Deck 30: Animal Origins and the Evolution of Body Plans
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/248
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Animal Origins and the Evolution of Body Plans
1
Both fungi and animals are characterized by
A) heterotrophy and internal digestion.
B) multicellularity and a nervous system.
C) internal digestion and movement.
D) multicellularity and movement.
E) heterotrophy and multicellularity.
A) heterotrophy and internal digestion.
B) multicellularity and a nervous system.
C) internal digestion and movement.
D) multicellularity and movement.
E) heterotrophy and multicellularity.
E
2
In reptiles, the presence of a large body of acellular yolk within the fertilized egg creates a(n) _______ cleavage pattern in which the dividing cells form an embryo on top of the yolk mass.
A) complete
B) radial
C) incomplete
D) spiral
E) determinate
A) complete
B) radial
C) incomplete
D) spiral
E) determinate
C
3
The ancestor of the animal clade was probably a
A) colonial flagellated protist.
B) triploblastic acoelomate with spiral cleavage.
C) ciliated protist.
D) ctenophore.
E) protostome.
A) colonial flagellated protist.
B) triploblastic acoelomate with spiral cleavage.
C) ciliated protist.
D) ctenophore.
E) protostome.
A
4
Which of the following cannot be used as a clue to the evolutionary relationships of animals?
A) The fossil record
B) Patterns of embryonic development
C) Comparative morphology and physiology
D) Genomic sequence patterns
E) Size and number of offspring
A) The fossil record
B) Patterns of embryonic development
C) Comparative morphology and physiology
D) Genomic sequence patterns
E) Size and number of offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about the placozoan Trichoplax adhaerens is false?
A) It has four cell types.
B) Mature forms have a mouth leading to a simple gut.
C) It is an evolutionary reversal from a more complex body form.
D) It has the smallest genome of any known animal.
E) It is not closely related to other major animal groups.
A) It has four cell types.
B) Mature forms have a mouth leading to a simple gut.
C) It is an evolutionary reversal from a more complex body form.
D) It has the smallest genome of any known animal.
E) It is not closely related to other major animal groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Spiral cleavage is found in which of the following taxa?
A) Lophotrochozoans, such as earthworms
B) Xenoturbellids
C) Ecdysozoans, such as insects
D) Hemichordates
E) Vertebrates
A) Lophotrochozoans, such as earthworms
B) Xenoturbellids
C) Ecdysozoans, such as insects
D) Hemichordates
E) Vertebrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which trait(s) is/are not shared by all animals?
A) Specific types of cell-cell junctions
B) A common set of extracellular matrix molecules
C) A complete gut
D) Multicellularity
E) Similarities in Hox genes
A) Specific types of cell-cell junctions
B) A common set of extracellular matrix molecules
C) A complete gut
D) Multicellularity
E) Similarities in Hox genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a difference between fungi and animals?
A) Only fungi are heterotrophic.
B) Only fungi are multicellular.
C) Only fungi have external digestion.
D) Only animals have external digestion.
E) Only fungi are unicellular.
A) Only fungi are heterotrophic.
B) Only fungi are multicellular.
C) Only fungi have external digestion.
D) Only animals have external digestion.
E) Only fungi are unicellular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which feature is a synapomorphy of the animals?
A) Cells that contain chitin
B) Vascular systems
C) Similarities in Hox genes
D) Bilateral symmetry
E) Spiral cleavage
A) Cells that contain chitin
B) Vascular systems
C) Similarities in Hox genes
D) Bilateral symmetry
E) Spiral cleavage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which characteristics are unique to animals?
A) Heterotrophic metabolism and motility
B) Muscle tissue and a nervous system
C) Multicellularity and motility
D) Internal digestion and heterotrophic metabolism
E) A nervous system and heterotrophy
A) Heterotrophic metabolism and motility
B) Muscle tissue and a nervous system
C) Multicellularity and motility
D) Internal digestion and heterotrophic metabolism
E) A nervous system and heterotrophy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Because all animals must take in nutrients from their environment, the nutritional mode of animals is called
A) heterotrophic.
B) photoheterotrophic.
C) photoautotrophic.
D) chemolithotrophic.
E) chemoautotrophic.
A) heterotrophic.
B) photoheterotrophic.
C) photoautotrophic.
D) chemolithotrophic.
E) chemoautotrophic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bilaterally symmetrical animals can be divided into two major groups that separated during the Cambrian.These two lineages differ fundamentally in their
A) modes of reproduction.
