Deck 4: Community Ecology, Population Ecology, and the Human Population
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Community Ecology, Population Ecology, and the Human Population
1
The relationship between honeybees and flowers is
A)competition.
B)commensalism.
C)parasitism.
D)mutualism.
E)predation.
A)competition.
B)commensalism.
C)parasitism.
D)mutualism.
E)predation.
D
2
Which of the following is a specialist species?
A)flies
B)cockroach
C)raccoons
D)rats
E)pandas
A)flies
B)cockroach
C)raccoons
D)rats
E)pandas
E
3
Which of the following predators avoid competition by being active at different times?
A)lions and tigers
B)hummingbirds and bees
C)hawks and owls
D)zebras and antelopes
E)lions and cheetahs
A)lions and tigers
B)hummingbirds and bees
C)hawks and owls
D)zebras and antelopes
E)lions and cheetahs
C
4
Ticks feeding on the blood of a field mouse exemplify
A)competition.
B)predation.
C)parasitism.
D)mutualism.
E)commensalism.
A)competition.
B)predation.
C)parasitism.
D)mutualism.
E)commensalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Species that migrate or are accidentally introduced into an ecosystem are called
A)nonnative species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)indicator species.
A)nonnative species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)indicator species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Parasitism can be viewed as a special form of:
A)predation.
B)mutualism.
C)commensalism.
D)resource partitioning.
E)interspecific competition.
A)predation.
B)mutualism.
C)commensalism.
D)resource partitioning.
E)interspecific competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Silverfish insects travel with army ants to share the food the ants leave behind after eating. This is an example of ____.
A)mutualism
B)commensalism
C)succession
D)parasitism
E)specism
A)mutualism
B)commensalism
C)succession
D)parasitism
E)specism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A species' ecological niche is its
A)habitat.
B)food supply.
C)role in the ecosystem.
D)length of survival.
E)need for specialized food sources.
A)habitat.
B)food supply.
C)role in the ecosystem.
D)length of survival.
E)need for specialized food sources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In which location is secondary succession most likely to occur?
A)Cooled volcanic lava
B)A new sandbar exposed by the ocean
C)A heavily polluted stream that has been cleaned up
D)A bare rock outcrop
E)A newly formed, shallow freshwater pond
A)Cooled volcanic lava
B)A new sandbar exposed by the ocean
C)A heavily polluted stream that has been cleaned up
D)A bare rock outcrop
E)A newly formed, shallow freshwater pond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The relationship between clownfish and anemones is
A)competition.
B)mutualism.
C)parasitism.
D)predation.
E)commensalism.
A)competition.
B)mutualism.
C)parasitism.
D)predation.
E)commensalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a keystone species?
A)honeybee
B)robin
C)daisy
D)opossum
E)trout
A)honeybee
B)robin
C)daisy
D)opossum
E)trout

