Deck 23: The Respiratory System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: The Respiratory System
1
Tuberculosis results from an infection by the bacterium
A) Clostridium difficile.
B) Staphylococcus aureus.
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
D) Vancomycin-resistant streptococcus.
E) Tuberculin plumonae.
A) Clostridium difficile.
B) Staphylococcus aureus.
C) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
D) Vancomycin-resistant streptococcus.
E) Tuberculin plumonae.
C
2
The nasopharynx transitions into the oropharynx at the level of the
A) hard palate.
B) soft palate.
C) cribriform plate.
D) internal nares.
E) pharyngeal septum.
A) hard palate.
B) soft palate.
C) cribriform plate.
D) internal nares.
E) pharyngeal septum.
B
3
The larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles all make up the
A) upper respiratory tract.
B) lower respiratory tract.
C) internal respiratory tract.
D) alveoli of the respiratory tract.
E) respiratory mucosa.
A) upper respiratory tract.
B) lower respiratory tract.
C) internal respiratory tract.
D) alveoli of the respiratory tract.
E) respiratory mucosa.
B
4
Inhaling through the nostrils is preferred over the mouth because
A) there is less resistance to air flow.
B) it combines olfaction with respiration.
C) it allows better conditioning of the inhaled air.
D) bacteria won't be inhaled from the oral cavity.
E) it dries out the mouth.
A) there is less resistance to air flow.
B) it combines olfaction with respiration.
C) it allows better conditioning of the inhaled air.
D) bacteria won't be inhaled from the oral cavity.
E) it dries out the mouth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An important component of the lamina propria in the upper respiratory system is
A) sweat glands.
B) ceruminous glands.
C) mucus glands.
D) serous glands.
E) smooth muscle cells.
A) sweat glands.
B) ceruminous glands.
C) mucus glands.
D) serous glands.
E) smooth muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The beating of the cilia of the respiratory passages in the direction of the pharynx forms a(n)
A) debris filter.
B) mucus escalator.
C) respiratory rhythmicity center.
D) smooth slick surface allowing particles to slide.
E) increased surface area for gas exchange.
A) debris filter.
B) mucus escalator.
C) respiratory rhythmicity center.
D) smooth slick surface allowing particles to slide.
E) increased surface area for gas exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The respiratory portion of the respiratory tract includes the
A) bronchi.
B) trachea.
C) larynx.
D) alveoli.
E) nose.
A) bronchi.
B) trachea.
C) larynx.
D) alveoli.
E) nose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The entire array of protective mechanisms in the respiratory system is called the
A) respiratory immunity.
B) macrophage complex.
C) respiratory defense system.
D) acquired respiratory defense.
E) mucus escalator.
A) respiratory immunity.
B) macrophage complex.
C) respiratory defense system.
D) acquired respiratory defense.
E) mucus escalator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The conchae
A) divide the nasal cavity into a right and a left side.
B) provide an opening into the pharynx.
C) provide a increase in surface area for the sense of smell.
D) create turbulence in the air to trap particulate matter in mucus.
E) provide an opening to paranasal sinuses.
A) divide the nasal cavity into a right and a left side.
B) provide an opening into the pharynx.
C) provide a increase in surface area for the sense of smell.
D) create turbulence in the air to trap particulate matter in mucus.
E) provide an opening to paranasal sinuses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Air entering the body is filtered, warmed, and humidified by the
A) upper respiratory tract.
B) lower respiratory tract.
C) lungs.
D) alveoli.
E) bronchioles.
A) upper respiratory tract.
B) lower respiratory tract.
C) lungs.
D) alveoli.
E) bronchioles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following organs is not part of the lower respiratory system?
A) pharynx
B) trachea
C) larynx
D) bronchi
E) alveoli
A) pharynx
B) trachea
C) larynx
D) bronchi
E) alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The openings to the nasal cavity are the
A) external nares.
B) internal nares.
C) nasal meatuses.
D) nasal conchae.
E) nasal sinuses.
A) external nares.
B) internal nares.
C) nasal meatuses.
D) nasal conchae.
E) nasal sinuses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Functions of the nasal cavity include all of the following except
A) filtering the air.
B) warming the air.
C) humidifying the air.
D) housing tonsils.
E) housing olfactory receptors.
A) filtering the air.
B) warming the air.
C) humidifying the air.
D) housing tonsils.
E) housing olfactory receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Harry suffers from cystic fibrosis and has severe breathing difficulties. His problems result from
A) genetic mutation in cilia production.