B) early embryological development.
C) modes of obtaining and storing energy.
D) environmental requirements.
E) metabolism.
A) modes of reproduction.
B) early embryological development.
C) modes of obtaining and storing energy.
D) environmental requirements.
E) metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following are deuterostomes?
A) Chickens, lizards, and fishes
B) Lancelets, mollusks, and humans
C) Elephants, lizards, mollusks, and chickens
D) Humans, snakes, chelicerates, and moose
E) Fishes, echinoderms, and arrow worms
A) Chickens, lizards, and fishes
B) Lancelets, mollusks, and humans
C) Elephants, lizards, mollusks, and chickens
D) Humans, snakes, chelicerates, and moose
E) Fishes, echinoderms, and arrow worms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which animal group lacks body symmetry?
A) Echinoderms
B) Chordates
C) Placozoans
D) Insects
E) Cnidarians
A) Echinoderms
B) Chordates
C) Placozoans
D) Insects
E) Cnidarians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The deuterostome mouth originates from the blastopore.
B) Diploblastic organisms have two embryonic layers: an outer ectoderm and an inner mesoderm.
C) Ctenophores have two embryonic layers: an outer endoderm and an inner ectoderm.
D) The protostome mouth originates from a second opening after formation of the blastopore.
E) Triploblastic organisms have three embryonic layers: an outer ectoderm, a mesoderm, and an inner endoderm.
A) The deuterostome mouth originates from the blastopore.
B) Diploblastic organisms have two embryonic layers: an outer ectoderm and an inner mesoderm.
C) Ctenophores have two embryonic layers: an outer endoderm and an inner ectoderm.
D) The protostome mouth originates from a second opening after formation of the blastopore.
E) Triploblastic organisms have three embryonic layers: an outer ectoderm, a mesoderm, and an inner endoderm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not a feature of the sponges?
A) Choanocytes
B) Pores
C) Spicules
D) Mesoderm
E) Eggs
A) Choanocytes
B) Pores
C) Spicules
D) Mesoderm
E) Eggs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following features is a synapomorphy of the bilaterians?
A) Development of the notochord
B) Blastopore that develops into the anus
C) Two embryonic layers
D) Radial cleavage
E) Bilateral symmetry along the anterior-posterior axis
A) Development of the notochord
B) Blastopore that develops into the anus
C) Two embryonic layers
D) Radial cleavage
E) Bilateral symmetry along the anterior-posterior axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following characteristics distinguishes deuterostomes from protostomes?
A) Segmentation
B) Presence of Hox genes
C) Embryological origin of the mouth
D) Appendages
E) Body symmetry
A) Segmentation
B) Presence of Hox genes
C) Embryological origin of the mouth
D) Appendages
E) Body symmetry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The flagella of choanocytes
A) create a current to bring food-bearing water across surfaces.
B) allow for locomotion of the sponge as a whole.
C) allow for locomotion of individual sponge cells.
D) produce gametes.
E) give support to the body of the sponge.
A) create a current to bring food-bearing water across surfaces.
B) allow for locomotion of the sponge as a whole.
C) allow for locomotion of individual sponge cells.
D) produce gametes.
E) give support to the body of the sponge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The placozoans are considered to be the sister group to which of the following taxa?
A) Ctenophores
B) Cnidarians
C) Calcareous sponges
D) Demosponges
E) Glass sponges
A) Ctenophores
B) Cnidarians
C) Calcareous sponges
D) Demosponges
E) Glass sponges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following structures is/are not involved with some mechanism of movement in animals?
A) Fluid-filled coelom
B) Segmentation
C) Appendages
D) Cilia
E) Blastopore
A) Fluid-filled coelom
B) Segmentation
C) Appendages
D) Cilia
E) Blastopore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Bilateral symmetry
A) is common in ctenophores.
B) is correlated with cephalization.
C) is a characteristic of animals that move in multiple directions.
D) means that two halves of an organism are identical.
E) is characteristic of placozoans.
A) is common in ctenophores.
B) is correlated with cephalization.
C) is a characteristic of animals that move in multiple directions.
D) means that two halves of an organism are identical.
E) is characteristic of placozoans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In terrestrial environments, fluid-filled body cavities function as hydrostatic skeletons and
A) make locomotion possible in smaller soft-bodied animals like snails.
B) are common in animals with protective hard skeletons.
