Deck 17: International Trade: Does It Jeopardize American Jobs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/86
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: International Trade: Does It Jeopardize American Jobs
1
In 2015, exports made up ____ percent of the U.S. economy.
A)1
B)5
C)14
D)17
A)1
B)5
C)14
D)17
C
2
Determining the absolute advantage of a country requires that you look at
A)opportunity cost.
B)the output per worker in each country.
C)accounting and economic profit.
D)external costs.
A)opportunity cost.
B)the output per worker in each country.
C)accounting and economic profit.
D)external costs.
A
3
The U.S. both imports and exports significant quantities of
A)transportation equipment.
B)petroleum and coal products.
C)Computer and electronic products.
D)All of these.
A)transportation equipment.
B)petroleum and coal products.
C)Computer and electronic products.
D)All of these.
D
4
In 2015, which of the following were prominent imports into the U.S.?
A)petroleum
B)electrical machinery and audio and video equipment
C)transportation equipment
D)all of the answers are correct
A)petroleum
B)electrical machinery and audio and video equipment
C)transportation equipment
D)all of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In Table 17.1 the United States has 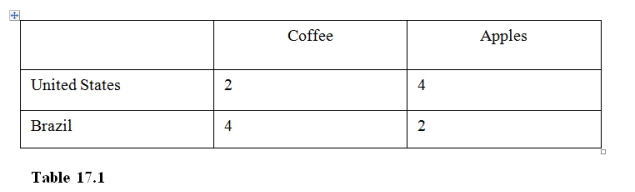
A)An absolute and comparative advantage in apples.
B)An absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)An absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)An absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee.

A)An absolute and comparative advantage in apples.
B)An absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)An absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)An absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In 2015, the trading partner from whom the U.S. received the greatest volume of imports was
A)Mexico.
B)OPEC.
C)China.
D)Africa.
A)Mexico.
B)OPEC.
C)China.
D)Africa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In 2015, the trading partner with which the U.S. had the largest trade deficit was
A)Africa.
B)Europe.
C)OPEC.
D)China.
A)Africa.
B)Europe.
C)OPEC.
D)China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a country can, with a single unit of labor, produce more of both clothing and computers than another country, then the first country has
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in both goods.
C)both a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage in one good and a comparative advantage in the other.
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in both goods.
C)both a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage in one good and a comparative advantage in the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In 2015, the U.S. experienced a deficit in its balance of trade with
A)China.
B)Mexico.
C)Canada.
D)all of the answers are correct.
A)China.
B)Mexico.
C)Canada.
D)all of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In 2015, the volume of U.S. imports from China were
A)larger than the volume of U.S. imports from Canada and Mexico combined.
B)larger than the volume of U.S. imports from Mexico.
C)larger than the volume of U.S. imports from Europe.
D)none of the options are correct.
A)larger than the volume of U.S. imports from Canada and Mexico combined.
B)larger than the volume of U.S. imports from Mexico.
C)larger than the volume of U.S. imports from Europe.
D)none of the options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Determining the comparative advantage of a country requires that you look at the economic notion of
A)opportunity cost.
B)ceteris paribus.
C)accounting and economic profit.
D)external costs.
A)opportunity cost.
B)ceteris paribus.
C)accounting and economic profit.
D)external costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In 2015, which of the following were prominent exports of the U.S.?
A)petroleum
B)financial services
C)transportation equipment
D)all of the answers are correct
A)petroleum
B)financial services
C)transportation equipment
D)all of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In 2015, the U.S. trade deficit with the world was approximately
A)$736 million.
B)$736 billion.
C)$7.36 trillion.
D)$73.6 trillion.
A)$736 million.
B)$736 billion.
C)$7.36 trillion.
D)$73.6 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The U.S. both imports and exports significant quantities of
A)coffee.
B)industrial equipment.
C)services.
D)industrial equipment and services.
A)coffee.
B)industrial equipment.
C)services.
D)industrial equipment and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In 2015, the trading partner to whom the U.S. shipped the greatest volume of exports was
A)Mexico.
B)Canada.
C)OPEC.
D)China.
A)Mexico.
B)Canada.
C)OPEC.
D)China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In Table 17.1, 
A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in apples only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in coffee only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in apples while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in apples only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in coffee only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in apples while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In 2015, the U.S. imports from the rest of the world were approximately
A)$2.852 billion.
B)$2,852 million.
C)$2.852 trillion.
D)$2,852 trillion.
A)$2.852 billion.
B)$2,852 million.
