Deck 10: Chromosomes and Human Genetics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Chromosomes and Human Genetics
1
The gender of a human child determined by the sperm because
A) all sperm contain the SRY gene.
B) all eggs contain the SRY gene.
C) only eggs may contain the SRY gene.
D) only sperm may contain the SRY gene.
A) all sperm contain the SRY gene.
B) all eggs contain the SRY gene.
C) only eggs may contain the SRY gene.
D) only sperm may contain the SRY gene.
D
2
Which of the following genetic changes would NOT be heritable?
A) a mutation in a skin cell
B) the loss of a chromosome in a sperm cell
C) the addition of a chromosome in an egg cell
D) a mutation in a gene in a gamete
A) a mutation in a skin cell
B) the loss of a chromosome in a sperm cell
C) the addition of a chromosome in an egg cell
D) a mutation in a gene in a gamete
A
3
The "actual results" in the experiment depicted in the following figure differ significantly from the "expected results" predicted by Mendel's laws because the gene for body color and the gene for wing length 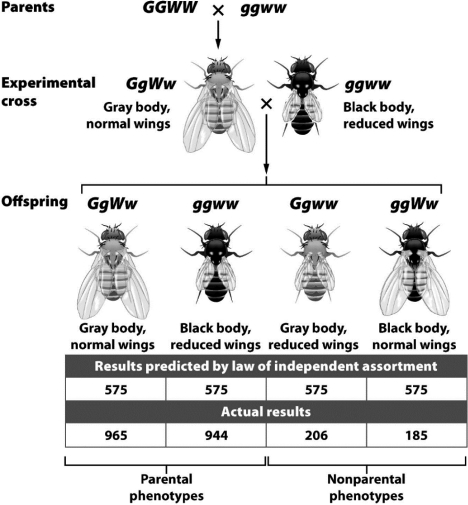
A) are both recessive.
B) are close together on a single chromosome.
C) undergo independent assortment.
D) are located on completely opposite ends of the same chromosome.

A) are both recessive.
B) are close together on a single chromosome.
C) undergo independent assortment.
D) are located on completely opposite ends of the same chromosome.
B
4
Refer to the following figure depicting fly genetic crosses.Which actual result indicates that the genes for body color and wing length in fruit flies are linked? 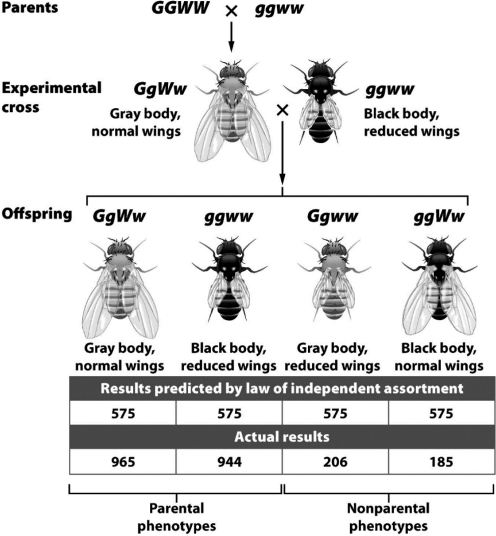
A) Four different phenotypes are present in the offspring.
B) Parental genotypes are present in the offspring.
C) Nonparental genotypes are present in the offspring.
D) A low percentage of nonparental genotypes is present in the offspring.

A) Four different phenotypes are present in the offspring.
B) Parental genotypes are present in the offspring.
C) Nonparental genotypes are present in the offspring.
D) A low percentage of nonparental genotypes is present in the offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements about crossing-over is true?
A) It lowers the likelihood of genetic recombination.
B) It disrupts the linkage between genes.
C) It results in the production of extra chromosomes.
D) It is usually fatal.
A) It lowers the likelihood of genetic recombination.
B) It disrupts the linkage between genes.
C) It results in the production of extra chromosomes.
D) It is usually fatal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following decreases the probable variation between individuals?