C) are common in animals that move using muscles attached to limbs.
D) are important for movement in humans.
E) are commonly associated with hard skeletons that support muscular limbs.
A) make locomotion possible in smaller soft-bodied animals like snails.
B) are common in animals with protective hard skeletons.
C) are common in animals that move using muscles attached to limbs.
D) are important for movement in humans.
E) are commonly associated with hard skeletons that support muscular limbs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not considered part of the body plan of an organism?
A) The symmetry of the body
B) The structure of the body cavity
C) The segmentation of the body
D) External appendages
E) The larval morphology
A) The symmetry of the body
B) The structure of the body cavity
C) The segmentation of the body
D) External appendages
E) The larval morphology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Segmentation of animals is important evolutionarily because it
A) allows organisms to grow much larger than they could without segmentation.
B) has allowed organisms to alter their body forms in complex ways.
C) increases the mobility of an organism.
D) reduces the surface area-to-volume ratio.
E) allows for asexual reproduction.
A) allows organisms to grow much larger than they could without segmentation.
B) has allowed organisms to alter their body forms in complex ways.
C) increases the mobility of an organism.
D) reduces the surface area-to-volume ratio.
E) allows for asexual reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Coordinated movement in animals is achieved because of
A) a peritoneum.
B) a central nervous system.
C) a coelom.
D) radial symmetry.
E) a dorsal surface.
A) a peritoneum.
B) a central nervous system.
C) a coelom.
D) radial symmetry.
E) a dorsal surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The main difference between a coelom and a pseudocoel is a coelom is
A) enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the outside only; a pseudocoel is enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the inside only.
B) not enclosed by mesodermal tissues; a pseudocoel is completely surrounded by mesodermal tissues.
C) enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the inside and the outside; a pseudocoel is surrounded by mesodermal tissues on the outside only.
D) enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the inside only; a pseudocoel is a solid structure.
E) derived from endodermal cells; a pseudocoel is derived from mesodermal cells.
A) enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the outside only; a pseudocoel is enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the inside only.
B) not enclosed by mesodermal tissues; a pseudocoel is completely surrounded by mesodermal tissues.
C) enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the inside and the outside; a pseudocoel is surrounded by mesodermal tissues on the outside only.
D) enclosed by mesodermal tissues on the inside only; a pseudocoel is a solid structure.
E) derived from endodermal cells; a pseudocoel is derived from mesodermal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The terms "acoelomate," "pseudocoelomate," and "coelomate" refer to
A) levels of cephalization.
B) the origin of the blastopore.
C) ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, respectively.
D) the vertebrate body plan.
E) the body cavities of animals.
A) levels of cephalization.
B) the origin of the blastopore.
C) ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, respectively.
D) the vertebrate body plan.
E) the body cavities of animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A pseudocoelomate animal lacks a
A) body cavity.
B) fluid-filled body cavity.
C) fluid-filled body cavity lined on the outside with mesoderm.
D) fluid-filled body cavity lined on the outside and inside with mesoderm.
E) pseudocoel.
A) body cavity.
B) fluid-filled body cavity.
C) fluid-filled body cavity lined on the outside with mesoderm.
D) fluid-filled body cavity lined on the outside and inside with mesoderm.
E) pseudocoel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The body cavity of coelomate animals develops within the
A) endoderm.
B) ectoderm.
C) mesoderm.
D) pseudocoel.
E) mesoglea.
A) endoderm.
B) ectoderm.
C) mesoderm.
D) pseudocoel.
E) mesoglea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The overall shape of an animal can be described by its
A) number of germ layers.
B) body cavity structure.
C) cephalization.
D) internal organ structure.
E) body symmetry.
A) number of germ layers.
B) body cavity structure.
C) cephalization.
D) internal organ structure.
E) body symmetry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A coelom differs from a pseudocoel in that
A) a coelom is filled with mesenchyme, while a pseudocoel has no mesenchyme.
B) a coelom acts as a hydrostatic skeleton in some animals, but not in pseudocoelomates.
C) a coelom is fluid-filled, while a pseudocoel is not.
D) a coelom develops within the mesoderm, while a pseudocoel is enclosed by mesoderm only on the outside.
E) a coelom is lined with endoderm, while a pseudocoel is lined with a peritoneum.
A) a coelom is filled with mesenchyme, while a pseudocoel has no mesenchyme.
B) a coelom acts as a hydrostatic skeleton in some animals, but not in pseudocoelomates.
