Deck 25: Diagnostic Clinical Microbiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Diagnostic Clinical Microbiology
1
Which of the following is considered to be a sterile body site?
A) cerebrospinal fluid
B) nasopharynx
C) urethra
D) large intestine
A) cerebrospinal fluid
B) nasopharynx
C) urethra
D) large intestine
A
2
Which of the following samples would be LEAST likely to require anaerobic incubation?
A) nasopharyngeal swab
B) cerebrospinal fluid
C) blood
D) synovial fluid
A) nasopharyngeal swab
B) cerebrospinal fluid
C) blood
D) synovial fluid
D
3
Which of the following samples would be expected to contain normal microbiota?
A) peritoneal fluid
B) cerebrospinal fluid
C) blood
D) fecal stool sample
A) peritoneal fluid
B) cerebrospinal fluid
C) blood
D) fecal stool sample
D
4
In which of the following scenarios would selective media most likely be used to DECREASE the number of normal microbiota?
A) A nasopharyngeal swab is used to collect a sample from a young woman with inflamed tonsils.
B) A midstream clean catch is used to collect urine in a young woman with a suspected urinary tract infection.
C) Venipuncture is used to collect blood from an elderly man with a possible blood infection.
D) A lumbar puncture is used to collect cerebrospinal fluid from a toddler exhibiting signs of meningitis.
A) A nasopharyngeal swab is used to collect a sample from a young woman with inflamed tonsils.
B) A midstream clean catch is used to collect urine in a young woman with a suspected urinary tract infection.
C) Venipuncture is used to collect blood from an elderly man with a possible blood infection.
D) A lumbar puncture is used to collect cerebrospinal fluid from a toddler exhibiting signs of meningitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Twenty-five individuals with shigellosis are reported within a community.Which of the following pieces of information would be most useful to public health officials who are trying to stop the spread of this infection?
A) whether all individuals are infected with the same strain of bacteria
B) the antibiotic sensitivity of the causative agents
C) the complete health history of infected individuals
D) the day care centers attended by any children of infected individuals
A) whether all individuals are infected with the same strain of bacteria
B) the antibiotic sensitivity of the causative agents
C) the complete health history of infected individuals
D) the day care centers attended by any children of infected individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The figure shown illustrates a small portion of an algorithm used to identify Gram-negative rods.This diagram is referred to as a(n)
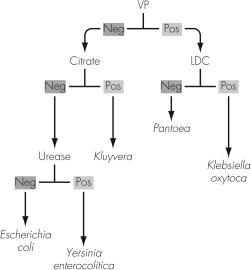
A) dichotomous key.
B) API 20E reading.
C) selective algorithm.
D) binary test.

A) dichotomous key.
B) API 20E reading.
C) selective algorithm.
D) binary test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following would typically be the initial indicator of bacteria growing within a blood culture tube?
A) An automated incubator will detect fluorescence.
B) Bacterial colonies will appear on blood agar.
C) Bacterial colonies will appear on MacConkey agar.
D) Centrifugation will cause sediment to appear at the end of the tube.
A) An automated incubator will detect fluorescence.
B) Bacterial colonies will appear on blood agar.
C) Bacterial colonies will appear on MacConkey agar.
D) Centrifugation will cause sediment to appear at the end of the tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following samples would be expected to be free of microorganisms unless an infection is present?
A) blood
B) fecal stool sample
C) nasopharyngeal swab
D) urethral swab
A) blood
B) fecal stool sample
C) nasopharyngeal swab
D) urethral swab