C)$2.852 trillion.
D)$2,852 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2015, imports made up ____ percent of the U.S. economy.
A)1
B)5
C)14
D)17
A)1
B)5
C)14
D)17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Between 1995 and 2015 the U.S. trade with China went from a
A)small surplus to a larger surplus.
B)small surplus to a small deficit.
C)small deficit to a small surplus.
D)large deficit to an even larger deficit.
A)small surplus to a larger surplus.
B)small surplus to a small deficit.
C)small deficit to a small surplus.
D)large deficit to an even larger deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In 2015, the U.S. experienced a deficit in its balance of trade with
A)Europe.
B)Africa.
C)OPEC.
D)all of the answers are correct.
A)Europe.
B)Africa.
C)OPEC.
D)all of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In Table 17.2 the Brazil has 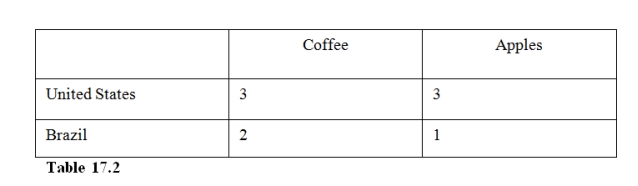
A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in apples.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)a comparative advantage in coffee but not an absolute advantage.

A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in apples.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)a comparative advantage in coffee but not an absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If with one unit of labor the U.S. can produce 20 units of computer software and 10 units of computer hardware and China can produce 6 units of software and 4 units of hardware then trade can make
A)the U.S. better off but not China.
B)China better off but not the U.S.
C)neither better off.
D)both better off.
A)the U.S. better off but not China.
B)China better off but not the U.S.
C)neither better off.
D)both better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If it takes one country two units of labor to produce a computer and three units of labor to produce a TV but it takes the other country three units of labor to produce a computer and four to produce a TV, then the first country has
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in TVs but a comparative advantage in computers.
C)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in computers only.
D)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in TVs only.
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in TVs but a comparative advantage in computers.
C)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in computers only.
D)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in TVs only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In Table 17.3, 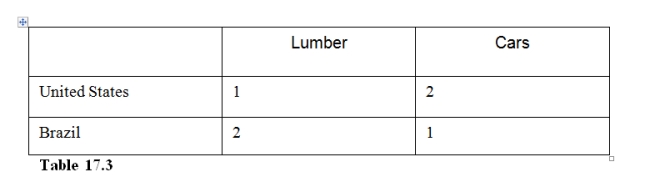
A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in cars only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in lumber only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in Cars while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in cars only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in lumber only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in Cars while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If it takes one country three units of labor to produce a computer and two units of labor to produce a TV but it takes the other country four units of labor to produce a computer and five to produce a TV, then the first country has
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in TVs but a comparative advantage in computers.
C)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in computers only.
D)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in TVs only.
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in TVs but a comparative advantage in computers.
C)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in computers only.
D)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in TVs only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In Table 17.1 the Brazil has 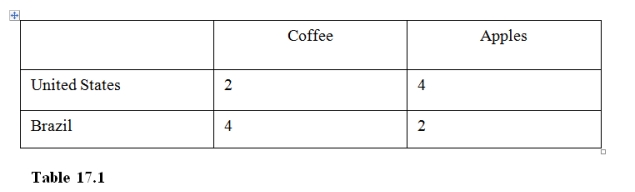
A)An absolute and comparative advantage in apples.
B)An absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)An absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)An absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee.

A)An absolute and comparative advantage in apples.
B)An absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)An absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)An absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If it takes one country one unit of labor to produce either a computer or a TV but it takes the other country two units of labor to produce a computer and only one to produce a TV, then the first country has
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in both goods.
C)both a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute and comparative advantage in production of computers.
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in both goods.
C)both a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute and comparative advantage in production of computers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If with one unit of labor the U.S. can produce 20 units of computer software and 10 units of computer hardware and China can produce 5 units of software and 5 units of hardware then
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)China has a comparative advantage in hardware and the U.S. has a comparative advantage in software.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)China has a comparative advantage in hardware and the U.S. has a comparative advantage in software.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If with one unit of labor the U.S. can produce 20 units of computer software and 10 units of computer hardware and China can produce 4 units of software and 4 units of hardware then
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In Table 17.4 
A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in cars only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in lumber only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in Cars while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in cars only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in lumber only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in Cars while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In Table 17.4 the United States has 
A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in lumber.

