Deck 36: Economics of K-12 Education
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Economics of K-12 Education
1
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. The amount of external benefits associated with K-12 education in this market is _____ per student: 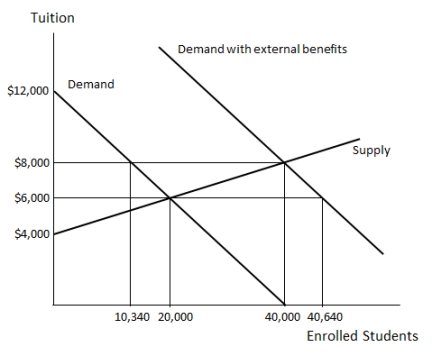 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1
A)$4,000
B)$6,000
C)$8,000
D)$12,000
 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1A)$4,000
B)$6,000
C)$8,000
D)$12,000
C
2
In the presence of positive externalities, a market will charge ______ and produce _____.
A)the correct amount; the correct amount
B)too much; the correct amount
C)the correct amount; too little
D)too little; too little
A)the correct amount; the correct amount
B)too much; the correct amount
C)the correct amount; too little
D)too little; too little
D
3
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. If the market is unsubsidized, the equilibrium number of students educated is 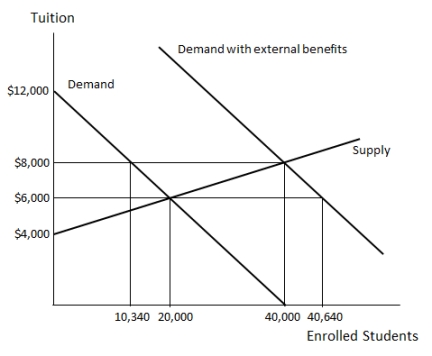 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1
A)10,340.
B)20,000.
C)40,000.
D)40,640.
 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1A)10,340.
B)20,000.
C)40,000.
D)40,640.
B
4
The form of capital through which education increases productivity is
A)physical capital.
B)human capital.
C)human principal.
D)brain capital.
A)physical capital.
B)human capital.
C)human principal.
D)brain capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the presence of positive external benefits, the efficient price to charge parents for the education of their children is
A)always zero.
B)greater than the market price.
C)always positive.
D)less than the market price.
A)always zero.
B)greater than the market price.
C)always positive.
D)less than the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Quick conclusions about the behavior of real per student spending must be made with care because
A)more money is spent on special education, and less is spent on everything else.
B)more money is spent on non-instructional needs, and less is spent on instruction.
C)less money is spent on special education and less is also spent on everything else.
D)though more money is spent per student, an increasing share goes to non-instructional needs.
A)more money is spent on special education, and less is spent on everything else.
B)more money is spent on non-instructional needs, and less is spent on instruction.
C)less money is spent on special education and less is also spent on everything else.
D)though more money is spent per student, an increasing share goes to non-instructional needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. If K-12 education is completely subsidized, _____ the optimal tuition per student is 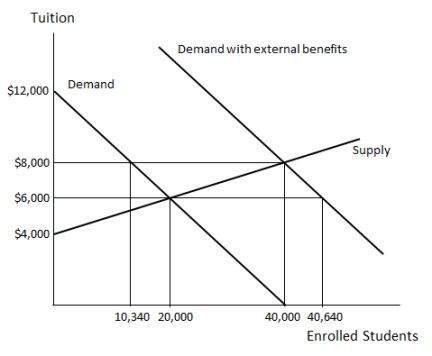 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1
A)$2,000.
B)$1,500.
C)$500.
D)$0
 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1A)$2,000.
B)$1,500.
C)$500.
D)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Since the 1960's student-teacher ratios have ___________ from _____ to ______.
