Deck 42: Energy Prices
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 42: Energy Prices
1
If gas prices today were $1.50 per gallon, in terms of history this would be
A)an all-time low in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time low in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time low but rather low in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
A)an all-time low in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time low in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time low but rather low in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
C
2
If gas prices today were $3.00 per gallon, in terms of history this would be
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)near an all-time high in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time high but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)near an all-time high in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time high but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
C
3
The large increase in the elasticity of supply in crude oil during 2014-2015 created ____ price volatility.
A)enormously greater
B)slightly greater
C)lesser
D)zero
A)enormously greater
B)slightly greater
C)lesser
D)zero
C
4
If gas prices today were $2.00 per gallon, in terms of history this would be
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time high in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time high but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-inflation-adjustedterm historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time high in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time high but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-inflation-adjustedterm historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If gas prices today were $2.50 per gallon, in terms of history this would be
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time high in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time high but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time high in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time high but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Iran-Iraq War of the 1980s generally contributed to
A)oil conservation efforts in the west.
B)high oil and gasoline prices in the west.
C)a rapid expansion of alternative fuels exploration in the west.
D)dramatically falling world oil prices.
A)oil conservation efforts in the west.
B)high oil and gasoline prices in the west.
C)a rapid expansion of alternative fuels exploration in the west.
D)dramatically falling world oil prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The large decrease in gasoline prices during 2014-2015 was attributable to
A)hydraulic fracturing.
B)directional drilling.
C)hyperaccurate seismologic mapping.
D)all of these.
A)hydraulic fracturing.
B)directional drilling.
C)hyperaccurate seismologic mapping.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In 1998, adjusted for inflation, crude oil and gasoline prices were
A)quite high.
B)about average.
C)quite low.
D)slightly above average.
A)quite high.
B)about average.
C)quite low.
D)slightly above average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The large decrease in crude oil prices during 2014-2015 was attributable to
A)hydraulic fracturing.
B)directional drilling.
C)hyperaccurate seismologic mapping.
D)all of these.
A)hydraulic fracturing.
B)directional drilling.
C)hyperaccurate seismologic mapping.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The majority of proven world oil reserves are
A)in the Persian Gulf region.
B)held by non-Persian Gulf OPEC members.
C)under Alaska.
D)in the former Soviet Union.
A)in the Persian Gulf region.
B)held by non-Persian Gulf OPEC members.
C)under Alaska.
D)in the former Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
High oil prices in the 1970s motivated _______ to look for oil, which was found in _______.
A)the Soviet Union; the Ural Mountains
B)the United Kingdom; the North Sea
C)the United States; Oklahoma
D)Saudi Arabia; their desert
A)the Soviet Union; the Ural Mountains
B)the United Kingdom; the North Sea
C)the United States; Oklahoma
D)Saudi Arabia; their desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
OPEC stands for
A)Oil and Petroleum Exporting Companies.
B)Organization of Petrol Exploiting Companies.
C)Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.
D)Oil Producing and Exploiting Countries.
A)Oil and Petroleum Exporting Companies.
B)Organization of Petrol Exploiting Companies.
C)Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.
D)Oil Producing and Exploiting Countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If gas prices today were $1.00 per gallon, in terms of history this would be
A)an all-time low in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time low in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time low but rather low in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
A)an all-time low in inflation-adjusted terms.
B)an all-time low in nominal terms.
C)not an all-time low but rather low in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
At the current pace of oil consumption and given what oil is known to exist and what oil is expected to be discovered, oil reserves are likely to
A)never run out.
B)run out sometime between 2050 and 2100.
C)run out sometime between 2025 and 2050.
D)run out before 2025.
A)never run out.
B)run out sometime between 2050 and 2100.
C)run out sometime between 2025 and 2050.
D)run out before 2025.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The large increase in the elasticity of supply in crude oil during 2014-2015 was attributable to
A)hydraulic fracturing.
B)directional drilling.
C)hyperaccurate seismologic mapping.
D)all of these.
A)hydraulic fracturing.
B)directional drilling.
C)hyperaccurate seismologic mapping.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The run up in gasoline prices during 1999 and 2000
A)put them much above their long-term inflation adjusted average.
B)put them about the same as their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
C)still had them much below their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
D)put them well above their all-time high.
