Deck 38: Plant Responses to Environmental Challenges
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/246
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 38: Plant Responses to Environmental Challenges
1
The ability of plants to employ resistance genes to counter specific pathogen Avr genes is called
A) physical isolation.
B) a receptor mechanism.
C) gene-for-gene resistance.
D) a pathogen response.
E) signaling.
A) physical isolation.
B) a receptor mechanism.
C) gene-for-gene resistance.
D) a pathogen response.
E) signaling.
C
2
Gene-for-gene resistance is an example of
A) an inducible defense.
B) a signal transduction pathway.
C) an evolutionary arms race.
D) a defense against herbivory.
E) phytoremediation.
A) an inducible defense.
B) a signal transduction pathway.
C) an evolutionary arms race.
D) a defense against herbivory.
E) phytoremediation.
C
3
The molecules peroxide and superoxide that are produced in plants in response to pathogens
A) stimulate plant metabolism.
B) are toxic to the pathogens.
C) initiate hormone signaling.
D) specifically target retroviruses.
E) function as effector molecules.
A) stimulate plant metabolism.
B) are toxic to the pathogens.
C) initiate hormone signaling.
D) specifically target retroviruses.
E) function as effector molecules.
B
4
Plants acquire systemic resistance in much the same way that people acquire resistance to pathogens; however, the mechanism of systemic acquired resistance is quite different in plants.Which of the following does not have a role in acquired resistance in plants?
A) Salicylic acid
B) R genes
C) Methyl salicylate
D) PR proteins
E) All of the above have a role in acquired resistance in plants.
A) Salicylic acid
B) R genes
C) Methyl salicylate
D) PR proteins
E) All of the above have a role in acquired resistance in plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A pathogen-damaged wild plant is found to have high levels of expression of PR proteins, but the plant is not presently under attack by pathogens.The best explanation for this situation is that
A) plant defenses have already defeated the pathogens.
B) the pathogens were eaten by birds.
C) the plant is a genetically engineered mutant.
D) the plant mistook a pollinator for an herbivore.
E) the plant will be defended against pathogens for its entire life.
A) plant defenses have already defeated the pathogens.
B) the pathogens were eaten by birds.
C) the plant is a genetically engineered mutant.
D) the plant mistook a pollinator for an herbivore.
E) the plant will be defended against pathogens for its entire life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Defensive strategies in plants that are always turned on are called _______ defenses.
A) induced
B) transgenic
C) alternating
D) constitutive
E) gene-for-gene
A) induced
B) transgenic
C) alternating
D) constitutive
E) gene-for-gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In response to tissue damage caused by pathogens,
A) both plants and animals seal off damaged tissues.
B) both plants and animals repair damaged tissues.
C) both plants and animals sometimes seal off and sometimes repair damaged tissues.
D) animals repair damaged tissues, and plants seal off damaged tissues.
E) animals seal off damaged tissues, and plants repair damaged tissues.
A) both plants and animals seal off damaged tissues.
B) both plants and animals repair damaged tissues.
C) both plants and animals sometimes seal off and sometimes repair damaged tissues.
D) animals repair damaged tissues, and plants seal off damaged tissues.
E) animals seal off damaged tissues, and plants repair damaged tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A newly discovered gene in a petunia plant produces an integral membrane protein that helps the petunia resist pathogens.This gene probably codes for a
A) receptor protein.
B) cytoskeletal protein.
C) G protein.
D) nucleoporin.
E) transporter protein.
A) receptor protein.
B) cytoskeletal protein.
C) G protein.
D) nucleoporin.
E) transporter protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following compounds is not known to play a major role in plant defense?
A) Terpenes
B) Alkaloids
C) Gibberellins
D) Phenolics
E) Salicylic acid
A) Terpenes
B) Alkaloids
C) Gibberellins
D) Phenolics
E) Salicylic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Refer to the figure, showing gene-for-gene resistance. 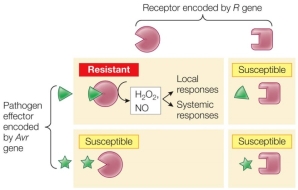 What would a resistant plant use to help defend itself against a pathogen closely related to the one that produced the wedge-shaped molecule?
What would a resistant plant use to help defend itself against a pathogen closely related to the one that produced the wedge-shaped molecule?
