Deck 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/167
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
1
Lymphatic organs differ from lymphatic tissues in what way?
A) They contain T lymphocytes and lymphatic tissues do not.
B) They are found in the digestive tract and lymphatic tissues are found in the thorax.
C) They are surrounded by a fibrous capsule and lymphatic tissues are not.
D) They cannot produce antibodies, whereas lymphatic tissues can.
E) They occur throughout the body except in the head.
A) They contain T lymphocytes and lymphatic tissues do not.
B) They are found in the digestive tract and lymphatic tissues are found in the thorax.
C) They are surrounded by a fibrous capsule and lymphatic tissues are not.
D) They cannot produce antibodies, whereas lymphatic tissues can.
E) They occur throughout the body except in the head.
C
2
The lymphatic system is composed of all of the following except
A) lymphatic vessels.
B) the venae cavae.
C) the spleen.
D) lymph nodes.
E) lymph.
A) lymphatic vessels.
B) the venae cavae.
C) the spleen.
D) lymph nodes.
E) lymph.
B
3
The primary function of the lymphatic system is
A) the transport of hormones.
B) circulation of nutrients and dissolved gases.
C) defending the body against both external and internal threats.
D) the production and distribution of plasma proteins.
E) the production and maturation of leukocytes.
A) the transport of hormones.
B) circulation of nutrients and dissolved gases.
C) defending the body against both external and internal threats.
D) the production and distribution of plasma proteins.
E) the production and maturation of leukocytes.
C
4
The medulla of a lymph node contains ________ lymphocytes and macrophages.
A) cytotoxic T
B) medullary
C) NK
D) B
E) cordal
A) cytotoxic T
B) medullary
C) NK
D) B
E) cordal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Lymphatic vessels begin in peripheral tissues and ultimately drain into
A) veins.
B) peripheral capillary beds.
C) arteries.
D) the kidneys.
E) arterioles.
A) veins.
B) peripheral capillary beds.
C) arteries.
D) the kidneys.
E) arterioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The merging of ________ forms the right lymphatic duct.
A) the right jugular, right subclavian, and right bronchomediastinal trunks
B) the right lumbar, right subclavian, and right bronchomediastinal trunks
C) two great vessels
D) the thoracic and mediastinal ducts
E) superior and inferior lymphatic ducts
A) the right jugular, right subclavian, and right bronchomediastinal trunks
B) the right lumbar, right subclavian, and right bronchomediastinal trunks
C) two great vessels
D) the thoracic and mediastinal ducts
E) superior and inferior lymphatic ducts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
________ are large lymphatic nodules that are located in the walls of the pharynx.
A) Tonsils
B) Peyer's patches
C) Lymph nodes
D) Immune complexes
E) Spleens
A) Tonsils
B) Peyer's patches
C) Lymph nodes
D) Immune complexes
E) Spleens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
T Lymphocytes are produced and stored in all of the following except
A) the thymus.
B) lymphatic nodules.
C) lymph node organs.
D) the spleen.
E) the brain.
A) the thymus.
B) lymphatic nodules.
C) lymph node organs.
D) the spleen.
E) the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The lymphatic system does all of the following except
A) helps maintain normal blood volume.
B) transports gases to and away from lymph nodes.
C) eliminates variations in the composition of interstitial fluid.
D) transports lipids from the digestive tract.
E) fights infection.
A) helps maintain normal blood volume.
B) transports gases to and away from lymph nodes.
C) eliminates variations in the composition of interstitial fluid.
D) transports lipids from the digestive tract.
E) fights infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements about lymph flow in a node is false?
A) Lymph enters in an afferent lymphatic.
B) Lymph first enters the subcapsular space.
C) Lymph flows past dendritic cells.
D) The efferent lymphatic exits at the hilum.
E) The afferent lymphatic enters at the hilum.
A) Lymph enters in an afferent lymphatic.
B) Lymph first enters the subcapsular space.
C) Lymph flows past dendritic cells.
D) The efferent lymphatic exits at the hilum.
E) The afferent lymphatic enters at the hilum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Most of the lymph returns to the venous circulation by way of the
A) right lymphatic duct.
B) thoracic duct.
C) cisterna chyli.
D) hepatic portal vein.
E) dural sinus.
A) right lymphatic duct.
