water and then unite.
D) sperm must swim through water to reach and fertilize eggs.
E) spores are released only after the outer coat of the sporangium dissolves in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The evolutionary importance of plant tissue composed of tracheids is that it provides
A) a plant vascular system and structural support.
B) structural support and increased growth.
C) enhanced photosynthesis and anchoring.
D) enhanced photosynthesis and a plant vascular system.
E) enhanced water conservation and anchoring.
A) a plant vascular system and structural support.
B) structural support and increased growth.
C) enhanced photosynthesis and anchoring.
D) enhanced photosynthesis and a plant vascular system.
E) enhanced water conservation and anchoring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the figure, which shows hornworts.  In which part of this hornwort would you find an egg cell?
In which part of this hornwort would you find an egg cell?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) The relevant structure is not shown.
E) Hornworts do not reproduce sexually.
 In which part of this hornwort would you find an egg cell?
In which part of this hornwort would you find an egg cell?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) The relevant structure is not shown.
E) Hornworts do not reproduce sexually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
This group's gametophyte starts as a branched filamentous structure called a protonema, and many types contain hydroid cells.
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the figure, which shows hornworts.  From which part of this hornwort would spores be released?
From which part of this hornwort would spores be released?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) The relevant structure is not shown.
E) Hornworts do not form spores.
 From which part of this hornwort would spores be released?
From which part of this hornwort would spores be released?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) The relevant structure is not shown.
E) Hornworts do not form spores.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Hornwort sporophytes have a basal region of cell division rather than an apical region.What effect does this have on sporophyte function in hornworts, as compared with mosses?
A) It provides a place for symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria to live, while in mosses the apical cell division creates structures for mycorrhizal fungi.
B) It allows spores to be continually made and released as long as the sporophyte lives, while in mosses only one set of spores is made per sporophyte.
C) It limits division of sporophytes to the base so hornworts do not get as tall as mosses.
D) It keeps making green tissue to support growth of the gametophyte, while in mosses the gametophyte supports the sporophyte.
E) It helps raise the spores so they can be more easily dispersed by symbiotic fungi, while in mosses the spores are dispersed by wind.
A) It provides a place for symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria to live, while in mosses the apical cell division creates structures for mycorrhizal fungi.
B) It allows spores to be continually made and released as long as the sporophyte lives, while in mosses only one set of spores is made per sporophyte.
C) It limits division of sporophytes to the base so hornworts do not get as tall as mosses.
D) It keeps making green tissue to support growth of the gametophyte, while in mosses the gametophyte supports the sporophyte.
E) It helps raise the spores so they can be more easily dispersed by symbiotic fungi, while in mosses the spores are dispersed by wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
This group's sporophyte exhibits indeterminate growth and develops no stalk, and there is a single large chloroplast in each cell.
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes
A) Liverworts
B) Hornworts
C) Mosses
D) Stoneworts
E) Coleochaetophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One important benefit of the evolution of xylem was the development of a mechanism for
A) sugar transport.
B) sperm transport.
C) water retention.
D) rigid structural support.
E) increased gas exchange.
A) sugar transport.
B) sperm transport.
C) water retention.
D) rigid structural support.
E) increased gas exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the figure, which shows a nonvascular plant.  The underside of the starlike structure of the plant body is the location of the _______ generation.
The underside of the starlike structure of the plant body is the location of the _______ generation.
A) gametophyte
B) sporophyte
C) meiotic
D) zygotic
E) alternate
 The underside of the starlike structure of the plant body is the location of the _______ generation.
The underside of the starlike structure of the plant body is the location of the _______ generation.A) gametophyte
B) sporophyte
C) meiotic
D) zygotic
E) alternate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the figure, which shows hornworts.  In which order did this hornwort plant develop, from oldest to newest growth?
In which order did this hornwort plant develop, from oldest to newest growth?
A) B A C
B) A B C
C) A C B
D) C A B
E) C B A
 In which order did this hornwort plant develop, from oldest to newest growth?
In which order did this hornwort plant develop, from oldest to newest growth?A) B A C
B) A B C
C) A C B
D) C A B
E) C B A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If lignin-containing cell walls had not evolved in land plants, we might now have
A) fields of tall plants that have rhizoids but lack stomata.
B) forests of tall animals instead of tall plants.