A) A new R gene
B) Its existing R gene
C) Flavonoids
D) Phytoalexins
E) Polysaccharides
 What would a resistant plant use to help defend itself against a pathogen closely related to the one that produced the wedge-shaped molecule?
What would a resistant plant use to help defend itself against a pathogen closely related to the one that produced the wedge-shaped molecule?A) A new R gene
B) Its existing R gene
C) Flavonoids
D) Phytoalexins
E) Polysaccharides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
After being attacked by a smut fungus, a group of corn plants becomes more resistant to further attack.These plants now have
A) increased tolerance.
B) general acquired resistance.
C) systemic acquired resistance.
D) antifungal proteins.
E) antifreeze proteins.
A) increased tolerance.
B) general acquired resistance.
C) systemic acquired resistance.
D) antifungal proteins.
E) antifreeze proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A scientist claims to have found a way to induce the production of animal-type antibodies in nontransgenic plants, which will render the plant resistant to certain plant pathogens.Which response would be most appropriate?
A) No induction is needed because plants make these antibodies naturally.
B) This has already been done.
C) This is not possible because the defense systems of plants are different from those of animals.
D) Animals do not have antibodies.
E) The resistance will be effective only in the short term.
A) No induction is needed because plants make these antibodies naturally.
B) This has already been done.
C) This is not possible because the defense systems of plants are different from those of animals.
D) Animals do not have antibodies.
E) The resistance will be effective only in the short term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A healthy plant fighting off an attack by a bacterial pathogen develops dry brown spots on its leaves.These spots are _______ produced by the plant to isolate the pathogen.
A) abscission zones
B) areas of abscisic acid
C) necrotic lesions
D) callose deposits
E) avirulent regions
A) abscission zones
B) areas of abscisic acid
C) necrotic lesions
D) callose deposits
E) avirulent regions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a tobacco plant that shows gene-for-gene resistance to some fungi is killed by a smut fungus, the most likely explanation is that the plant's R genes did not match the fungus's
A) R gene.
B) tRNA.
C) virus.
D) Avr gene.
E) bacterium.
A) R gene.
B) tRNA.
C) virus.
D) Avr gene.
E) bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Refer to the figure, showing induced resistance mechanisms. 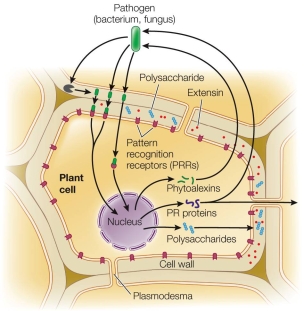 If the number of polysaccharides shown in the figure increased tenfold, they would
If the number of polysaccharides shown in the figure increased tenfold, they would
A) poison the herbivore.
B) block PR protein transport.
C) coat pathogens.
D) strengthen the cell wall.
E) signal the nucleus to make more PR proteins.
 If the number of polysaccharides shown in the figure increased tenfold, they would
If the number of polysaccharides shown in the figure increased tenfold, they wouldA) poison the herbivore.
B) block PR protein transport.
C) coat pathogens.
D) strengthen the cell wall.
E) signal the nucleus to make more PR proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Phytoalexin production is an example of a(n)
A) constitutive plant defense.
B) environmental challenge.
C) induced plant defense.
D) mechanical defense.
E) gene-for-gene response.
A) constitutive plant defense.
B) environmental challenge.
C) induced plant defense.
D) mechanical defense.
E) gene-for-gene response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Daisies that are attacked by pathogens produce extra cytochrome c protein to defeat the invading pathogens.In this case, cytochrome c is functioning as a(n)
A) expansin.
B) pathogenesis-related protein.
C) antibiotic.
D) phytoalexin.
E) local defender.
A) expansin.
B) pathogenesis-related protein.
C) antibiotic.
D) phytoalexin.
E) local defender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a plant has one gene related to a particular pathogen and that pathogen has a corresponding gene, the plant can develop
A) tolerance.
B) hardening.
C) plasmodesmata.
D) alkaloids.
E) gene-for-gene resistance.
A) tolerance.
B) hardening.
C) plasmodesmata.
D) alkaloids.
E) gene-for-gene resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Pathogens employ _______ genes that code for molecules called elicitors.