A)increased; 15; 26
B)decreased; 26; 15
C)decreased; 35; 15
D)decreased; 17; 15
A)increased; 15; 26
B)decreased; 26; 15
C)decreased; 35; 15
D)decreased; 17; 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. Suppose the K-12 education market is subsidized. The tax payers pay _____ per student. 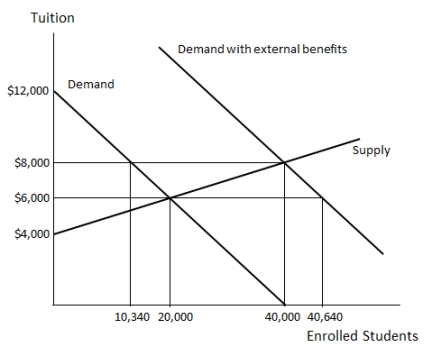 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1
A)$4,000
B)$6,000
C)$8,000
D)$12,000
 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1A)$4,000
B)$6,000
C)$8,000
D)$12,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The economic argument that it is in society's best economic interest to pay for the education of "someone else's child" is the
A)positive marginal benefit argument.
B)positive externalities argument.
C)positive marginal cost argument.
D)moral obligation argument.
A)positive marginal benefit argument.
B)positive externalities argument.
C)positive marginal cost argument.
D)moral obligation argument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Quick conclusions about the behavior of SAT scores should be made with care because
A)fewer, and on average more academically capable, people take the exam now than years ago.
B)more, and on average more academically capable, people take the exam now than years ago.
C)fewer, and on average less academically capable, people take the exam now than years ago.
D)more, and on average less academically capable people, take the exam now than years ago.
A)fewer, and on average more academically capable, people take the exam now than years ago.
B)more, and on average more academically capable, people take the exam now than years ago.
C)fewer, and on average less academically capable, people take the exam now than years ago.
D)more, and on average less academically capable people, take the exam now than years ago.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Quick conclusions about real per student spending should be made with care because
A)more money is spent on special education, and less is spent on everything else.
B)more money is spent on non-instructional spending, and less is spent on instructional spending.
C)less money is spent on special education, and less is also spent on everything else.
D)more money is devoted education generally, but an increasing share is spent on special education.
A)more money is spent on special education, and less is spent on everything else.
B)more money is spent on non-instructional spending, and less is spent on instructional spending.
C)less money is spent on special education, and less is also spent on everything else.
D)more money is devoted education generally, but an increasing share is spent on special education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a child is more apt to grow up to become a successful contributing member of society because of an education, this benefit to society is called a
A)negative externality.
B)positive marginal private benefit.
C)positive externality.
D)positive marginal private cost.
A)negative externality.
B)positive marginal private benefit.
C)positive externality.
D)positive marginal private cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Since 1960, high school graduation rates have
A)increased for whites but not for Hispanics and African Americans.
B)increased for African Americans and Hispanics but not for whites.
C)decreased across the board.
D)increased across the board, but proportionally more for African Americans.
A)increased for whites but not for Hispanics and African Americans.
B)increased for African Americans and Hispanics but not for whites.
C)decreased across the board.
D)increased across the board, but proportionally more for African Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. If K-12 education is completely subsidized, _____ students will be educated. 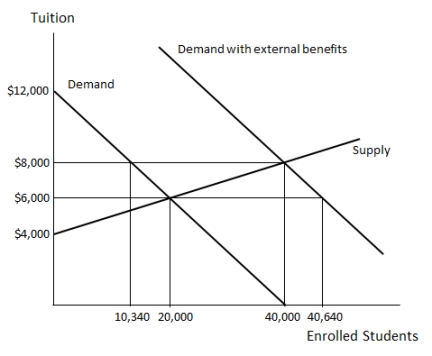 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1
A)10,340.
B)20,000.
C)40,000.
D)40,640.
 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1A)10,340.
B)20,000.
C)40,000.
D)40,640.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In determining whether a further investment in education for a individual is worth the costs, an economist would look at whether the sum of the
A)annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of annual income to the person.
B)annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of the increases in income that are attributable to the increased education.
C)present value of the annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of the present value of the annual income to the person.