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Predator-prey relationships are beneficial at the ____ level, but harmful at the ____ level.
A)individual; population
B)population; individual
C)individual; species
D)individual; landscape
E)landscape; species
A)individual; population
B)population; individual
C)individual; species
D)individual; landscape
E)landscape; species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Species that serve as an early warning of damage to a community are called
A)indicator species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)nonnative species.
A)indicator species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)nonnative species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Ecological succession
A)is initiated by indicator species.
B)never results in mutualistic species interactions.
C)generally results in very simple ecosystems.
D)rarely occurs as an orderly progression through clearly established stages.
E)always begins when vegetation grows on rock exposed by a retreating glacier.
A)is initiated by indicator species.
B)never results in mutualistic species interactions.
C)generally results in very simple ecosystems.
D)rarely occurs as an orderly progression through clearly established stages.
E)always begins when vegetation grows on rock exposed by a retreating glacier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A species whose role in an ecosystem is vital to the abundance of other species in an ecosystem is called a(n)
A)indicator species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)nonnative species.
A)indicator species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)nonnative species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which term is synonymous with the term "invasive species"?
A)exotic species
B)native species
C)keystone species
D)harbinger species
E)indicator species
A)exotic species
B)native species
C)keystone species
D)harbinger species
E)indicator species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An environmentally relevant benefit to protecting the world's sharks is to
A)support shark hunting.
B)provide pet food ingredients.
C)remove dead or dying fish from the ocean.
D)support movies that need sharks for props.
E)supply Asian countries with vital food resources.
A)support shark hunting.
B)provide pet food ingredients.
C)remove dead or dying fish from the ocean.
D)support movies that need sharks for props.
E)supply Asian countries with vital food resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Resource partitioning among different species
A)develops mutualism.
B)creates a predator-prey relationship.
C)allows sharing of similar, scarce resources.
D)undermines commensalism.
E)fights parasitism.
A)develops mutualism.
B)creates a predator-prey relationship.
C)allows sharing of similar, scarce resources.
D)undermines commensalism.
E)fights parasitism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement about generalists and specialists is true?
A)When environmental conditions are changing rapidly, a generalist is usually better off than a specialist.
B)A specialist typically has a broader niche than a generalist.
C)When environmental conditions are changing rapidly, a specialist is usually better off than a generalist.
D)A generalist typically has a more narrow niche than a specialist.
E)The habitat of generalists or specialists represent their niche.
A)When environmental conditions are changing rapidly, a generalist is usually better off than a specialist.
B)A specialist typically has a broader niche than a generalist.
C)When environmental conditions are changing rapidly, a specialist is usually better off than a generalist.
D)A generalist typically has a more narrow niche than a specialist.
E)The habitat of generalists or specialists represent their niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Species that normally live and thrive in a particular ecosystem are known as
A)nonnative species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)indicator species.
A)nonnative species.
B)native species.
C)keystone species.
D)specialist species.
E)indicator species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The three main factors that led to a rapid increase in the global human population are
A)available habitat, agriculture, and pesticides.
B)agriculture, medicine, and media alerts.
C)medicine, available habitat, and migration.
D)available habitat, agriculture, and medicine.
E)agriculture, medicine, and pesticides
A)available habitat, agriculture, and pesticides.
B)agriculture, medicine, and media alerts.
C)medicine, available habitat, and migration.
D)available habitat, agriculture, and medicine.
E)agriculture, medicine, and pesticides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Carrying capacity is determined by
A)ecological succession.
B)biotic potential and environmental resistance.
C)unlimited resources.
D)the ratio of male to female offspring.
E)growth curves.
A)ecological succession.
B)biotic potential and environmental resistance.
C)unlimited resources.
D)the ratio of male to female offspring.
E)growth curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Logistic growth
A)refers to an exponential increase in population size.
B)produces a J-shaped growth curve in a population/time plot.
C)exceeds the intrinsic growth rate of a population.
D)is experienced by few populations.
E)results in a population close to carrying capacity.
A)refers to an exponential increase in population size.
B)produces a J-shaped growth curve in a population/time plot.
C)exceeds the intrinsic growth rate of a population.
D)is experienced by few populations.
E)results in a population close to carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which country has the second largest number of people?
A)USA
B)China
C)India
D)Russia
E)Indonesia
A)USA
B)China
C)India
D)Russia
E)Indonesia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A population crash occurs when
A)a population approaches its carrying capacity.
B)environmental resistance comes into play gradually.
C)resources are essentially unlimited.
D)a population overshoots the carrying capacity and environmental pressures and shortfalls begin to exert their effects.
E)the population growth rate slows.
A)a population approaches its carrying capacity.
B)environmental resistance comes into play gradually.
C)resources are essentially unlimited.
D)a population overshoots the carrying capacity and environmental pressures and shortfalls begin to exert their effects.
E)the population growth rate slows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In 1845, the human population of Ireland experienced a major crash as a result of
A)the plague.
B)the potato fungus.
C)an influenza epidemic.
D)a prolonged drought.
E)HIV/AIDS.
A)the plague.
B)the potato fungus.
C)an influenza epidemic.
D)a prolonged drought.
E)HIV/AIDS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A population will decrease as
A)birth rate increases.
B)mortality decreases.
C)biotic potential increases.
D)environmental resistance increases.
E)immigration increases
A)birth rate increases.
B)mortality decreases.
C)biotic potential increases.
D)environmental resistance increases.
E)immigration increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The biotic potential of a population
A)is its capacity for ideal growth under ideal conditions.
B)is its current rate of growth of a population.
C)is an expression of how many offspring survive to reproduce.
D)can be determined only by studying an age structure diagram.
E)is the future rate of growth of a population.
A)is its capacity for ideal growth under ideal conditions.
B)is its current rate of growth of a population.
C)is an expression of how many offspring survive to reproduce.
D)can be determined only by studying an age structure diagram.
E)is the future rate of growth of a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Earth's carrying capacity for the human species has
A)remained largely unchanged over time.
B)created large amounts of energy.
C)increased as a result of technological, social and cultural changes.
D)decreased as a result of technological, social and cultural changes.
E)follows a consistent upward growth trend regardless of population crashes
A)remained largely unchanged over time.
B)created large amounts of energy.
C)increased as a result of technological, social and cultural changes.
D)decreased as a result of technological, social and cultural changes.
E)follows a consistent upward growth trend regardless of population crashes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In which location is primary succession most likely to occur?
A)rock exposed by a retreating glacier
B)an abandoned farm
C)a forest that had been clear-cut
D)an existing pond
E)forest that has been burned
A)rock exposed by a retreating glacier
B)an abandoned farm
C)a forest that had been clear-cut
D)an existing pond
E)forest that has been burned

