Deck 7: The Axial Skeleton
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/146
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: The Axial Skeleton
1
Which of the following is not part of the axial skeleton?
A) skull
B) false ribs
C) sternum
D) hyoid bone
E) pelvic girdle
A) skull
B) false ribs
C) sternum
D) hyoid bone
E) pelvic girdle
E
2
The occipital ________ are where the occipital bone articulates with the first cervical vertebra.
A) processes
B) condyles
C) foramina
D) fossae
E) tubercles
A) processes
B) condyles
C) foramina
D) fossae
E) tubercles
B
3
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) mandible: movable facial bone in skull
B) maxilla: alveolar processes
C) sphenoid: external acoustic meatus
D) frontal: glabella
E) occipital: foramen magnum
A) mandible: movable facial bone in skull
B) maxilla: alveolar processes
C) sphenoid: external acoustic meatus
D) frontal: glabella
E) occipital: foramen magnum
C
4
The auditory ossicles are housed in which cranial bone?
A) sphenoid
B) ethmoid
C) zygomatic
D) temporal
E) lacrimal
A) sphenoid
B) ethmoid
C) zygomatic
D) temporal
E) lacrimal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The olfactory foramina are found in which of the following bones?
A) ethmoid
B) sphenoid
C) temporal
D) nasal
E) zygomatic
A) ethmoid
B) sphenoid
C) temporal
D) nasal
E) zygomatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the mismatched pair.
A) skull bones: 8 cranial and 14 facial bones
B) bones associated with the skull: 6 auditory ossicles and 1 hyoid bone
C) vertebral column: 24 vertebrae and 1 sacrum and 1 coccyx
D) thoracic cage: sternum and 24 ribs and 2 clavicles
E) There is no mismatched pair.
A) skull bones: 8 cranial and 14 facial bones
B) bones associated with the skull: 6 auditory ossicles and 1 hyoid bone
C) vertebral column: 24 vertebrae and 1 sacrum and 1 coccyx
D) thoracic cage: sternum and 24 ribs and 2 clavicles
E) There is no mismatched pair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In some individuals the supra-orbital foramen is incomplete and called the
A) supra-orbital fissure.
B) supra-orbital suture.
C) supra-orbital fontanelle.
D) supra-orbital notch.
E) supra-orbital meatus.
A) supra-orbital fissure.
B) supra-orbital suture.
C) supra-orbital fontanelle.
D) supra-orbital notch.
E) supra-orbital meatus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Delicate projections that form from the ethmoidal labyrinth are
A) olfactory foramina.
B) pterygoid processes.
C) sphenoidal sinuses.
D) superior and middle nasal conchae.
E) auditory ossicles.
A) olfactory foramina.
B) pterygoid processes.
C) sphenoidal sinuses.
D) superior and middle nasal conchae.
E) auditory ossicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The ________ is the bony chamber that protects and supports the brain.
A) skull
B) centrum
C) cranium
D) cephalum
E) cortex
A) skull
B) centrum
C) cranium
D) cephalum
E) cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not true regarding the axial skeleton?
A) has 80 bones
B) includes the skull
C) includes the pelvic and pectoral girdles
D) includes auditory ossicles
E) includes the thoracic cage
A) has 80 bones
B) includes the skull
C) includes the pelvic and pectoral girdles
D) includes auditory ossicles
E) includes the thoracic cage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a cranial bone?
A) frontal
B) parietal
C) palatine
D) temporal
E) occipital
A) frontal
B) parietal
C) palatine
D) temporal
E) occipital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which paired bones form the lateral, posterior portions of the cranium?
A) frontal
B) maxilla
C) sphenoid
D) parietal
E) zygomatic
A) frontal
B) maxilla
C) sphenoid
D) parietal
E) zygomatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which portion of the temporal bone houses the structures of the internal ear?
A) squamous
B) petrous
C) styloid
D) zygomatic
E) mastoid
A) squamous
B) petrous
C) styloid
D) zygomatic
E) mastoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following articulate in the mandibular fossa?