B) laryngospasms.
C) thick secretions that are difficult to transport.
D) lack of neural control of respiration.
E) reduced mucus secretions in the trachea.
A) genetic mutation in cilia production.
B) laryngospasms.
C) thick secretions that are difficult to transport.
D) lack of neural control of respiration.
E) reduced mucus secretions in the trachea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx constitute the ________ portion of the airway.
A) conducting
B) exchange
C) respiratory
D) sinus
E) primary
A) conducting
B) exchange
C) respiratory
D) sinus
E) primary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of these is not part of the upper respiratory system?
A) larynx
B) pharynx
C) nasal cavity
D) nose
E) sinuses
A) larynx
B) pharynx
C) nasal cavity
D) nose
E) sinuses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The ________ is shared by the respiratory and digestive systems.
A) pharynx
B) esophagus
C) trachea
D) windpipe
E) right mainstem bronchus
A) pharynx
B) esophagus
C) trachea
D) windpipe
E) right mainstem bronchus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The respiratory epithelium of the conducting airways consists of
A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) simple squamous epithelium.
D) ciliated squamous epithelium.
E) stratified squamous epithelium.
A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) simple squamous epithelium.
D) ciliated squamous epithelium.
E) stratified squamous epithelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The respiratory mucosa consists of
A) epithelium and underlying layer of areolar tissue.
B) dense irregular connective and adipose tissue.
C) ciliated stratified squamous and columnar cells.
D) fibrocartilage and mucous cells.
E) dense regular connective and areolar tissue.
A) epithelium and underlying layer of areolar tissue.
B) dense irregular connective and adipose tissue.
C) ciliated stratified squamous and columnar cells.
D) fibrocartilage and mucous cells.
E) dense regular connective and areolar tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
________ is the most common lethal inherited disease affecting individuals of Northern European descent.
A) MRSA
B) Congestive heart failure
C) Cystic fibrosis
D) Myasthenia gravis
E) Parkinson's disease
A) MRSA
B) Congestive heart failure
C) Cystic fibrosis
D) Myasthenia gravis
E) Parkinson's disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The superior region of the pharynx is called the
A) nasal cavity.
B) nasopharynx.
C) oropharynx.
D) laryngopharynx.
E) superior nasal conchae.
A) nasal cavity.
B) nasopharynx.
C) oropharynx.
D) laryngopharynx.
E) superior nasal conchae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The nasal cavity opens into the nasopharynx through a connection known as the
A) oropharynx.
B) nasal meatus.
C) nasal vestibule.
D) internal nares.
E) auditory canal.
A) oropharynx.
B) nasal meatus.
C) nasal vestibule.
D) internal nares.
E) auditory canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
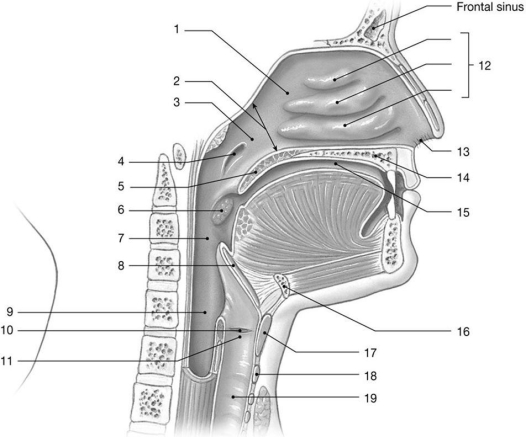
Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "7."
A) internal nares
B) esophagus
C) glottis
D) oropharynx
E) laryngopharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is false about the pharynx?
A) It is shared by the integumentary and respiratory systems.
B) The nasopharynx is superior.
C) The oropharynx connects to oral cavity.
D) The laryngopharynx ends at esophagus opening.
E) Solids, liquids, and gases pass through.
A) It is shared by the integumentary and respiratory systems.
B) The nasopharynx is superior.
C) The oropharynx connects to oral cavity.
D) The laryngopharynx ends at esophagus opening.
E) Solids, liquids, and gases pass through.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The ________ is lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
A) nasopharynx
B) trachea
C) oropharynx
D) larynx
E) nasal cavity
A) nasopharynx
B) trachea
C) oropharynx
D) larynx
E) nasal cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Air flows between nasal conchae through the
A) dorsum nasi.
B) apex.
C) external nares.
D) nasal vestibule.
E) superior, middle, and inferior nasal meatuses.
