Deck 6: Bones and Bone Structure
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/165
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Bones and Bone Structure
1
The carpal bones are examples of ________ bones.
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) irregular
E) sesamoid
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) irregular
E) sesamoid
B
2
The humerus is an example of a(n) ________ bone.
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) irregular
E) sesamoid
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) irregular
E) sesamoid
A
3
The proximal and distal ends of a long bone are called the
A) epiphyses.
B) diaphyses.
C) epiphyseal plates.
D) metaphyses.
E) periphyses.
A) epiphyses.
B) diaphyses.
C) epiphyseal plates.
D) metaphyses.
E) periphyses.
A
4
A________ is a smooth, grooved bone process shaped like a pulley.
A) tubercle
B) trochanter
C) trochlea
D) tuberosity
E) trabeculae
A) tubercle
B) trochanter
C) trochlea
D) tuberosity
E) trabeculae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following bones is classified as "irregular" in shape?
A) patella
B) frontal
C) vertebra
D) metatarsal
E) ulna
A) patella
B) frontal
C) vertebra
D) metatarsal
E) ulna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The patella is an example of a(n) ________ bone.
A) irregular
B) sesamoid
C) sutural
D) sagittal
E) flat
A) irregular
B) sesamoid
C) sutural
D) sagittal
E) flat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
________ bones develop inside tendons, commonly near the knees, hands, and feet.
A) Irregular
B) Sesamoid
C) Short
D) Long
E) Flat
A) Irregular
B) Sesamoid
C) Short
D) Long
E) Flat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The adult skeleton contains ________ major bones.
A) 88
B) 115
C) 174
D) 206
E) 251
A) 88
B) 115
C) 174
D) 206
E) 251

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Achamber within a bone normally filled with air is a
A) foramen.
B) sinus.
C) fossa.
D) canal.
E) meatus.
A) foramen.
B) sinus.
C) fossa.
D) canal.
E) meatus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A rib is an example of a ________ bone.
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) sutural
E) sesamoid
A) long
B) short
C) flat
D) sutural
E) sesamoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The shaft of long bones is called the
A) epiphysis.
B) metaphysis.
C) diaphysis.
D) paraphysis.
E) endophysis.
A) epiphysis.
B) metaphysis.
C) diaphysis.
D) paraphysis.
E) endophysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Small bones that fill gaps between bones of the skull are called ________ bones.
A) irregular
B) sesamoid
C) sutural
D) sagittal
E) tendon
A) irregular
B) sesamoid
C) sutural
D) sagittal
E) tendon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of following is a function of the skeletal system?
A) body support
B) calcium homeostasis
C) protection of internal organs
D) blood cell production
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) body support
B) calcium homeostasis
C) protection of internal organs
D) blood cell production
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The expanded articular end of an epiphysis that is separated from the shaft by a narrower neck is calleda
A) head.
B) crown.
C) capitulum.
D) corona.
E) bulb.
A) head.
B) crown.
C) capitulum.
D) corona.
E) bulb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Asmall rough bump on bone where a tendon attaches is called a
A) tubercle.
B) trochanter.
C) trochlea.
D) tuberosity.
E) trabecula.
A) tubercle.
B) trochanter.
C) trochlea.
D) tuberosity.
E) trabecula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following are not components of the skeletal system?
A) tendons
B) bones
C) ligaments
D) cartilage
E) other tissues that connect bones
A) tendons
B) bones
C) ligaments
D) cartilage
E) other tissues that connect bones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A ________ is a large rough proximal projection on a bone.
A) ramus
B) trochanter
C) tuberosity
D) tubercle
E) condyle
A) ramus
B) trochanter
C) tuberosity
D) tubercle
E) condyle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A________ is a rounded passageway for passage of blood vessels and/or nerves.
A) sinus
B) fossa
C) meatus
D) foramen
E) cavernosa
A) sinus
B) fossa
C) meatus
D) foramen
E) cavernosa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A rounded passage or hole through a bone is called a
A) ramus.
B) foramen.
C) linea.
D) tubercle.
E) facet.
A) ramus.
B) foramen.
C) linea.
D) tubercle.
E) facet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The smooth, rounded articular process of a bone is termed a
A) crest.
B) ridge.
C) head.
D) condyle.
E) trochlea.
A) crest.
B) ridge.
C) head.
D) condyle.