A) independent assortment of chromosomes
B) crossing-over
C) genetic linkage
D) random fertilization of gametes
A) independent assortment of chromosomes
B) crossing-over
C) genetic linkage
D) random fertilization of gametes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The independent assortment of chromosomes increases the
A) variation between individuals.
B) uniformity between individuals.
C) the DNA sequences shared by individuals
D) the chances of mating between individuals
A) variation between individuals.
B) uniformity between individuals.
C) the DNA sequences shared by individuals
D) the chances of mating between individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Because two genes are only very rarely separated from each other by crossing-over,it can be concluded that the two genes are
A) close to each other on the same chromosome.
B) far apart from each other on the same chromosome
C) on two different chromosomes.
D) on homologous chromosomes.
A) close to each other on the same chromosome.
B) far apart from each other on the same chromosome
C) on two different chromosomes.
D) on homologous chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The chromosome theory of inheritance states that
A) chromosomes are made of DNA.
B) genes are located on chromosomes.
C) genes are inherited.
D) patterns of inheritance are based on probability.
A) chromosomes are made of DNA.
B) genes are located on chromosomes.
C) genes are inherited.
D) patterns of inheritance are based on probability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How do genes on autosomes play a role in sex determination?
A) The "master switch" gene for maleness is on an autosome.
B) The SRY gene is on an autosome.
C) The X and Y chromosomes are autosomes.
D) The SRY gene product has an effect on autosomal genes.
A) The "master switch" gene for maleness is on an autosome.
B) The SRY gene is on an autosome.
C) The X and Y chromosomes are autosomes.
D) The SRY gene product has an effect on autosomal genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Genes A and B are located on the same chromosome.Two parent organisms with the genotypes AABB and aabb were crossed.One of the resulting AaBb offspring was experimentally crossed with an aabb individual.The final offspring genotypes were AaBb,aabb,Aabb,and aaBb. Which of the final offspring genotypes were produced through crossing-over?
A) None of the genotypes were produced through crossing-over.
B) All of the genotypes were produced through crossing-over.
C) AaBb and aabb
D) Aabb and aaBb
A) None of the genotypes were produced through crossing-over.
B) All of the genotypes were produced through crossing-over.
C) AaBb and aabb
D) Aabb and aaBb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements would be true if the linkage between two traits were complete?
A) Only the parental combinations of phenotypes could appear in the progeny.
B) The rules of independent assortment would hold true.
C) Combinations of phenotypes different from those seen in the parents would be produced.
D) The exchange of genetic material between chromosomes would be frequent.
A) Only the parental combinations of phenotypes could appear in the progeny.
B) The rules of independent assortment would hold true.
C) Combinations of phenotypes different from those seen in the parents would be produced.
D) The exchange of genetic material between chromosomes would be frequent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Because an individual with an XX genotype is a female,is an individual with an XO (no second sex chromosome)a male?
A) No, because the X always overrides the Y and makes that embryo female.
B) No, because the Y chromosome contains the gene that makes an embryo male.
C) Yes, because if there is only one X, the embryo cannot become female.
D) Yes, because all embryos start off as males.
A) No, because the X always overrides the Y and makes that embryo female.
B) No, because the Y chromosome contains the gene that makes an embryo male.
C) Yes, because if there is only one X, the embryo cannot become female.
D) Yes, because all embryos start off as males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A genetically normal human who has a homozygous genotype for a gene locus on the X chromosome
A) must be a male.
B) must be a female.
C) cannot be a female.
D) may be either male or female.
A) must be a male.
B) must be a female.
C) cannot be a female.
D) may be either male or female.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Chromosomes that are NOT involved in determining gender are known as
A) autosomes.
B) sex chromosomes.
C) homologous.
D) linked.
A) autosomes.
B) sex chromosomes.
C) homologous.
D) linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Genes that are located on opposite ends of the same chromosome are
A) not affected by crossing-over.
B) affected by crossing-over at the same frequency as genes that are located next to each other on the same chromosome.