C) plants that grow underground instead of upward.
D) the same plant communities that we have now, because they would still have cellulose walls.
E) land areas of the planet covered with mats of low-lying plants and no trees.
A) fields of tall plants that have rhizoids but lack stomata.
B) forests of tall animals instead of tall plants.
C) plants that grow underground instead of upward.
D) the same plant communities that we have now, because they would still have cellulose walls.
E) land areas of the planet covered with mats of low-lying plants and no trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Approximately _______ species of moss (Bryophyta) have been described.
A) 15
B) 100
C) 1,200
D) 9,000
E) 15,000
A) 15
B) 100
C) 1,200
D) 9,000
E) 15,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement about the hornworts is true?
A) They form the sister group of seed plants.
B) Their cells contain multiple chloroplasts.
C) Their sporophytes exhibit determinate growth.
D) They have tracheids.
E) They possess stomata.
A) They form the sister group of seed plants.
B) Their cells contain multiple chloroplasts.
C) Their sporophytes exhibit determinate growth.
D) They have tracheids.
E) They possess stomata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The cyanobacteria found in the internal mucilage-filled cavities of hornworts serve to
A) provide structural support for the plant.
B) obtain mineral nutrients for the plant.
C) convert atmospheric nitrogen gas into a form usable by the plant.
D) convert atmospheric sulfur dioxide gas into a form usable by the plant.
E) provide carbohydrates to the plant.
A) provide structural support for the plant.
B) obtain mineral nutrients for the plant.
C) convert atmospheric nitrogen gas into a form usable by the plant.
D) convert atmospheric sulfur dioxide gas into a form usable by the plant.
E) provide carbohydrates to the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the figure, which shows a nonvascular plant.  The nonvascular plant shown is a
The nonvascular plant shown is a
A) liverwort (Hepatophyta).
B) hornwort (Anthocerophyta).
C) moss (Bryophyta).
D) stonewort (green algae).
E) club moss (Lycophyta).
 The nonvascular plant shown is a
The nonvascular plant shown is aA) liverwort (Hepatophyta).
B) hornwort (Anthocerophyta).
C) moss (Bryophyta).
D) stonewort (green algae).
E) club moss (Lycophyta).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Vascular plants are thought to be the result of a single evolutionary event: the evolution of a wholly new cell type, the tracheid.This cell type
A) provides a mechanism for the storage of a new type of carbohydrate, starch.
B) is the first cell type to contain chloroplasts.
C) permits fertilization in the absence of water, thus permitting plants to invade dry habitats.
D) forms the sporangium.
E) is the principal water-conducting element of the xylem in all early vascular plants.
A) provides a mechanism for the storage of a new type of carbohydrate, starch.
B) is the first cell type to contain chloroplasts.
C) permits fertilization in the absence of water, thus permitting plants to invade dry habitats.
D) forms the sporangium.
E) is the principal water-conducting element of the xylem in all early vascular plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
You find a mat of short green plants growing on your neighbor's front lawn.You look at them through a microscope and see that they lack vascular tissue and are dispersing lots of spores from small brown stalks.The plants are most likely a colony of
A) liverworts.
B) hornworts.
C) mosses.
D) horsetails.
E) ferns.
A) liverworts.
B) hornworts.
C) mosses.
D) horsetails.
E) ferns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The nonvascular plant clades (including moss) require liquid water for fertilization during sexual reproduction because
A) they have no vascular system for transporting water to the developing sporophyte.
B) eggs are fertilized by a flagellated sperm that swims to the egg.
C) the neck of the archegonium has to degrade to allow the sperm to enter.
D) spores must swim to the egg for fertilization.
E) embryos develop in a water-filled sac.
A) they have no vascular system for transporting water to the developing sporophyte.
B) eggs are fertilized by a flagellated sperm that swims to the egg.
C) the neck of the archegonium has to degrade to allow the sperm to enter.
D) spores must swim to the egg for fertilization.
E) embryos develop in a water-filled sac.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The most likely reason that nonvascular land plants have never evolved to the size of vascular plants is that they lack
A) a photosynthetic mechanism.
B) an efficient mode of respiration.
C) an efficient system for conducting water and minerals long distances against gravity.
D) nutrient and water absorption mechanisms.
E) effective spore dispersal mechanisms.