C) a coelom is fluid-filled, while a pseudocoel is not.
D) a coelom develops within the mesoderm, while a pseudocoel is enclosed by mesoderm only on the outside.
E) a coelom is lined with endoderm, while a pseudocoel is lined with a peritoneum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An infinite number of planes passing through the central point can divide an organism into mirror-image halves in
A) spherically symmetrical organisms.
B) radially symmetrical organisms.
C) echinoderms.
D) bilaterally symmetrical organisms.
E) deuterostomes.
A) spherically symmetrical organisms.
B) radially symmetrical organisms.
C) echinoderms.
D) bilaterally symmetrical organisms.
E) deuterostomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A radially symmetrical, sessile animal that possesses some sort of straining device would most likely be a(n)
A) herbivore.
B) detritivore.
C) carnivore.
D) grazer.
E) parasite.
A) herbivore.
B) detritivore.
C) carnivore.
D) grazer.
E) parasite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement about the symmetry of organisms is false?
A) Radial symmetry is common in ctenophores and cnidarians. b. Radial symmetry is common in segmented animals.
C) Spherical symmetry is common in unicellular protists.
D) The back of a bilaterally symmetrical organism is the dorsal surface.
E) Sensory organs in a bilaterally symmetrical organism are located on the anterior end of the organism.
A) Radial symmetry is common in ctenophores and cnidarians. b. Radial symmetry is common in segmented animals.
C) Spherical symmetry is common in unicellular protists.
D) The back of a bilaterally symmetrical organism is the dorsal surface.
E) Sensory organs in a bilaterally symmetrical organism are located on the anterior end of the organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Cnidarians have the type of symmetry known as _______ symmetry.
A) asymmetrical
B) radial
C) spherical
D) bilateral
E) axial
A) asymmetrical
B) radial
C) spherical
D) bilateral
E) axial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Cephalization is most commonly associated with
A) spherical symmetry.
B) radial symmetry.
C) sessile animals.
D) bilateral symmetry.
E) lophophorate animals.
A) spherical symmetry.
B) radial symmetry.
C) sessile animals.
D) bilateral symmetry.
E) lophophorate animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following would not be an example of segmentation related to movement or feeding?
A) Claws of a lobster
B) Limbs of a frog
C) Poison claws of a centipede
D) Setae of marine annelids
E) Antennae of insects
A) Claws of a lobster
B) Limbs of a frog
C) Poison claws of a centipede
D) Setae of marine annelids
E) Antennae of insects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following would be an example of enhanced movement due to appendages?
A) Modified limbs that allow animals to use powered flight
B) A fluid-filled body cavity that supports an animal on land
C) A distinct head region with concentration of sensory organs
D) Multiple repeated body segments
E) Possession of a nerve net
A) Modified limbs that allow animals to use powered flight
B) A fluid-filled body cavity that supports an animal on land
C) A distinct head region with concentration of sensory organs
D) Multiple repeated body segments
E) Possession of a nerve net

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Animals with a coelom have an advantage over other triploblastic animals because they
A) have better control over movement than other triploblasts.
B) have more appendages than other triploblasts.
C) show less cephalization than other triploblasts.
D) lack mesenchyme, providing more space for internal organs.
E) possess a nerve net, which enhances their ability to feed.
A) have better control over movement than other triploblasts.
B) have more appendages than other triploblasts.
C) show less cephalization than other triploblasts.
D) lack mesenchyme, providing more space for internal organs.
E) possess a nerve net, which enhances their ability to feed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement best distinguishes herbivores from predators?
A) Herbivores consume detritus, while predators consume other animals.
B) Herbivores consume other animals, while predators consume detritus.
C) Herbivores stalk and pursue their prey, while predators passively filter food.
D) Herbivores do not expend energy in subduing prey, while predators do.
E) Herbivores have simple guts, while predators have complex guts.
A) Herbivores consume detritus, while predators consume other animals.
B) Herbivores consume other animals, while predators consume detritus.
C) Herbivores stalk and pursue their prey, while predators passively filter food.
D) Herbivores do not expend energy in subduing prey, while predators do.
E) Herbivores have simple guts, while predators have complex guts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which two food acquisition methods often involve feeding on other organisms without killing or significantly damaging them?