A) phytoalexin
B) hypersensitive-response
C) extensin
D) lignin
E) Avr
A) phytoalexin
B) hypersensitive-response
C) extensin
D) lignin
E) Avr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Extensin serves to
A) store water in plants.
B) defend against plant pathogen attacks.
C) repel plant predators because they are toxic to animals.
D) act as salt glands in plants.
E) strengthen cell walls to form a barrier against the internal spread of a plant pathogen.
A) store water in plants.
B) defend against plant pathogen attacks.
C) repel plant predators because they are toxic to animals.
D) act as salt glands in plants.
E) strengthen cell walls to form a barrier against the internal spread of a plant pathogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Some insects evade latex-based plant defenses by
A) draining the latex.
B) digesting the latex.
C) inducing polymerization of the latex while it is still in the plant.
D) diluting the latex to a safe concentration.
E) building up immunity to the latex.
A) draining the latex.
B) digesting the latex.
C) inducing polymerization of the latex while it is still in the plant.
D) diluting the latex to a safe concentration.
E) building up immunity to the latex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which compounds are plant secondary metabolites?
A) Enzymes
B) Lipids
C) Alkaloids
D) Pectins
E) Nucleic acids
A) Enzymes
B) Lipids
C) Alkaloids
D) Pectins
E) Nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A newly discovered relative of the rubber tree most likely uses _______ as its main and most effective defense against herbivores.
A) sucrose
B) latex
C) pathogenesis-related proteins
D) salicylic acid
E) pectin
A) sucrose
B) latex
C) pathogenesis-related proteins
D) salicylic acid
E) pectin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that a plant has been biochemically fractionated and the defense compounds that repulse caterpillars are found to contain high levels of nitrogen.This plant makes
A) phenolics.
B) anthocyanins.
C) terpenoids.
D) terpenes.
E) alkaloids.
A) phenolics.
B) anthocyanins.
C) terpenoids.
D) terpenes.
E) alkaloids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Typically, when leaves are damaged by herbivory, plants start to produce defensive compounds that are classified as belonging to what group of chemicals?
A) Nucleic acids
B) Primary metabolites
C) Lipids
D) Trichomes
E) Secondary metabolites
A) Nucleic acids
B) Primary metabolites
C) Lipids
D) Trichomes
E) Secondary metabolites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The nicotine in tobacco is an example of a plant
A) alkaloid.
B) flavonoid.
C) glycoside.
D) steroid.
E) tannin.
A) alkaloid.
B) flavonoid.
C) glycoside.
D) steroid.
E) tannin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which action is not one of the hypersensitive reactions of a plant to infection?
A) Production of phytoalexins by cells around the infection
B) Death of cells near the infection
C) Death of infected cells
D) Synthesis of pathogenesis-related proteins
E) Transport of phytoalexins to all parts of the plant
A) Production of phytoalexins by cells around the infection
B) Death of cells near the infection
C) Death of infected cells
D) Synthesis of pathogenesis-related proteins
E) Transport of phytoalexins to all parts of the plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nicotine helps to defend plants against herbivores by acting as a(n)
A) hormone analog.
B) hormone inhibitor.
C) inhibitor of cell division.
D) neurotoxin.
E) feeding deterrent.
A) hormone analog.
B) hormone inhibitor.
C) inhibitor of cell division.
D) neurotoxin.
E) feeding deterrent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which evidence best supports the hypothesis that the presence of toxic latex in leaves deters insects from feeding on a plant?
A) Many insects do not feed on latex-producing plants.
B) Latex-producing plants release milky latex when their leaves are damaged.
C) Beetles that drain latex out of a leaf part then feed on the latex-free part.
D) Beetles that cut veins in the leaves then feed on the released latex.
E) Latex-producing plants have high survival rates.
A) Many insects do not feed on latex-producing plants.
B) Latex-producing plants release milky latex when their leaves are damaged.
C) Beetles that drain latex out of a leaf part then feed on the latex-free part.
D) Beetles that cut veins in the leaves then feed on the released latex.
E) Latex-producing plants have high survival rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
_______ serve as phytoalexins in plant defense strategies.
A) Monoterpenes
B) Triterpenes
C) Flavonoids
D) Sterols
E) Polyterpenes
A) Monoterpenes
B) Triterpenes
C) Flavonoids
D) Sterols
E) Polyterpenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An RNA virus attack on a plant triggers the production of interference RNA (RNAi) such as siRNA.This siRNA is derived from the RNA of the _______ and causes the plant to _______.