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A young child arrives at a local hospital with neck stiffness,nausea,and vomiting.The attending physician suspects bacterial meningitis and sends a sample of cerebrospinal fluid to the hospital laboratory.Which of the following actions would most quickly identify the bacterial species?
A) using sequential biochemical tests in which each test dictates the next test
B) carrying out a series of tests simultaneously and then interpreting the tests sequentially
C) plating the species first on selective media to eliminate the number of normal microbiota
D) obtaining a sequence of the patient's genome to determine his or her susceptibility to specific microbes
A) using sequential biochemical tests in which each test dictates the next test
B) carrying out a series of tests simultaneously and then interpreting the tests sequentially
C) plating the species first on selective media to eliminate the number of normal microbiota
D) obtaining a sequence of the patient's genome to determine his or her susceptibility to specific microbes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following organisms would be able to grow on both blood agar and Hektoen agar plates?
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
B) Escherichia coli
C) Staphylococcus epidermidis
D) Streptococcus pyogenes
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
B) Escherichia coli
C) Staphylococcus epidermidis
D) Streptococcus pyogenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Lumbar puncture is the most common method for obtaining a sample of
A) blood.
B) cerebrospinal fluid.
C) synovial fluid.
D) peritoneal fluid.
A) blood.
B) cerebrospinal fluid.
C) synovial fluid.
D) peritoneal fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How are API strips inoculated with a bacterium interpreted?
A) Strips with positive reactions for each test indicate a bacterium is Gram negative.
B) Strips with positive reactions for each test indicate a bacterium is Gram positive.
C) Lab personnel interpret strips by using a dichotomous key and beginning with a key reaction.
D) Lab personnel interpret strips by determining the pH of each individual well.
A) Strips with positive reactions for each test indicate a bacterium is Gram negative.
B) Strips with positive reactions for each test indicate a bacterium is Gram positive.
C) Lab personnel interpret strips by using a dichotomous key and beginning with a key reaction.
D) Lab personnel interpret strips by determining the pH of each individual well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A swab from an infected lesion is streaked onto a blood agar plate,a plate with blood agar that also contains colistin and nalidixic acid (a CNA plate),and a MacConkey agar plate.Growth occurs on both the blood agar and CNA plates.The organism growing must be
A) Gram positive.
B) Gram negative,enteric.
C) Gram negative,nonenteric.
D) acid fast.
A) Gram positive.
B) Gram negative,enteric.
C) Gram negative,nonenteric.
D) acid fast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Streptococcus pyogenes is a medically significant member of the Lancefield group
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the figure shown to identify the organism described.A nasophargyngeal swab is used to isolate a Gram-positive coccus.Tests reveal the organism produces bubbles when a colony is mixed with H₂O₂ and converts fibrinogen into fibrin to produce a coagulated tube of plasma.The organism is identified as
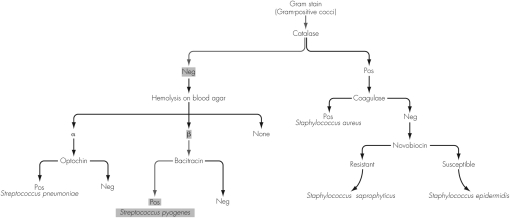
A) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
B) Streptococcus pyogenes.
C) Staphylococcus epidermidis.
D) Staphylococcus aureus.

A) Streptococcus pneumoniae.
B) Streptococcus pyogenes.
C) Staphylococcus epidermidis.
D) Staphylococcus aureus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A lab technician intern is asked to apply a 10% KOH (potassium hydroxide)solution on a sample.There are four patient samples sitting on the lab bench and he is trying to remember which sample should be treated.Which of the following four samples would require treatment with KOH?
A) a skin scraping from a site suspected to be a fungal infection
B) a nasopharyngeal swab suspected of containing Bordetella pertussis
C) a sputum sample from a patient with tuberculosis
D) a fecal sample from an individual with bloody diarrhea
A) a skin scraping from a site suspected to be a fungal infection
B) a nasopharyngeal swab suspected of containing Bordetella pertussis
C) a sputum sample from a patient with tuberculosis
D) a fecal sample from an individual with bloody diarrhea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identifying infectious agents is important because
A) it costs less money to run numerous tests than to treat with antibiotics empirically.
B) antibiotic-resistant bacteria are becoming a major global threat.
C) pathogens must be identified before antibiotics are effective.
D) antibiotics are only effective against viruses.
A) it costs less money to run numerous tests than to treat with antibiotics empirically.
B) antibiotic-resistant bacteria are becoming a major global threat.
C) pathogens must be identified before antibiotics are effective.
D) antibiotics are only effective against viruses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Jose is seen for a draining abscess on his left forearm.Which of the following would most likely be used to collect a sample from this site?
A) needle aspiration
B) skin scraping
C) sputum sample
D) swab
A) needle aspiration
B) skin scraping
C) sputum sample
D) swab

