Deck 17: Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
1
Nucleosome location may be changed by a process called ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling.
True
2
Chromatin remodeling complexes alter nucleosomes,this occurs when
A) remodeling proteins bind to TFIID to promote or inhibit nucleosome formation.
B) complexes of ATP-dependent protein degrade histones and release the DNA from nucleosomes.
C) complexes of ATP-dependent proteins may reposition, evict, or change nucleosome composition.
D) remodeling proteins increase the supercoiling of the DNA, which can inhibit nucleosome formation.
A) remodeling proteins bind to TFIID to promote or inhibit nucleosome formation.
B) complexes of ATP-dependent protein degrade histones and release the DNA from nucleosomes.
C) complexes of ATP-dependent proteins may reposition, evict, or change nucleosome composition.
D) remodeling proteins increase the supercoiling of the DNA, which can inhibit nucleosome formation.
C
3
Activator proteins bind to silencer sequences and repressor proteins bind to enhancer sequences.
False
4
What would be the result of a mutation in HSP90 that blocked HSP90's ability to bind to the glucocorticoid receptor?
A) Glucocorticoid receptor could not form a dimer.
B) The nuclear localization signal would no longer function.
C) Glucocorticoid regulated genes would not be controlled even in the absence of glucocorticoid.
D) The hormone would not be able to bind to the glucocorticoid receptor.
A) Glucocorticoid receptor could not form a dimer.
B) The nuclear localization signal would no longer function.
C) Glucocorticoid regulated genes would not be controlled even in the absence of glucocorticoid.
D) The hormone would not be able to bind to the glucocorticoid receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Genomic imprinting is a result of
A) nucleosome location.
B) histone activation.
C) DNA methylation.
D) serine to leucine changes in the genetic code.
A) nucleosome location.
B) histone activation.
C) DNA methylation.
D) serine to leucine changes in the genetic code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is a major difference between the general and regulatory transcription factors?
A) General transcription factors only regulate the housekeeping genes while regulatory transcription factors control all of the other genes.
B) General transcription factors are essential for any transcription for all genes while regulatory transcription factors regulate transcription of specific genes.
C) General transcription factors act as heterodimers while regulatory transcription factors act as monomers.
D) General transcription factors regulate basal genes while regulatory transcription factors control all of the other genes.
A) General transcription factors only regulate the housekeeping genes while regulatory transcription factors control all of the other genes.
B) General transcription factors are essential for any transcription for all genes while regulatory transcription factors regulate transcription of specific genes.
C) General transcription factors act as heterodimers while regulatory transcription factors act as monomers.
D) General transcription factors regulate basal genes while regulatory transcription factors control all of the other genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Regulatory transcription factors may influence gene expression in which of the following ways?
A) recruiting proteins to the promoter that enhance chromatin compaction
B) by directly interacting with TFIII to inhibit its binding to the core promoter
C) influencing the ability of the RNA polymerase to perform elongation
D) directly recruiting RNA polymerase to the promoter without interacting with any other proteins
A) recruiting proteins to the promoter that enhance chromatin compaction
B) by directly interacting with TFIII to inhibit its binding to the core promoter
C) influencing the ability of the RNA polymerase to perform elongation
D) directly recruiting RNA polymerase to the promoter without interacting with any other proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is incorrect regarding the glucocorticoid hormones?
A) They interact with receptors located in the plasma membrane of the cell.
B) After interacting with the receptor, they release HSP90.
C) The receptors form a homodimer that travels to the nucleus.
D) The homodimer interacts with GRE, activating transcription.
A) They interact with receptors located in the plasma membrane of the cell.
B) After interacting with the receptor, they release HSP90.
C) The receptors form a homodimer that travels to the nucleus.
D) The homodimer interacts with GRE, activating transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Regulatory transcription factors may be regulated by
A) phosphorylation.
B) binding of carbohydrates.
C) lipid modifications.
D) sulfation.
A) phosphorylation.
B) binding of carbohydrates.
C) lipid modifications.
D) sulfation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
CpG islands are associated with which of the following?
A) nucleosome location
B) DNA methylation
C) steroid hormone activity
D) termination of translation
A) nucleosome location
B) DNA methylation
C) steroid hormone activity
D) termination of translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
DNA methylation activates gene expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Where is the IRE located in the ferritin gene?