A) a photosynthetic mechanism.
B) an efficient mode of respiration.
C) an efficient system for conducting water and minerals long distances against gravity.
D) nutrient and water absorption mechanisms.
E) effective spore dispersal mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match the description below with the correct group of seedless vascular plants from the list that follows.
They are sometimes called the scouring rushes because the silica deposits in their cell walls make them useful for cleaning; their reduced true leaves form distinct whorls around the stem.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes
They are sometimes called the scouring rushes because the silica deposits in their cell walls make them useful for cleaning; their reduced true leaves form distinct whorls around the stem.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which plant tissue would not be affected by treatment with a chemical that disrupts chromosome pairing for crossing over?
A) Hornwort antheridium
B) Moss sporangium
C) Fern sorus
D) Club moss strobilus
E) Horsetail sporangium
A) Hornwort antheridium
B) Moss sporangium
C) Fern sorus
D) Club moss strobilus
E) Horsetail sporangium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the description with the correct group of seedless vascular plants from the list that follows.
They bear simple leaves arranged spirally on a stem and exhibit apical growth; the sporangia are contained within conelike structures called strobili.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes
They bear simple leaves arranged spirally on a stem and exhibit apical growth; the sporangia are contained within conelike structures called strobili.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the figure, which shows alternation of generations in the life cycle of a land plant. 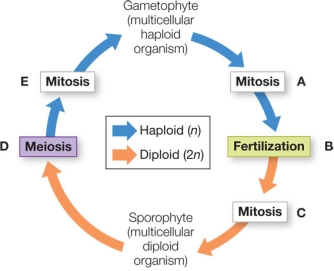 In a fern, the structure being formed at step C in the diagram would be
In a fern, the structure being formed at step C in the diagram would be
A) smaller than the gametophyte and lack chloroplasts.
B) larger than the gametophyte and lack chloroplasts.
C) larger than the gametophyte and nutritionally independent.
D) smaller than the gametophyte and might or might not be nutritionally independent.
E) larger than and nutritionally dependent on the gametophyte.
 In a fern, the structure being formed at step C in the diagram would be
In a fern, the structure being formed at step C in the diagram would beA) smaller than the gametophyte and lack chloroplasts.
B) larger than the gametophyte and lack chloroplasts.
C) larger than the gametophyte and nutritionally independent.
D) smaller than the gametophyte and might or might not be nutritionally independent.
E) larger than and nutritionally dependent on the gametophyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match the description below with the correct group of seedless vascular plants from the list that follows.
This ancient group lacked roots and leaves but had a central column of xylem running through its stems.It had dichotomously branching aerial stems that were occasionally topped by sporangia.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes
This ancient group lacked roots and leaves but had a central column of xylem running through its stems.It had dichotomously branching aerial stems that were occasionally topped by sporangia.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which group is unlikely to have contributed significantly to the world's current energy supply?
A) Marine algae
B) Sphagnum moss
C) Club mosses
D) Tree ferns
E) Liverworts
A) Marine algae
B) Sphagnum moss
C) Club mosses
D) Tree ferns
E) Liverworts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
An abundant type of coal is formed almost entirely from plant material buried during the Carboniferous period.Which plant group was most likely a major contributor to these coal deposits?
A) Hornworts
B) Mosses
C) Liverworts
D) Chlorophytes
E) Club mosses
A) Hornworts
B) Mosses
C) Liverworts
D) Chlorophytes
E) Club mosses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Match the description below with the correct group of seedless vascular plants from the list that follows.
They typically have large leaves with branching vascular strands, some can reach heights of up to 20 m, and the sporangia are usually clustered in groups called sori.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes
They typically have large leaves with branching vascular strands, some can reach heights of up to 20 m, and the sporangia are usually clustered in groups called sori.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which structures characteristic of vascular plants developed first in the lycophytes?