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How does identifying the cause of an infectious disease help prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria?
A) Knowing the identity and properties of the causative agent allows targeting with an appropriate drug.
B) Treating bacterial infections with multiple antibiotics helps prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
C) Knowing the identity and properties of the causative agent allows a physician to empirically treat an infection.
D) Treating viral infections with multiple antibiotics helps prevent secondary infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
A) Knowing the identity and properties of the causative agent allows targeting with an appropriate drug.
B) Treating bacterial infections with multiple antibiotics helps prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
C) Knowing the identity and properties of the causative agent allows a physician to empirically treat an infection.
D) Treating viral infections with multiple antibiotics helps prevent secondary infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The algorithm shown indicates bacitracin sensitivity for only one group of Gram-positive cocci.Why is bacitracin sensitivity NOT tested in all of the cases shown?
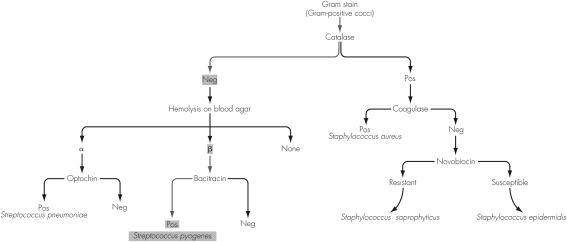
A) Testing antibiotic sensitivity in nonhemolytic streptococci is too time-consuming.
B) All group A beta-hemolytic streptococci are bacitracin sensitive.
C) Only beta-hemolytic streptococci possess characteristics that make them sensitive to bacitracin.
D) Nonhemolytic and alpha-hemolytic bacteria are only susceptible to optochin.