A) 5′ end of DNA
B) 5′ end of mRNA
C) 3′ end of DNA
D) 3′ end of mRNA
A) 5′ end of DNA
B) 5′ end of mRNA
C) 3′ end of DNA
D) 3′ end of mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The CpG islands upstream of housekeeping genes are unmethylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What effect will a mutation in IRP that prevents it from binding to iron have on an individual?
A) Ferritin will not be made, so iron intake must be maximized.
B) There will be excess ferritin, so iron intake must be lowered.
C) Transferrin will not be made, so iron intake must be maximized.
D) There will be excess transferrin, so iron intake must be lowered.
A) Ferritin will not be made, so iron intake must be maximized.
B) There will be excess ferritin, so iron intake must be lowered.
C) Transferrin will not be made, so iron intake must be maximized.
D) There will be excess transferrin, so iron intake must be lowered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
DNA that contains actively transcribed genes would most likely contain chromatin in the closed configuration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A repressor protein would enhance the ability of TFIID to bind to the TATA box of the promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What general transcription factor is most often affected by regulatory transcription factors?
A) TFIIB
B) TFIID
C) TFIIE
D) TFIIF
A) TFIIB
B) TFIID
C) TFIIE
D) TFIIF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Steroid hormones are an example of an effector which regulates regulatory transcription factor activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Acetylation of histones results in
A) formation of an open chromatin structure.
B) removal of histones from the histone octomer.
C) formation of a closed chromatin structure.
D) termination of transcription.
A) formation of an open chromatin structure.
B) removal of histones from the histone octomer.
C) formation of a closed chromatin structure.
D) termination of transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Combinatorial factors include activators and repressors as well as
A) small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, and DNA methylation.
B) small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, DNA methylation, and basal transcription factors.
C) small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, but not DNA methylation.
D) proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes and DNA methylation, but not small effector moecules.
A) small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, and DNA methylation.
B) small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, DNA methylation, and basal transcription factors.
C) small effector molecules, proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes, but not DNA methylation.
D) proteins that alter the composition of nucleosomes and DNA methylation, but not small effector moecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What are some of the steps in eukaryotic transcriptional control?
A) A transcriptional repressor recruits nucleosome remodeling proteins that alter nucelosome positioning, modification, and composition. This allows for the formation of a closed chromatin complex, and binding of general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Histone cores remain on the gene as transcript elongation occurs.
B) A transcriptional repressor recruits general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II without affecting nucleosome positioning.
C) A transcriptional activator recruits nucleosome remodeling proteins that alter nucleosome positioning, modification and composition. This allows for the formation of an open chromatin complex, and binding of general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Finally as transcription elongation occurs, histone cores are evicted from the DNA to allow the RNA polymerase to transcribe the gene.
D) A transcriptional activator recruits general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Finally as transcription elongation occurs, histone cores remain with the DNA.
A) A transcriptional repressor recruits nucleosome remodeling proteins that alter nucelosome positioning, modification, and composition. This allows for the formation of a closed chromatin complex, and binding of general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Histone cores remain on the gene as transcript elongation occurs.
B) A transcriptional repressor recruits general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II without affecting nucleosome positioning.
C) A transcriptional activator recruits nucleosome remodeling proteins that alter nucleosome positioning, modification and composition. This allows for the formation of an open chromatin complex, and binding of general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Finally as transcription elongation occurs, histone cores are evicted from the DNA to allow the RNA polymerase to transcribe the gene.
D) A transcriptional activator recruits general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. Finally as transcription elongation occurs, histone cores remain with the DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How many Barr bodies would an individual with a XXY genotype possess?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) None of the answers are correct.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) None of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The differentially methylated region (DMR)is associated with which of the following?
A) X-chromosome inactivation
B) Genomic imprinting
C) Polycomb group (PcG) proteins
D) mRNA stability
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) X-chromosome inactivation
B) Genomic imprinting
C) Polycomb group (PcG) proteins
D) mRNA stability
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Expression of ________ would inhibit X-chromosome inactivation.
A) Xic
B) Xist
C) Tsix
D) All of the answers are correct
E) None of the answers are correct
A) Xic
B) Xist
C) Tsix
D) All of the answers are correct
E) None of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Both parents usually imprint the same gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What are some types of the molecular changes that underlie epigenetic gene regulation?