E) trochlea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Canaliculi are
A) also known as Volkmann's channels.
B) the same as Haversian canals.
C) narrow passageways in the matrix connecting lacunae to blood supply.
D) layers of bony matrix laid down in rings.
E) have both a fibrous outer layer and a cellular inner layer.
A) also known as Volkmann's channels.
B) the same as Haversian canals.
C) narrow passageways in the matrix connecting lacunae to blood supply.
D) layers of bony matrix laid down in rings.
E) have both a fibrous outer layer and a cellular inner layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of following is/are produced from the monocyte stem cells?
A) osteoblasts
B) osteoclasts
C) osteocytes
D) osteoprogenitor cells
E) osteogenic cells
A) osteoblasts
B) osteoclasts
C) osteocytes
D) osteoprogenitor cells
E) osteogenic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Bones that are boxy with approximately equal dimensions are
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The region of a long bone between the end and the shaft is known as the
A) diaphysis.
B) epiphysis.
C) osseophysis.
D) metaphysis.
E) medullary cavity.
A) diaphysis.
B) epiphysis.
C) osseophysis.
D) metaphysis.
E) medullary cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not true of osteocytes?
A) Osteocytes maintain protein and mineral content of matrix.
B) Osteocytes take part in repair of damaged bone.
C) Osteocytes form cytoplasmic extensions within canaliculi.
D) Osteocytes are located within lacunae.
E) Osteocytes have 50 or more nuclei.
A) Osteocytes maintain protein and mineral content of matrix.
B) Osteocytes take part in repair of damaged bone.
C) Osteocytes form cytoplasmic extensions within canaliculi.
D) Osteocytes are located within lacunae.
E) Osteocytes have 50 or more nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true of osteoclasts?
A) Osteoclasts maintain protein and mineral content of matrix.
B) Osteoclasts are responsible for laying down osteoid.
C) Osteoclasts form cytoplasmic extensions within canaliculi.
D) Osteoclasts are located within lacunae.
E) Osteoclasts secretes protein digesting enzymes and acids that dissolve matrix.
A) Osteoclasts maintain protein and mineral content of matrix.
B) Osteoclasts are responsible for laying down osteoid.
C) Osteoclasts form cytoplasmic extensions within canaliculi.
D) Osteoclasts are located within lacunae.
E) Osteoclasts secretes protein digesting enzymes and acids that dissolve matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Through the action of osteoclasts,
A) new bone is formed.
B) an organic framework is formed.
C) bony matrix is dissolved.
D) osteoid is calcified.
E) fractured bones regenerate.
A) new bone is formed.
B) an organic framework is formed.
C) bony matrix is dissolved.
D) osteoid is calcified.
E) fractured bones regenerate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A shallow depression on a bone is termed a
A) fossa.
B) sulcus.
C) facet.
D) fissure.
E) line.
A) fossa.
B) sulcus.
C) facet.
D) fissure.
E) line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Bones that have complex shapes are
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
________ cells are located in the inner cellular layer of the periosteum.
A) Osteocyte
B) Osteoclast
C) Osteoid
D) Osteogenic
E) Osteolytic
A) Osteocyte
B) Osteoclast
C) Osteoid
D) Osteogenic
E) Osteolytic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Bone is composed of ________ percent cells.
A) 25
B) 10
C) 2
D) 15
E) 50
A) 25
B) 10
C) 2
D) 15
E) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following chemicals is not present in bone?
A) calcium phosphate
B) collagen fibers
C) calcium carbonate
D) chondroitin sulfate
E) hydroxyapatite
A) calcium phosphate
B) collagen fibers
C) calcium carbonate
D) chondroitin sulfate
E) hydroxyapatite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
________ account(s) for almost two-thirds of the weight of bone.
A) Water
B) Calcium carbonate
C) Collagen fibers
D) Fluoride
E) Calcium phosphate
A) Water
B) Calcium carbonate
C) Collagen fibers
D) Fluoride
E) Calcium phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Bones that have thin parallel surfaces are
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Cells that secrete the organic components of the bone matrix are called
A) osteocytes.
B) osteoprogenitor cells.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteoclasts.
E) osteoid cells.
A) osteocytes.
B) osteoprogenitor cells.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteoclasts.
E) osteoid cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following labels best matches osteocyte?