A) virus; die from a viral infection
B) plant; become immune to the virus
C) plant; form mechanical barriers to the virus
D) virus; become immune to the virus
E) virus; form mechanical barriers to the virus
A) virus; die from a viral infection
B) plant; become immune to the virus
C) plant; form mechanical barriers to the virus
D) virus; become immune to the virus
E) virus; form mechanical barriers to the virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
_______ is a thick white suspension produced by some plants as a mechanical defense.
A) Salt suspension
B) Protein emulsion
C) P-slime
D) Latex
E) Mucilage
A) Salt suspension
B) Protein emulsion
C) P-slime
D) Latex
E) Mucilage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A plant's first line of defense against herbivore damage is its
A) epidermis.
B) root system.
C) apical meristem.
D) lenticels.
E) vascular system.
A) epidermis.
B) root system.
C) apical meristem.
D) lenticels.
E) vascular system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which group of plant chemicals is generally produced constitutively as a defense against herbivores?
A) Primary metabolites
B) Amino acids
C) Secondary metabolites
D) Proteins
E) Tertiary metabolites
A) Primary metabolites
B) Amino acids
C) Secondary metabolites
D) Proteins
E) Tertiary metabolites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Phytoalexins
A) are toxic to many different fungi and bacteria.
B) are made uniformly throughout a plant.
C) are always present in plants.
D) bind to a specific receptor on the invading pathogen.
E) function as effector molecules.
A) are toxic to many different fungi and bacteria.
B) are made uniformly throughout a plant.
C) are always present in plants.
D) bind to a specific receptor on the invading pathogen.
E) function as effector molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Secondary metabolites
A) are essential for basic cellular processes in the plant body.
B) are similar in all plants.
C) occur more often in animals than in plants.
D) may attract or inhibit other organisms.
E) are usually of high molecular weight.
A) are essential for basic cellular processes in the plant body.
B) are similar in all plants.
C) occur more often in animals than in plants.
D) may attract or inhibit other organisms.
E) are usually of high molecular weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Plants can be treated with _______ to stimulate the production of pathogenesis-related proteins.
A) salicylic acid
B) PR-inducer protease inhibitor
C) phytoalexins
D) cellulose
E) extensin
A) salicylic acid
B) PR-inducer protease inhibitor
C) phytoalexins
D) cellulose
E) extensin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Pathogens can be walled off during the hypersensitive response by the process of
A) isolation.
B) programmed cell death.
C) senescence.
D) systemic acquired resistance.
E) Avr release.
A) isolation.
B) programmed cell death.
C) senescence.
D) systemic acquired resistance.
E) Avr release.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Glucosinolates help to protect plants against herbivores by
A) acting as neurotoxins.
B) inhibiting respiration.
C) blocking cell division.
D) disrupting muscle function.
E) blocking animal hormones.
A) acting as neurotoxins.
B) inhibiting respiration.
C) blocking cell division.
D) disrupting muscle function.
E) blocking animal hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Pyrethrin is an example of a defensive secondary metabolite called a(n)
A) monoterpene.
B) terpene.
C) flavonoid.
D) anthocyanin.
E) polyterpene.
A) monoterpene.
B) terpene.
C) flavonoid.
D) anthocyanin.
E) polyterpene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Laticifers are
A) specialized cells for containing sodium ions.
B) cells in roots that take up water in dry environments.
C) waxy cells in the epidermis.
D) cells that produce poisons such as alkaloids.
E) tubes for storing hydrophobic secondary metabolites.
A) specialized cells for containing sodium ions.
B) cells in roots that take up water in dry environments.
C) waxy cells in the epidermis.
D) cells that produce poisons such as alkaloids.
E) tubes for storing hydrophobic secondary metabolites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Defensive water-soluble secondary compounds formed by plants are most commonly stored in the
A) vacuoles.
B) nuclei.
C) cell walls.
D) cytoplasm.
E) membrane proteins.
A) vacuoles.
B) nuclei.
C) cell walls.
D) cytoplasm.
E) membrane proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement about plants and heavy metals is false?
A) Plants take up heavy metals.
B) All populations of a plant species have the same capacity to tolerate heavy metals.