A) depurination of cytosine and thymidine residues
B) DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling
C) DNA methylation and depurination of cytosine residues
D) depurination and chromatin remodeling
A) depurination of cytosine and thymidine residues
B) DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling
C) DNA methylation and depurination of cytosine residues
D) depurination and chromatin remodeling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In imprinting of the Igf2 gene in mice,are the ICR and DMR methylated on the maternal or paternal chromosome? Which chromosome expresses Igf2?
A) Paternal, paternal
B) Paternal, maternal
C) Maternal, paternal
D) Maternal, maternal
A) Paternal, paternal
B) Paternal, maternal
C) Maternal, paternal
D) Maternal, maternal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements are correct?
A) Changes in gene expression based on environmental conditions are not considered normal while developmental changes are
B) Environmental epigenetic changes can vary due to the exposure of the organism to different environmental conditions, while those programmed during development are the result of stimuli generated by the organism itself
C) Environmental epigenetic gene regulation only occurs in reptiles and insects, while developmental epigenetic regulation occurs in all animals
D) Environmental epigenetic gene regulation is typically reversible while developmental epigenetic gene regulation is typically not reversible.
A) Changes in gene expression based on environmental conditions are not considered normal while developmental changes are
B) Environmental epigenetic changes can vary due to the exposure of the organism to different environmental conditions, while those programmed during development are the result of stimuli generated by the organism itself
C) Environmental epigenetic gene regulation only occurs in reptiles and insects, while developmental epigenetic regulation occurs in all animals
D) Environmental epigenetic gene regulation is typically reversible while developmental epigenetic gene regulation is typically not reversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is an example of epigenetic inheritance?
A) Expression of the Igf2 gene based on methylation of the ICR and DMR regions
B) Inheritance of flower color as studied by Mendel
C) Control of mRNA stability by an RNA-binding protein
D) Activation of transcription by a general transcription factor
A) Expression of the Igf2 gene based on methylation of the ICR and DMR regions
B) Inheritance of flower color as studied by Mendel
C) Control of mRNA stability by an RNA-binding protein
D) Activation of transcription by a general transcription factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the molecular mechanism for imprinting a gene?
A) Acetylation
B) Nitration
C) Phosphorylation
D) Methylation
A) Acetylation
B) Nitration
C) Phosphorylation
D) Methylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Most genes imprinted by methylation are silenced.What is one exception to this rule?
A) H19
B) Igf2
C) Xist
D) Agouti
A) H19
B) Igf2
C) Xist
D) Agouti

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What gene is most responsible for X-chromosome inactivation?
A) Xic
B) Xist
C) Tsix
D) Xce
A) Xic
B) Xist
C) Tsix
D) Xce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
One definition of epigenetics would be
A) the study of irreversible changes in DNA sequence.
B) the study of reversible mechanisms that lead to changes in gene expression that involve changes in DNA sequence.
C) the study of irreversible mechanisms that lead to changes in gene expression that do not involve changes in DNA sequence.
D) the study of reversible mechanisms that lead to changes in gene expression that do not involve changes in DNA sequence.
A) the study of irreversible changes in DNA sequence.
B) the study of reversible mechanisms that lead to changes in gene expression that involve changes in DNA sequence.
C) the study of irreversible mechanisms that lead to changes in gene expression that do not involve changes in DNA sequence.
D) the study of reversible mechanisms that lead to changes in gene expression that do not involve changes in DNA sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Epigenetic inheritance may occur at which of the following stages?
A) Oogenesis
B) Spermatogenesis
C) Embryogenesis
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) Oogenesis
B) Spermatogenesis
C) Embryogenesis
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What gene(s)is/are encoded in the Xic?
A) Xce
B) Xist
C) Tsix
D) Both the Tsix and Xist are genes are in the Xic region
A) Xce
B) Xist
C) Tsix
D) Both the Tsix and Xist are genes are in the Xic region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What are histone variants?
A) histone proteins that have slightly different amino acid sequences and have specialized functions
B) histone proteins that have slightly different amino acid sequences but are found in nucleosomes throughout the chromosomes
C) histone proteins that have been modified by acetylation
D) histone proteins that have been modified by acetylation and phosphorylation
A) histone proteins that have slightly different amino acid sequences and have specialized functions
B) histone proteins that have slightly different amino acid sequences but are found in nucleosomes throughout the chromosomes
C) histone proteins that have been modified by acetylation
D) histone proteins that have been modified by acetylation and phosphorylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One difference between developmental and environmental epigenetic changes is that
A) environmental epigenetic control is the result developmental processes interacting with the environment.