A) Testing antibiotic sensitivity in nonhemolytic streptococci is too time-consuming.
B) All group A beta-hemolytic streptococci are bacitracin sensitive.
C) Only beta-hemolytic streptococci possess characteristics that make them sensitive to bacitracin.
D) Nonhemolytic and alpha-hemolytic bacteria are only susceptible to optochin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is an advantage of using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)instead of relying on biochemical tests?
A) PCR can be completed within hours instead of days.
B) Only PCR provides a conclusive identification of a bacterium.
C) PCR provides information about antibiotic sensitivity.
D) PCR does not require specialized equipment.
A) PCR can be completed within hours instead of days.
B) Only PCR provides a conclusive identification of a bacterium.
C) PCR provides information about antibiotic sensitivity.
D) PCR does not require specialized equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Fluorescent antibody staining involves stain binding to the bacterium's
A) nucleus.
B) cell membrane.
C) cytoplasm.
D) capsule.
A) nucleus.
B) cell membrane.
C) cytoplasm.
D) capsule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Eosin methylene blue (EMB)agar contains dyes that inhibit the growth of Gram-positive organisms and bile salts that prevent the growth of Gram-negative bacteria other than fecal coliforms.Also included in EMB are stains that show a color change when an organism ferments lactose.This media is best described as
A) selective.
B) differential.
C) selective and differential.
D) nonselective.
A) selective.
B) differential.
C) selective and differential.
D) nonselective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A sample of bacteria is plated on Hektoen agar.Growth is observed and the medium changes to an orange color.What does the given information indicate?
A) The organism ferments lactose and is Gram positive.
B) The organism ferments sucrose and is Gram positive.
C) The organism ferments lactose and is Gram negative.
D) The organism ferments sucrose and is Gram negative.
A) The organism ferments lactose and is Gram positive.
B) The organism ferments sucrose and is Gram positive.
C) The organism ferments lactose and is Gram negative.
D) The organism ferments sucrose and is Gram negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Of the molecular techniques listed below,which would be most useful in identifying whether patients infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis are part of the same outbreak?
A) real-time PCR
B) biochemical tests
C) multiplex PCR
D) restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)
A) real-time PCR
B) biochemical tests
C) multiplex PCR
D) restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is considered a DISADVANTAGE of a point-of-care (POC)test?
A) Technicians are not required to culture the pathogen.
B) Clinicians are able to rapidly recognize a chain of infection.
C) Antibiotics can be avoided in cases of viral infection.
D) Multiple infections are more likely to go undetected.
A) Technicians are not required to culture the pathogen.
B) Clinicians are able to rapidly recognize a chain of infection.
C) Antibiotics can be avoided in cases of viral infection.
D) Multiple infections are more likely to go undetected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If red colloidal gold particles were inadvertently left out of a batch of immunochromatographic assays known to have a sensitivity of 0.99 for HIV,which of the following would most likely occur when testing patients infected with HIV?
A) Neither a test line nor a control line would be present.
B) Only a test line would be present.
C) Only a control line would be present.
D) Both a test line and a control line would be present.
A) Neither a test line nor a control line would be present.
B) Only a test line would be present.
C) Only a control line would be present.
D) Both a test line and a control line would be present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the function of goat anti-rabbit IgG antibodies in a typical point-of-care immunochromatographic assay?
A) In the absence of antibodies in a clinical specimen,they bind to red colloidal gold particles.
B) They are conjugated with red colloidal gold particles and are used to bind to antigen in a clinical specimen.
C) In the presence of antigen in a clinical specimen,they prevent complexes from forming with rabbit antibodies.
D) In the absence of antigen in a clinical specimen,they bind rabbit antibodies attached to red colloidal gold particles.
A) In the absence of antibodies in a clinical specimen,they bind to red colloidal gold particles.
B) They are conjugated with red colloidal gold particles and are used to bind to antigen in a clinical specimen.
C) In the presence of antigen in a clinical specimen,they prevent complexes from forming with rabbit antibodies.
D) In the absence of antigen in a clinical specimen,they bind rabbit antibodies attached to red colloidal gold particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The image shown is a gel from a multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR)used to identify toxin genes in Clostridium botulinum.Why are there three lines associated with the patient shown?
A) The patient is infected by three different species of bacteria.
B) Restriction fragments cut the patient DNA sample into three fragments.
C) The patient is infected by a strain of Clostridium botulinum that contains three toxin genes.
D) Molecular beacon probes are causing fluorescence of three regions.

A) The patient is infected by three different species of bacteria.
B) Restriction fragments cut the patient DNA sample into three fragments.
C) The patient is infected by a strain of Clostridium botulinum that contains three toxin genes.
D) Molecular beacon probes are causing fluorescence of three regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Biochemical tests would most likely be used to diagnose
A) whooping cough.
B) strep throat.
C) HIV.
D) Lyme disease.
A) whooping cough.
B) strep throat.
C) HIV.
D) Lyme disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
This figure shows a newly developed immunochromatography test (ICT)for anti-Ebola antibodies.The three individuals tested are known to NOT have Ebola.What information does the sample of tests shown give you?
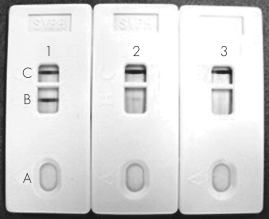
A) The sensitivity of the test is low because a false positive is shown on one test.
B) The specificity of the test is low because a false positive is shown on one test.
C) The sensitivity of the test is high because a false positive is shown on one test.
D) The sensitivity and specificity cannot be determined from a small sample size.