A) stem cell
B) dissolves matrix
C) mature bone cell
D) secretes organic matrix
E) immature bone cell
A) stem cell
B) dissolves matrix
C) mature bone cell
D) secretes organic matrix
E) immature bone cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The space occupied by an osteocyte is called
A) Volkmann's canal.
B) a lacuna.
C) a trabecula.
D) a Haversian canal.
E) a canaliculus.
A) Volkmann's canal.
B) a lacuna.
C) a trabecula.
D) a Haversian canal.
E) a canaliculus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Bones that are small, round and tend to develop in tendons are
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
________ are stem cells that develop into osteoblasts.
A) Osteoclasts
B) Osteocytes
C) Osteomedullary cells
D) Osteogenic cells
E) Osteoid cells
A) Osteoclasts
B) Osteocytes
C) Osteomedullary cells
D) Osteogenic cells
E) Osteoid cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Bones that are relatively long and slender, consisting of a shaft with two ends are
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.
A) long bones.
B) flat bones.
C) sesamoid bones.
D) short bones.
E) irregular bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Cells that free calcium from bone to maintain blood calcium levels are called
A) osteolytics.
B) osteoclasts.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteogenics.
E) osteocytes.
A) osteolytics.
B) osteoclasts.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteogenics.
E) osteocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The central canal of an osteon contains
A) bone marrow.
B) osteocytes.
C) concentric lamellae.
D) blood vessels.
E) lacunae.
A) bone marrow.
B) osteocytes.
C) concentric lamellae.
D) blood vessels.
E) lacunae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The organic component of the matrix in developing or repairing bone is called
A) osteon.
B) osteoid.
C) hydroxyapatite.
D) mesenchymal tissue.
E) calcium phosphate.
A) osteon.
B) osteoid.
C) hydroxyapatite.
D) mesenchymal tissue.
E) calcium phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The layer of bone that is interwoven with tendons is the
A) circumferential lamellae.
B) periosteum.
C) endosteum.
D) concentric lamellae.
E) perichondrium.
A) circumferential lamellae.
B) periosteum.
C) endosteum.
D) concentric lamellae.
E) perichondrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In bone, the calcium phosphate forms crystals of
A) osteoid matrix.
B) calcium carbonate.
C) hydroxyapatite.
D) calcitriol.
E) proteolytic enzymes.
A) osteoid matrix.
B) calcium carbonate.
C) hydroxyapatite.
D) calcitriol.
E) proteolytic enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
________ prevents damaging bone-to-bone contact within movable joints.
A) A synovial membrane
B) Elastic cartilage
C) A serous membrane
D) Articular cartilage
E) Serous fluid
A) A synovial membrane
B) Elastic cartilage
C) A serous membrane
D) Articular cartilage
E) Serous fluid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How would removing hydroxyapatite from bone matrix affect the physical properties of a bone?
A) The bone would be less flexible.
B) The bone would be stronger.
C) The bone would be more brittle.
D) The bone would be more flexible.
E) The bone would be more compressible.
A) The bone would be less flexible.
B) The bone would be stronger.
C) The bone would be more brittle.
D) The bone would be more flexible.
E) The bone would be more compressible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Connective tissue fibers incorporated into bone tissue from ligaments are called
A) elastic fibers.
B) reticular fibers.
C) perforating fibers.
D) superficial fibers.
E) calcified fibers.
A) elastic fibers.
B) reticular fibers.
C) perforating fibers.
D) superficial fibers.
E) calcified fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The narrow passageways that contain cytoplasmic extensions of osteocytes are called
A) central canals.
B) lacunae.
C) canaliculi.
D) medullary cavities.
E) foramina.
A) central canals.
B) lacunae.
C) canaliculi.
D) medullary cavities.
E) foramina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Layers of bony matrix at the outer and inner surfaces of bone and covered by the periosteum and the endosteum are
A) concentric lamellae.
B) osteons.
C) Haversian systems.
D) interstitial lamellae.
E) circumferential lamellae.
A) concentric lamellae.
B) osteons.
C) Haversian systems.
D) interstitial lamellae.
E) circumferential lamellae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The interconnecting tiny arches of bone tissue found in spongy bone are called
A) osteons.
B) trabeculae.
C) concentric lamellae.
D) interstitial lamellae.
E) lacunae.
A) osteons.
B) trabeculae.
C) concentric lamellae.