B) thoracic duct.
C) cisterna chyli.
D) hepatic portal vein.
E) dural sinus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Dividing lymphocytes can be found in the ________ of the lymphatic nodule.
A) sinus regions
B) germinal center
C) cortical layer
D) capsular space
E) stroma
A) sinus regions
B) germinal center
C) cortical layer
D) capsular space
E) stroma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which class of cells is particularly abundant in the red pulp of the spleen?
A) T lymphocytes
B) macrophages
C) B lymphocytes
D) neutrophils
E) Natural Killer cells
A) T lymphocytes
B) macrophages
C) B lymphocytes
D) neutrophils
E) Natural Killer cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Areas of the spleen that contain large aggregations of lymphocytes are known as
A) Peyer's patches.
B) adenoids.
C) white pulp.
D) red pulp.
E) lymph nodes.
A) Peyer's patches.
B) adenoids.
C) white pulp.
D) red pulp.
E) lymph nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Lymphatic capillaries are known for all of the following except
A) being the starting point of the lymphatic circulation.
B) being the smallest lymphatic vessels.
C) having larger diameters and looser walls than blood capillaries.
D) having shingle-like endothelial cells.
E) allowing nutrient and gas exchange.
A) being the starting point of the lymphatic circulation.
B) being the smallest lymphatic vessels.
C) having larger diameters and looser walls than blood capillaries.
D) having shingle-like endothelial cells.
E) allowing nutrient and gas exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All of the following are true of the thymus gland except that it
A) activates B cells.
B) reaches its greatest relative size during the second year of life.
C) involutes after puberty.
D) produces T cells.
E) lies in the anterior mediastinum.
A) activates B cells.
B) reaches its greatest relative size during the second year of life.
C) involutes after puberty.
D) produces T cells.
E) lies in the anterior mediastinum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
________ are clusters of lymphatic nodules deep to the epithelial lining of the small intestine.
A) Tonsils
B) Adenoids
C) Peyer's patches
D) Immune complexes
E) Lymph glands
A) Tonsils
B) Adenoids
C) Peyer's patches
D) Immune complexes
E) Lymph glands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The term lymphadenopathy refers to
A) a congenital lack or malformation of lymph nodes.
B) a chronic or excessive enlargement of lymph nodes.
C) accumulations of lymph in the tissue space.
D) the lack of lymphocytes in peripheral circulation.
E) increased numbers of circulating lymphocytes.
A) a congenital lack or malformation of lymph nodes.
B) a chronic or excessive enlargement of lymph nodes.
C) accumulations of lymph in the tissue space.
D) the lack of lymphocytes in peripheral circulation.
E) increased numbers of circulating lymphocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Compared to blood capillaries, lymph capillaries exhibit all of the following except that they
A) have no basement membrane.
B) have only a tunica interna.
C) have walls of endothelial cells that overlap like shingles.
D) are smaller in diameter.
E) are frequently irregular in shape.
A) have no basement membrane.
B) have only a tunica interna.
C) have walls of endothelial cells that overlap like shingles.
D) are smaller in diameter.
E) are frequently irregular in shape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Lymph nodes do all of the following except
A) produce antibodies through B cells.
B) monitor the contents of lymph.
C) remove debris and pathogens from the lymph.
D) accumulate cancer cells.
E) remove excess nutrients from the lymph.
A) produce antibodies through B cells.
B) monitor the contents of lymph.
C) remove debris and pathogens from the lymph.
D) accumulate cancer cells.
E) remove excess nutrients from the lymph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
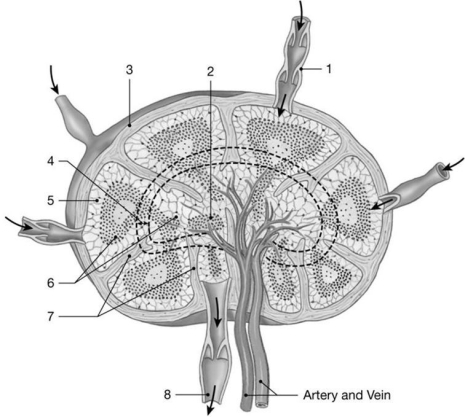
Figure 22-1 The Structure of a Lymph Node
Use Figure 22-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "2."