D)present value of the annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of the present value of the increases in income that are attributable to the increased education.
A)annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of annual income to the person.
B)annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of the increases in income that are attributable to the increased education.
C)present value of the annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of the present value of the annual income to the person.
D)present value of the annual education costs is exceeded by the sum of the present value of the increases in income that are attributable to the increased education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
From 1960 to 2010 the amount of money spent on K-12 education has _______ in dollar terms, ______ in real terms and _______ in real dollars per student terms.
A)increased; decreased; decreased.
B)decreased; increased; decreased
C)increased; decreased; increased.
D)increased; increased; increased.
A)increased; decreased; decreased.
B)decreased; increased; decreased
C)increased; decreased; increased.
D)increased; increased; increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
SAT scores are ________ than they were in the 1960's ___________ they were in 1980.
A)higher; and much higher than
B)lower; and much lower than
C)lower; but higher than
D)lower; but about the same as
A)higher; and much higher than
B)lower; and much lower than
C)lower; but higher than
D)lower; but about the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Though there is no tuition to public elementary and secondary schools, economists do not say that it is free because
A)parents have to buy pencils and paper.
B)taxpayers pick up the tab for considerable costs of education.
C)parents have to help their kids learn.
D)teachers do not love to teach bad students.
A)parents have to buy pencils and paper.
B)taxpayers pick up the tab for considerable costs of education.
C)parents have to help their kids learn.
D)teachers do not love to teach bad students.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Examine Figure 36.1, which shows the market for K-12 education in an economy. If the market is unsubsidized, the equilibrium tuition fees per student for K-12 education is  Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1
A)$4,000.
B)$6,000.
C)$8,000.
D)$12,000.
 Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1A)$4,000.
B)$6,000.
C)$8,000.
D)$12,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The educational production function shows the _____ relationship between _____ and _____.
A)positive; test scores; teacher quality
B)negative; test scores; teacher quality
C)positive; student enrollments; tuition
D)negative; student enrollments; tuition
A)positive; test scores; teacher quality
B)negative; test scores; teacher quality
C)positive; student enrollments; tuition
D)negative; student enrollments; tuition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true of the structure of the public education system in the United States?
A)School principals do not have budgetary incentives to make bad teachers better.
B)Parents can threaten principals to move their kids to a private school if they are disappointed with the quality of education.
C)Teachers are paid based solely on their performance and abilities.
D)Teachers receive monetary incentives to educate students with special needs.
A)School principals do not have budgetary incentives to make bad teachers better.
B)Parents can threaten principals to move their kids to a private school if they are disappointed with the quality of education.
C)Teachers are paid based solely on their performance and abilities.
D)Teachers receive monetary incentives to educate students with special needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The academic ability of students studying to be teachers has
A)remained roughly the same in time.
B)increased markedly in recent years.
C)decreased markedly, particularly among men, in recent years.
D)decreased markedly, particularly among women, in recent years.
A)remained roughly the same in time.
B)increased markedly in recent years.
C)decreased markedly, particularly among men, in recent years.
D)decreased markedly, particularly among women, in recent years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Tenure for a public school teacher means that
A)they have taught at least ten years.
B)they have received a teaching award.
C)they cannot be fired unless they commit a particularly onerous violation of the rules.
D)they are a member of the union.
A)they have taught at least ten years.
B)they have received a teaching award.
C)they cannot be fired unless they commit a particularly onerous violation of the rules.
D)they are a member of the union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
It is generally _____ to fire a bad public school teacher ________.
A)easy,; who has little interest in teaching any longer.
B)easy; who has tenure
C)impossible; who has committed a felony.
D)difficult; who has tenure.
A)easy,; who has little interest in teaching any longer.
B)easy; who has tenure
C)impossible; who has committed a felony.
D)difficult; who has tenure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The educational outcomes at private schools are generally _____ those in public schools.