D) interstitial lamellae.
E) lacunae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The structural units of mature compact bone are called
A) trabeculae.
B) osteocytes.
C) osteons.
D) canaliculi.
E) lamellae.
A) trabeculae.
B) osteocytes.
C) osteons.
D) canaliculi.
E) lamellae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Cells that secrete protein fibers in bone are called
A) osteolytic cells.
B) osteoclasts.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteocytes.
E) osteogenic cells.
A) osteolytic cells.
B) osteoclasts.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteocytes.
E) osteogenic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The type of bone that is adapted to withstand stresses that arrive from many directions is ________ bone.
A) spongy
B) osteon
C) compact
D) lamellar
E) irregular
A) spongy
B) osteon
C) compact
D) lamellar
E) irregular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ________ interactions allow bone to be strong, somewhat flexible, and highly resistant to shattering.
A) collagen-fiber
B) protein-crystal
C) mineral-crystal
D) protein-protein
E) hydroxyapatite-crystal
A) collagen-fiber
B) protein-crystal
C) mineral-crystal
D) protein-protein
E) hydroxyapatite-crystal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Stem cells that can differentiate into osteoblasts are called ________ cells.
A) osteopropagator
B) osteoforming
C) osteocreator
D) osteotrophic
E) osteogenic
A) osteopropagator
B) osteoforming
C) osteocreator
D) osteotrophic
E) osteogenic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The lacunae of osseous tissue contain
A) blood cells.
B) osteocytes.
C) chondroblasts.
D) bone marrow.
E) capillaries.
A) blood cells.
B) osteocytes.
C) chondroblasts.
D) bone marrow.
E) capillaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The most abundant cell type in bone is
A) osteoclasts.
B) osteoblasts.
C) osteolytes.
D) osteoprogenitor cells.
E) osteocytes.
A) osteoclasts.
B) osteoblasts.
C) osteolytes.
D) osteoprogenitor cells.
E) osteocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Adipose tissue is stored within the
A) medullary cavity.
B) metaphysis.
C) spongy bone.
D) epiphysis.
E) diaphysis.
A) medullary cavity.
B) metaphysis.
C) spongy bone.
D) epiphysis.
E) diaphysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cells that are found in small depressions on the endosteal surfaces are the
A) osteolytic cells.
B) osteoclasts.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteocytes.
E) osteogenic cells.
A) osteolytic cells.
B) osteoclasts.
C) osteoblasts.
D) osteocytes.
E) osteogenic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement is true regarding calcium in bone matrix?
A) Calcium is found in crystals called hydroxyapatite.
B) Calcium is secreted by osteoblasts into the matrix.
C) Once deposited, calcium cannot be removed from bone.
D) Calcium provides flexibility to the bone matrix.
E) Calcium is the organic part of the matrix.
A) Calcium is found in crystals called hydroxyapatite.
B) Calcium is secreted by osteoblasts into the matrix.
C) Once deposited, calcium cannot be removed from bone.
D) Calcium provides flexibility to the bone matrix.
E) Calcium is the organic part of the matrix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The layers of bone tissue immediately deep to the periosteum are
A) circumferential lamellae.
B) osteoid plates.
C) trabeculae.
D) concentric lamellae.
E) epiphseal ridges.
A) circumferential lamellae.
B) osteoid plates.
C) trabeculae.
D) concentric lamellae.
E) epiphseal ridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The process by which osteoblasts add layers to circumferential lamellae is
A) appositional growth.
B) interstitial growth.
C) intramembranous growth.
D) endochondral ossification.
E) epiphyseal ossification.
A) appositional growth.
B) interstitial growth.
C) intramembranous growth.
D) endochondral ossification.
E) epiphyseal ossification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
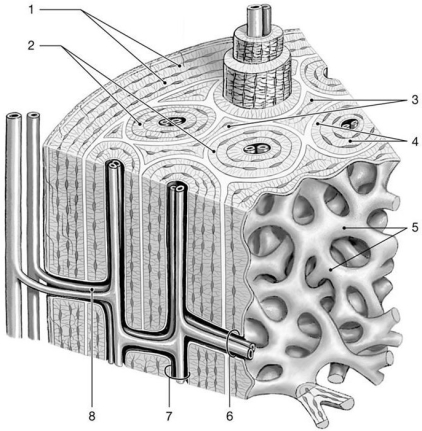
Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
The structure labeled "3" is the result of which process?