C) Populations of plants that tolerate heavy metals can evolve rapidly.
D) A plant's tolerance to heavy metals is determined by its genotype.
E) Plants in areas with heavy metals usually experience little competition.
A) Plants take up heavy metals.
B) All populations of a plant species have the same capacity to tolerate heavy metals.
C) Populations of plants that tolerate heavy metals can evolve rapidly.
D) A plant's tolerance to heavy metals is determined by its genotype.
E) Plants in areas with heavy metals usually experience little competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the figure. 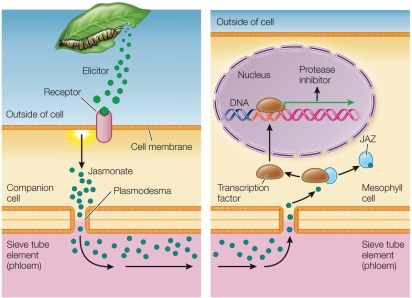 If a moth larva chewed on a dandelion plant, elicitors would be produced in
If a moth larva chewed on a dandelion plant, elicitors would be produced in
A) the plant.
B) the herbivore.
C) either the plant or the herbivore.
D) beneficial microbes.
E) the surrounding soil.
 If a moth larva chewed on a dandelion plant, elicitors would be produced in
If a moth larva chewed on a dandelion plant, elicitors would be produced inA) the plant.
B) the herbivore.
C) either the plant or the herbivore.
D) beneficial microbes.
E) the surrounding soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Plants can produce the respiratory poison cyanide without poisoning themselves because plants
A) do not respire.
B) store a cyanide precursor in one compartment and activating enzymes in another.
C) store water-soluble cyanide in laticifers.
D) possess enzymes that are unaffected by cyanide.
E) also produce proteins that bind and inhibit cyanide.
A) do not respire.
B) store a cyanide precursor in one compartment and activating enzymes in another.
C) store water-soluble cyanide in laticifers.
D) possess enzymes that are unaffected by cyanide.
E) also produce proteins that bind and inhibit cyanide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Certain sterols produced by plants are known to
A) attract pollinators and animals that disperse seeds.
B) affect the nervous systems of animals.
C) inhibit fungal action.
D) block hormone action in insects.
E) impair growth of competing plants.
A) attract pollinators and animals that disperse seeds.
B) affect the nervous systems of animals.
C) inhibit fungal action.
D) block hormone action in insects.
E) impair growth of competing plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which statement about compounds that plants make to ward off predators and infection is true?
A) They may be produced in response to infection.
B) They are usually injurious to the plant.
C) They are sequestered in chloroplasts.
D) They are released only in response to herbivore damage.
E) They do not include proteins.
A) They may be produced in response to infection.
B) They are usually injurious to the plant.
C) They are sequestered in chloroplasts.
D) They are released only in response to herbivore damage.
E) They do not include proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The amino acid canavanine is an insecticide that is made naturally by some plants and can be applied topically to plants that do not produce it.The effect of canavanine is to
A) inhibit respiration in insects.
B) cause defects in the structure and function of insect proteins.
C) interfere with protein digestion in the guts of insects.
D) burn insect tissues due to its high acidity.
E) inhibit the synthesis of reproductive hormones in insects.
A) inhibit respiration in insects.
B) cause defects in the structure and function of insect proteins.
C) interfere with protein digestion in the guts of insects.
D) burn insect tissues due to its high acidity.
E) inhibit the synthesis of reproductive hormones in insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the figure. 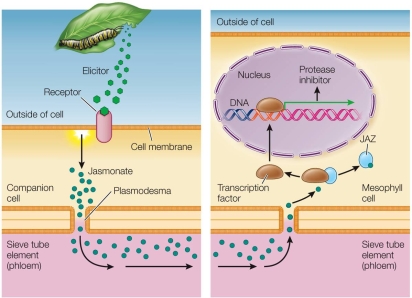 Insects raised on a diet of plant materials grow more slowly than those grown on a nonplant nutrient medium in the lab.This implies that the gene shown in the right panel of the figure is important for producing which defense compounds?
Insects raised on a diet of plant materials grow more slowly than those grown on a nonplant nutrient medium in the lab.This implies that the gene shown in the right panel of the figure is important for producing which defense compounds?