A)the same as
B)better than
C)worse than
D)incomparable to
A)the same as
B)better than
C)worse than
D)incomparable to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Economists Hoxby and Leigh have identified that, over the years,
A)less bright women are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
B)brighter women are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
C)less bright men are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
D)brighter men are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
A)less bright women are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
B)brighter women are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
C)less bright men are shifting more toward teaching jobs.
D)brighter men are shifting more toward teaching jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
School voucher programs
A)are universally hailed by teachers unions.
B)have not been tried in the United States.
C)have had modest success in some experimental locations.
D)have had students perform much worse than equally-situated students in public schools.
A)are universally hailed by teachers unions.
B)have not been tried in the United States.
C)have had modest success in some experimental locations.
D)have had students perform much worse than equally-situated students in public schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The empirical evidence suggests that greater spending on public education in the 1980's and 1990's _____________ impact on education outcomes.
A)had an enormous positive
B)had a small positive
C)had a perversely negative
D)had no significant
A)had an enormous positive
B)had a small positive
C)had a perversely negative
D)had no significant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Unions in general, and teachers' union in particular, prefer that salaries be based solely on _____ of the worker.
A)education and income class
B)gender and education
C)education and seniority
D)gender and seniority
A)education and income class
B)gender and education
C)education and seniority
D)gender and seniority

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the analysis of educational spending on outcomes, it is generally the case that
A)only the spending devoted to raising teacher salaries matters.
B)only the spending on reducing class size matters.
C)spending on raising teacher salaries and reducing class size matters.
D)neither higher salaries nor reduced class size matters.
A)only the spending devoted to raising teacher salaries matters.
B)only the spending on reducing class size matters.
C)spending on raising teacher salaries and reducing class size matters.
D)neither higher salaries nor reduced class size matters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The empirical finding that increased spending has no significant impact on educational outcomes.
A)is absolutely inconsistent with the idea of an educational production function.
B)is consistent with the "steep part of the curve" on the educational production function.
C)is consistent with the "flat part of the curve" on the educational production function.
D)has been shown to be a lie propagated by the anti-public education movement.
A)is absolutely inconsistent with the idea of an educational production function.
B)is consistent with the "steep part of the curve" on the educational production function.
C)is consistent with the "flat part of the curve" on the educational production function.
D)has been shown to be a lie propagated by the anti-public education movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The academic ability of women studying to be teachers has declined in recent years because
A)bright women have other, more economically lucrative opportunities.
B)the rate of pay for female teachers is much less than for equally qualified male teachers.
C)the nominal rate of pay for all teachers has decreased.
D)of the increased outsourcing of teaching jobs.
A)bright women have other, more economically lucrative opportunities.
B)the rate of pay for female teachers is much less than for equally qualified male teachers.
C)the nominal rate of pay for all teachers has decreased.
D)of the increased outsourcing of teaching jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Quick conclusions about high school graduation rates should be made with care because
A)the significant increase in the granting of less valuable GEDs.
B)the phenomenon of social promotion.
C)the phenomenon of social promotion and the significant increase in the granting of less valuable GEDs.
D)the decrease in reported graduation rates reflects more stringent graduation standards.
A)the significant increase in the granting of less valuable GEDs.
B)the phenomenon of social promotion.
C)the phenomenon of social promotion and the significant increase in the granting of less valuable GEDs.
D)the decrease in reported graduation rates reflects more stringent graduation standards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
It is difficult to directly compare outcomes at private schools with those at public schools because
A)private schools universally spend more per child than public schools.
B)private schools generally have children whose parents earn more income and value education.
C)private schools generally have teachers with more advanced degrees.
D)private schools are generally religious and religious students do not do as well.
A)private schools universally spend more per child than public schools.
B)private schools generally have children whose parents earn more income and value education.
C)private schools generally have teachers with more advanced degrees.
D)private schools are generally religious and religious students do not do as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Most public school systems operate in a
A)purely private, monopolistic environment.
B)purely public, monopolistic environment.