A)put them much above their long-term inflation adjusted average.
B)put them about the same as their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
C)still had them much below their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
D)put them well above their all-time high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Proven oil reserves in the world amount to
A)1,653 barrels.
B)1,653 million barrels.
C)1,653 billion barrels.
D)1,653 trillion barrels.
A)1,653 barrels.
B)1,653 million barrels.
C)1,653 billion barrels.
D)1,653 trillion barrels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
World oil consumption runs approximately
A)96 barrels a day.
B)96 thousand barrels a day.
C)96 million barrels a day.
D)96 billion barrels a day.
A)96 barrels a day.
B)96 thousand barrels a day.
C)96 million barrels a day.
D)96 billion barrels a day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The run up in gasoline prices between 1999 and 2007
A)put them much above their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
B)put them about the same as their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
C)still had them much below their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
D)still had them slightly below their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
A)put them much above their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
B)put them about the same as their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
C)still had them much below their long-term inflation-adjusted average.
D)still had them slightly below their long-term inflation-adjusted average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If gas prices today were $4.00 per gallon, in terms of history this would be
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms, but not nominal terms.
B)an all-time high in nominal terms and inflation-adjusted terms.
C)not an all-time high, but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.
A)an all-time high in inflation-adjusted terms, but not nominal terms.
B)an all-time high in nominal terms and inflation-adjusted terms.
C)not an all-time high, but rather high in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)about the long-term historical average in inflation-adjusted terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The key reason hurricanes affect gasoline prices is
A)demand for gasoline spikes as people drive to safety.
B)a significant portion of U.S. refining capacity is located along the Gulf of Mexico.
C)all U.S. gasoline is produced from oil coming out of the Gulf of Mexico.
D)oil companies have an excuse to raise prices.
A)demand for gasoline spikes as people drive to safety.
B)a significant portion of U.S. refining capacity is located along the Gulf of Mexico.
C)all U.S. gasoline is produced from oil coming out of the Gulf of Mexico.
D)oil companies have an excuse to raise prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following nations is NOT part of OPEC?
A)Kuwait
B)Iran
C)Indonesia
D)Mexico
A)Kuwait
B)Iran
C)Indonesia
D)Mexico

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following are true about cartels?
A)They are stable because once they set a high price no one has a motive to increase production.
B)Prices are high because perfect competition supplants monopoly.
C)Prices are high because monopoly supplants perfect competition.
D)High prices encourage reduced competitor production.
A)They are stable because once they set a high price no one has a motive to increase production.
B)Prices are high because perfect competition supplants monopoly.
C)Prices are high because monopoly supplants perfect competition.
D)High prices encourage reduced competitor production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the expected future price of oil falls, then
A)the current equilibrium price and quantity will both fall.
B)the current equilibrium price will fall and the current equilibrium quantity will fall.
C)the equilibrium price and quantity will not change.
D)the equilibrium price will fall but the change in the equilibrium quantity will depend on whether the demand change outweighs the supply change.
A)the current equilibrium price and quantity will both fall.
B)the current equilibrium price will fall and the current equilibrium quantity will fall.
C)the equilibrium price and quantity will not change.
D)the equilibrium price will fall but the change in the equilibrium quantity will depend on whether the demand change outweighs the supply change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
OPEC is an example of a
A)perfect competitor.
B)natural monopolist.
C)complete competitor.
D)cartel (though an imperfect example).
A)perfect competitor.
B)natural monopolist.
C)complete competitor.
D)cartel (though an imperfect example).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the expected price of oil rises then
A)the current equilibrium price and quantity will both rise.
B)the current equilibrium price will rise and the current equilibrium quantity will fall.
C)the equilibrium price and quantity will not change.
D)the equilibrium price will rise but the change in the equilibrium quantity will depend on whether the demand change outweighs the supply change.
A)the current equilibrium price and quantity will both rise.
B)the current equilibrium price will rise and the current equilibrium quantity will fall.
C)the equilibrium price and quantity will not change.
D)the equilibrium price will rise but the change in the equilibrium quantity will depend on whether the demand change outweighs the supply change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Oil price changes are best explained using a model of
A)supply and demand and the effect of expectations.
B)the cartel effect.
C)the collusive behavior of the big oil companies.
D)supply and demand, the effect of expectations and the cartel effect.
