Deck 9: Imperfect Information, External Benefits, and External Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/416
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Imperfect Information, External Benefits, and External Costs
1
If buyers believe that the percentage of high quality goods on the market is greater than the actual percentage of high quality goods on the market
A) buyers will be willing to pay a price that is higher than the price they would pay with perfect information.
B) the most that buyers will be willing to pay is less than the price they would pay with perfect information.
C) sellers of low quality goods will be driven from the market.
D) the market will be in a short run equilibrium.
A) buyers will be willing to pay a price that is higher than the price they would pay with perfect information.
B) the most that buyers will be willing to pay is less than the price they would pay with perfect information.
C) sellers of low quality goods will be driven from the market.
D) the market will be in a short run equilibrium.
buyers will be willing to pay a price that is higher than the price they would pay with perfect information.
2
In equilibrium in a mixed market
A) the percent of low quality goods on the market equals the buyers' estimate of the percent of low quality goods on the market.
B) the percent of low quality goods on the market equals the sellers' estimate of the percent of low quality goods on the market.
C) 50% of the goods on the market are low quality and 50% are high quality.
D) all low quality goods have been driven out of the market.
A) the percent of low quality goods on the market equals the buyers' estimate of the percent of low quality goods on the market.
B) the percent of low quality goods on the market equals the sellers' estimate of the percent of low quality goods on the market.
C) 50% of the goods on the market are low quality and 50% are high quality.
D) all low quality goods have been driven out of the market.
the percent of low quality goods on the market equals the buyers' estimate of the percent of low quality goods on the market.
3
Which of the following is the least likely example of asymmetric information?
A) King Solomon and two women who claim to be the mother of a baby
B) a job applicant and a prospective employer
C) an auto mechanic and a transient customer
D) a retailer of used books and prospective customers
A) King Solomon and two women who claim to be the mother of a baby
B) a job applicant and a prospective employer
C) an auto mechanic and a transient customer
D) a retailer of used books and prospective customers
a retailer of used books and prospective customers
4
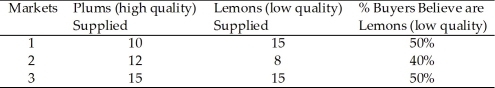 Table 9.1
Table 9.1Table 9.1 represents 3 markets for used computers. Which of the markets in Table 14.1 are in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
There exists asymmetric information in a market
A) if both sides of the market have the same information about the good.
B) only if buyers have better information about the good than sellers.
C) only if sellers have better information about the good than buyers.
D) if either buyers or sellers have better information than the other group.
A) if both sides of the market have the same information about the good.
B) only if buyers have better information about the good than sellers.
C) only if sellers have better information about the good than buyers.
D) if either buyers or sellers have better information than the other group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Table 9.1
Table 9.1Table 9.1 represents 3 markets for used computers. Which of the markets in Table 14.1 are NOT in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the seller knows more about the good than the buyer knows there exists
A) an externality.
B) asymmetric information.
C) moral hazard.
D) a public goods problem.
A) an externality.
B) asymmetric information.
C) moral hazard.
D) a public goods problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following is an example of asymmetric information?
A) A supermarket repackages packages of stale meat and sells them.
B) A homeowner knowingly sells a house that has hidden electrical problems.
C) A company hires an employee who has an addiction to sleeping pills.
D) all of the above
A) A supermarket repackages packages of stale meat and sells them.
B) A homeowner knowingly sells a house that has hidden electrical problems.
C) A company hires an employee who has an addiction to sleeping pills.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose buyers in the used car market are willing to pay $4,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $2,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 50% of the used cars on the market are lemons (low quality), what would they be willing to pay for a used car?
A) $2000
B) $3000
C) $3500
D) $4000
A) $2000
B) $3000
C) $3500
D) $4000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Asymmetric information exists in the market for used cars because
A) sellers have better information concerning the quality of used cars than buyers.
B) buyers have better information concerning the quality of used cars than sellers.
C) buyers and sellers have equal information concerning the quality of used cars.
D) it is impossible for buyers or sellers to determine the quality of used cars.
A) sellers have better information concerning the quality of used cars than buyers.
B) buyers have better information concerning the quality of used cars than sellers.
C) buyers and sellers have equal information concerning the quality of used cars.
D) it is impossible for buyers or sellers to determine the quality of used cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose buyers in the used car market are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $2,500 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 50% of the used cars on the market are lemons (low quality), what would they be willing to pay for a used car?