A) deep cortex
B) capsule
C) subcapsular space
D) trabeculae
E) medullary cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The lymphoid organ that acts like a filter as lymph passes through is
A) appendix.
B) tonsils.
C) adenoids.
D) lymph nodes.
E) thymus.
A) appendix.
B) tonsils.
C) adenoids.
D) lymph nodes.
E) thymus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Large lymphatic vessels have a wall structure most similar to which blood vessel?
A) veins
B) venules
C) capillaries
D) arterioles
E) arteries
A) veins
B) venules
C) capillaries
D) arterioles
E) arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Specialized lymphatic capillaries called lacteals are
A) located primarily in the large intestine.
B) necessary for the transport of dietary lipids.
C) part of the fenestrated capillary group.
D) more numerous than blood capillaries.
E) located throughout the body.
A) located primarily in the large intestine.
B) necessary for the transport of dietary lipids.
C) part of the fenestrated capillary group.
D) more numerous than blood capillaries.
E) located throughout the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The cell that dominates the deep cortical region of a lymph node is the ________ cell.
A) B
B) T
C) plasma
D) nodule
E) NK
A) B
B) T
C) plasma
D) nodule
E) NK

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Lymph fluid enters the venous circulation via the
A) right atrium.
B) subclavian veins.
C) brachiocephalic trunks.
D) jugular veins.
E) superior and inferior vena cava.
A) right atrium.
B) subclavian veins.
C) brachiocephalic trunks.
D) jugular veins.
E) superior and inferior vena cava.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Lymphatic tissue is found in the greatest quantity in
A) the adult spleen.
B) the adult thymus.
C) bone marrow.
D) the tonsils.
E) Peyer's patches.
A) the adult spleen.
B) the adult thymus.
C) bone marrow.
D) the tonsils.
E) Peyer's patches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Stem cells that can form all types of lymphocytes are concentrated in the
A) circulation.
B) thymus.
C) red bone marrow.
D) spleen.
E) yellow marrow.
A) circulation.
B) thymus.
C) red bone marrow.
D) spleen.
E) yellow marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

Figure 22-1 The Structure of a Lymph Node
Use Figure 22-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "3."
A) deep cortex
B) capsule
C) subcapsular space
D) trabeculae
E) outer cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ________ lymphatics leave the lymph node at the hilum.
A) ascending
B) lateral
C) afferent
D) descending
E) efferent
A) ascending
B) lateral
C) afferent
D) descending
E) efferent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The blood-thymus barrier is made up of
A) immature T cells.
B) mature T cells.
C) macrophages.
D) plasma cells.
E) epithelial reticular cells.
A) immature T cells.
B) mature T cells.
C) macrophages.
D) plasma cells.
E) epithelial reticular cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The primary lymphoid tissues include
A) the bone marrow.
B) the thymus.
C) the bone marrow and thymus.
D) the lymph nodes and tonsils.
E) the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and lymph nodes.
A) the bone marrow.
B) the thymus.
C) the bone marrow and thymus.
D) the lymph nodes and tonsils.
E) the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and lymph nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not a secondary lymphoid tissue or organ?
A) spleen
B) tonsils
C) MALT
D) thymus
E) lymph nodes
A) spleen
B) tonsils
C) MALT
D) thymus
E) lymph nodes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
T cells develop from stem cells in the
A) bone marrow.
B) liver.
C) spleen.
D) thymus.
E) kidneys.
A) bone marrow.
B) liver.
C) spleen.
D) thymus.
E) kidneys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An accumulation of lymph in a region where lymphatic drainage has been blocked is called
A) lymphopenia.
B) lymphadenopathy.
C) lymphoma.
D) lymphedema.
E) lymphosis.
A) lymphopenia.
B) lymphadenopathy.
C) lymphoma.
D) lymphedema.
E) lymphosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Lymphatic capillaries are not found in
A) the digestive system.
B) the skin.
C) cornea of the eye.
D) skeletal muscles.
E) the liver.
A) the digestive system.
B) the skin.
C) cornea of the eye.
D) skeletal muscles.
E) the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Figure 22-1 The Structure of a Lymph Node
Use Figure 22-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "1."
A) efferent lymphatic vessel
B) venule
C) arteriole
D) afferent lymphatic vessel
E) lymphatic nodule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the thymus shrank and stopped making thymosins, we would expect to see an immediate decrease in the number of
A) B lymphocytes.