C) only affected by crossover events that occur between two nonhomologous chromosomes.
D) affected by crossing-over so frequently that they may appear to undergo independent assortment.
A) not affected by crossing-over.
B) affected by crossing-over at the same frequency as genes that are located next to each other on the same chromosome.
C) only affected by crossover events that occur between two nonhomologous chromosomes.
D) affected by crossing-over so frequently that they may appear to undergo independent assortment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following processes is NOT a method of generating new combinations of alleles in the offspring of two individuals?
A) crossing-over between chromosomes
B) fertilization of an egg by a sperm
C) independent assortment of chromosomes
D) linkage of genes
A) crossing-over between chromosomes
B) fertilization of an egg by a sperm
C) independent assortment of chromosomes
D) linkage of genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
We now know that the gene for flower color and the gene for seed color are both on chromosome 1 of the pea plants once studied by Mendel.According to Mendel's results,flower color and seed color undergo independent assortment.Which of the following explanations is most likely?
A) Nonhomologous chromosomes containing the two genes underwent crossing-over to create a new "hybrid" chromosome containing both genes.
B) During a round of meiosis, the female part of a flower failed to separate a homologous pair, forcing the seed color gene to pair up with the flower color gene.
C) Between the time that Mendel studied peas and modern times, one of the genes was translocated onto chromosome 1, so that in modern times, two genes that were once on separate chromosomes are now linked.
D) These genes are so far apart on chromosome 1 that they undergo independent assortment.
A) Nonhomologous chromosomes containing the two genes underwent crossing-over to create a new "hybrid" chromosome containing both genes.
B) During a round of meiosis, the female part of a flower failed to separate a homologous pair, forcing the seed color gene to pair up with the flower color gene.
C) Between the time that Mendel studied peas and modern times, one of the genes was translocated onto chromosome 1, so that in modern times, two genes that were once on separate chromosomes are now linked.
D) These genes are so far apart on chromosome 1 that they undergo independent assortment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Inheritance is said to be both stable and variable because
A) chromosome structure ensures that the DNA sequence of a chromosome never changes but allows offspring to inherit individual chromosomes randomly.
B) the process of gamete formation never changes, but the number of chromosomes in a gamete differs in different offspring.
C) most of the time, genetic material is transferred with complete accuracy to the next generation while still creating unique individuals.
D) each new individual is a mixture of different chromosomes, but the same genes are found on every chromosome in that individual.
A) chromosome structure ensures that the DNA sequence of a chromosome never changes but allows offspring to inherit individual chromosomes randomly.
B) the process of gamete formation never changes, but the number of chromosomes in a gamete differs in different offspring.
C) most of the time, genetic material is transferred with complete accuracy to the next generation while still creating unique individuals.
D) each new individual is a mixture of different chromosomes, but the same genes are found on every chromosome in that individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In humans,which of the following chromosomes would probably carry the fewest genes?
A) the Y chromosome
B) chromosome 4
C) the X chromosome
D) chromosome 14
A) the Y chromosome
B) chromosome 4
C) the X chromosome
D) chromosome 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
This chromosomal disorder known as Cri du chat syndrome is the result of missing a part of chromosome 5,an example of chromosome
A) inversion.
B) deletion.
C) translocation.
D) duplication.
A) inversion.
B) deletion.
C) translocation.
D) duplication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
During cell division,a piece of a chromosome breaks away and is added to the end of its homologue.The homologue with the addition is an example of
A) duplication.
B) inversion.
C) translocation.
D) deletion.
A) duplication.
B) inversion.
C) translocation.
D) deletion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During translocation,
A) pieces of DNA are exchanged between the non-sister chromatids of a homologous pair.
B) a segment of DNA is broken off of a chromosome and reattached to the same chromosome but backward in orientation.
C) segments of DNA involved in crossing-over undergo somatic mutations.
D) a segment of DNA breaks off one chromosome and is attached to a nonhomologous chromosome.