A)supply and demand and the effect of expectations.
B)the cartel effect.
C)the collusive behavior of the big oil companies.
D)supply and demand, the effect of expectations and the cartel effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In order to maintain high prices a cartel must get its members to
A)reduce production.
B)increase production.
C)to leave production unchanged.
D)develop new sources.
A)reduce production.
B)increase production.
C)to leave production unchanged.
D)develop new sources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Cartels are not stable because it is in the interest of each of the members to ____ beyond what is in the cartel's general interest.
A)reduce production
B)raise prices
C)raise production
D)lower prices
A)reduce production
B)raise prices
C)raise production
D)lower prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refining capacity in the United States is
A)rather evenly spread out across the country.
B)concentrated in the industrial mid-west.
C)concentrated on the coasts.
D)located almost entirely in Alaska.
A)rather evenly spread out across the country.
B)concentrated in the industrial mid-west.
C)concentrated on the coasts.
D)located almost entirely in Alaska.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During the 1999-2005 period gasoline prices
A)quintupled (went up 5 times)in price.
B)tripled in price.
C)remained relatively constant in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)fell.
A)quintupled (went up 5 times)in price.
B)tripled in price.
C)remained relatively constant in inflation-adjusted terms.
D)fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Cartel members are motivated to increase production beyond their quotas because they are at a point where, if they can increase their own production without affecting the cartel price,
A)they are making a profit.
B)they are making a loss.
C)their marginal cost exceeds their marginal revenue.
D)their marginal revenue exceeds their marginal costs.
A)they are making a profit.
B)they are making a loss.
C)their marginal cost exceeds their marginal revenue.
D)their marginal revenue exceeds their marginal costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The underlying reason why gasoline prices at neighboring stations is usually identical is that
A)collusion is legal in the energy sector.
B)collusion is prevalent in the energy sector.
C)because under oligopoly, it can be in each firms best interest to independently charge a price equal to their competition's price.
D)these operators are usually friends and benefit from the other's presence.
A)collusion is legal in the energy sector.
B)collusion is prevalent in the energy sector.
C)because under oligopoly, it can be in each firms best interest to independently charge a price equal to their competition's price.
D)these operators are usually friends and benefit from the other's presence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The stability of cartel prices is challenged because
A)cartels never exist.
B)though they increase profits they are vulnerable to egalitarian interests.
C)they never increase the profitability of their members.
D)though they increase profits, they are vulnerable to those that seek to make more profit by breaking the agreements that generated them.
A)cartels never exist.
B)though they increase profits they are vulnerable to egalitarian interests.
C)they never increase the profitability of their members.
D)though they increase profits, they are vulnerable to those that seek to make more profit by breaking the agreements that generated them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Energy prices rose during 2005 largely because of
A)increased demand in Central America.
B)increased demand in China.
C)weather related (hurricanes)in the Gulf of Mexico.
D)increased demand in China and weather related (hurricanes)in the Gulf of Mexico.
A)increased demand in Central America.
B)increased demand in China.
C)weather related (hurricanes)in the Gulf of Mexico.
D)increased demand in China and weather related (hurricanes)in the Gulf of Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The underlying reason why the expected future price of gasoline plays an important role in the current price of gasoline is because
A)along the supply chain firms want to hold onto gasoline when they think the price is about to rise and sell it quickly when they think the price is about to fall.
B)the market is overly regulated.
C)the market is governed by two major players.
D)the government is in complete control of the energy market.
A)along the supply chain firms want to hold onto gasoline when they think the price is about to rise and sell it quickly when they think the price is about to fall.
B)the market is overly regulated.
C)the market is governed by two major players.
D)the government is in complete control of the energy market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Although crude oil prices briefly fell below $55 per barrel in late 2006, they quickly rebounded and throughout much of 2007 remained well above
A)$60 per barrel.
B)$80 per barrel.
C)$100 per barrel.
D)$125 per barrel.
A)$60 per barrel.
B)$80 per barrel.
C)$100 per barrel.
D)$125 per barrel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A cartel is formed when
A)monopolists in different industries merge into one.
B)perfect competitors in the same industry collude to form a monopoly.
C)perfect competitors in different industries merge into one company.
D)a company spins off a low profit unit.
A)monopolists in different industries merge into one.