C)purely private, perfectly competitive environment.
D)purely public, perfectly competitive environment.
A)purely private, monopolistic environment.
B)purely public, monopolistic environment.
C)purely private, perfectly competitive environment.
D)purely public, perfectly competitive environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
It is difficult to directly compare outcomes at private schools with those at public schools because
A)private schools universally spend more per child than public schools.
B)private schools generally have children whose parents are more involved in their children's education.
C)private schools generally have teachers with more advanced degrees.
D)private schools are generally religious and religious students do not do as well.
A)private schools universally spend more per child than public schools.
B)private schools generally have children whose parents are more involved in their children's education.
C)private schools generally have teachers with more advanced degrees.
D)private schools are generally religious and religious students do not do as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Most public school teachers are
A)free agents, negotiating their salaries each year as individuals.
B)members of a union, with pay determined by a scale recognizing only teacher quality.
C)members of a union, with pay determined by a scale recognizing only length of service and educational attainment.
D)members of a union, but must negotiate their pay as individuals.
A)free agents, negotiating their salaries each year as individuals.
B)members of a union, with pay determined by a scale recognizing only teacher quality.
C)members of a union, with pay determined by a scale recognizing only length of service and educational attainment.
D)members of a union, but must negotiate their pay as individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Eric Hanushek, from his research, concluded that
A)K-12 teachers should be paid high salaries.
B)K-12 education should be completely subsidized.
C)spending more on education is a waste of taxpayers' resources.
D)the higher is the class size, the higher will be spending per student.
A)K-12 teachers should be paid high salaries.
B)K-12 education should be completely subsidized.
C)spending more on education is a waste of taxpayers' resources.
D)the higher is the class size, the higher will be spending per student.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Social promotion suggests that students are
A)only allowed to proceed to the next grade if they meet minimum behavioral standards.
B)granted diplomas for survival, rather than for achievement.
C)only allowed to graduate after taking a state exam.
D)given an opportunity to go back and take courses to improve their grades.
A)only allowed to proceed to the next grade if they meet minimum behavioral standards.
B)granted diplomas for survival, rather than for achievement.
C)only allowed to graduate after taking a state exam.
D)given an opportunity to go back and take courses to improve their grades.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In 2014, the U.S. spent ________ to educate _________ elementary and secondary school students.
A)$223 million; 152 million
B)$440 billion; 152 million
C)$599 billion; 110 million
D)$700 billion; 63 million
A)$223 million; 152 million
B)$440 billion; 152 million
C)$599 billion; 110 million
D)$700 billion; 63 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
As real interest rates increase, other things equal, the net present value of education is likely to
A)increase.
B)remain unchanged.
C)decrease, possibly becoming negative.
D)decrease, but necessarily remain positive, since more knowledge is always a good thing.
A)increase.
B)remain unchanged.
C)decrease, possibly becoming negative.
D)decrease, but necessarily remain positive, since more knowledge is always a good thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is true of the of the school voucher program in the U.S.?
A)Both Republican and Democrats prefer the school voucher program.
B)Both Republican and Democrats advocate against the school voucher program.
C)Republicans prefer the school voucher program, whereas the Democrats do not.
D)Democrats prefer the school voucher program, whereas the Republicans do not.
A)Both Republican and Democrats prefer the school voucher program.
B)Both Republican and Democrats advocate against the school voucher program.
C)Republicans prefer the school voucher program, whereas the Democrats do not.
D)Democrats prefer the school voucher program, whereas the Republicans do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Teacher pensions in the U.S. are frequently defined by the "_____" clause.
A)rule of 60
B)rule of 65
C)rule of 70
D)rule of 85
A)rule of 60
B)rule of 65
C)rule of 70
D)rule of 85

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Cherry picking is the act of
A)admitting the most expensive students, leaving the less expensive ones to public schools.
B)admitting students who are easy to educate, leaving the harder ones to public schools.