A) Amino acids
B) Phytoalexins
C) Anthocyanins
D) Protease inhibitors
E) Prostaglandins
 Insects raised on a diet of plant materials grow more slowly than those grown on a nonplant nutrient medium in the lab.This implies that the gene shown in the right panel of the figure is important for producing which defense compounds?
Insects raised on a diet of plant materials grow more slowly than those grown on a nonplant nutrient medium in the lab.This implies that the gene shown in the right panel of the figure is important for producing which defense compounds?A) Amino acids
B) Phytoalexins
C) Anthocyanins
D) Protease inhibitors
E) Prostaglandins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The presence of pneumatophores in plants is an adaptation for success in a _______ habitat.
A) desert
B) mountain
C) grassland
D) seashore
E) swamp
A) desert
B) mountain
C) grassland
D) seashore
E) swamp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Beetles taken from a tropical tree show signs of serious physiological distress.Upon further toxicological examination, they are found to have ingested compounds blocking ion transport.The researchers conclude that they may have eaten
A) monoterpenes.
B) triterpenes.
C) flavonoids.
D) anthocyanins.
E) polyterpenes.
A) monoterpenes.
B) triterpenes.
C) flavonoids.
D) anthocyanins.
E) polyterpenes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A plant in a nursery survives repeated cold nights.At the end of several weeks of this weather, this plant can be described as
A) osmotically adjusted.
B) cold-hardened.
C) prestressed.
D) tolerant.
E) hyperaccumulated.
A) osmotically adjusted.
B) cold-hardened.
C) prestressed.
D) tolerant.
E) hyperaccumulated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
_______ are volatile neurotoxins from the terpene group used by plants for defense.
A) Monoterpenes
B) Triterpenes
C) Flavonoids
D) Anthocyanins
E) Polyterpenes
A) Monoterpenes
B) Triterpenes
C) Flavonoids
D) Anthocyanins
E) Polyterpenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A precursor of a toxic compound is found in the vacuoles in a leaf.The enzymes that convert this precursor into the toxic compound are most likely present in
A) the vacuole.
B) the roots.
C) the fruit.
D) another compartment in the same cell.
E) the pollen.
A) the vacuole.
B) the roots.
C) the fruit.
D) another compartment in the same cell.
E) the pollen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
_______ are antifeeding secondary metabolites used by plants for defense.
A) Monoterpenes
B) Triterpenes
C) Flavonoids
D) Anthocyanins
E) Polyterpenes
A) Monoterpenes
B) Triterpenes
C) Flavonoids
D) Anthocyanins
E) Polyterpenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Non-water-soluble (hydrophobic) poisons are stored in a plant's
A) chloroplasts.
B) laticifers or epidermal waxes.
C) Golgi bodies.
D) mitochondria.
E) vacuoles.
A) chloroplasts.
B) laticifers or epidermal waxes.
C) Golgi bodies.
D) mitochondria.
E) vacuoles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A plant that produces tannins in response to attack by an herbivore is trying to
A) inhibit digestive enzymes made by the herbivore.
B) inhibit herbivore hormones.
C) inhibit herbivore cell division.
D) attack the herbivore with a neurotoxin.
E) localize herbivore feeding.
A) inhibit digestive enzymes made by the herbivore.
B) inhibit herbivore hormones.
C) inhibit herbivore cell division.
D) attack the herbivore with a neurotoxin.
E) localize herbivore feeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Coumarins help to defend plants against herbivores by acting as
A) hormone analogs.
B) hormone inhibitors.
C) inhibitors of cell division.
D) neurotoxins.
E) feeding deterrents.
A) hormone analogs.
B) hormone inhibitors.
C) inhibitors of cell division.
D) neurotoxins.
E) feeding deterrents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which method is not used by plants to protect themselves from toxins they produce?
A) Building up a tolerance to the toxins
B) Compartmentalizing the toxins
C) Adjusting the timing of toxin production
D) Storing the toxins in waxes
E) Storing the toxins in vacuoles
A) Building up a tolerance to the toxins
B) Compartmentalizing the toxins
C) Adjusting the timing of toxin production
D) Storing the toxins in waxes
E) Storing the toxins in vacuoles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The fatty acid derivative jasmonate is a
A) nucleic acid.
B) steroid.
C) hormone.
D) protease.
E) polypeptide.
A) nucleic acid.
B) steroid.