B)perfect competitors in the same industry collude to form a monopoly.
C)perfect competitors in different industries merge into one company.
D)a company spins off a low profit unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The decrease in gasoline price volatility in 2015 and 2016 was a result of
A)decreased energy usage.
B)increased supply elasticity.
C)decreased demand elasticity.
D)decreased supply elasticity.
A)decreased energy usage.
B)increased supply elasticity.
C)decreased demand elasticity.
D)decreased supply elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When prices are the same at two neighboring gas stations, economists attribute this to the market forces of
A)perfect competition.
B)monopoly.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopolistic competition.
A)perfect competition.
B)monopoly.
C)oligopoly.
D)monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Under perfect competition the market quantity is 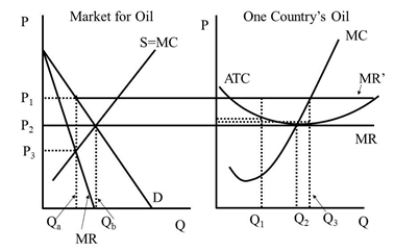 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which geographic coincidence affected gasoline prices the most during 2005
A)two major hurricanes affected the refining intensive areas of New Orleans and Houston.
B)a tsunami hit the one area in the world most responsible for producing U.S. gasoline, Indonesia.
C)an earthquake happened to hit the energy sensitive areas in and around Iran.
D)there were tornado related electrical outages in the industrial Midwest.
A)two major hurricanes affected the refining intensive areas of New Orleans and Houston.
B)a tsunami hit the one area in the world most responsible for producing U.S. gasoline, Indonesia.
C)an earthquake happened to hit the energy sensitive areas in and around Iran.
D)there were tornado related electrical outages in the industrial Midwest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An event driving gasoline prices higher from 2006 to 2008 was
A)growing energy use in China and India.
B)Hurricanes Katrina and Rita.
C)conflict in Nigeria.
D)all of the answers are correct.
A)growing energy use in China and India.
B)Hurricanes Katrina and Rita.
C)conflict in Nigeria.
D)all of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The residential electricity market is characterized by
A)unregulated simple monopoly.
B)unregulated natural monopoly.
C)regulated (usually natural)monopoly.
D)unregulated perfect competition.
A)unregulated simple monopoly.
B)unregulated natural monopoly.
C)regulated (usually natural)monopoly.
D)unregulated perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If regulators were to force a natural monopoly to set the price of its product equal to its marginal cost of production (in order to encourage economically efficient use of the product), the natural monopoly will
A)shut down immediately.
B)earn a normal profit.
C)earn an economic loss.
D)understate its true costs of production.
A)shut down immediately.
B)earn a normal profit.
C)earn an economic loss.
D)understate its true costs of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
To get at the large pool of oil embedded in porous rock deep below North Dakota a process known as ____ is employed.
A)hydraulic fracturing (fracking)
B)explosive mining
C)compressive extraction
D)chemical immersion
A)hydraulic fracturing (fracking)
B)explosive mining
C)compressive extraction
D)chemical immersion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Whether in a natural monopoly or a simple monopoly, the regulated price of electricity is theoretically supposed to be set where
A)marginal cost equals zero.
B)there is no economic profit.
C)there is no accounting profit.
D)marginal revenue is zero.
A)marginal cost equals zero.
B)there is no economic profit.
C)there is no accounting profit.
D)marginal revenue is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In Figure 42.1, what is the price a regulated monopolist will charge (assuming the regulator strives for zero economic profit)? 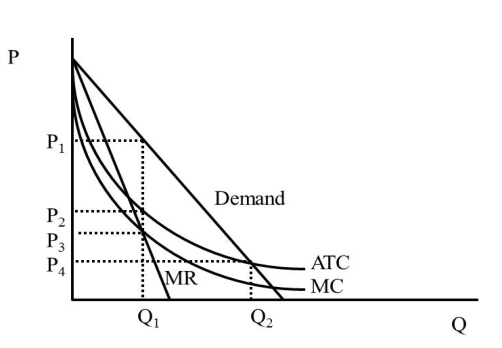 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1
A)P1
B)P2
C)P3
D)P4
 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1A)P1
B)P2
C)P3
D)P4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A state that has a large pool of oil embedded in porous rock deep below its surface is
A)North Dakota.