A) Parasitism and predation
B) Omnivory and detritivory
C) Predation and parasitism
D) Herbivory and predation
E) Parasitism and herbivory
A) Parasitism and predation
B) Omnivory and detritivory
C) Predation and parasitism
D) Herbivory and predation
E) Parasitism and herbivory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A larva is
A) a young animal of any species, such as a puppy.
B) the pupa of a butterfly.
C) the adult form of an organism.
D) the immature early life stage of an animal before the adult form is assumed.
E) the sessile form of an organism.
A) a young animal of any species, such as a puppy.
B) the pupa of a butterfly.
C) the adult form of an organism.
D) the immature early life stage of an animal before the adult form is assumed.
E) the sessile form of an organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The bilaterally symmetrical larval form of many crustaceans is called a
A) trochophore.
B) nauplius.
C) planula.
D) caterpillar.
E) polyp.
A) trochophore.
B) nauplius.
C) planula.
D) caterpillar.
E) polyp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Earthworms break down organic matter and build up rich soils.They are an example of
A) omnivores.
B) herbivores.
C) detritivores.
D) parasites.
E) nematocysts.
A) omnivores.
B) herbivores.
C) detritivores.
D) parasites.
E) nematocysts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Colonial animals differ from multicellular animals in that
A) colonies may consist of physiologically integrated individuals.
B) colonial animals may be genetically different from each other.
C) individuals within a colony have identical functions.
D) colonial animals are always unicellular.
E) some colonies of animals are produced through fission.
A) colonies may consist of physiologically integrated individuals.
B) colonial animals may be genetically different from each other.
C) individuals within a colony have identical functions.
D) colonial animals are always unicellular.
E) some colonies of animals are produced through fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A trochophore is
A) a spherically symmetrical larval form.
B) the larval form of polychaete worms and mollusks.
C) the larval form of crustaceans.
D) a bilaterally symmetrical larval form.
E) a type of coral.
A) a spherically symmetrical larval form.
B) the larval form of polychaete worms and mollusks.
C) the larval form of crustaceans.
D) a bilaterally symmetrical larval form.
E) a type of coral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following can function without a digestive system?
A) Ectoparasites
B) Endoparasites
C) Detritivores
D) Herbivores
E) Carnivores
A) Ectoparasites
B) Endoparasites
C) Detritivores
D) Herbivores
E) Carnivores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following stages is not part of the typical life cycle of a butterfly?
A) Trochophore
B) Egg
C) Pupa
D) Larva
E) Adult
A) Trochophore
B) Egg
C) Pupa
D) Larva
E) Adult

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which statement about endoparasites is true?
A) They consume bacteria on the surface of their hosts.
B) They kill their hosts with toxins.
C) They feed on dead material in soil.
D) They consume dead skin cells.
E) They do not need a digestive system because they absorb predigested nutrients from their hosts.
A) They consume bacteria on the surface of their hosts.
B) They kill their hosts with toxins.
C) They feed on dead material in soil.
D) They consume dead skin cells.
E) They do not need a digestive system because they absorb predigested nutrients from their hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Most parasite species have a
A) simple life cycle and a single larval stage.
B) simple life cycle and a single host.
C) complex life cycle, multiple larval stages, and a single host.
D) complex life cycle, a single larval stage, and multiple hosts.
E) complex life cycle, multiple larval stages, and multiple hosts.
A) simple life cycle and a single larval stage.
B) simple life cycle and a single host.
C) complex life cycle, multiple larval stages, and a single host.
D) complex life cycle, a single larval stage, and multiple hosts.
E) complex life cycle, multiple larval stages, and multiple hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why are bryozoans considered to be colonial animals?
A) They consist of genetically heterogeneous individuals.
B) They consist of physiologically isolated individuals.
C) They reproduce sexually.
D) They produce many small eggs.
E) They consist of genetically homogeneous individuals.
A) They consist of genetically heterogeneous individuals.
B) They consist of physiologically isolated individuals.
C) They reproduce sexually.
D) They produce many small eggs.
E) They consist of genetically homogeneous individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An animal, such as a snake, that waits in one spot for food is an example of a(n)
A) herbivore.
B) filter feeder.
C) carnivore.
D) detritovore.
E) trochophore.
A) herbivore.
B) filter feeder.
C) carnivore.
D) detritovore.
E) trochophore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The complex life cycles of parasites provide an evolutionary advantage by
A) facilitating dispersal.
B) helping the host overcome parasite defenses.
C) allowing the parasite to acquire host DNA.
D) overwhelming the host with toxins.