A) bone cells adding matrix between existing osteons
B) surface growth of bone
C) remodeling of compact bone
D) remodeling of spongy bone
E) osteoporosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65

Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
Which structure is characteristic of spongy bone?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Blood is distributed from the surface of a bone to deeper central canals through channels known as
A) perforating canals.
B) canaliculi.
C) interstitial canals.
D) concentric ducts.
E) concentric canals.
A) perforating canals.
B) canaliculi.
C) interstitial canals.
D) concentric ducts.
E) concentric canals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
________ marrow is found between the trabeculae of spongy bone.
A) Blue
B) Yellow
C) White
D) Gray
E) Red
A) Blue
B) Yellow
C) White
D) Gray
E) Red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
________ fibers are stronger than steel when stretched.
A) Calcium
B) Mineral
C) Elastic
D) Carbon
E) Collagen
A) Calcium
B) Mineral
C) Elastic
D) Carbon
E) Collagen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The trabeculae of spongy bone
A) are organized parallel to the long axis of the bone.
B) are organized along stress lines.
C) are composed mostly of cartilage.
D) will collapse under stress.
E) are concentrated in the cortex of the diaphysis.
A) are organized parallel to the long axis of the bone.
B) are organized along stress lines.
C) are composed mostly of cartilage.
D) will collapse under stress.
E) are concentrated in the cortex of the diaphysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In relationship to the diaphysis of a long bone, the osteons are
A) radial.
B) anterior.
C) parallel.
D) proximal.
E) diagonal.
A) radial.
B) anterior.
C) parallel.
D) proximal.
E) diagonal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
________ bone reduces the weight of the skeleton and reduces the load on muscles.
A) Short
B) Irregular
C) Spongy
D) Compact
E) Long
A) Short
B) Irregular
C) Spongy
D) Compact
E) Long

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During endochondral ossification these vessels invade the cartilage of the diaphysis.
A) metaphyseal vessels
B) nutrient arteries and veins
C) periosteal vessels
D) endosteal vessels
E) diaphyseal artery and vein
A) metaphyseal vessels
B) nutrient arteries and veins
C) periosteal vessels
D) endosteal vessels
E) diaphyseal artery and vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
What lines the structure labeled "7"?
A) the endosteum
B) blood vessels
C) the central canal
D) spongy bone
E) trabeculae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The lining of the medullary cavity is called the
A) endosteum.
B) periosteum.
C) epiosteum.
D) mediosteum.
E) paraosteum.
A) endosteum.
B) periosteum.
C) epiosteum.
D) mediosteum.
E) paraosteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
Which structure is called an osteon?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The femur can withstand ________ times the body's weight without breaking.
A) 3
B) 5 to 10
C) 8
D) 10 to 15
E) 30
A) 3
B) 5 to 10
C) 8
D) 10 to 15
E) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is a characteristic of bone?
A) The bone matrix is very dense and contains deposits of calcium salts.
B) The matrix of the bone contains osteoclasts and chondroblasts.
C) Narrow channels pass through the matrix to allow for muscle attachment.
D) The matrix of bone is mostly collagen with very little calcium.
E) For strength, compact bone is organized into a meshwork of matrix called trabeculae.
A) The bone matrix is very dense and contains deposits of calcium salts.
B) The matrix of the bone contains osteoclasts and chondroblasts.
C) Narrow channels pass through the matrix to allow for muscle attachment.
D) The matrix of bone is mostly collagen with very little calcium.
E) For strength, compact bone is organized into a meshwork of matrix called trabeculae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The superficial membrane of a bone is called the
A) endosteum.
B) ectosteum.
C) cortical membrane.
D) periosteum.
E) osteoid collar.
A) endosteum.
B) ectosteum.
C) cortical membrane.
D) periosteum.
E) osteoid collar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
During the process of ________, an existing tissue is replaced by bone.
A) phosphorylation
B) resorption
C) ossification
D) osteopropagation
E) remodeling
A) phosphorylation
B) resorption
C) ossification
D) osteopropagation
E) remodeling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

Figure 6-1 The Structure of Compact Bone
Use Figure 6-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structures labeled "4."
A) concentric lamellae
B) circumferential lamellae
C) interstitial lamellae
D) trabeculae
E) periosteum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 165 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