A) condylar process
B) mastoid process
C) acromion process
D) coronoid process
E) zygomatic process
A) condylar process
B) mastoid process
C) acromion process
D) coronoid process
E) zygomatic process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
A) provides an attachment for muscles that move the appendicular skeleton
B) provides an attachment for muscles that move the head, neck, and trunk
C) provides an attachment for muscles involved in breathing
D) provides protection for the brain and spinal cord
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) provides an attachment for muscles that move the appendicular skeleton
B) provides an attachment for muscles that move the head, neck, and trunk
C) provides an attachment for muscles involved in breathing
D) provides protection for the brain and spinal cord
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Air-filled chambers found in several bones of the skull are called
A) conchae.
B) sinuses.
C) fontanelles.
D) sutures.
E) fossae.
A) conchae.
B) sinuses.
C) fontanelles.
D) sutures.
E) fossae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The skull and vertebral column are part of the ________ skeleton.
A) axial
B) apical
C) appendicular
D) articulated
E) sagittal
A) axial
B) apical
C) appendicular
D) articulated
E) sagittal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The parietal bones and occipital bone articulate at the ________ suture.
A) lambdoid
B) central
C) sagittal
D) coronal
E) posterior
A) lambdoid
B) central
C) sagittal
D) coronal
E) posterior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Athickening of the frontal bone that helps protect the eye is the
A) optic canal.
B) supra-orbital margin.
C) superior orbital fissure.
D) frontal suture.
E) frontal sinuses.
A) optic canal.
B) supra-orbital margin.
C) superior orbital fissure.
D) frontal suture.
E) frontal sinuses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The internal acoustic meatus is located in which bone?
A) occipital
B) ethmoid
C) sphenoid
D) temporal
E) parietal
A) occipital
B) ethmoid
C) sphenoid
D) temporal
E) parietal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The suture that forms the articulation of the parietal bones with the frontal bone is the ________ suture.
A) lambdoid
B) rostral
C) coronal
D) squamous
E) sagittal
A) lambdoid
B) rostral
C) coronal
D) squamous
E) sagittal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The foramen magnum is found in the ________ bone.
A) frontal
B) parietal
C) ethmoid
D) occipital
E) temporal
A) frontal
B) parietal
C) ethmoid
D) occipital
E) temporal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The hard palate of the roof of the mouth is mostly formed by the
A) palatine processes of the maxillae.
B) lesser wings of the sphenoid bone.
C) nasal bones.
D) zygomatic process.
E) palatine bones.
A) palatine processes of the maxillae.
B) lesser wings of the sphenoid bone.
C) nasal bones.
D) zygomatic process.
E) palatine bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A skull bone that could be described as looking like a bat with wings extended is the
A) maxilla.
B) crista galli.
C) sphenoid.
D) ethmoid.
E) temporal.
A) maxilla.
B) crista galli.
C) sphenoid.
D) ethmoid.
E) temporal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The zygomatic arch is formed by the articulation of processes from which two bones?
A) zygomatic and maxilla
B) frontal and temporal
C) sphenoid and temporal
D) zygomatic and sphenoid
E) temporal and zygomatic
A) zygomatic and maxilla
B) frontal and temporal
C) sphenoid and temporal
D) zygomatic and sphenoid
E) temporal and zygomatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The four primary sutures are lambdoid, coronal, sagittal, and
A) lateral.
B) cuboidal.
C) parietal.
D) squamous.
E) frontal.
A) lateral.
B) cuboidal.
C) parietal.
D) squamous.
E) frontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Each of the following structures is associated with the sphenoid bone except the
A) foramen ovale.
B) optic canals.
C) pterygoid processes.
D) sella turcica.
E) cribriform plate.
A) foramen ovale.
B) optic canals.
C) pterygoid processes.
D) sella turcica.
E) cribriform plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The nasal conchae
A) attach muscles that move the eye.
B) contain the nerves for olfaction.
C) create turbulence in the nasal passageways.
D) protect the pituitary gland.
E) attach muscles that move the mouth.
A) attach muscles that move the eye.
B) contain the nerves for olfaction.
C) create turbulence in the nasal passageways.
D) protect the pituitary gland.