A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in lumber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Table 17.3 the Brazil has 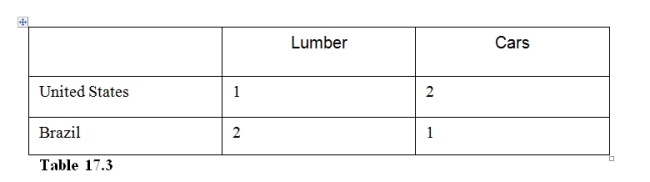
A)an absolute and comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in lumber.

A)an absolute and comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in lumber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In Table 17.3 the United States has 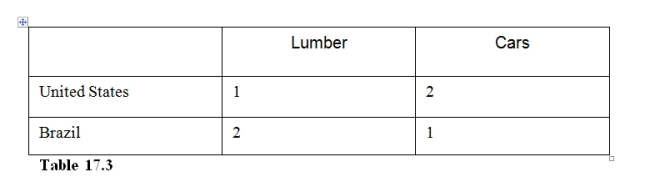
A)an absolute and comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in lumber.

A)an absolute and comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in lumber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If with one unit of labor the U.S. can produce 20 units of computer software and 10 units of computer hardware and China can produce 6 units of software and 6 units of hardware then trade can make
A)the U.S. better off but not China.
B)China better off but not the U.S.
C)neither better off.
D)both better off.
A)the U.S. better off but not China.
B)China better off but not the U.S.
C)neither better off.
D)both better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In Table 17.2 the United States has 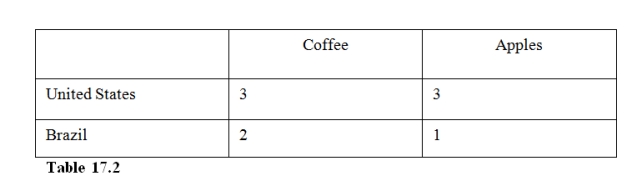
A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in apples.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee.

A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in apples.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In Table 17.4 the Brazil has 
A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)a comparative advantage in lumber but not an absolute advantage.

A)an absolute advantage but not a comparative advantage in cars.
B)an absolute and comparative advantage in lumber.
C)an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.
D)a comparative advantage in lumber but not an absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In Table 17.2, 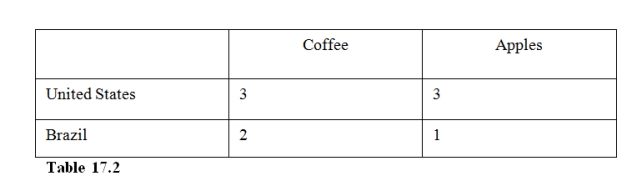
A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in apples only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in coffee only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in apples while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

A)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in apples only.
B)Brazil has an absolute advantage in both goods but a comparative advantage in coffee only.
C)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in apples while Brazil has an absolute and comparative advantage in coffee.
D)the United States has an absolute and comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If it takes one country one unit of labor to produce either a computer or a TV but it takes the other country three units of labor to produce a computer and four to produce a TV, then the first country has
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in TVs but a comparative advantage in computers.
C)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in computers only.
D)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in TVs only.
A)a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)an absolute advantage in TVs but a comparative advantage in computers.
C)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in computers only.
D)an absolute advantage in TVs and computers but a comparative advantage in TVs only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If with one unit of labor the U.S. can produce 20 units of computer software and 10 units of computer hardware and China can produce 5 units of software and 5 units of hardware then
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)the United States has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If with one unit of labor the U.S. can produce 20 units of computer software and 10 units of computer hardware and China can produce 6 units of software and 4 units of hardware then
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)China has a comparative advantage in hardware and the U.S. has a comparative advantage in software.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.
A)the United States has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
B)China has a comparative and absolute advantage in both goods.
C)China has a comparative advantage in hardware and the U.S. has a comparative advantage in software.
D)the United States has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A tariff will typically
A)increase the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers.
B)reduce the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers.
C)increase the price paid by consumers.
D)reduce the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers and increase the price paid by consumers.
A)increase the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers.
B)reduce the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers.
C)increase the price paid by consumers.
D)reduce the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers and increase the price paid by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If England limits the playing of U.S. music to no more than 5 hours per day
A)this is the same as a quota.
B)this is the same as a tariff.
C)this make U.S. producers of television wealthier that they would otherwise be.
D)economists would not call this a limit on trade since it is a service.
A)this is the same as a quota.
B)this is the same as a tariff.
C)this make U.S. producers of television wealthier that they would otherwise be.