B) developmental epigenetic control is a normal process that occurs in all offspring.
C) environmental epigenetic control is a normal process that occurs in all offspring.
D) the differences between the two lie in the mechanisms that each uses.
A) environmental epigenetic control is the result developmental processes interacting with the environment.
B) developmental epigenetic control is a normal process that occurs in all offspring.
C) environmental epigenetic control is a normal process that occurs in all offspring.
D) the differences between the two lie in the mechanisms that each uses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following are molecular mechanisms used in epigenetic gene regulation?
A) DNA methylation
B) Covalent histone modification
C) Chromatin remodeling
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) DNA methylation
B) Covalent histone modification
C) Chromatin remodeling
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What genes appear to be controlled by the Xic?
A) Xist and Tsix
B) Xist
C) TsiX
D) Xic
A) Xist and Tsix
B) Xist
C) TsiX
D) Xic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is part of the mechanism for epigenetic regulation of the Igf2 gene?
A) Methylation of the H19 locus
B) Methylation of the ICR and DMR domains
C) Binding of CTC factors to methylated sequences
A) Methylation of the H19 locus
B) Methylation of the ICR and DMR domains
C) Binding of CTC factors to methylated sequences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the difference between the trithorax (TrxG)and polycomb (PcG)complexes of proteins?
A) TrxG proteins methylate lysine 27 on histone H3 while PcG complexes methylate lysine 4 on H3
B) Methylation of lysine at position 4 on H3 results in silencing of gene expression
C) TrxG complex proteins activate gene expression by methylating lysine 4 on H3, while PcG complex proteins repress gene expression by methylating lysine 27 on H3.
D) Methylation of H3 on lysine 27 can result in activation of transcription
A) TrxG proteins methylate lysine 27 on histone H3 while PcG complexes methylate lysine 4 on H3
B) Methylation of lysine at position 4 on H3 results in silencing of gene expression
C) TrxG complex proteins activate gene expression by methylating lysine 4 on H3, while PcG complex proteins repress gene expression by methylating lysine 27 on H3.
D) Methylation of H3 on lysine 27 can result in activation of transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Lamarck is remembered for his theory of inheritance which hypothesized that physical characteristics acquired during an individuals lifetime were passed onto their offspring.How does this differ from epigenetic inheritance where the diet of the mother affects coat color of the offspring?
A) There is no difference between Lamarckian theories of inheritance and epigenetic inheritance.
B) These epigenetic changes affect a specific allele. If the allele is not present, then coat color will not be affected by diet.
C) The change in coat color occurs in the offspring and not in the mother.
A) There is no difference between Lamarckian theories of inheritance and epigenetic inheritance.
B) These epigenetic changes affect a specific allele. If the allele is not present, then coat color will not be affected by diet.
C) The change in coat color occurs in the offspring and not in the mother.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A queen bee is larger than the female worker bees in a hive.The queen develops functional ovaries that allow her to produce up to 2000 eggs a day.What determines which bees become queen bees?
A) A single dominant allele of the Queen gene
B) The larvae raised on a diet of royal jelly
C) The larvae raised on a diet of pollen and nectar
D) The egg that hatches first
A) A single dominant allele of the Queen gene
B) The larvae raised on a diet of royal jelly
C) The larvae raised on a diet of pollen and nectar
D) The egg that hatches first

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Feeding a specific diet to female mice may result in an increased proportion of pseudo-agouti offspring if
A) the diet is low in folic acid and vitamin B₁₂.
B) the offspring carry the Avy allele.
C) the transposon at the Avy locus in the progeny is hypermethylated.
A) the diet is low in folic acid and vitamin B₁₂.
B) the offspring carry the Avy allele.
C) the transposon at the Avy locus in the progeny is hypermethylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Vernalization in Arabidopsis involves epigenetic changes as cold temperatures induce histone modifications that influence expression of genes for germination or flowering in the spring when temperatures increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In cancer cells one allele of a tumor suppressor gene called p53 is frequently mutated so that the protein is inactive,not produced,or deleted. The other allele usually has a normal sequence and the promoter remains intact,but the gene is not expressed. Sequencing with sodium bisulfite modification of DNA can be used to detect which cytosines are methylated. If cancer cell DNA is sequenced,which of the following results would be expected?