A) The sensitivity of the test is low because a false positive is shown on one test.
B) The specificity of the test is low because a false positive is shown on one test.
C) The sensitivity of the test is high because a false positive is shown on one test.
D) The sensitivity and specificity cannot be determined from a small sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Organisms will resist Gram staining when they contain a waxy outer coat composed of
A) peptidoglycan.
B) mycolic acid.
C) lipopolysaccharide.
D) cellulose.
A) peptidoglycan.
B) mycolic acid.
C) lipopolysaccharide.
D) cellulose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The figure shown illustrates antigen-capture ELISA.An advantage of this technique over antibody-capture ELISA is that antigen-capture ELISA
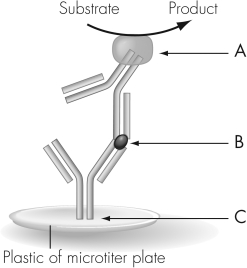
A) leads to a speedier diagnosis.
B) is more accurate than antibody-capture.
C) does not use serum from infectious patients.
D) provides a quantitative measure of patient antibody levels.

A) leads to a speedier diagnosis.
B) is more accurate than antibody-capture.
C) does not use serum from infectious patients.
D) provides a quantitative measure of patient antibody levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identification of the antigenic type(s)of Streptococcus pneumoniae in two patients with pneumonia is useful in
A) determining the appropriate antibiotic treatment.
B) determining whether the patients are producing antibodies.
C) identifying the source of the bacterium.
D) identifying whether the bacterium will grow easily in a laboratory.
A) determining the appropriate antibiotic treatment.
B) determining whether the patients are producing antibodies.
C) identifying the source of the bacterium.
D) identifying whether the bacterium will grow easily in a laboratory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What advantage does real-time PCR provide over tissue culture identification methods when a patient is infected by a virus such as West Nile virus?
A) Antibodies can be rapidly detected in body fluids.
B) The virus itself can be detected in body fluids.
C) The source of the virus can be traced.
D) The patient's antibody response can be measured in real time.
A) Antibodies can be rapidly detected in body fluids.
B) The virus itself can be detected in body fluids.
C) The source of the virus can be traced.
D) The patient's antibody response can be measured in real time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The figure shown illustrates antigen-capture ELISA.The structure labeled A in this figure is a(n)

A) monoclonal antibody.
B) antigen.
C) enzyme-conjugated antibody.
D) ELISA molecule.

A) monoclonal antibody.
B) antigen.
C) enzyme-conjugated antibody.
D) ELISA molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is considered an advantage of a point-of-care (POC)test?
A) Laboratory technicians have a lower risk of exposure to pathogens.
B) Clinicians are able to diagnose diseases based on clinical signs and symptoms alone.
C) Antibiotic therapy can begin without a delay of waiting for off-site laboratory results.
D) Detection of multiple infections is more likely.
A) Laboratory technicians have a lower risk of exposure to pathogens.
B) Clinicians are able to diagnose diseases based on clinical signs and symptoms alone.
C) Antibiotic therapy can begin without a delay of waiting for off-site laboratory results.
D) Detection of multiple infections is more likely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If your goal is to isolate Gram-negative bacteria from Gram-positive bacteria and you are not interested in biochemical differences between the Gram-negative bacteria,it would be best to use a growth media that is
A) selective.
B) differential.
C) selective and differential.
D) nonselective.
A) selective.
B) differential.
C) selective and differential.
D) nonselective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One immunochromatography test (ICT)for influenza has a test sensitivity of 0.50 and a specificity of 0.90.If 50 individuals known to be infected with influenza were tested using this particular ICT,how many of the tests would be expected to be false negatives?
A) 25
B) 50
C) 45
D) 10
A) 25
B) 50
C) 45
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The image shown is a gel from a multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR)used to identify toxin genes in Clostridium botulinum.Which of the following statements most accurately describes how this image was formed?
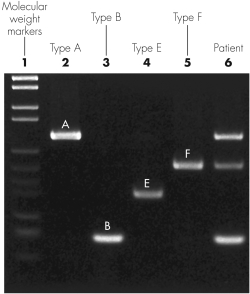
A) An amplified sample of DNA was combined with four sets of PCR primers.
B) Four patient samples were combined with one set of PCR primers.
C) A thermocycler was used to run four separate PCR amplification cycles.
D) A patient sample was combined with four sets of PCR primers.