C)employing highly educated teachers, leaving the less educated ones to public schools.
D)employing highly experienced teachers, leaving the less experienced ones to public schools.
A)admitting the most expensive students, leaving the less expensive ones to public schools.
B)admitting students who are easy to educate, leaving the harder ones to public schools.
C)employing highly educated teachers, leaving the less educated ones to public schools.
D)employing highly experienced teachers, leaving the less experienced ones to public schools.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Economists Lochner and Moretti have identified external benefits to education in the form of
A)improved melodies produced by better-educated musicians.
B)the higher quality of elected officials chosen by better-educated voters.
C)higher salaries earned by better-educated engineers.
D)education-related crime reductions.
A)improved melodies produced by better-educated musicians.
B)the higher quality of elected officials chosen by better-educated voters.
C)higher salaries earned by better-educated engineers.
D)education-related crime reductions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In 2011, these states saw challenges to the collective bargaining rights of their teachers.
A)Wisconsin and Indiana
B)New York and California
C)Nevada and Texas
D)Alabama and Florida
A)Wisconsin and Indiana
B)New York and California
C)Nevada and Texas
D)Alabama and Florida

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The difference between the present value of all benefits and the present value of all costs is the
A)"net present value" of an education.
B)current market value of knowledge.
C)subjective rate of return on an education.
D)external benefit from education.
A)"net present value" of an education.
B)current market value of knowledge.
C)subjective rate of return on an education.
D)external benefit from education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Over the years, teachers' salaries in the U.S. have _____ with inflation and _____ relative to the salaries of equally credentialed occupations.
A)increased; increased
B)increased; decreased
C)decreased; increased
D)decreased; decreased
A)increased; increased
B)increased; decreased
C)decreased; increased
D)decreased; decreased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Public teacher layoffs, in most states, would be
A)last in, first out.
B)first in, first out.
C)among the best teachers.
D)among the worst teachers.
A)last in, first out.
B)first in, first out.
C)among the best teachers.
D)among the worst teachers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A public teacher's pension is likely to be
A)defined benefit.
B)defined contribution.
C)whatever they saved for themselves because they are not eligible for a pension or for Social Security.
D)Social Security only.
A)defined benefit.
B)defined contribution.
C)whatever they saved for themselves because they are not eligible for a pension or for Social Security.
D)Social Security only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Research by Jonah Rockoff suggests that there is
A)a positive relationship between teacher performance and student achievements.
B)no relationship between teacher performance and student achievements.
C)a positive relationship between the number of teachers and class sizes.
D)no relationship between the number of teachers and class sizes.
A)a positive relationship between teacher performance and student achievements.
B)no relationship between teacher performance and student achievements.
C)a positive relationship between the number of teachers and class sizes.
D)no relationship between the number of teachers and class sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A teacher's pension is likely to be determined
A)by the number of years they taught and by a percentage of their last year's salary.
B)a state legislature that can increase or decrease it at will.
C)the amount they contributed.
D)a state governor that can increase or decrease it at will.
A)by the number of years they taught and by a percentage of their last year's salary.
B)a state legislature that can increase or decrease it at will.
C)the amount they contributed.
D)a state governor that can increase or decrease it at will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In 2011, Wisconsin and Indiana state legislatures were focused on which of the following costs of public education?
A)Material costs
B)Teacher salaries
C)Defined benefit pensions
D)Defined contribution pensions
A)Material costs
B)Teacher salaries
C)Defined benefit pensions
D)Defined contribution pensions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Research by Eric Hanushek and others suggests that increasing the number or quality of teachers will
A)reduce student test scores.
B)increase student test scores by ever-increasing amounts.
C)increase student test scores by ever-decreasing amounts.
D)foment unrest among unionized teachers and school administrators.
A)reduce student test scores.
B)increase student test scores by ever-increasing amounts.
C)increase student test scores by ever-decreasing amounts.
D)foment unrest among unionized teachers and school administrators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