A) Cytosines in or near the promoter region will be methylated
B) Cytosines in or near the promoter will not be methylated
C) Cytosines in the coding region will have an increased methylation
D) There will be no differences in the methylation pattern of the promoter of p53 from a cancer cell and a normal cell
A) Cytosines in or near the promoter region will be methylated
B) Cytosines in or near the promoter will not be methylated
C) Cytosines in the coding region will have an increased methylation
D) There will be no differences in the methylation pattern of the promoter of p53 from a cancer cell and a normal cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Expression of a gene can be impaired if its promoter is hypermethylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a human cell has two Barr bodies then the genotype of the individual could be
A) XXXY
B) XXXXY
C) XXY
D) XYY
A) XXXY
B) XXXXY
C) XXY
D) XYY

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is part of the process of X-chromosome inactivation?
A) Expression of Xist from both chromosomes at the start of the process
B) Binding of multiple Xist transcripts to Xic on the X chromosome that will be inactivated
C) Compaction of the active X chromosome into a Barr body
D) Binding of Tsix transcripts to the X chromosome to be inactivated after the Xist transcripts binds to Xic
A) Expression of Xist from both chromosomes at the start of the process
B) Binding of multiple Xist transcripts to Xic on the X chromosome that will be inactivated
C) Compaction of the active X chromosome into a Barr body
D) Binding of Tsix transcripts to the X chromosome to be inactivated after the Xist transcripts binds to Xic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Data suggests that the royal jelly fed to bee larvae causes inhibition of DNA methylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the regulation of Igf2,it is possible that the effects of the association of the ICR and DMR regions with the CTC factors could be distance dependent. An experiment could be devised in which the distances between these regions could be varied and the rates of transcription could be measured. The graph shows some possible results. Which letter represents the most likely outcome if increasing the distance between ICR and DMR does not greatly enhance transcription until a critical distance is reached?
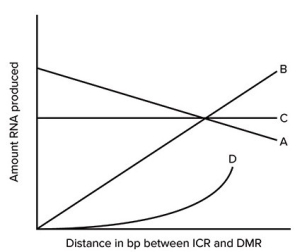
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Gene methylation can be detected through the use of restriction endonucleases. Usually these are used in pairs where one enzyme will digest only unmethylated DNA in its recognition sequence while the other is insensitive to methylation. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The enzyme that is insensitive to methylation serves as a control to make sure the inability of the other enzyme to digest DNA is not due to a mutation.
B) These are used in pairs because experiments have to be replicated and this one way of performing a replication of the experiment.
C) The experimental design is flawed because there should be a third enzyme that would serve as a positive control
D) This experimental design is able to identify the number of methylated C residues in a particular region of DNA.
A) The enzyme that is insensitive to methylation serves as a control to make sure the inability of the other enzyme to digest DNA is not due to a mutation.
B) These are used in pairs because experiments have to be replicated and this one way of performing a replication of the experiment.
C) The experimental design is flawed because there should be a third enzyme that would serve as a positive control
D) This experimental design is able to identify the number of methylated C residues in a particular region of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Covalent histone modification is sometimes involved in cell differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A common way of studying methylation in cells is to sequence DNA samples before and after modification with sodium bisulfite. The sodium bisulfite deaminates Cytosine residues,generating Uracil residues,therefore resulting in a change in the sequence as compared to the nonmodified DNA. Sodium bisulfite does not react with 5-methylcytosine so there will be no change in the sequence of those modified bases. When tumors are sequenced to study methylation patterns and epigenetic control,what would be the best control for sequencing using this technique?
A) Noncancerous tissue DNA from a different individual but from the same organ
B) Liver DNA from the same individual that the cancer sample is from
C) DNA from noncancerous tissue from the same individual's organ as the cancer
D) A combination of DNA from liver, brain and muscle from the same individual that has the cancer
A) Noncancerous tissue DNA from a different individual but from the same organ
B) Liver DNA from the same individual that the cancer sample is from
C) DNA from noncancerous tissue from the same individual's organ as the cancer
D) A combination of DNA from liver, brain and muscle from the same individual that has the cancer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Select all examples that are associated with expression of a single allele of a gene.
A) X-chromosome inactivation in female mammals
B) Genomic imprinting
C) Epigenetic modifications during cell differentiation
D) Development of queen bees determined by exposure to royal jelly
A) X-chromosome inactivation in female mammals
B) Genomic imprinting
C) Epigenetic modifications during cell differentiation
D) Development of queen bees determined by exposure to royal jelly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