A) A thick, waxy cuticle to prevent desiccation and pores called stomata to allow for gas exchange
B) Megaphylls and a specialized arrangement of vascular tissue to allow differentiation of water and sugar transport
C) An independent sporophyte and true roots that branch dichotomously
D) A protected embryo and pores called stomata to allow for gas exchange
E) True roots that branch dichotomously and a persistently green sporophyte
A) A thick, waxy cuticle to prevent desiccation and pores called stomata to allow for gas exchange
B) Megaphylls and a specialized arrangement of vascular tissue to allow differentiation of water and sugar transport
C) An independent sporophyte and true roots that branch dichotomously
D) A protected embryo and pores called stomata to allow for gas exchange
E) True roots that branch dichotomously and a persistently green sporophyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A field biologist has brought you a plant fossil to analyze.To determine whether it is a vascular plant, you would look for the presence of fossilized
A) tracheids.
B) antheridia.
C) archegonia.
D) protonema.
E) roots.
A) tracheids.
B) antheridia.
C) archegonia.
D) protonema.
E) roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the description below with the correct group of seedless vascular plants from the list that follows.
Their vascular tissue includes xylem and phloem, they have megaphylls, and there is a differentiation between the main stem and side branches rather than dichotomous branching.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes
Their vascular tissue includes xylem and phloem, they have megaphylls, and there is a differentiation between the main stem and side branches rather than dichotomous branching.
A) Club mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Ferns
D) Monilophytes
E) Rhyniophytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The horsetails and ferns are members of a single clade, the
A) lycophytes.
B) streptophytes.
C) euphyllophytes.
D) monilophytes.
E) bryophytes.
A) lycophytes.
B) streptophytes.
C) euphyllophytes.
D) monilophytes.
E) bryophytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the phylogeny of the living vascular plant groups, which clade made the earliest split from the common ancestor of vascular plants?
A) Rhyniophytes
B) Monilophytes
C) Lycophytes
D) Gymnosperms
E) Angiosperms
A) Rhyniophytes
B) Monilophytes
C) Lycophytes
D) Gymnosperms
E) Angiosperms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which statement describing how tracheids aided early plants in their terrestrial environment is false?
A) Tracheids provided a path for water to travel from a source of supply to regions of need in the plant body.
B) The cell walls of tracheids are reinforced with lignin, providing rigid structural support that allowed plants to grow upward toward the sun and against gravity.
C) Tracheids provided a path for sugars to travel from a source of supply to regions of need in the plant body.
D) The increase in plant height due to the presence of tracheids improved spore dispersal, allowing progeny to spread farther.
E) Tracheids provided a path for minerals to travel from a source of supply to regions of need in the plant body.
A) Tracheids provided a path for water to travel from a source of supply to regions of need in the plant body.
B) The cell walls of tracheids are reinforced with lignin, providing rigid structural support that allowed plants to grow upward toward the sun and against gravity.
C) Tracheids provided a path for sugars to travel from a source of supply to regions of need in the plant body.
D) The increase in plant height due to the presence of tracheids improved spore dispersal, allowing progeny to spread farther.
E) Tracheids provided a path for minerals to travel from a source of supply to regions of need in the plant body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A club moss sporophyte with a single terminal strobilus produces 12,000 spores.How many spores would the sporophyte have produced if it had dichotomously branched twice before the strobili developed?
A) 12,000
B) 24,000
C) 36,000
D) 48,000
E) 120,000
A) 12,000
B) 24,000
C) 36,000
D) 48,000
E) 120,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fossilized remains of a rhyniophyte show that these extinct plants lacked
A) roots.
B) xylem.
C) sporangia.
D) dichotomous branching.
E) stomata.
A) roots.
B) xylem.
C) sporangia.
D) dichotomous branching.
E) stomata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
There are approximately _______ living species of horsetails (a monilophyte).
A) 15
B) 100
C) 1,200
D) 9,000
E) 15,000
A) 15
B) 100
C) 1,200
D) 9,000
E) 15,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which land plant group possesses leaflike microphylls?
A) Mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Club mosses
D) Ferns
E) Liverworts
A) Mosses
B) Horsetails
C) Club mosses
D) Ferns
E) Liverworts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The first vascular plants were probably
A) rhyniophytes.
B) lycophytes.
C) mosses.
D) monilophytes.
E) liverworts.
A) rhyniophytes.
B) lycophytes.
C) mosses.
D) monilophytes.
E) liverworts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Lycophyte-fern forests arose in the Devonian period and persisted for _______ years.
A) 100,000
B) 2 million
C) 200 million
D) 600 million
E) 2 billion
A) 100,000
B) 2 million
C) 200 million
D) 600 million
E) 2 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 251 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