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following exemplifies an opportunistic reproductive pattern?
A)human
B)housefly
C)rhinoceros
D)saguaro cactus
E)cow
A)human
B)housefly
C)rhinoceros
D)saguaro cactus
E)cow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Population size is increased by
A)births.
B)deaths.
C)indicator species.
D)colonization.
E)emigration.
A)births.
B)deaths.
C)indicator species.
D)colonization.
E)emigration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Population change =
A)(Births + Deaths) (Immigration + Emigration)
(Immigration + Emigration)
B)(Births Emigration) + (Deaths
Emigration) + (Deaths  Immigration)
Immigration)
C)(Births Immigration) + (Deaths
Immigration) + (Deaths  Emigration)
Emigration)
D)(Births + Emigration) (Deaths + Immigration)
(Deaths + Immigration)
E)(Births + Immigration) (Deaths + Emigration)
(Deaths + Emigration)
A)(Births + Deaths)
 (Immigration + Emigration)
(Immigration + Emigration)B)(Births
 Emigration) + (Deaths
Emigration) + (Deaths  Immigration)
Immigration)C)(Births
 Immigration) + (Deaths
Immigration) + (Deaths  Emigration)
Emigration)D)(Births + Emigration)
 (Deaths + Immigration)
(Deaths + Immigration)E)(Births + Immigration)
 (Deaths + Emigration)
(Deaths + Emigration)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The current world population is approximately
A)1.5 billion.
B)4.2 billion.
C)7.1 billion.
D)10.1 billion.
E)15.8 billion.
A)1.5 billion.
B)4.2 billion.
C)7.1 billion.
D)10.1 billion.
E)15.8 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Organisms with opportunistic reproductive strategies generally
A)have a low biotic potential.
B)are small and short-lived.
C)give significant parental care to its offspring.
D)are not very adaptable to change.
E)are large and long-lived.
A)have a low biotic potential.
B)are small and short-lived.
C)give significant parental care to its offspring.
D)are not very adaptable to change.
E)are large and long-lived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An organism with a "few offspring" strategy generally
A)has a high genetic diversity.
B)is more responsive to environmental changes than other species.
C)exhibits a fast rate of evolution.
D)is less adaptable to change than other species.
E)is small and long lived.
A)has a high genetic diversity.
B)is more responsive to environmental changes than other species.
C)exhibits a fast rate of evolution.
D)is less adaptable to change than other species.
E)is small and long lived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which country has the largest number of people?
A)USA
B)China
C)India
D)Russia
E)Indonesia
A)USA
B)China
C)India
D)Russia
E)Indonesia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A country with a large proportion of its population in a preproductive age group (age 0-14) is most likely to experience a future population growth that
A)declines rapidly.
B)declines slowly.
C)remains stable (unchanging).
D)increases slowly.
E)increases rapidly.
A)declines rapidly.
B)declines slowly.
C)remains stable (unchanging).
D)increases slowly.
E)increases rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Carrying capacity refers to the
A)reproductive rate of a population.
B)interaction of birth rate and mortality.
C)maximum population size that the environment will support.
D)proportion of males to females.
E)intrinsic rate of increase.
A)reproductive rate of a population.
B)interaction of birth rate and mortality.
C)maximum population size that the environment will support.
D)proportion of males to females.
E)intrinsic rate of increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The size of a population is affected by
A)the number of indicator species in an ecosystem.
B)the number of niches available in an ecosystem.
C)whether the population is native or nonnative to an ecosystem.
D)the absence of indicator species in an ecosystem.
E)birth and death rates of the population in an ecosystem.
A)the number of indicator species in an ecosystem.
B)the number of niches available in an ecosystem.
C)whether the population is native or nonnative to an ecosystem.
D)the absence of indicator species in an ecosystem.
E)birth and death rates of the population in an ecosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ecological succession proceeds in an orderly fashion from primary to secondary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The drop in China's total fertility rate between 1972 and 2012 has caused the average age of that country's population to decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Most organisms have reproductive patterns between the opportunist and competitor extremes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Predation and parasitism are examples of ecological interactions that are harmful at the individual level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The size of a species' population, be that of an animal or plant, is influenced by births, deaths, immigration, and emigration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A population's growth rate will increase as the population reaches its carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Non-native or invasive