A) dorsum nasi.
B) apex.
C) external nares.
D) nasal vestibule.
E) superior, middle, and inferior nasal meatuses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which bone does not form part of the lateral or superior walls of the nasal cavity?
A) maxilla
B) mandible
C) nasal
D) ethmoid
E) sphenoid
A) maxilla
B) mandible
C) nasal
D) ethmoid
E) sphenoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the function of the structure labeled "8"?
A) forces air into the lungs
B) causes air to swirl within the respiratory passageway
C) prevents food from entering the larynx
D) acts like a supplementary air pump
E) adjusts tension of vocal folds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Physical damage to the lamina propria of the nasal mucosa is likely to result in
A) epistaxis.
B) nasal congestion.
C) nosebleeds.
D) a deviated septum.
E) epistaxis or nosebleeds.
A) epistaxis.
B) nasal congestion.
C) nosebleeds.
D) a deviated septum.
E) epistaxis or nosebleeds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The auditory tubes open into the
A) nasopharynx.
B) oropharynx.
C) laryngopharynx.
D) larynx.
E) nasal cavity.
A) nasopharynx.
B) oropharynx.
C) laryngopharynx.
D) larynx.
E) nasal cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The palatine tonsils lie in the walls of the
A) nasopharynx.
B) oropharynx.
C) laryngopharynx.
D) larynx.
E) nasal cavity.
A) nasopharynx.
B) oropharynx.
C) laryngopharynx.
D) larynx.
E) nasal cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The glottis is
A) the soft tissue that hangs off the end of the soft palate.
B) a flap of elastic cartilage.
C) the opening to the larynx.
D) the opening to the pharynx.
E) part of the hard palate.
A) the soft tissue that hangs off the end of the soft palate.
B) a flap of elastic cartilage.
C) the opening to the larynx.
D) the opening to the pharynx.
E) part of the hard palate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The common passageway shared by the respiratory and digestive systems is the
A) larynx.
B) glottis.
C) vestibule.
D) pharynx.
E) trachea.
A) larynx.
B) glottis.
C) vestibule.
D) pharynx.
E) trachea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Accidently sending fluid up out of the nose happens when the ________ fails to close off the ________.
A) epiglottis; larynx
B) epiglottis; nasopharynx
C) soft palate; nasopharynx
D) soft palate; larynx
E) soft palate; oropharynx
A) epiglottis; larynx
B) epiglottis; nasopharynx
C) soft palate; nasopharynx
D) soft palate; larynx
E) soft palate; oropharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The portion of the nasal cavity contained within the flexible tissues of the external nose is the
A) nasopharynx.
B) vestibule.
C) internal chamber.
D) conchae.
E) nasal septum.
A) nasopharynx.
B) vestibule.
C) internal chamber.
D) conchae.
E) nasal septum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "2."
A) olfactory organ
B) oropharynx
C) nasopharynx
D) internal nares
E) nasal sinus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
What is the function of the structure labeled "5"?
A) help olfaction
B) improve warming of air
C) cause air to swirl within the respiratory passageway
D) prevent food from entering the larynx
E) prevent food from entering the nasopharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The larynx contains ________ cartilages.
A) 14
B) 6
C) 9
D) 2
E) 5
A) 14
B) 6
C) 9
D) 2
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
Identify the structure labeled "5."
A) pharyngeal tonsil
B) palatine tonsil
C) epiglottis
D) soft palate
E) hard palate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by the
A) hard palate.
B) soft palate.
C) cribriform plate.
D) internal nares.
E) pharyngeal septum.
A) hard palate.
B) soft palate.
C) cribriform plate.
D) internal nares.
E) pharyngeal septum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The ring-shaped cartilage just inferior to the thyroid cartilage is the ________ cartilage.
A) epiglottis
B) cuneiform
C) corniculate
D) cricoid
E) arytenoid
A) epiglottis
B) cuneiform
C) corniculate
D) cricoid
E) arytenoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
During a choking episode, most foreign objects are lodged in the ________ bronchus due to its larger diameter and steeper angle.
A) right primary
B) left primary
C) right lobar
D) left lobar
E) medial
A) right primary
B) left primary
C) right lobar
D) left lobar
E) medial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Primary bronchi are to ________ as secondary bronchi are to ________.