B) NK cells.
C) T cells.
D) neutrophils.
E) red blood cells.
A) B lymphocytes.
B) NK cells.
C) T cells.
D) neutrophils.
E) red blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An infection and inflammation of the aggregated lymphatic nodules in the pharynx is called
A) laryngitis.
B) lymph edema.
C) tonsillitis.
D) indigestion.
E) lymphosis.
A) laryngitis.
B) lymph edema.
C) tonsillitis.
D) indigestion.
E) lymphosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The thoracic duct originates from an expanded chamber called the
A) thoracic sinus.
B) cisterna chyli.
C) thoracic trunk.
D) hilum.
E) thoracic ventricle.
A) thoracic sinus.
B) cisterna chyli.
C) thoracic trunk.
D) hilum.
E) thoracic ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

Figure 22-1 The Structure of a Lymph Node
Use Figure 22-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "6."
A) medulla
B) cortex
C) capsule
D) trabeculae
E) cortical sinus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Lymphocytes
A) are actively phagocytic.
B) destroy red blood cells.
C) respond to antigens.
D) are primarily found in red bone marrow.
E) decrease in number during infection.
A) are actively phagocytic.
B) destroy red blood cells.
C) respond to antigens.
D) are primarily found in red bone marrow.
E) decrease in number during infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The cells responsible for the production of circulating immunoglobulins are ________ cells.
A) NK
B) plasma
C) helper T
D) thymus
E) liver
A) NK
B) plasma
C) helper T
D) thymus
E) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sally has a tumor. In an effort to fight the cancerous cells her body increases the production of
A) neutrophils.
B) NK cells.
C) suppressor T cells.
D) memory B cells.
E) plasma cells.
A) neutrophils.
B) NK cells.
C) suppressor T cells.
D) memory B cells.
E) plasma cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Various types of macrophages are derived from
A) lymphocytes.
B) monocytes.
C) neutrophils.
D) eosinophils.
E) basophils.
A) lymphocytes.
B) monocytes.
C) neutrophils.
D) eosinophils.
E) basophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Each of the following is a physical barrier to infection except
A) body hair.
B) epithelium.
C) secretions.
D) complement.
E) basement membranes.
A) body hair.
B) epithelium.
C) secretions.
D) complement.
E) basement membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is not a lymphocyte?
A) NK cells
B) plasma cells
C) memory T cells
D) macrophages
E) suppressor T cells
A) NK cells
B) plasma cells
C) memory T cells
D) macrophages
E) suppressor T cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Plasma contains ________ special proteins that form the complement system.
A) about 3
B) exactly 10
C) roughly 18
D) exactly 25
E) more than 30
A) about 3
B) exactly 10
C) roughly 18
D) exactly 25
E) more than 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The body's innate defenses include all of the following except
A) the skin.
B) complement.
C) interferon.
D) inflammation.
E) antibodies.
A) the skin.
B) complement.
C) interferon.
D) inflammation.
E) antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Microphages include
A) monocytes.
B) Kupffer cells.
C) neutrophils.
D) eosinophils.
E) both neutrophils and eosinophils.
A) monocytes.
B) Kupffer cells.
C) neutrophils.
D) eosinophils.
E) both neutrophils and eosinophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Lymphocytes that destroy foreign cells or virus-infected cells are ________ cells.
A) plasma
B) B
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) suppressor T
A) plasma
B) B
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) suppressor T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In general, lymphocytes
A) spend most of their time in lymphatic tissue.
B) have relatively short life spans.
C) have two nuclei.
D) are produced and mature only in red bone marrow.
E) are located primarily in the blood stream.
A) spend most of their time in lymphatic tissue.
B) have relatively short life spans.
C) have two nuclei.
D) are produced and mature only in red bone marrow.
E) are located primarily in the blood stream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A substance that provokes an immune response is called an
A) immunoglobulin.
B) antihistamine.
C) antibody.
D) antigen.
E) allopath.
A) immunoglobulin.
B) antihistamine.
C) antibody.
D) antigen.
E) allopath.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Stem cells that will form B cells or NK cells are found only in the
A) red bone marrow.
B) liver.
C) spleen.
D) thymus.
E) kidneys.