B)Florida.
C)Delaware.
D)Kansas.
A)North Dakota.
B)Florida.
C)Delaware.
D)Kansas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In Figure 42.1, what is the quantity an unregulated monopolist will produce (assuming the regulator strives for zero economic profit)? 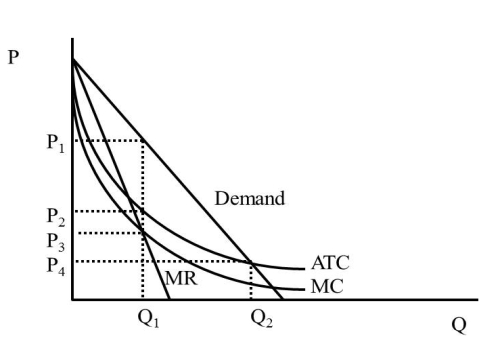 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Less than Q1
D)More than Q2
 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Less than Q1
D)More than Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Between July, 2008 and January, 2009, U.S. gasoline prices fell from
A)$6.50 per gallon to $5.00 per gallon.
B)$4.00 per gallon to $1.30 per gallon.
C)$4.00 per gallon to $2.00 per gallon.
D)$3.20 per gallon to $1.65 per gallon.
A)$6.50 per gallon to $5.00 per gallon.
B)$4.00 per gallon to $1.30 per gallon.
C)$4.00 per gallon to $2.00 per gallon.
D)$3.20 per gallon to $1.65 per gallon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A main factor determining gasoline demand between 2002 and 2008 was
A)Americans' increased use of more fuel-efficient vehicles.
B)shrinking demand in both India and China.
C)Americans' increased use of less fuel efficient vehicles.
D)a significant decrease in miles driven by the typical American.
A)Americans' increased use of more fuel-efficient vehicles.
B)shrinking demand in both India and China.
C)Americans' increased use of less fuel efficient vehicles.
D)a significant decrease in miles driven by the typical American.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
With a natural monopoly, a potentially insurmountable barrier to entry can be the
A)decreasing average total costs.
B)decreasing marginal costs.
C)high fixed costs.
D)low profit margins.
A)decreasing average total costs.
B)decreasing marginal costs.
C)high fixed costs.
D)low profit margins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In Figure 42.1, what is the price an unregulated monopolist will charge? 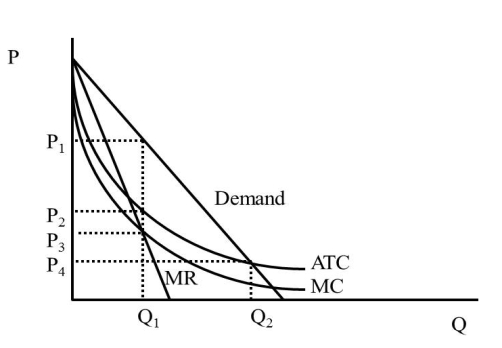 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1
A)P1
B)P2
C)P3
D)P4
 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1A)P1
B)P2
C)P3
D)P4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Under perfect competition the price is 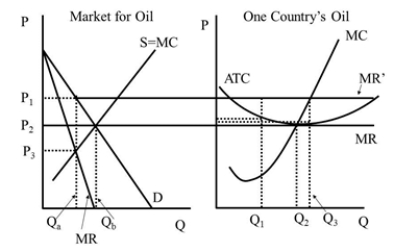 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)0)
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)0)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Under the cartel the price is 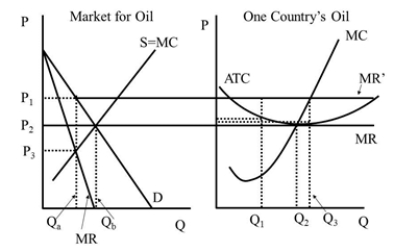 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)0)
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)0)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Non-inflation-adjusted ("nominal")gasoline prices reached their all-time highs in
A)1982.
B)1991.
C)2001.
D)2008.
A)1982.
B)1991.
C)2001.
D)2008.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the natural monopoly case, the regulated price will be where
A)ATC crosses demand.
B)MC equals MR.
C)MC crosses D.
D)MR is zero.
A)ATC crosses demand.
B)MC equals MR.
C)MC crosses D.
D)MR is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A natural monopoly occurs when
A)there are high fixed costs.