A) pieces of DNA are exchanged between the non-sister chromatids of a homologous pair.
B) a segment of DNA is broken off of a chromosome and reattached to the same chromosome but backward in orientation.
C) segments of DNA involved in crossing-over undergo somatic mutations.
D) a segment of DNA breaks off one chromosome and is attached to a nonhomologous chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following figure contains a pedigree for cystic fibrosis,an autosomal recessive disorder.Which of the following is true? 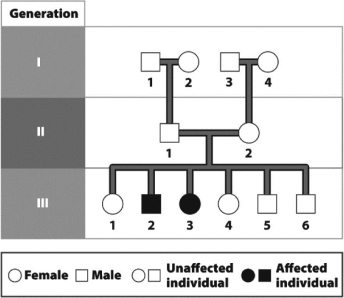
A) At least two of the members of Generation I are carriers of cystic fibrosis.
B) None of the members of Generation II is a carrier of cystic fibrosis.
C) Individual 2 in Generation II has cystic fibrosis.
D) The cystic fibrosis gene is found on a sex chromosome.

A) At least two of the members of Generation I are carriers of cystic fibrosis.
B) None of the members of Generation II is a carrier of cystic fibrosis.
C) Individual 2 in Generation II has cystic fibrosis.
D) The cystic fibrosis gene is found on a sex chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The allele responsible for causing Huntington disease is
A) dominant.
B) recessive.
C) sex-linked.
D) not heritable.
A) dominant.
B) recessive.
C) sex-linked.
D) not heritable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A man is a carrier for a recessive disease allele.A woman is not a carrier and does not have the disease.The couple has four children and
A) none of the children have the disease.
B) one of the children has the disease.
C) two of the children have the disease.
D) all of the male children have the disease.
A) none of the children have the disease.
B) one of the children has the disease.
C) two of the children have the disease.
D) all of the male children have the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The genetic disorder followed through this pedigree is 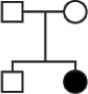
A) recessive and X-linked.
B) recessive and not X-linked.
C) dominant and X-linked.
D) dominant and not X-linked.

A) recessive and X-linked.
B) recessive and not X-linked.
C) dominant and X-linked.
D) dominant and not X-linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Most inherited human disorders are the result of
A) recessive mutations of genes located on autosomes.
B) recessive mutations of genes located on the X chromosome.
C) recessive mutations of genes located on the Y chromosome.
D) simultaneous mutations of the same gene on homologous chromosomes.
A) recessive mutations of genes located on autosomes.
B) recessive mutations of genes located on the X chromosome.
C) recessive mutations of genes located on the Y chromosome.
D) simultaneous mutations of the same gene on homologous chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A woman who is a carrier for a recessive X-linked disorder has children with a man who does not have the disease.Which of the following is true of the couple's children?
A) All of their daughters will be carriers.
B) Their sons have a 50 percent chance of being carriers.
C) Their sons have a 50 percent chance of having the disorder.
D) Their daughters have a 50 percent chance of having the disorder.
A) All of their daughters will be carriers.
B) Their sons have a 50 percent chance of being carriers.
C) Their sons have a 50 percent chance of having the disorder.
D) Their daughters have a 50 percent chance of having the disorder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why are X-linked recessive genetic disorders more commonly seen in males?
A) For an X-linked disorder to occur, an individual must receive one allele only found on the X chromosome and a second allele found only on the Y chromosome, which females do not have.
B) Females must receive two copies of the recessive allele to exhibit the disorder, but males need only one copy.
C) The alleles of sex-linked genes are carried only on the Y chromosome, which females do not have.
D) Females only have X chromosomes, and genes on the X chromosome are not expressed.
A) For an X-linked disorder to occur, an individual must receive one allele only found on the X chromosome and a second allele found only on the Y chromosome, which females do not have.
B) Females must receive two copies of the recessive allele to exhibit the disorder, but males need only one copy.
C) The alleles of sex-linked genes are carried only on the Y chromosome, which females do not have.