E) attach muscles that move the mouth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The inferior portion of the nasal septum is formed by the
A) nasal bone.
B) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
C) inferior nasal conchae.
D) vomer.
E) palatine bone.
A) nasal bone.
B) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
C) inferior nasal conchae.
D) vomer.
E) palatine bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A point of attachment for muscles that rotate or extend the head is the
A) styloid process.
B) mastoid process.
C) palatine process.
D) coronoid process.
E) zygomatic process.
A) styloid process.
B) mastoid process.
C) palatine process.
D) coronoid process.
E) zygomatic process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Infection of the large process on the temporal bone would be called
A) tinnitus.
B) encephalitis.
C) meningitis.
D) petrositis.
E) mastoiditis.
A) tinnitus.
B) encephalitis.
C) meningitis.
D) petrositis.
E) mastoiditis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Each of the following regions/markings is associated with the occipital bone except the
A) superior and inferior nuchal lines.
B) foramen magnum.
C) hypoglossal canals.
D) glabella.
E) external occipital crest.
A) superior and inferior nuchal lines.
B) foramen magnum.
C) hypoglossal canals.
D) glabella.
E) external occipital crest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of these is not one of the facial bones?
A) frontal
B) maxilla
C) vomer
D) mandible
E) zygomatic
A) frontal
B) maxilla
C) vomer
D) mandible
E) zygomatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The hypophyseal fossa of the sella turcica contains the ________ gland.
A) lacrimal
B) pituitary
C) olfactory
D) nasal
E) sellar
A) lacrimal
B) pituitary
C) olfactory
D) nasal
E) sellar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The prominent bulge just posterior and inferior to the external auditory meatus is the
A) mastoid process.
B) styloid process.
C) occipital condyle.
D) condyloid process.
E) temporal process.
A) mastoid process.
B) styloid process.
C) occipital condyle.
D) condyloid process.
E) temporal process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The calvaria (or skullcap) is formed by the ________ bones.
A) frontal, temporal, and parietal
B) frontal, parietal, and occipital
C) temporal, parietal, and occipital
D) frontal, temporal, and occipital
E) frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital
A) frontal, temporal, and parietal
B) frontal, parietal, and occipital
C) temporal, parietal, and occipital
D) frontal, temporal, and occipital
E) frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Each of the following is associated with the temporal bone except the
A) mastoid cells.
B) petrous portion.
C) sella turcica.
D) internal acoustic meatus.
E) mandibular fossa.
A) mastoid cells.
B) petrous portion.
C) sella turcica.
D) internal acoustic meatus.
E) mandibular fossa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Ligaments that support the hyoid bone are attached to the
A) styloid process.
B) mastoid process.
C) palatine process.
D) coronoid process.
E) zygomatic process.
A) styloid process.
B) mastoid process.
C) palatine process.
D) coronoid process.
E) zygomatic process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The optic nerve passes through which structure?
A) superior orbital fissure
B) inferior orbital fissure
C) optic canal
D) internal optic meatus
E) external acoustic meatus
A) superior orbital fissure
B) inferior orbital fissure
C) optic canal
D) internal optic meatus
E) external acoustic meatus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The ________ bone is unusual because it doesn't contact another bone.
A) vomer
B) lacrimal
C) hyoid
D) atlas
E) ethmoid
A) vomer
B) lacrimal
C) hyoid
D) atlas
E) ethmoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
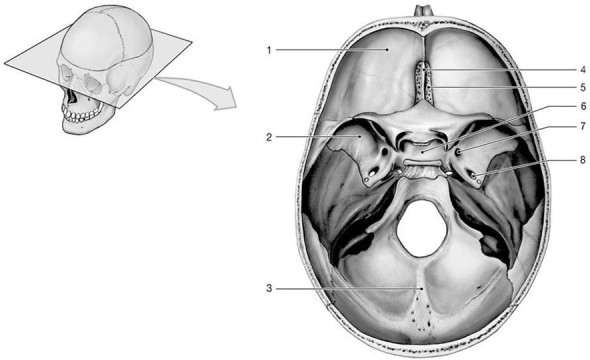
Figure 7-1 Floor of the Cranial Cavity
Use Figure 7-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the sphenoid bone.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The bony portion of the nasal septum is formed by the
A) nasal bones.
B) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
C) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and vomer bone.
D) vomer and sphenoid bone.
E) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and sphenoid bone.
A) nasal bones.
B) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
C) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and vomer bone.
D) vomer and sphenoid bone.
E) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and sphenoid bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Of the following bones, which is unpaired?
A) vomer
B) maxillae
C) palatine
D) nasal
E) lacrimal
A) vomer
B) maxillae
C) palatine
D) nasal
E) lacrimal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Jack gets into a fight and is punched in the nose. Which of the following bones might be fractured?
A) ethmoid bone
B) zygomatic bone
C) temporal bone
D) mandible
E) parietal bone
A) ethmoid bone
B) zygomatic bone
C) temporal bone
D) mandible
E) parietal bone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
While playing softball, Gina is struck in the frontal bone by a wild pitch. Which of the following complaints would you expect her to have?
A) a sore jaw
B) a black eye
C) a headache
D) a sore chest
E) a sore back
A) a sore jaw
B) a black eye
C) a headache
D) a sore chest
E) a sore back

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46

Figure 7-1 Floor of the Cranial Cavity
Use Figure 7-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the name of the structure labeled "7"?
A) optic canal
B) foramen spinosum
C) foramen rotundum
D) foramen lacerum
E) foramen ovale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Ridges that anchor muscles that stabilize the head are the
A) anterior and posterior nuchal lines.
B) anterior and superior nuchal lines.
C) inferior and superior nuchal lines.
D) medial and lateral nuchal lines.
E) cranial and caudal nuchal lines.
A) anterior and posterior nuchal lines.
B) anterior and superior nuchal lines.
C) inferior and superior nuchal lines.
D) medial and lateral nuchal lines.
E) cranial and caudal nuchal lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The hyoid bone
A) attaches to tongue muscles.
B) is linked to the styloid process by a ligament.
C) is superior to the larynx.
D) does not directly articulate with other bones.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) attaches to tongue muscles.
B) is linked to the styloid process by a ligament.
C) is superior to the larynx.
D) does not directly articulate with other bones.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The alveolar processes of the mandible
A) support the upper teeth.
B) support the lower teeth.
C) anchor the tongue.
D) are part of the temporomandibular joint.
E) articulate with the hyoid bone.
A) support the upper teeth.
B) support the lower teeth.
C) anchor the tongue.
D) are part of the temporomandibular joint.
E) articulate with the hyoid bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Damage to the temporal bone would most likely affect the sense(s) of
A) balance.
B) hearing and balance.
C) smell and taste.
D) vision.
E) touch and pressure.
A) balance.
B) hearing and balance.
C) smell and taste.
D) vision.
E) touch and pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

Figure 7-1 Floor of the Cranial Cavity
Use Figure 7-1 to answer the following questions:
Which structure encloses the pituitary gland?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Your friend Greg is hit in the jaw and when looking at him, his face looks misaligned. You immediately takehim to the emergency room and are not surprised to learn that he has a broken
A) temporal bone.
B) zygomatic bone.
C) mandible.
D) external auditory meatus.
E) clavicle.
A) temporal bone.
B) zygomatic bone.
C) mandible.
D) external auditory meatus.
E) clavicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The styloid process, zygomatic process, and auditory ossicles are associated with the
A) parietal bone.
B) occipital bone.
C) sphenoid bone.
D) temporal bone.
E) lacrimal bone.
A) parietal bone.
B) occipital bone.
C) sphenoid bone.
D) temporal bone.
E) lacrimal bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
As the result of an accident, Bill suffers a dislocated jaw. This injury would involve the
A) stylohyoid ligaments.
B) hyoid bone.
C) condylar process of the mandible.
D) alveolar process of the mandible.
E) greater horn of the hyoid bone.
A) stylohyoid ligaments.
B) hyoid bone.
C) condylar process of the mandible.
D) alveolar process of the mandible.