E) killing the host before the host can reproduce.
A) facilitating dispersal.
B) helping the host overcome parasite defenses.
C) allowing the parasite to acquire host DNA.
D) overwhelming the host with toxins.
E) killing the host before the host can reproduce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What type of animal generally has the most complex life cycle?
A) Herbivore
B) Parasite
C) Detritivore
D) Carnivore
E) Filter feeder
A) Herbivore
B) Parasite
C) Detritivore
D) Carnivore
E) Filter feeder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following feeding strategies is most likely to be associated with a sessile organism?
A) Filter feeding
B) Herbivory
C) Predation
D) Parasitism
E) Detritus feeding
A) Filter feeding
B) Herbivory
C) Predation
D) Parasitism
E) Detritus feeding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A caterpillar feeds on a single plant, metamorphoses into a pupa, and into an adult moth, and flies away.This is an example of
A) migration.
B) dispersal.
C) reproduction.
D) a nauplius.
E) a trochophore larva.
A) migration.
B) dispersal.
C) reproduction.
D) a nauplius.
E) a trochophore larva.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Motile filter feeders include
A) flamingos.
B) corals.
C) polychaetes.
D) sponges.
E) placozoans.
A) flamingos.
B) corals.
C) polychaetes.
D) sponges.
E) placozoans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Fleas and ticks are _______ that are _______.
A) colonial animals; endoparasites
B) ecdysozoans; endoparasites
C) deuterostomes; endoparasites
D) deuterostomes; ectoparasites
E) ecdysozoans; ectoparasites
A) colonial animals; endoparasites
B) ecdysozoans; endoparasites
C) deuterostomes; endoparasites
D) deuterostomes; ectoparasites
E) ecdysozoans; ectoparasites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is/are not an adaptation for predatory feeding?
A) Toxins
B) Camouflage
C) Long and complex digestive systems
D) Sensitive sense organs
E) Sharp teeth and claws
A) Toxins
B) Camouflage
C) Long and complex digestive systems
D) Sensitive sense organs
E) Sharp teeth and claws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement about colonial animals is false?
A) They include the Portuguese man-of-war.
B) They are all genetically identical clones.
C) They have arisen only once in evolution.
D) In some species, different groups of individuals can be specialized for different functions.
E) Members function as a single integrated organism.
A) They include the Portuguese man-of-war.
B) They are all genetically identical clones.
C) They have arisen only once in evolution.
D) In some species, different groups of individuals can be specialized for different functions.
E) Members function as a single integrated organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which example does not illustrate an evolutionary trade-off in a life cycle?
A) Production of a large number of large eggs
B) Production of defensive structures at the expense of growth
C) Production of a small number of large eggs
D) Larger energy stores in eggs of precocial young
E) Inability of filter feeders to capture large prey items
A) Production of a large number of large eggs
B) Production of defensive structures at the expense of growth
C) Production of a small number of large eggs
D) Larger energy stores in eggs of precocial young
E) Inability of filter feeders to capture large prey items

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Sponges differ from other animals in that they
A) do not form true organs.
B) are sessile.
C) are triploblastic.
D) have trochophore larvae.
E) are diploblastic.
A) do not form true organs.
B) are sessile.
C) are triploblastic.
D) have trochophore larvae.
E) are diploblastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following can be cited as evidence for the bilaterians as a clade?
A) A blastopore that develops into the mouth
B) Two embryonic cell layers
C) Radial symmetry
D) Bilateral symmetry
E) A blastopore that develops into the anus
A) A blastopore that develops into the mouth
B) Two embryonic cell layers
C) Radial symmetry
D) Bilateral symmetry
E) A blastopore that develops into the anus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which taxa is considered the sister group of all other animals?
A) Sponges
B) Placozoans
C) Ctenophores
D) Cnidarians
E) Phoronids
A) Sponges
B) Placozoans
C) Ctenophores
D) Cnidarians
E) Phoronids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which type of sponge cell is specialized for creating the currents that draw food particles into the sponge?
A) Spicule
B) Pore cell
C) Osculum
D) Choanocyte
E) Nematocyst
A) Spicule
B) Pore cell
C) Osculum
D) Choanocyte
E) Nematocyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Of the more than 9,000 species of sponges, _______ live in fresh water.