D) Females only have X chromosomes, and genes on the X chromosome are not expressed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The gene for a certain sex-linked trait is found only on the Y chromosome.If the male parent carries this gene,which of the following statements about the inheritance of that trait is true?
A) The trait will be expressed in 100 percent of the female offspring.
B) The trait will be expressed in 50 percent of the female offspring.
C) The trait will be expressed in 100 percent of the male offspring.
D) The trait will be expressed in 50 percent of the male offspring.
A) The trait will be expressed in 100 percent of the female offspring.
B) The trait will be expressed in 50 percent of the female offspring.
C) The trait will be expressed in 100 percent of the male offspring.
D) The trait will be expressed in 50 percent of the male offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a recessive allele causes a fatal disease that kills the affected individual before he or she can reproduce,why doesn't that allele quickly become extinct in the population?
A) Alleles are never lost from a population.
B) The homozygous-dominant individuals protect the recessive allele in their genomes.
C) The recessive allele is carried in the genome of heterozygotes, who do not have the disease.
D) The homozygous-recessive individuals give their alleles to other individuals before they die from the disease.
A) Alleles are never lost from a population.
B) The homozygous-dominant individuals protect the recessive allele in their genomes.
C) The recessive allele is carried in the genome of heterozygotes, who do not have the disease.
D) The homozygous-recessive individuals give their alleles to other individuals before they die from the disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An allele that appears to "skip generations" is most likely
A) dominant.
B) recessive.
C) sex-linked.
D) autosomal.
A) dominant.
B) recessive.
C) sex-linked.
D) autosomal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following figure contains a pedigree for brachydactyly,an autosomal dominant disorder.Which of the following is true? 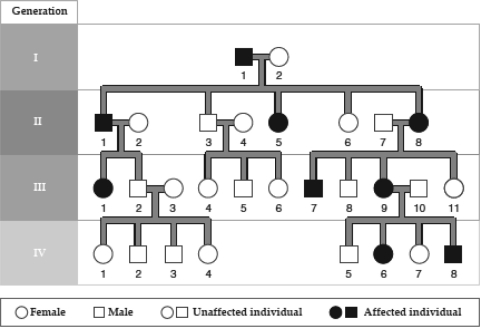
A) Individual 5 in Generation II inherited brachydactyly from her mother.
B) Individual 2 in Generation II is a carrier of brachydactyly.
C) Individual 5 in Generation III cannot pass brachydactyly to his offspring.
D) Individual 8 in Generation IV is an affected female.

A) Individual 5 in Generation II inherited brachydactyly from her mother.
B) Individual 2 in Generation II is a carrier of brachydactyly.
C) Individual 5 in Generation III cannot pass brachydactyly to his offspring.
D) Individual 8 in Generation IV is an affected female.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The parents in the following figure are carriers of a genetic disorder.Based on the Punnett square,the allele that causes the disorder must 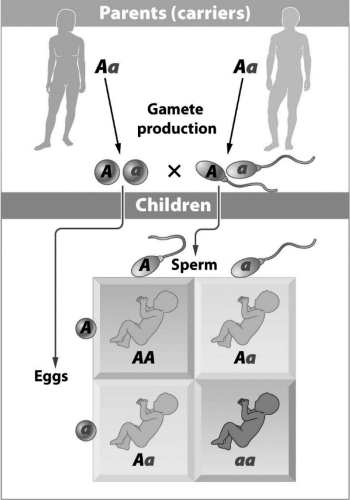
A)
A) be autosomal.
B) be sex-linked.
C) be incompletely dominant.
D) result from the linkage of A and

A)
A) be autosomal.
B) be sex-linked.
C) be incompletely dominant.
D) result from the linkage of A and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Among children with parents who are both carriers of Tay-Sachs,an autosomal recessive disorder,chances are that
A) 75 percent will be carriers.
B) 50 percent will die in a few years.
C) 75 percent will not carry the recessive Tay-Sachs's allele.