C) hormone.
D) protease.
E) polypeptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement about heat shock proteins is false?
A) They are formed in response to heat stress.
B) They include chaperonins.
C) They are formed within minutes of a plant's exposure to elevated temperatures.
D) They can shield other proteins from denaturation.
E) They are synthesized in all plants in response to the same threshold temperature.
A) They are formed in response to heat stress.
B) They include chaperonins.
C) They are formed within minutes of a plant's exposure to elevated temperatures.
D) They can shield other proteins from denaturation.
E) They are synthesized in all plants in response to the same threshold temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A plant that thrives in Iceland, where it is exposed to freezing night temperatures and warm days, most likely produces _______ proteins.
A) cytoskeletal
B) heat shock
C) transcription factor
D) antifreeze
E) thaw-inducing
A) cytoskeletal
B) heat shock
C) transcription factor
D) antifreeze
E) thaw-inducing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Leaves adapted to a dry environment are least likely to exhibit
A) reduction in size to become spines.
B) stomata in sunken cavities.
C) dense epidermal hairs.
D) fleshy leaves.
E) large surface area.
A) reduction in size to become spines.
B) stomata in sunken cavities.
C) dense epidermal hairs.
D) fleshy leaves.
E) large surface area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A plant whose leaves contain large spaces between cells that make the leaves especially buoyant would likely be a(n) _______ plant.
A) desert
B) rainforest
C) grassland
D) aquatic
E) halophytic
A) desert
B) rainforest
C) grassland
D) aquatic
E) halophytic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure. 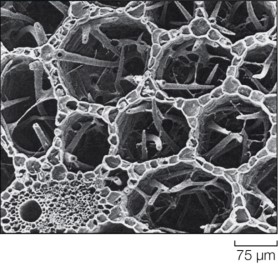 A plant with the type of stem structure shown in the image would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.
A plant with the type of stem structure shown in the image would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.
A) tundra
B) aquatic
C) wet terrestrial
D) grassland
E) dry/desert
 A plant with the type of stem structure shown in the image would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.
A plant with the type of stem structure shown in the image would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.A) tundra
B) aquatic
C) wet terrestrial
D) grassland
E) dry/desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the figure.  What advantage does the type of tissue shown in the image provide to the plant?
What advantage does the type of tissue shown in the image provide to the plant?
A) It helps isolate pathogens to prevent their spread in the plant.
B) It helps dissipate heat in desert environments.
C) It aids in defense against herbivores by letting distress signals diffuse more easily.
D) It increases buoyancy and diffusion of oxygen in submerged parts of the plant.
E) It stores water for survival in dry environments.
 What advantage does the type of tissue shown in the image provide to the plant?
What advantage does the type of tissue shown in the image provide to the plant?A) It helps isolate pathogens to prevent their spread in the plant.
B) It helps dissipate heat in desert environments.
C) It aids in defense against herbivores by letting distress signals diffuse more easily.
D) It increases buoyancy and diffusion of oxygen in submerged parts of the plant.
E) It stores water for survival in dry environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
By accumulating the amino acid proline, plants
A) become toxic to most herbivores.
B) can carry out alcoholic fermentation.
C) can extract more water from relatively dry soils.
D) can avoid toxic effects from sodium.
E) attract animals that disperse seeds.
A) become toxic to most herbivores.
B) can carry out alcoholic fermentation.
C) can extract more water from relatively dry soils.
D) can avoid toxic effects from sodium.
E) attract animals that disperse seeds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which adaptation is least likely to be used by xerophytes as a means of dealing with dry conditions?
A) Thick cuticles
B) Stomata in crypts
C) Succulence
D) Trichomes that diffract light
E) Abundant leaves
A) Thick cuticles
B) Stomata in crypts
C) Succulence
D) Trichomes that diffract light
E) Abundant leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The pneumatophores of swamp plants are modified
A) flowers.
B) leaves.
C) roots.
D) spines.
E) stems.
A) flowers.
B) leaves.
C) roots.
D) spines.
E) stems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In response to low temperatures plants may
A) produce heat shock proteins.
B) increase the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in their cell membranes.
C) exhibit systemic acquired resistance.
D) produce siRNAs.
E) increase the phytoalexin content in their cells.
A) produce heat shock proteins.
B) increase the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in their cell membranes.