E) greater horn of the hyoid bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Kristen went to the dentist complaining of jaw tenderness and popping noises when she opens and closes hermouth. He notices abnormal wearing on the articulating surfaces of her teeth. Which of the following conditions does she most likely suffer from?
A) deviated nasal septum
B) cleft palate
C) temporomandibular joint syndrome
D) dislocated jaw
E) sinusitis
A) deviated nasal septum
B) cleft palate
C) temporomandibular joint syndrome
D) dislocated jaw
E) sinusitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The skull contains ________ bones.
A) 32
B) 22
C) 42
D) 12
E) 27
A) 32
B) 22
C) 42
D) 12
E) 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
During development a cleft palate forms when which bones fail to meet along the midline of the hard palate?
A) temporal
B) maxillae
C) zygomatic
D) sphenoid
E) ethmoid
A) temporal
B) maxillae
C) zygomatic
D) sphenoid
E) ethmoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58

Figure 7-1 Floor of the Cranial Cavity
Use Figure 7-1 to answer the following questions:
Which bone structure has foramina for the olfactory nerves?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 8
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Premature closure of the sagittal suture would result in
A) a long and narrow head.
B) a very broad head.
C) an unusually small head.
D) a distorted head with one side being longer than the other.
E) death.
A) a long and narrow head.
B) a very broad head.
C) an unusually small head.
D) a distorted head with one side being longer than the other.
E) death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The smallest facial bones are the
A) ethmoid bones.
B) lacrimal bones.
C) lacerum bones.
D) nasal bones.
E) zygomatic bones.
A) ethmoid bones.
B) lacrimal bones.
C) lacerum bones.
D) nasal bones.
E) zygomatic bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement(s) about the functions of the paranasal sinuses is/are not true?
A) They provide an extensive area of mucous epithelium.
B) They make skull bones lighter.
C) The mucus they secrete enters the oral cavities.
D) They support cilia that move the mucus.
E) They are located in the sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal, palatine and maxillae.
A) They provide an extensive area of mucous epithelium.
B) They make skull bones lighter.
C) The mucus they secrete enters the oral cavities.
D) They support cilia that move the mucus.
E) They are located in the sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal, palatine and maxillae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Sinus inflammation is called
A) sinusitis.
B) asthma.
C) congestion.
D) postnasal drip.
E) encephalitis.
A) sinusitis.
B) asthma.
C) congestion.
D) postnasal drip.
E) encephalitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The greater wings of which bone form a large portion of the posterior wall orbit?
A) lacrimal
B) ethmoid
C) sphenoid
D) nasal
E) zygomatic
A) lacrimal
B) ethmoid
C) sphenoid
D) nasal
E) zygomatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The nasal complex includes the bones that enclose the nasal cavity and the ________ sinuses.
A) hyponasal
B) paranasal
C) endonasal
D) epinasal
E) intranasal
A) hyponasal
B) paranasal
C) endonasal
D) epinasal
E) intranasal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Each of the following statements concerning the development of the skull is true except that
A) all the bones of the skull develop from one single ossification center.
B) at birth the cranial bones are connected by areas of fibrous connective tissue.
C) the growth of the cranium is usually coordinated with the growth of the brain.
D) the skulls of infants and adults differ in shape and structure of the skeletal elements.
E) the most significant growth of the skull occurs before the age of 5.
A) all the bones of the skull develop from one single ossification center.
B) at birth the cranial bones are connected by areas of fibrous connective tissue.
C) the growth of the cranium is usually coordinated with the growth of the brain.
D) the skulls of infants and adults differ in shape and structure of the skeletal elements.
E) the most significant growth of the skull occurs before the age of 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The ________ passes through the ________.
A) vagus nerve; foramen magnum
B) optic nerve; foramen ovale
C) vestibulocochlear nerve; external acoustic meatus
D) internal jugular vein; jugular foramen
E) internal carotid artery; jugular foramen
A) vagus nerve; foramen magnum
B) optic nerve; foramen ovale
C) vestibulocochlear nerve; external acoustic meatus
D) internal jugular vein; jugular foramen
E) internal carotid artery; jugular foramen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The floor of the orbital complex is formed mainly by the
A) maxilla.