A) 20
B) 50
C) 1,000
D) 4,500
E) 8,000
A) 20
B) 50
C) 1,000
D) 4,500
E) 8,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the table, which compares 27 amino acid positions for ten different species. 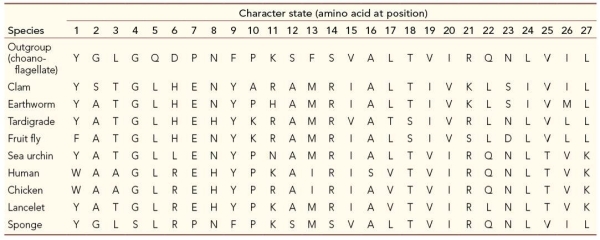 Which lancelet character has a state that is shared with the protostomes?
Which lancelet character has a state that is shared with the protostomes?
A) 3
B) 11
C) 13
D) 22
E) 23
 Which lancelet character has a state that is shared with the protostomes?
Which lancelet character has a state that is shared with the protostomes?A) 3
B) 11
C) 13
D) 22
E) 23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following may be part of an evolutionary trade-off that confronts animal species?
A) Long egg incubation period
B) Ability to filter large food particles out of water
C) Continuous breeding
D) Production of precocial young
E) Production of mobile larvae
A) Long egg incubation period
B) Ability to filter large food particles out of water
C) Continuous breeding
D) Production of precocial young
E) Production of mobile larvae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the sponge body plan?
A) Gastrovascular cavity
B) No distinct tissue layers or organs
C) No separation between the different cell layers
D) Organization around a water canal system
E) Asymmetry
A) Gastrovascular cavity
B) No distinct tissue layers or organs
C) No separation between the different cell layers
D) Organization around a water canal system
E) Asymmetry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following are not eumetazoans?
A) Deuterostomes
B) Sponges
C) Cnidarians
D) Bilaterians
E) Protostomes
A) Deuterostomes
B) Sponges
C) Cnidarians
D) Bilaterians
E) Protostomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the table, which compares 27 amino acid positions for ten different species. 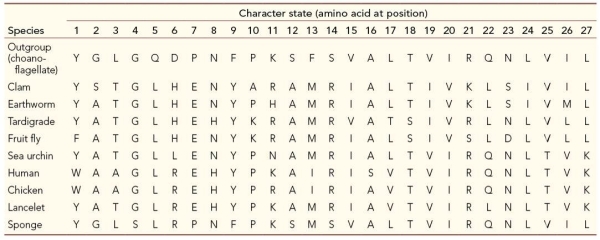 Which character state(s) is/are unique in the earthworm?
Which character state(s) is/are unique in the earthworm?
A) 10
B) 10 and 26
C) 10 and 11
D) 10, 11, and 26
E) 11 and 26
 Which character state(s) is/are unique in the earthworm?
Which character state(s) is/are unique in the earthworm?A) 10
B) 10 and 26
C) 10 and 11
D) 10, 11, and 26
E) 11 and 26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
With a fixed amount of available energy, a female animal is restricted in the size and number of eggs she can produce.This is not consistent with which of the following statements?
A) She can produce many large eggs.
B) She can produce many small eggs.
C) She can produce a few large eggs.
D) This is an example of an energy trade-off.
E) Energy used to make shells cannot be used for her own growth.
A) She can produce many large eggs.
B) She can produce many small eggs.
C) She can produce a few large eggs.
D) This is an example of an energy trade-off.
E) Energy used to make shells cannot be used for her own growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the table, which compares 27 amino acid positions for ten different species. 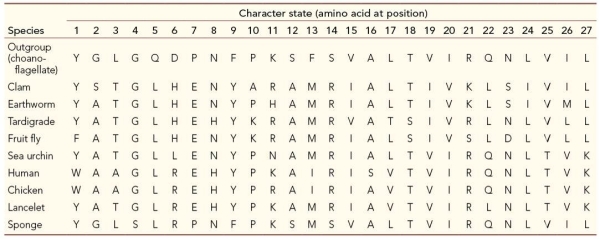 Which of the following characters have shared, derived character states for deuterostomes?
Which of the following characters have shared, derived character states for deuterostomes?
A) 2 and 25
B) 10, 25, and 26
C) 14, 19, and 26
D) 17 and 19
E) 25, 26, and 27
 Which of the following characters have shared, derived character states for deuterostomes?