D) 50 percent will be carriers.
A) 75 percent will be carriers.
B) 50 percent will die in a few years.
C) 75 percent will not carry the recessive Tay-Sachs's allele.
D) 50 percent will be carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Even though it is deadly,the Huntington disease allele can remain in the population,because
A) the dominant allele sometimes reverts to a recessive form.
B) it is sex-linked to the male gamete, and females do not carry the allele.
C) people with the disorder often live long enough to reproduce.
D) it is autosomal and can be masked by a codominant harmless allele.
A) the dominant allele sometimes reverts to a recessive form.
B) it is sex-linked to the male gamete, and females do not carry the allele.
C) people with the disorder often live long enough to reproduce.
D) it is autosomal and can be masked by a codominant harmless allele.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a genetic disorder is caused by a dominant allele,individuals with which of the following genotypes would be affected by the disorder?
A) AA and aa
B) aa and Aa
C) AA and Aa
D) AA, Aa, and aa
A) AA and aa
B) aa and Aa
C) AA and Aa
D) AA, Aa, and aa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One chromosomal abnormality that is usually fatal is
A) a mutation in a gene on the chromosome.
B) the exchange of material between homologous chromosomes.
C) a change in the number of sex chromosomes.
D) the addition of an extra autosomal chromosome.
A) a mutation in a gene on the chromosome.
B) the exchange of material between homologous chromosomes.
C) a change in the number of sex chromosomes.
D) the addition of an extra autosomal chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
This pedigree diagrams an X-linked gene.The individual indicated by the question mark is ________ for the gene. 
A) heterozygous
B) homozygous
C) autosomal
D) There is not enough information to determine the answer.

A) heterozygous
B) homozygous
C) autosomal
D) There is not enough information to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Down syndrome results from trisomy of chromosome 21.Which of the following is NOT an example of how this may have happened?
A) translocation of chromosome 21
B) failure of the homologous pair for chromosome 21 to separate in meiosis I
C) inversion of a portion of chromosome 21 during S phase
D) failure of the sister chromatids in a duplicated chromosome 21 to separate in meiosis II
A) translocation of chromosome 21
B) failure of the homologous pair for chromosome 21 to separate in meiosis I
C) inversion of a portion of chromosome 21 during S phase
D) failure of the sister chromatids in a duplicated chromosome 21 to separate in meiosis II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Two chromosomes that have the same set of genes,but perhaps different versions of those genes,are called ________ chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The farther apart on the same chromosome that two genes are located,the more likely they are to undergo ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ________ gene is responsible for activating many genes involved in "maleness" during embryonic development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A chart that shows genetic relationships within a family over several generations is called a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
During meiosis,"new" chromosomes are generated when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Spontaneous abortions are often due to the addition or deletion of whole ________ in the gametes that fused to form the zygote.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A parent who is a carrier for the recessive autosomal disorder B has the genotype ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The X and Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes while the other chromosomes are called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Two gametes that are both diploid for the sex chromosomes join to form a zygote.Which of the following genotypes would result?
A) XXXX
B) XXY
C) X
D) XX
A) XXXX
B) XXY
C) X
D) XX

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
All sex-linked genes are either X-linked or ________-linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An individual with a heterozygous genotype who does not express the recessive trait but can pass it along to offspring is called a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Lethal ________ mutations are not eliminated from a population because they can be "hidden" in symptom-free individuals also carrying dominant alleles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is true with regard to understanding the results of genetic testing?
A) If the test shows that you have the allele for a genetic disorder, you will, eventually, show symptoms of that disorder.
B) If the test shows that you have the allele for a genetic disorder, you may be able to reduce your risk of developing that disorder with lifestyle changes.
C) If the test shows that you do not carry the allele for a particular disorder, there is no chance that you will get that disorder.
D) Because we know the functions of all the genes in the human genome, genetic tests can give you complete and accurate information regarding your medical health.