B) ethmoid.
C) zygomatic.
D) sphenoid.
E) frontal.
A) maxilla.
B) ethmoid.
C) zygomatic.
D) sphenoid.
E) frontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Sutures can be found at all of the joints of an adult skull except between
A) the mandible and the cranium.
B) the zygomatic bone and the maxillary bone.
C) the occipital bone and the parietal bone.
D) the vomer and the zygomatic bone.
E) the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.
A) the mandible and the cranium.
B) the zygomatic bone and the maxillary bone.
C) the occipital bone and the parietal bone.
D) the vomer and the zygomatic bone.
E) the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The condition in which distortions of the skull occur due to the premature closure of fontanelles is called
A) anencephaly.
B) microcephaly.
C) craniostenosis.
D) membranitis.
E) epicranial block.
A) anencephaly.
B) microcephaly.
C) craniostenosis.
D) membranitis.
E) epicranial block.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the condition known as ________, premature closure of all of the cranial sutures results in restricted brain growth and an undersized head.
A) anencephaly
B) microcephaly
C) craniostenosis
D) membranitis
E) epicranial block
A) anencephaly
B) microcephaly
C) craniostenosis
D) membranitis
E) epicranial block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

Figure 7-1 Floor of the Cranial Cavity
Use Figure 7-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the name of the structure labeled "8"?
A) sella turcica
B) foramen ovale
C) foramen rotundum
D) carotid canal
E) foramen spinosum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A bent nasal septum that slows or prevents sinus drainage is known clinically as a ________ septum.
A) deviated
B) crooked
C) obstructive
D) deviant
E) restrictive
A) deviated
B) crooked
C) obstructive
D) deviant
E) restrictive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The nasal complex consists of all of the following bones except the
A) zygomatic.
B) ethmoid.
C) sphenoid.
D) frontal.
E) maxillary.
A) zygomatic.
B) ethmoid.
C) sphenoid.
D) frontal.
E) maxillary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The large foramen that serves as a passageway for the medulla of the brain and the accessory nerve (XI)isthe
A) foramen lacerum.
B) foramen rotundum.
C) carotid canal.
D) jugular foramen.
E) foramen magnum.
A) foramen lacerum.
B) foramen rotundum.
C) carotid canal.
D) jugular foramen.
E) foramen magnum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Nerves carrying sensory information from the lips and the chin pass through the
A) ramus of the mandible.
B) condylar process.
C) mental foramina.
D) mandibular foramen.
E) maxillary foramina.
A) ramus of the mandible.
B) condylar process.
C) mental foramina.
D) mandibular foramen.
E) maxillary foramina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The largest sinus is within which bone?
A) nasal
B) sphenoid
C) ethmoid
D) frontal
E) maxilla
A) nasal
B) sphenoid
C) ethmoid
D) frontal
E) maxilla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
How many bones make up the orbital complex?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The role(s) of the sinuses include(s)
A) making the skull lighter.
B) production of mucus that moistens and cleans the air.
C) increasing surface area for gas exchange.
D) extra source of air and increasing surface area for gas exchange.
E) making the skull lighter and production of mucus that moistens and cleans the air.
A) making the skull lighter.
B) production of mucus that moistens and cleans the air.
C) increasing surface area for gas exchange.
D) extra source of air and increasing surface area for gas exchange.
E) making the skull lighter and production of mucus that moistens and cleans the air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Each of the following bones is a component of the orbital complex except the ________ bone.
A) lacrimal
B) nasal
C) sphenoid
D) ethmoid
E) frontal
A) lacrimal
B) nasal
C) sphenoid
D) ethmoid
E) frontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The facial nerve (VII) passes through the internal acoustic meatus and then through the
A) mastoid foramen.
B) stylomastoid foramen.
C) jugular foramen.
D) carotid foramen.
E) foramen lacerum.
A) mastoid foramen.
B) stylomastoid foramen.
C) jugular foramen.
D) carotid foramen.
E) foramen lacerum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