A) main bronchi; lobar bronchi
B) lobar bronchi; segmental bronchi
C) segmental bronchi; lobar bronchi
D) trachea; pharynx
E) lobar bronchi; alveolar ducts
A) main bronchi; lobar bronchi
B) lobar bronchi; segmental bronchi
C) segmental bronchi; lobar bronchi
D) trachea; pharynx
E) lobar bronchi; alveolar ducts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The C shape of the tracheal cartilages is important because
A) large masses of food can move through the esophagus.
B) large masses of air can pass through the trachea and thus the bronchi.
C) it facilitates turning of the head.
D) the bronchi are also C-shaped.
E) it permits the trachea to pinch shut prior to sneezing.
A) large masses of food can move through the esophagus.
B) large masses of air can pass through the trachea and thus the bronchi.
C) it facilitates turning of the head.
D) the bronchi are also C-shaped.
E) it permits the trachea to pinch shut prior to sneezing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Air passing through the glottis vibrates the vocal folds and produces
A) speech.
B) articulation.
C) phonation.
D) whistling.
E) ululation.
A) speech.
B) articulation.
C) phonation.
D) whistling.
E) ululation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The elastic cartilage that covers the opening to the larynx during swallowing is the
A) thyroid cartilage.
B) cricoid cartilage.
C) corniculate cartilage.
D) cuneiform cartilage.
E) epiglottis.
A) thyroid cartilage.
B) cricoid cartilage.
C) corniculate cartilage.
D) cuneiform cartilage.
E) epiglottis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An acute infection of the throat that can lead to swelling and closure of the glottis and cause suffocationis known as
A) laryngitis.
B) laryngospasm.
C) acute epiglottitis.
D) strep throat.
E) acute pharyngitis.
A) laryngitis.
B) laryngospasm.
C) acute epiglottitis.
D) strep throat.
E) acute pharyngitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The vocal folds are located within the
A) nasopharynx.
B) oropharynx.
C) larynx.
D) trachea.
E) bronchi.
A) nasopharynx.
B) oropharynx.
C) larynx.
D) trachea.
E) bronchi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The largest cartilage of the larynx is the ________ cartilage.
A) thyroid
B) cricoid
C) cuneiform
D) arytenoid
E) epiglottic
A) thyroid
B) cricoid
C) cuneiform
D) arytenoid
E) epiglottic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements about the trachea is false?
A) It is lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) Tracheal cartilages prevent tracheal collapse.
C) It contains many mucous glands.
D) It alters its diameter in response to the autonomic nervous system.
E) It is completely wrapped in smooth muscle.
A) It is lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) Tracheal cartilages prevent tracheal collapse.
C) It contains many mucous glands.
D) It alters its diameter in response to the autonomic nervous system.
E) It is completely wrapped in smooth muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The laryngeal cartilage which is not composed of hyaline cartilage is the
A) arytenoid.
B) corniculate.
C) cricoid.
D) epiglottis.
E) thyroid.
A) arytenoid.
B) corniculate.
C) cricoid.
D) epiglottis.
E) thyroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A pair of ligaments covered by laryngeal epithelium that function in sound production are the
A) intrinsic ligaments.
B) extrinsic ligaments.
C) ventricular folds.
D) vocal folds.
E) intrinsic laryngeal muscles.
A) intrinsic ligaments.
B) extrinsic ligaments.
C) ventricular folds.
D) vocal folds.
E) intrinsic laryngeal muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Tina is singing a song. At a certain point in the song, she forces a large volume of air out of the glottisand at the same time increases the tension on her vocal cords. The sound that she produces is
A) low pitched and loud.
B) high pitched and loud.
C) low pitched and soft.
D) high pitched and soft.
E) medium pitched and soft.
A) low pitched and loud.
B) high pitched and loud.
C) low pitched and soft.
D) high pitched and soft.
E) medium pitched and soft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Contraction of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles can
A) move the cricoid cartilage.
B) close the glottis.
C) constrict the trachea.
D) move food from the larynx to the esophagus.
E) assist in breathing during exercise.
A) move the cricoid cartilage.
B) close the glottis.
C) constrict the trachea.
D) move food from the larynx to the esophagus.
E) assist in breathing during exercise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ________ branch from the trachea at the carina.
A) terminal bronchioles
B) lobar bronchi
C) segmental bronchi
D) primary bronchi
E) alveolar ducts
A) terminal bronchioles
B) lobar bronchi
C) segmental bronchi
D) primary bronchi
E) alveolar ducts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The adult human trachea is about ________ in diameter and contains ________ tracheal cartilages.