A) If the test shows that you have the allele for a genetic disorder, you will, eventually, show symptoms of that disorder.
B) If the test shows that you have the allele for a genetic disorder, you may be able to reduce your risk of developing that disorder with lifestyle changes.
C) If the test shows that you do not carry the allele for a particular disorder, there is no chance that you will get that disorder.
D) Because we know the functions of all the genes in the human genome, genetic tests can give you complete and accurate information regarding your medical health.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A female who is a carrier of the sex-linked gene A has the genotype ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Human males have one chromosome that females do not,known as the ________ chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The tendency to develop diseases,such as cancer and heart disease,is
A) usually the result of a mutation in one gene.
B) the result of new combinations of alleles formed during meiosis.
C) the result of the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors.
D) the result of multiple mutations caused by crossing-over.
A) usually the result of a mutation in one gene.
B) the result of new combinations of alleles formed during meiosis.
C) the result of the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors.
D) the result of multiple mutations caused by crossing-over.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is NOT true with regard to Huntington disease?
A) The discovery of the gene has led to a test that can identify people who will have the disease before they show symptoms.
B) The disease can be traced using pedigrees.
C) Now that the gene is known, a cure has been found.
D) The gene for Huntington disease is located on chromosome 4.
A) The discovery of the gene has led to a test that can identify people who will have the disease before they show symptoms.
B) The disease can be traced using pedigrees.
C) Now that the gene is known, a cure has been found.
D) The gene for Huntington disease is located on chromosome 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An XX individual develops as a male.Which of the following statements offers the most likely explanation?
A) This is the usual situation for an XX individual.
B) This occurs when the sperm does not contribute any genetic material.
C) A piece of a Y chromosome has become attached to one of the X chromosomes.
D) This occurs when the egg does not contribute any genetic material.
A) This is the usual situation for an XX individual.
B) This occurs when the sperm does not contribute any genetic material.
C) A piece of a Y chromosome has become attached to one of the X chromosomes.
D) This occurs when the egg does not contribute any genetic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The following diagrams show the same cell,but the homologous pairs are arranged differently in each diagram.The different arrangements of the homologous pairs in version A compared with version B provide an example of the concept of ________.
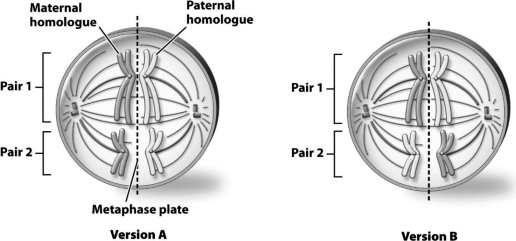


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All inherited diseases are the result of mutations of single genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Crossing-over is expected to occur infrequently for genes located very close together on the same chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A specific gene can be found in several possible places on a given chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Ichthyosis is a recessive X-linked disorder that causes a person's skin to flake off like fish scales.A normal man and a normal woman produce a child with ichthyosis.This child cannot be female.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Because chromosomal alterations such as duplications often affect several genes,they tend to have serious impacts,including slowed growth and mental retardation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
All genes on the same chromosome are linked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Scientists are able to determine what alleles are present in your DNA because every gene in a human occupies a specific position or ________ in your chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Males with a recessive X-linked allele that causes a disorder do not always show symptoms because they can also carry a dominant allele on their Y chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Translocation occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange equal pieces of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The chance that any two siblings will be genetically identical is astronomically small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If DNA testing reveals that you carry alleles for a particular genetic disorder,you will definitely get that disorder at some point in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Sex-linked genes are found on either the X chromosome or the Y chromosome but not both.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
All humans are capable of producing gametes containing different sex chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Recessive genetic disorders are quickly eliminated from human populations because people who have them die before they can reproduce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Genes become linked when crossing-over occurs between nonhomologous chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The following diagram demonstrates what happens during a change in chromosomal structure known as a deletion.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Many experiments have been performed on humans to study the inheritance of genetic traits through generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