A) red bone marrow.
B) liver.
C) spleen.
D) thymus.
E) kidneys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The cells responsible for humoral immunity are the ________ cells.
A) NK
B) B
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) suppressor T
A) NK
B) B
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) suppressor T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
T is to ________ as B is to ________.
A) top-located; bottom-located
B) thymus-dependent; bone marrow-derived
C) thyroid-drawn; bowel-developed
D) non-thymus-dependent; bottom-located
E) trabeculae-descended; bursa-origin
A) top-located; bottom-located
B) thymus-dependent; bone marrow-derived
C) thyroid-drawn; bowel-developed
D) non-thymus-dependent; bottom-located
E) trabeculae-descended; bursa-origin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The release of endogenous pyrogen (or interleukin-1) by active macrophages would
A) cause inflammation.
B) produce a fever.
C) activate complement.
D) opsonize pathogens.
E) activate antibodies.
A) cause inflammation.
B) produce a fever.
C) activate complement.
D) opsonize pathogens.
E) activate antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An inflammatory response is triggered when
A) red blood cells release pyrogens.
B) T cells release interferon.
C) mast cells release histamine and heparin.
D) neutrophils phagocytize bacteria.
E) blood flow to an area increases.
A) red blood cells release pyrogens.
B) T cells release interferon.
C) mast cells release histamine and heparin.
D) neutrophils phagocytize bacteria.
E) blood flow to an area increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The cells directly responsible for cellular immunity are the ________ cells.
A) dendritic
B) plasma
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) suppressor T
A) dendritic
B) plasma
C) helper T
D) cytotoxic T
E) suppressor T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

Figure 22-1 The Structure of a Lymph Node
Use Figure 22-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the dominant cell type in the area labeled "6."
A) T cells
B) B cells
C) erythrocytes
D) platelets
E) dendritic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The cells that perform immunological surveillance are the ________ cells.
A) NK
B) plasma
C) B
D) helper T
E) suppressor T
A) NK
B) plasma
C) B
D) helper T
E) suppressor T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Cytokines that make a cell and its neighbors resistant to virus infection are called
A) complement.
B) interferons.
C) interleukins.
D) immunoglobulins.
E) transferrins.
A) complement.
B) interferons.
C) interleukins.
D) immunoglobulins.
E) transferrins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The first line of cellular defense against pathogens are the
A) T cells.
B) B cells.
C) NK cells.
D) phagocytes.
E) plasma cells.
A) T cells.
B) B cells.
C) NK cells.
D) phagocytes.
E) plasma cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The movement of phagocytes through the capillary wall is called
A) chemotaxis.
B) diapedesis.
C) adherens.
D) transcytosis.
E) diffusion.
A) chemotaxis.
B) diapedesis.
C) adherens.
D) transcytosis.
E) diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Place the following steps of NK cell killing in order.
1) Secretion of perforin
2) Realignment of Golgi apparatus
3) Lysis of abnormal cell
4) Recognition and adhesion
A) 4, 2, 1, 3
B) 2, 1, 4, 3
C) 4, 1, 2, 3
D) 1, 2, 4, 3
E) 1, 4, 3, 2
1) Secretion of perforin
2) Realignment of Golgi apparatus
3) Lysis of abnormal cell
4) Recognition and adhesion
A) 4, 2, 1, 3
B) 2, 1, 4, 3
C) 4, 1, 2, 3
D) 1, 2, 4, 3
E) 1, 4, 3, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Interferons
A) prevent viruses from leaving a cell.
B) prevent viruses from entering a cell.
C) bind to viruses and destroy them.
D) interfere with viral replication.
E) reduce macrophage chemotaxis to the infection.
A) prevent viruses from leaving a cell.
B) prevent viruses from entering a cell.
C) bind to viruses and destroy them.
D) interfere with viral replication.
E) reduce macrophage chemotaxis to the infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
________ are fixed macrophages found in the liver.
A) Astrocytes
B) Oligodendrocytes
C) Microglia
D) Kupffer cells
E) Ventricular macrophages
A) Astrocytes
B) Oligodendrocytes
C) Microglia
D) Kupffer cells
E) Ventricular macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The effects of activating the complement system include all of the following except
A) destruction of target cell plasma membranes.
B) stimulation of inflammation.