D)economists would not call this a limit on trade since it is a service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A quota will typically
A)increase the price received by sellers.
B)reduce the price received by sellers.
C)reduce the price paid by consumers.
D)have no effect on price.
A)increase the price received by sellers.
B)reduce the price received by sellers.
C)reduce the price paid by consumers.
D)have no effect on price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the opportunity cost of producing a ton of coffee in the U.S. is twenty tons of rice, while the opportunity cost of producing coffee in Costa Rica is two tons of rice,
A)the U.S. has a comparative advantage in rice production.
B)Costa Rica has a comparative advantage in rice production.
C)the U.S. has a comparative advantage in coffee production.
D)the U.S. would be better off not trading with Costa Rica.
A)the U.S. has a comparative advantage in rice production.
B)Costa Rica has a comparative advantage in rice production.
C)the U.S. has a comparative advantage in coffee production.
D)the U.S. would be better off not trading with Costa Rica.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If France limits the showing of U.S. produced television shows to 2 hours per day
A)this is the same as a quota.
B)this is the same as a tariff.
C)this make U.S. producers of television wealthier that they would otherwise be.
D)economists would not call this a limit on trade since it is a service.
A)this is the same as a quota.
B)this is the same as a tariff.
C)this make U.S. producers of television wealthier that they would otherwise be.
D)economists would not call this a limit on trade since it is a service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A country that is limiting imports of a good by requiring a lengthy inspection process is using
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)non-tariff regulatory barriers.
D)buy "American advertising".
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)non-tariff regulatory barriers.
D)buy "American advertising".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A tariff will typically
A)increase the price paid by consumers.
B)increase the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers.
C)reduce the price paid by consumers.
D)have no effect on price.
A)increase the price paid by consumers.
B)increase the price, net of the tariff, that is received by sellers.
C)reduce the price paid by consumers.
D)have no effect on price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the opportunity cost of producing a ton of coffee in the U.S. is twenty tons of rice, while the opportunity cost of producing a ton coffee in Costa Rica is four tons of rice and the terms of trade is ten tons of rice delivered per ton of coffee received,
A)the U.S. can benefit by trading rice to Costa Rica for coffee.
B)Costa Rica can benefit by trading rice to the U.S. for coffee.
C)Costa Rica can benefit by trading coffee to the U.S. for rice.
D)the U.S. can benefit by trading rice to Costa Rica for coffee and Costa Rica can benefit by trading coffee to the U.S. for rice.
A)the U.S. can benefit by trading rice to Costa Rica for coffee.
B)Costa Rica can benefit by trading rice to the U.S. for coffee.
C)Costa Rica can benefit by trading coffee to the U.S. for rice.
D)the U.S. can benefit by trading rice to Costa Rica for coffee and Costa Rica can benefit by trading coffee to the U.S. for rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Limiting trade can be accomplished with
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)non-tariff regulatory barriers.
D)all of the options are correct.
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)non-tariff regulatory barriers.
D)all of the options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the opportunity cost of producing a ton of coffee in the U.S. is sixteen tons of rice, while the opportunity cost of producing a ton of coffee in Costa Rica is four tons of rice, the U.S. and Costa Rica could both benefit from specialization and trade if the terms of trade (measured in tons of rice delivered per ton of coffee received)were any number between A)one and four.
B)one and sixteen.
C)four and sixteen.
D)eight and sixteen.
B)one and sixteen.
C)four and sixteen.
D)eight and sixteen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A quota will typically
A)increase the price received by sellers.
B)reduce the price received by sellers.
C)increase the price paid by consumers.
D)increate the price received by sellers and increase the price paid by consumers.
A)increase the price received by sellers.
B)reduce the price received by sellers.
C)increase the price paid by consumers.
D)increate the price received by sellers and increase the price paid by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
One of the reasons economists approve of limiting trade would be
A)the desire not to encourage the employment of children.
B)the preservation of a high employment company.
C)the preservation of a high wage company.
D)the preservation of a large production company.
A)the desire not to encourage the employment of children.
B)the preservation of a high employment company.
C)the preservation of a high wage company.
D)the preservation of a large production company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One of the reasons economists approve of limiting trade would be
A)the protection of the environment.
B)the preservation of a high employment company.
C)the preservation of a high wage company.
D)the preservation of a large production company.
A)the protection of the environment.
B)the preservation of a high employment company.
C)the preservation of a high wage company.
D)the preservation of a large production company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The country with a comparative advantage in production of a good or service is the country with the
A)absolute advantage in production of that good or service.