A) 1.0 cm; 15-20
B) 1.0 cm; 10-15
C) 2.5 cm; 15-20
D) 2.5 cm; 40-50
E) 4.5 cm; 60-80
A) 1.0 cm; 15-20
B) 1.0 cm; 10-15
C) 2.5 cm; 15-20
D) 2.5 cm; 40-50
E) 4.5 cm; 60-80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The airway that connects the larynx to the bronchial tree is the
A) trachea.
B) bronchiole.
C) laryngopharynx.
D) alveolar duct.
E) bronchus.
A) trachea.
B) bronchiole.
C) laryngopharynx.
D) alveolar duct.
E) bronchus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The paired cartilages that articulate with the superior border of the cricoid cartilage are the ________cartilages.
A) cricothyroid
B) innominate
C) cuneiform
D) corniculate
E) arytenoid
A) cricothyroid
B) innominate
C) cuneiform
D) corniculate
E) arytenoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A common site to place a tracheostomy tube is through the ligament that connects the cricoid cartilage to the ________ cartilage.
A) thyroid
B) cuneiform
C) corniculate
D) epiglottic
E) vestibular
A) thyroid
B) cuneiform
C) corniculate
D) epiglottic
E) vestibular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Roughly ________ terminal bronchioles arise from each segmental bronchus.
A) 1,500
B) 3,000
C) 6,500
D) 10,000
E) 100,000
A) 1,500
B) 3,000
C) 6,500
D) 10,000
E) 100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Asthma is
A) a collapsed lung resulting from insufficient production of surfactant.
B) due to an excessive stimulation of smooth muscle in bronchioles.
C) an obstructive tumor targeting primarily the terminal bronchioles.
D) characterized by fluid buildup in the alveoli.
E) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
A) a collapsed lung resulting from insufficient production of surfactant.
B) due to an excessive stimulation of smooth muscle in bronchioles.
C) an obstructive tumor targeting primarily the terminal bronchioles.
D) characterized by fluid buildup in the alveoli.
E) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Primary bronchi enter their respective lungs along with pulmonary vessels, nerves, and lymphatics at whichregion?
A) base
B) apex
C) hilum
D) cardiac notch
E) superior lobe
A) base
B) apex
C) hilum
D) cardiac notch
E) superior lobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The right lung is to ________ as the left lung is to ________.
A) three lobes; two lobes
B) two lobes; two lobes
C) two lobes; three lobes
D) three lobes; three lobes
E) four lobes; three lobes
A) three lobes; two lobes
B) two lobes; two lobes
C) two lobes; three lobes
D) three lobes; three lobes
E) four lobes; three lobes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The interlobular septa divide the lungs into
A) lobes.
B) pulmonary lobules.
C) alveolar sacs.
D) vital capacity and residual volume.
E) visceral pleura and fibrous trabeculae.
A) lobes.
B) pulmonary lobules.
C) alveolar sacs.
D) vital capacity and residual volume.
E) visceral pleura and fibrous trabeculae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Respiratory function deteriorates as a result of pneumonia because inflammation
A) causes fluids to leak into the alveoli.
B) causes respiratory bronchioles to swell and dilate.
C) causes the lungs to leak air into the thorax.
D) reduces movement of the epiglottis.
E) reduces the size of the pleural cavity.
A) causes fluids to leak into the alveoli.
B) causes respiratory bronchioles to swell and dilate.
C) causes the lungs to leak air into the thorax.
D) reduces movement of the epiglottis.
E) reduces the size of the pleural cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
JJ is suffering from laryngitis. He will most likely experience which of the following symptoms?
A) coughing
B) hoarseness
C) sneezing
D) suffocation
E) impaired swallowing
A) coughing
B) hoarseness
C) sneezing
D) suffocation
E) impaired swallowing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The blood air barrier consists of
A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) 1 layer of moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) 2 layers of simple squamous epithelium.
D) stratified squamous epithelium.
E) surfactant cells.
A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) 1 layer of moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) 2 layers of simple squamous epithelium.
D) stratified squamous epithelium.
E) surfactant cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The following is a list of some airways. What is the order in which air passes through them?