Which of the following characters have shared, derived character states for deuterostomes?A) 2 and 25
B) 10, 25, and 26
C) 14, 19, and 26
D) 17 and 19
E) 25, 26, and 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Refer to the table, which compares 27 amino acid positions for ten different species. 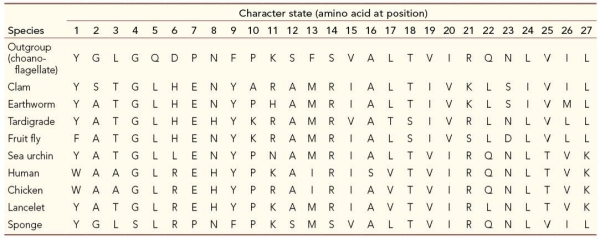 What is the phylogenetic significance of character state 11 for the earthworm?
What is the phylogenetic significance of character state 11 for the earthworm?
A) The earthworm is the only species with this state.
B) It distinguishes the earthworm as a protostome.
C) It distinguishes the earthworm as a deuterostome.
D) It distinguishes the earthworm as radially symmetrical.
E) It is the same as the outgroup.
 What is the phylogenetic significance of character state 11 for the earthworm?
What is the phylogenetic significance of character state 11 for the earthworm?A) The earthworm is the only species with this state.
B) It distinguishes the earthworm as a protostome.
C) It distinguishes the earthworm as a deuterostome.
D) It distinguishes the earthworm as radially symmetrical.
E) It is the same as the outgroup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Refer to the table, which compares 27 amino acid positions for ten different species. 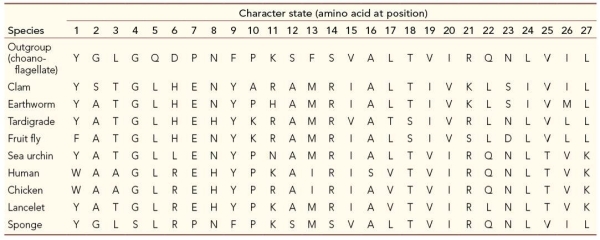 Which are shared, derived character states of bilaterians?
Which are shared, derived character states of bilaterians?
A) 5 and 12
B) 7 and 9
C) 10 and 14
D) 10 and 22
E) 15 and 27
 Which are shared, derived character states of bilaterians?
Which are shared, derived character states of bilaterians?A) 5 and 12
B) 7 and 9
C) 10 and 14
D) 10 and 22
E) 15 and 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Refer to the table, which compares 27 amino acid positions for ten different species. 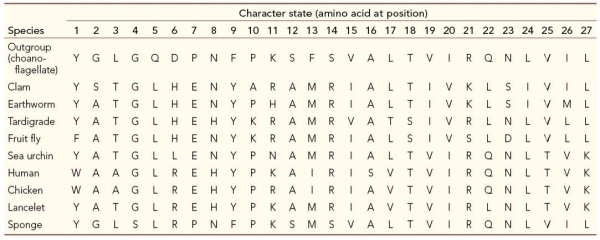 Which two character states are the same only in the outgroup and the sponge?
Which two character states are the same only in the outgroup and the sponge?
A) 2 and 22
B) 5 and 25
C) 7 and 14
D) 9 and 17
E) 12 and 27
 Which two character states are the same only in the outgroup and the sponge?
Which two character states are the same only in the outgroup and the sponge?A) 2 and 22
B) 5 and 25
C) 7 and 14
D) 9 and 17
E) 12 and 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which statement about sponges is false?
A) Their tissues are organized into distinct organs.
B) Their body plan consists of an aggregation of cells built around a water canal system.
C) They are sessile organisms.
D) They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
E) They have no distinct embryonic cell layers.
A) Their tissues are organized into distinct organs.
B) Their body plan consists of an aggregation of cells built around a water canal system.
C) They are sessile organisms.
D) They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
E) They have no distinct embryonic cell layers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Precocial birds
A) incubate their eggs for a short period of time.
B) produce many large eggs.
C) produce small numbers of eggs.
D) produce few small eggs.
E) incubate their eggs for a long period of time.
A) incubate their eggs for a short period of time.
B) produce many large eggs.
C) produce small numbers of eggs.
D) produce few small eggs.
E) incubate their eggs for a long period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Diploblastic marine animals with mesoglea between the two cell layers, a complete gut, and locomotion provided by beating cilia are
A) parasites.
B) ctenophores.
C) scyphozoans.
D) anthozoans.
E) sponges.
A) parasites.
B) ctenophores.
C) scyphozoans.
D) anthozoans.
E) sponges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 248 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