B)absolute advantage in production of some other good or service.
C)lowest opportunity cost of producing that good or service.
D)ability to produce the larges quantity of that good or service.
A)absolute advantage in production of that good or service.
B)absolute advantage in production of some other good or service.
C)lowest opportunity cost of producing that good or service.
D)ability to produce the larges quantity of that good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
One of the reasons economists approve of limiting trade would be
A)the protection of national security.
B)the preservation of a high employment company.
C)the preservation of a high wage company.
D)the preservation of a large production company.
A)the protection of national security.
B)the preservation of a high employment company.
C)the preservation of a high wage company.
D)the preservation of a large production company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
On a supply and demand diagram, a tariff works by
A)moving the supply curve vertically down by the amount of the tariff.
B)moving the supply curve vertically up by the amount of the tariff.
C)limiting the amount that can be sold to a specific amount.
D)moving the demand curve vertically up by the amount of the tariff.
A)moving the supply curve vertically down by the amount of the tariff.
B)moving the supply curve vertically up by the amount of the tariff.
C)limiting the amount that can be sold to a specific amount.
D)moving the demand curve vertically up by the amount of the tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A country that is limiting imports of a good by allowing only a certain number to be imported is using
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)non-tariff regulatory barriers.
D)buy "American advertising".
A)tariffs.
B)quotas.
C)non-tariff regulatory barriers.
D)buy "American advertising".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Comparative advantage in production of the good measured on the horizontal axis is identified with a straight-line production possibilities frontier that has a slope that is
A)larger in magnitude (or absolute value).
B)smaller in magnitude (or absolute value).
C)positive.
D)larger in magnitude (or absolute value.)and positive.
A)larger in magnitude (or absolute value).
B)smaller in magnitude (or absolute value).
C)positive.
D)larger in magnitude (or absolute value.)and positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following works to limit trade by explicitly raising prices (i.e. as a tax)?
A)Tariffs
B)Quotas
C)Non-tariff regulatory barriers
D)Buy "American advertising"
A)Tariffs
B)Quotas
C)Non-tariff regulatory barriers
D)Buy "American advertising"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the language of international trade, "dumping" is the act of
A)selling goods of substandard quality.
B)selling goods cheaper than the competition.
C)selling goods below cost so as to drive competitors out of business.
D)producing goods without consideration of their environmental consequences.
A)selling goods of substandard quality.
B)selling goods cheaper than the competition.
C)selling goods below cost so as to drive competitors out of business.
D)producing goods without consideration of their environmental consequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exports from the United States (as a percentage of GDP)have
A)remained constant for the last 50 years.
B)increased over the last 50 years.
C)decreased over the last 50 years.
D)increased from 1960 to 1980 but has been steady since.
A)remained constant for the last 50 years.
B)increased over the last 50 years.
C)decreased over the last 50 years.
D)increased from 1960 to 1980 but has been steady since.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exports of U.S. rice to Japan tend to
A)harm U.S. consumers and help Japanese rice producers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm U.S. rice producers.
C)help U.S. consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
D)help Japanese consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
A)harm U.S. consumers and help Japanese rice producers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm U.S. rice producers.
C)help U.S. consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
D)help Japanese consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A quota that limits U.S. imports of cane sugar
A)harms U.S. sugar consumers.
B)helps U.S. cane sugar producers.
C)helps U.S. corn syrup (sweetener)producers.
D)all of the options are correct.
A)harms U.S. sugar consumers.
B)helps U.S. cane sugar producers.
C)helps U.S. corn syrup (sweetener)producers.
D)all of the options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Imports of Japanese passenger vehicles into the U.S. tend to
A)harm U.S. consumers and help Japanese automakers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm U.S. automakers.
C)help U.S. consumers and harm Japanese automakers.
D)harm Japanese consumers and help U.S. automakers.
A)harm U.S. consumers and help Japanese automakers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm U.S. automakers.
C)help U.S. consumers and harm Japanese automakers.
D)harm Japanese consumers and help U.S. automakers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Imports into the United States (as a percentage of GDP)have
A)remained constant for the last 50 years.
B)increased over the last 50 years.
C)decreased over the last 50 years.
D)increased from 1960 to 1980 but has been steady since.
A)remained constant for the last 50 years.
B)increased over the last 50 years.
C)decreased over the last 50 years.
D)increased from 1960 to 1980 but has been steady since.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Tariffs imposed upon U.S. rice imported into Japan tend to
A)harm Japanese consumers and help Japanese rice producers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
C)harm U.S. consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
D)help Japanese consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
A)harm Japanese consumers and help Japanese rice producers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
C)harm U.S. consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.