C) exhibit systemic acquired resistance.
D) produce siRNAs.
E) increase the phytoalexin content in their cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which character is not a plant adaptation to a dry environment?
A) Deep taproot
B) Aerial roots
C) Higher accumulation of the amino acid proline
D) Fleshy leaves
E) Shallow but extensive root system
A) Deep taproot
B) Aerial roots
C) Higher accumulation of the amino acid proline
D) Fleshy leaves
E) Shallow but extensive root system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Plants concentrate the harmless amino acid proline in their cells to
A) generate a more negative water potential in their root cells.
B) increase their rate of transpiration.
C) increase their resistance to grazing.
D) decrease cellular salt loss.
E) decrease water uptake.
A) generate a more negative water potential in their root cells.
B) increase their rate of transpiration.
C) increase their resistance to grazing.
D) decrease cellular salt loss.
E) decrease water uptake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A gardener is wondering where to plant a newly acquired unlabeled plant.You notice the plant has pneumatophores, so you advise the gardener plant it in
A) sand.
B) loamy soil.
C) heavy clay.
D) orchid bark.
E) standing water.
A) sand.
B) loamy soil.
C) heavy clay.
D) orchid bark.
E) standing water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the figure. 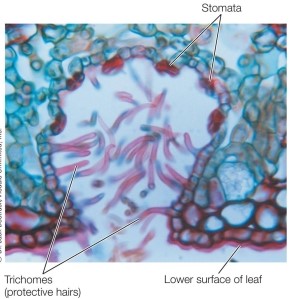 A plant with the leaf structure shown here would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.
A plant with the leaf structure shown here would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.
A) tundra
B) aquatic
C) wet terrestrial
D) grassland
E) dry/desert
 A plant with the leaf structure shown here would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.
A plant with the leaf structure shown here would most likely thrive in a(n) _______ habitat.A) tundra
B) aquatic
C) wet terrestrial
D) grassland
E) dry/desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Compared to plants native to moist forests, annual plants in the deserts of the southwestern United States are more likely to
A) have long growing seasons.
B) tolerate drought by blooming during the dry season.
C) avoid drought by surviving as seeds.
D) sense and respond to the photoperiod.
E) require several months of growth before flowering.
A) have long growing seasons.
B) tolerate drought by blooming during the dry season.
C) avoid drought by surviving as seeds.
D) sense and respond to the photoperiod.
E) require several months of growth before flowering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which statement offers the most likely reason that a plant living in the deserts of the southwestern United States loses its leaves?
A) It sheds leaves in the fall in response to decreasing day length.
B) It sheds leaves in response to cold nights.
C) It sheds leaves in response to hot weather.
D) It sheds leaves in response to drought.
E) It sheds leaves after rain.
A) It sheds leaves in the fall in response to decreasing day length.
B) It sheds leaves in response to cold nights.
C) It sheds leaves in response to hot weather.
D) It sheds leaves in response to drought.
E) It sheds leaves after rain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which environment is typical for an annual plant with a brief growing period and seeds capable of long dormant periods?
A) Salt marsh
B) Freshwater marsh
C) Environment contaminated with heavy metals
D) Desert
E) Grazed field
A) Salt marsh
B) Freshwater marsh
C) Environment contaminated with heavy metals
D) Desert
E) Grazed field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In conditions in which soil water is plentiful but oxygen is scarce, plants respond by
A) rapidly growing roots that penetrate deeply into the soil.
B) slowing root growth and making aerenchyma.
C) inhibiting the production of ATP.
D) producing oxygen from water.
E) using their leaves to collect oxygen.
A) rapidly growing roots that penetrate deeply into the soil.
B) slowing root growth and making aerenchyma.
C) inhibiting the production of ATP.
D) producing oxygen from water.
E) using their leaves to collect oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A plant sample that is found to contain high levels of proline most likely derived from a plant adapted to a _______ habitat.
A) wet
B) dry
C) windy
D) brightly lit
E) cold
A) wet
B) dry
C) windy
D) brightly lit
E) cold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Drought stress can lead to the increased production of
A) LEA proteins.
B) PAMPs.
C) JAZ.
D) protease inhibitors.
E) phytoalexins.
A) LEA proteins.
B) PAMPs.
C) JAZ.
D) protease inhibitors.
E) phytoalexins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 246 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