B)continuously decreasing average total costs.
C)continuously increasing marginal costs.
D)there are high fixed costs and continuously decreasing average total costs.
A)there are high fixed costs.
B)continuously decreasing average total costs.
C)continuously increasing marginal costs.
D)there are high fixed costs and continuously decreasing average total costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In Figure 42.1, what is the quantity an unregulated monopolist will produce? 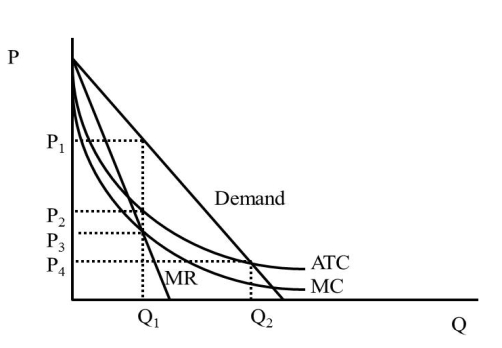 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Less than Q1
D)More than Q2
 Figure 42.1
Figure 42.1A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Less than Q1
D)More than Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Under the cartel the individual firm's quantity is (assuming it obeys its quot
A) Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.
A)
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Under the cartel the individual firm's quantity is (assuming that it wants to cheat on its quot
A)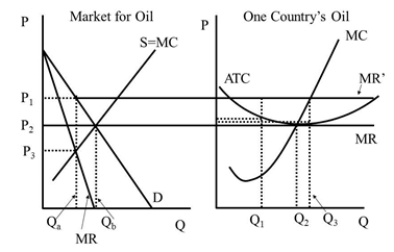 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Qb.
A)
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Qb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Under perfect competition the individual firm's economic profit is 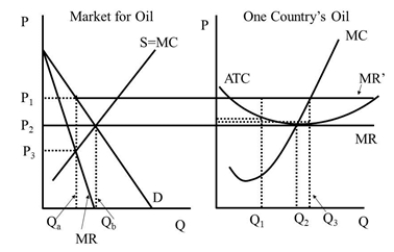 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)zero.
B)the smaller of the dashed line boxes.
C)the larger of the dashed line boxes.
D)between the size of the two dashed line boxes.
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)zero.
B)the smaller of the dashed line boxes.
C)the larger of the dashed line boxes.
D)between the size of the two dashed line boxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Under the cartel the market quantity is 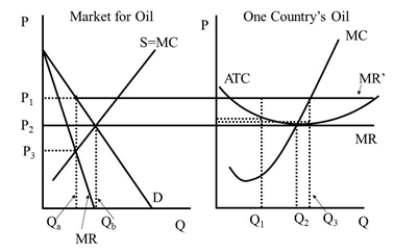 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Under perfect competition the individual firm's quantity is 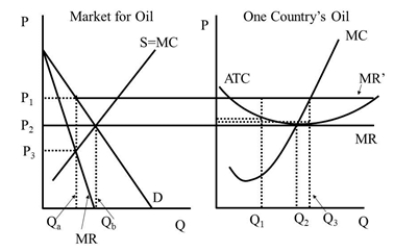 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Qa.
D)Qb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Under the cartel the individual firm's economic profit is (assuming it obeys its quot
A) Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)zero.
B)the smaller of the dashed line boxes
C)the larger of the dashed line boxes
D)between the size of the two dashed line boxes.
A)
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)zero.
B)the smaller of the dashed line boxes
C)the larger of the dashed line boxes
D)between the size of the two dashed line boxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Under the cartel the individual firm's economic profit is (assuming that it wants to cheat on its quot
A)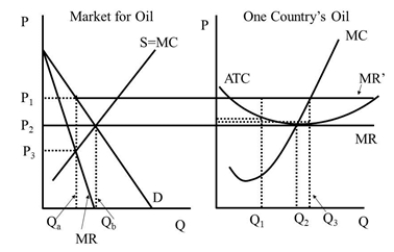 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2
A)zero.
B)the smaller of the dashed line boxes.
C)the larger of the dashed line boxes.
D)between the size of the two dashed line boxes.
A)
 Figure 42.2
Figure 42.2A)zero.
B)the smaller of the dashed line boxes.
C)the larger of the dashed line boxes.
D)between the size of the two dashed line boxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