C) inhibition of the immune response.
D) opsonization.
E) chemotaxis.
A) destruction of target cell plasma membranes.
B) stimulation of inflammation.
C) inhibition of the immune response.
D) opsonization.
E) chemotaxis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The complement system works closely with and complements the action of
A) interferons.
B) antibodies.
C) pyrogens.
D) phagocytes.
E) microphages.
A) interferons.
B) antibodies.
C) pyrogens.
D) phagocytes.
E) microphages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The classic pathway of complement activation begins when the protein C1 binds to
A) the cell wall of bacteria.
B) the plasma membrane of bacteria.
C) two antibodies attached to an antigen.
D) a cell surface antigen.
E) a plasma protein.
A) the cell wall of bacteria.
B) the plasma membrane of bacteria.
C) two antibodies attached to an antigen.
D) a cell surface antigen.
E) a plasma protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
NK cells use ________ to lyse abnormal cells.
A) pyrogen
B) perforin
C) interferon
D) complement
E) phagocytosis
A) pyrogen
B) perforin
C) interferon
D) complement
E) phagocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A sample of John's blood shows a high level of pyrogens. This would indicate that John
A) is feeling achy.
B) is producing T lymphocytes.
C) has a sore throat.
D) is running a fever.
E) has swollen lymph nodes.
A) is feeling achy.
B) is producing T lymphocytes.
C) has a sore throat.
D) is running a fever.
E) has swollen lymph nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Histamine increases blood flow and vascular permeability. This would account for all of the following changes that occur during inflammation except
A) redness of the inflamed tissue.
B) chemotaxis of phagocytes.
C) heat of the inflamed tissue.
D) movement of defense proteins and cells into the interstitial space.
E) swelling of the inflamed tissue.
A) redness of the inflamed tissue.
B) chemotaxis of phagocytes.
C) heat of the inflamed tissue.
D) movement of defense proteins and cells into the interstitial space.
E) swelling of the inflamed tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Fixed macrophages that are found in the central nervous system are called
A) astrocytes.
B) oligodendrocytes.
C) microglia.
D) Kupffer cells.
E) ventricular macrophages.
A) astrocytes.
B) oligodendrocytes.
C) microglia.
D) Kupffer cells.
E) ventricular macrophages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Leslie has a severe sore throat and the lymph nodes in her neck are swollen. This would indicate that
A) the focus of the infection is the lymph nodes.
B) lymph is not flowing consistently through these lymph nodes.
C) the lymph nodes contain an increased number of lymphocytes.
D) the lymph nodes are actively producing phagocytes.
E) the lymph nodes have increased their secretion of thymosin.
A) the focus of the infection is the lymph nodes.
B) lymph is not flowing consistently through these lymph nodes.
C) the lymph nodes contain an increased number of lymphocytes.
D) the lymph nodes are actively producing phagocytes.
E) the lymph nodes have increased their secretion of thymosin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Cancer cells can be detected by NK cells when they show
A) interferons.
B) complement proteins.
C) tumor-specific antigens.
D) opsonization.
E) CD4 markers.
A) interferons.
B) complement proteins.
C) tumor-specific antigens.
D) opsonization.
E) CD4 markers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Free phagocytes found in the air sacs of the lungs are called
A) alveolar macrophages.
B) histiocytes.
C) Kupffer cells.
D) pleurocytes.
E) microglia.
A) alveolar macrophages.
B) histiocytes.
C) Kupffer cells.
D) pleurocytes.
E) microglia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An important protein in the activation of the alternative pathway of complement activation is
A) properdin.
B) interferon.
C) histamine.
D) fibrin.
E) C1.
A) properdin.
B) interferon.
C) histamine.
D) fibrin.
E) C1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The phagocytic antigen-presenting cells belong to the ________ group.
A) tumor-suppressing
B) complement
C) interferon
D) monocyte-macrophage
E) lymphatic
A) tumor-suppressing
B) complement
C) interferon
D) monocyte-macrophage
E) lymphatic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The attraction or repulsion of certain cells to chemicals in their environment is called
A) polarity.
B) diapedesis.
C) cytotoxicity.
D) infection.
E) chemotaxis.
A) polarity.
B) diapedesis.
C) cytotoxicity.
D) infection.
E) chemotaxis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 167 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