A) An amplified sample of DNA was combined with four sets of PCR primers.
B) Four patient samples were combined with one set of PCR primers.
C) A thermocycler was used to run four separate PCR amplification cycles.
D) A patient sample was combined with four sets of PCR primers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A young child with meningitis is given an antibiotic prior to the identification of the causative pathogen.What is the appropriate term for this approach,and when would this approach most likely be used?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the group of bacteria classified by Lancefield classification and explain the differences that define the classifications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
CASE HISTORY
A four-year-old boy,Evan,was admitted to the hospital to evaluate and treat persistent pain in the rectal area.His problem began about one week earlier with ill-defined pain in the same region.He had a white blood cell count of 24,900 with 87% granulocytes (neutrophils).An abdominal computed tomography scan revealed an abscess (walled-off region of infectious bacteria)next to his rectum.A needle aspiration of the abscess drained 20 milliliters of yellowish,foul-smelling fluid.The specimen was plated on blood agar under aerobic conditions,but the culture was negative despite evidence of bacteria in the abscess drainage.(Blood agar is a rich medium containing 5% sheep red blood cells. )
Which statement regarding specimen collection is FALSE?
A) Specimen collection procedures are generally divided into those for sterile and nonsterile body sites.
B) Internal abscesses should be collected under conditions that allow the survival of anaerobic pathogens.
C) Samples from both sterile and nonsterile body sites should be plated on selective media.
D) Sterile body site samples are easily contaminated by normal flora in the collection process.
A four-year-old boy,Evan,was admitted to the hospital to evaluate and treat persistent pain in the rectal area.His problem began about one week earlier with ill-defined pain in the same region.He had a white blood cell count of 24,900 with 87% granulocytes (neutrophils).An abdominal computed tomography scan revealed an abscess (walled-off region of infectious bacteria)next to his rectum.A needle aspiration of the abscess drained 20 milliliters of yellowish,foul-smelling fluid.The specimen was plated on blood agar under aerobic conditions,but the culture was negative despite evidence of bacteria in the abscess drainage.(Blood agar is a rich medium containing 5% sheep red blood cells. )
Which statement regarding specimen collection is FALSE?
A) Specimen collection procedures are generally divided into those for sterile and nonsterile body sites.
B) Internal abscesses should be collected under conditions that allow the survival of anaerobic pathogens.
C) Samples from both sterile and nonsterile body sites should be plated on selective media.
D) Sterile body site samples are easily contaminated by normal flora in the collection process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A point-of-care (POC)assay that fails to identify 50% of individuals with a disease has low ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The figure shown illustrates antigen-capture ELISA.The structure labeled B in this figure is a(n)________.
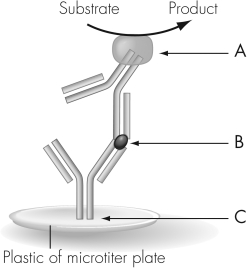