species are threatening and should be eradicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The gradual establishment of communities in areas where soil did not previously exist is known as ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The ____________________ rate of increase is the rate a population would grow if it had unlimited resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A(n) ____________________ is a species whose roles have a large effect on the types and abundance of other species in an ecosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Different species within a community, whether native or nonnative, play similar roles in the community's ecology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The polar bear is a(n)____________________ species to cold regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The population of the United States is growing because the replacement fertility rate exceeds the total fertility rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Although total fertility rates have decreased, the world's population has still not stabilized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In ____________________, species interact in order to gain access to limited resources such as food or space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
As economic development increases, birth and death rates decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Less-developed countries generally have high population growth rates because birth rates are high and death rates are low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a rapidly changing environment, the generalist species is better able to survive than the specialist species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Resource partitioning is one solution to the problems associated with ecological succession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Primary ecological succession occurs when native species take over abandoned farm fields.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How do keystone species differ from indicator species?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the difference between mutualism and commensalism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the major difference between generalist species and specialist species?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Whales are examples of ____________________ because they reproduce slowly and produce few, well nurtured offspring to ensure survival of the species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
India's population increased from 400 million in 1952 to 1.26 billion in 2012 mostly as a result of ____________________ rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Populations can decline by increasing death rates. If this decline is gradual, the harmful effects can be mitigated. List three major problems associated with rapid population decline. Can you think of any positive outcomes of rapid population decline?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Humans can extend the earth's carrying capacity for the species. Can the earth adequately support an exponentially growing human population?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
____________________ is the combination of all factors that limit the growth of a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
____________ provides educational and clinical services to help couples choose how many children to have and when to have them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Labeling
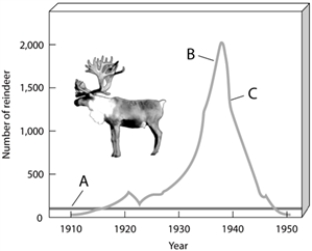
On the exponential growth of reindeer figure, choose the portion of the graph that represents the number of reindeer that can be sustained indefinitely in a given area.

On the exponential growth of reindeer figure, choose the portion of the graph that represents the number of reindeer that can be sustained indefinitely in a given area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Labeling

On the exponential growth of reindeer figure, choose the portion of the graph that represents the number of reindeer that exceeded the carrying capacity of their environment.

On the exponential growth of reindeer figure, choose the portion of the graph that represents the number of reindeer that exceeded the carrying capacity of their environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Rats are examples of ____________________ because they reproduce and disperse rapidly and produce many offspring to ensure survival of the species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why is predation considered beneficial at the population level but harmful at the individual level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Labeling

On the exponential growth of reindeer figure, choose the portion of the graph that can referred to as "dieback."

On the exponential growth of reindeer figure, choose the portion of the graph that can referred to as "dieback."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If total fertility rates are decreasing, why is the world's human population still increasing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