D)help Japanese consumers and harm Japanese rice producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Of the arguments for limiting trade which one is the most appealing to economists
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)protecting an industry important to a nation's identity or culture.
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)protecting an industry important to a nation's identity or culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a textile worker earns $38,000 per year working in the textile mill on a job that was saved by a protective tariff costing consumers $148,000 per year (for that job alone), the textile worker could be paid $48,000 to stay at home all day watching TV when the protective tariff is eliminated, and consumers would still be better off by approximately
A)$18,000 per year.
B)$48,000 per year.
C)$100,000 per year.
D)$168,000 per year.
A)$18,000 per year.
B)$48,000 per year.
C)$100,000 per year.
D)$168,000 per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Of approximately 140 million jobs in the U.S., each year approximately
A)31 million are eliminated and 30 million are created.
B)30 million are eliminated and 31 million are created.
C)all jobs eliminated are attributable to global outsourcing.
D)all jobs eliminated pay lower wages than the new jobs created.
A)31 million are eliminated and 30 million are created.
B)30 million are eliminated and 31 million are created.
C)all jobs eliminated are attributable to global outsourcing.
D)all jobs eliminated pay lower wages than the new jobs created.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Trade as a percentage of GDP has
A)remained constant for the last 50 years.
B)increased over the last 50 years.
C)decreased over the last 50 years.
D)increased from 1960 to 1980 but has been steady since.
A)remained constant for the last 50 years.
B)increased over the last 50 years.
C)decreased over the last 50 years.
D)increased from 1960 to 1980 but has been steady since.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Per job saved, consumers lose
A)slightly less than those jobs pay.
B)about the same as those jobs pay.
C)significantly more than those jobs pay.
D)significantly less than those jobs pay
A)slightly less than those jobs pay.
B)about the same as those jobs pay.
C)significantly more than those jobs pay.
D)significantly less than those jobs pay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Of the arguments for limiting trade which one is the most appealing to economists
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)preventing other countries from getting a comparative advantage by their use of child labor.
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)preventing other countries from getting a comparative advantage by their use of child labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The trading partner where the deficit has increased the most in the last 20 years is
A)China.
B)Mexico.
C)Canada.
D)Saudi Arabia.
A)China.
B)Mexico.
C)Canada.
D)Saudi Arabia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Of the arguments for limiting trade which one is the most appealing to economists
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)protecting an industry important to a nation's defense.
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)protecting an industry important to a nation's defense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A quota that limits U.S. imports of cane sugar
A)harms U.S. consumers more than it helps U.S. producers.
B)helps U.S. producers more than it hurts U.S. consumers.
C)harms foreign producers more than it helps U.S. producers.
D)helps both U.S. consumers and U.S. producers at the expense of foreign producers.
A)harms U.S. consumers more than it helps U.S. producers.
B)helps U.S. producers more than it hurts U.S. consumers.
C)harms foreign producers more than it helps U.S. producers.
D)helps both U.S. consumers and U.S. producers at the expense of foreign producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Protectionism is generally a cost effective method of saving jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
It is impossible to export or import services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Tariffs imposed upon Japanese passenger vehicle imports into the U.S. tend to
A)harm U.S. consumers and help Japanese automakers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm U.S. automakers.
C)harm U.S. consumers and help U.S. automakers.
D)harm Japanese consumers and help U.S. automakers.
A)harm U.S. consumers and help Japanese automakers.
B)help U.S. consumers and harm U.S. automakers.
C)harm U.S. consumers and help U.S. automakers.
D)harm Japanese consumers and help U.S. automakers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Jobs in the U.S. textile industry can be saved by imposing tariffs upon textiles imported into the U.S., but the cost to U.S. consumers is estimated to be approximately
A)$23,000 annually per job saved.
B)$49,000 annually per job saved.
C)$94,000 annually, per job saved.
D)$148,000 annually, per job saved.
A)$23,000 annually per job saved.
B)$49,000 annually per job saved.
C)$94,000 annually, per job saved.
D)$148,000 annually, per job saved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Of the arguments for limiting trade which one is the most appealing to economists
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)preventing other countries from getting a comparative advantage by their use of environmentally irresponsible actions.
A)helping an industry that is in trouble.
B)protecting the jobs of citizens.
C)protecting the profits of companies.
D)preventing other countries from getting a comparative advantage by their use of environmentally irresponsible actions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