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
CASE HISTORY
Cindy,a 38-year-old woman with no significant previous medical history,came to the emergency department complaining of a mild sore throat persisting for three days.Her symptoms included arthralgia (joint pain),myalgia (muscle pain),and low-grade fever.The day before,she had a severe headache with neck stiffness,nausea,and vomiting.She was not taking medications,had no known drug allergies,and did not smoke.Cindy lived with her husband and two children,all of whom were well.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)was collected from a spinal tap and sent to the diagnostic laboratory.The CSF appeared cloudy (it should be clear)and contained 871 white blood cells (mainly neutrophils)per microliter (normal is 0-10/ml);the glucose level was 1 mg/dl (normal is 50-80 mg/dl);and the total protein level was 417 mg/dl (normal is under 45 mg/dl).Gram stain of a CSF smear revealed Gram-negative rods.The sample was streaked onto chocolate,blood,and Hektoen agars for microbial identification.
Why was the sample taken from Cindy streaked onto three separate agar plates? Describe the use of selective and differential media in the identification of pathogens-how might the growth on three media differ,and how will that alter the next steps in identifying a pathogen?
Cindy,a 38-year-old woman with no significant previous medical history,came to the emergency department complaining of a mild sore throat persisting for three days.Her symptoms included arthralgia (joint pain),myalgia (muscle pain),and low-grade fever.The day before,she had a severe headache with neck stiffness,nausea,and vomiting.She was not taking medications,had no known drug allergies,and did not smoke.Cindy lived with her husband and two children,all of whom were well.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)was collected from a spinal tap and sent to the diagnostic laboratory.The CSF appeared cloudy (it should be clear)and contained 871 white blood cells (mainly neutrophils)per microliter (normal is 0-10/ml);the glucose level was 1 mg/dl (normal is 50-80 mg/dl);and the total protein level was 417 mg/dl (normal is under 45 mg/dl).Gram stain of a CSF smear revealed Gram-negative rods.The sample was streaked onto chocolate,blood,and Hektoen agars for microbial identification.
Why was the sample taken from Cindy streaked onto three separate agar plates? Describe the use of selective and differential media in the identification of pathogens-how might the growth on three media differ,and how will that alter the next steps in identifying a pathogen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Ten patients are diagnosed with shigellosis.Explain the importance of having a clinical laboratory identify the strains of Shigella in each patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A patient suspected of having septicemia is having blood samples drawn from both of her arms.Why is it important to draw blood samples from two different sites?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Body sites that contain no microorganisms are considered to be ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
To eliminate or decrease the number of normal microbiota,pathogens with samples collected from nonsterile sites are typically plated on ________ media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
List two advantages of using real-time quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR)over tissue culture techniques when monitoring a patient with West Nile virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
This figure shows a "red colloidal gold" test used to test for the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae.This typical point-of-care laboratory test is known as a(n)________ assay.
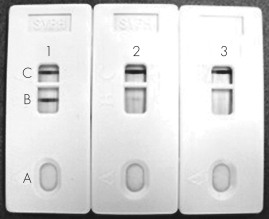


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Applying fluorescently tagged antibody stain to pleural fluid from a patient with Legionnaires' disease and viewing the stained tissue using a fluorescence microscope is an example of ________ microscopy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Mannitol salt agar (MSA)contains a high concentration of salt that restricts the growth of most bacterial species.MSA also changes from pink to yellow when mannitol is fermented by some organisms.Describe the characteristics that make MSA both selective and differential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
CASE HISTORY
A 55-year-old man complaining of headache,high fever,and neck stiffness was admitted to a local hospital.The man appeared confused and disoriented.He also complained of muscle weakness.History indicated that he had received several mosquito bites approximately two weeks earlier.CSF and blood specimens were sent to the laboratory.The report the next day indicated no bacterial infection,but real-time PCR tests for various possible viral causes revealed that the patient was suffering from West Nile virus.
This patient is almost certainly pleased that his medical team made use of real-time PCR in the diagnostic process;however,PCR is not an automatic diagnostic for all potential causes of disease.Discuss why PCR cannot be used as the exclusive diagnostic method for patients presenting with symptoms similar to this patient's.
A 55-year-old man complaining of headache,high fever,and neck stiffness was admitted to a local hospital.The man appeared confused and disoriented.He also complained of muscle weakness.History indicated that he had received several mosquito bites approximately two weeks earlier.CSF and blood specimens were sent to the laboratory.The report the next day indicated no bacterial infection,but real-time PCR tests for various possible viral causes revealed that the patient was suffering from West Nile virus.
This patient is almost certainly pleased that his medical team made use of real-time PCR in the diagnostic process;however,PCR is not an automatic diagnostic for all potential causes of disease.Discuss why PCR cannot be used as the exclusive diagnostic method for patients presenting with symptoms similar to this patient's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A patient with a suspected Clostridium difficile infection is tested using a point-of-care (POC)rapid diagnostic test.List two disadvantages of using a POC rapid test to identify this disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
API 20E test strips contain wells with media that test for specific ________ reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is best identified by using a staining technique called a(n)________ stain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Growth of a bacterium in the presence of bile salts indicates the organism is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain why polymerase chain reaction (PCR)is required to detect nucleic acids in many clinical samples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