1) lobar bronchus
2) bronchioles
3) alveolar ducts
4) primary bronchus
5) respiratory bronchiole
6) alveoli
7) terminal bronchiole
A) 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6
B) 4, 1, 2, 5, 7, 3, 6
C) 1, 4, 2, 5, 7, 3, 6
D) 1, 4, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6
E) 2, 4, 1, 7, 5, 3, 6
1) lobar bronchus
2) bronchioles
3) alveolar ducts
4) primary bronchus
5) respiratory bronchiole
6) alveoli
7) terminal bronchiole
A) 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6
B) 4, 1, 2, 5, 7, 3, 6
C) 1, 4, 2, 5, 7, 3, 6
D) 1, 4, 2, 7, 5, 3, 6
E) 2, 4, 1, 7, 5, 3, 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The condition resulting from inadequate production of surfactant and the resultant collapse of alveoli is
A) respiratory distress syndrome.
B) COPD.
C) anoxia.
D) pulmonary embolism.
E) pneumothorax.
A) respiratory distress syndrome.
B) COPD.
C) anoxia.
D) pulmonary embolism.
E) pneumothorax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The thyroid cartilage is also called the
A) vestibular fold.
B) vocal cord.
C) laryngeal prominence.
D) Adam's apple.
E) laryngeal prominence and Adam's apple.
A) vestibular fold.
B) vocal cord.
C) laryngeal prominence.
D) Adam's apple.
E) laryngeal prominence and Adam's apple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The flap-like structure that prevents food from entering the larynx is called the
A) uvula.
B) soft palate.
C) epiglottis.
D) thyroid cartilage.
E) cricoid cartilage.
A) uvula.
B) soft palate.
C) epiglottis.
D) thyroid cartilage.
E) cricoid cartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Children have slender, short vocal cords so their voices tend to be
A) louder.
B) softer.
C) higher pitched.
D) lower pitched.
E) deeper toned.
A) louder.
B) softer.
C) higher pitched.
D) lower pitched.
E) deeper toned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following descriptions best matches the term bronchiolar smooth muscle?
A) accessory muscle of expiration
B) accessory muscle of inspiration
C) primary muscle of inspiration
D) contraction increases airway resistance
E) affects lung compliance
A) accessory muscle of expiration
B) accessory muscle of inspiration
C) primary muscle of inspiration
D) contraction increases airway resistance
E) affects lung compliance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A patient with a connective tissue disease experiences increased pulmonary vascular resistance. Over a period of time, you would expect to observe
A) increased cardiac output from the right ventricle.
B) increased cardiac output from the left ventricle.
C) increased thickness of the right ventricular wall.
D) distension of the pulmonary veins from the right lung.
E) no appreciable changes in heart structure or function.
A) increased cardiac output from the right ventricle.
B) increased cardiac output from the left ventricle.
C) increased thickness of the right ventricular wall.
D) distension of the pulmonary veins from the right lung.
E) no appreciable changes in heart structure or function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The most superior portion of the lung is called the
A) base.
B) apex.
C) cardiac notch.
D) hilus.
E) epipleurium.
A) base.
B) apex.
C) cardiac notch.
D) hilus.
E) epipleurium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An elastic ________ ligament and the ________ muscle connect the ends of tracheal cartilage.
A) tracheal; trachealis
B) anular; trachealis
C) tracheal; anular
D) cricoid; anular
E) cricoid; trachealis
A) tracheal; trachealis
B) anular; trachealis
C) tracheal; anular
D) cricoid; anular
E) cricoid; trachealis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The ligament bridging the larynx with the trachea is the ________ ligament.
A) cricoid
B) thyrohyoid
C) vestibular
D) cricothyroid
E) cricotracheal
A) cricoid
B) thyrohyoid
C) vestibular
D) cricothyroid
E) cricotracheal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Surfactant is produced by what cell type in the alveolus?
A) smooth muscle cells
B) pneumocytes Type I
C) pneumocytes Type II
D) pneumocytes Type I and Type II
E) alveolar macrophages
A) smooth muscle cells
B) pneumocytes Type I
C) pneumocytes Type II
D) pneumocytes Type I and Type II
E) alveolar macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The actual sites of gas exchange within the lungs are the
A) bronchioles.
B) terminal bronchioles.
C) spaces between the parietal and visceral pleura.
D) blood air barrier of the alveoli.
E) interlobular septa.
A) bronchioles.
B) terminal bronchioles.
C) spaces between the parietal and visceral pleura.
D) blood air barrier of the alveoli.
E) interlobular septa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The resulting pain and inflammation when pleural fluid is unable to prevent friction between the opposing pleural surfaces is known as
A) pleurisy.
B) pulmonary hypertension.
C) asthma.
D) emphysema.
E) COPD.
A) pleurisy.
B) pulmonary hypertension.
C) asthma.
D) emphysema.
E) COPD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