A) $2500
B) $3000
C) $3750
D) $5000
A) $2500
B) $3000
C) $3750
D) $5000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose buyers in the used car market are willing to pay $6,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 75% of the used cars on the market are lemons (low quality), what would they be willing to pay for a used car?
A) $4,250
B) $4,000
C) $3,750
D) $3,500
A) $4,250
B) $4,000
C) $3,750
D) $3,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Relative to a market with perfect information, in a market with imperfect information
A) some goods will be sold in small quantities or not at all.
B) more than the equilibrium quantity of goods will be sold.
C) the equilibrium quantity will be sold, but at a price higher than the equilibrium price.
D) the equilibrium quantity will be sold for the equilibrium price.
A) some goods will be sold in small quantities or not at all.
B) more than the equilibrium quantity of goods will be sold.
C) the equilibrium quantity will be sold, but at a price higher than the equilibrium price.
D) the equilibrium quantity will be sold for the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If in the market for used bikes only sellers can distinguish between good quality and bad quality used bikes, then in that market there exists
A) perfect information.
B) asymmetric information.
C) public information.
D) duopoly information.
A) perfect information.
B) asymmetric information.
C) public information.
D) duopoly information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A mixed market is one in which
A) consumers can be buyers and sellers and producers can be sellers and buyers.
B) there are different qualities of a good being sold in the market and there is imperfect information about the quality of each good.
C) a seller of a good requires that the purchase of one good be tied to the purchase of another.
D) demand is positively sloped and supply is negatively sloped.
A) consumers can be buyers and sellers and producers can be sellers and buyers.
B) there are different qualities of a good being sold in the market and there is imperfect information about the quality of each good.
C) a seller of a good requires that the purchase of one good be tied to the purchase of another.
D) demand is positively sloped and supply is negatively sloped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose buyers in the used car market are willing to pay $8,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 20% of the used cars on the market are lemons (low quality), what would they be willing to pay for a used car?
A) $7,000
B) $6,000
C) $5,000
D) $4,000
A) $7,000
B) $6,000
C) $5,000
D) $4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In some markets for used goods
A) the seller has more information than the buyer about the quality of the good.
B) the buyer has more information than the seller about the quality of the good.
C) low-quality used goods will be underpriced.
D) the quality of used goods sold in the market will typically rise over time.
A) the seller has more information than the buyer about the quality of the good.
B) the buyer has more information than the seller about the quality of the good.
C) low-quality used goods will be underpriced.
D) the quality of used goods sold in the market will typically rise over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the least likely example of asymmetric information?
A) an insurance company and a client who just obtained a driver license
B) a seller of used cars and a prospective customer
C) a seller of fresh fruit and a buyer
D) a retailer of music CDs and a buyer
A) an insurance company and a client who just obtained a driver license
B) a seller of used cars and a prospective customer
C) a seller of fresh fruit and a buyer
D) a retailer of music CDs and a buyer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One assumption of the basic model of supply and demand is that
A) buyers and sellers have enough information to make informed choices.
B) buyers and sellers will benefit equally from a voluntary transaction.
C) sellers will always have more information than buyers.
D) buyers will always have more information than sellers.
A) buyers and sellers have enough information to make informed choices.
B) buyers and sellers will benefit equally from a voluntary transaction.
C) sellers will always have more information than buyers.
D) buyers will always have more information than sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In markets with imperfect information
A) buyers and sellers will use resources to acquire information before making decisions.
B) buyers will use resources to acquire information before making a decision, but sellers do not need to acquire additional information before making a decision.
C) sellers will use resources to acquire information before making a decision, but buyers do not need to acquire additional information before making a decision.
D) neither buyers nor sellers will be able to acquire information in order to make decisions.
A) buyers and sellers will use resources to acquire information before making decisions.
B) buyers will use resources to acquire information before making a decision, but sellers do not need to acquire additional information before making a decision.
C) sellers will use resources to acquire information before making a decision, but buyers do not need to acquire additional information before making a decision.
D) neither buyers nor sellers will be able to acquire information in order to make decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
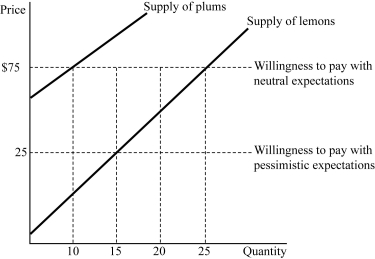 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of the used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how much will pay for a used camera?
A) $25
B) $50
C) $75
D) $125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
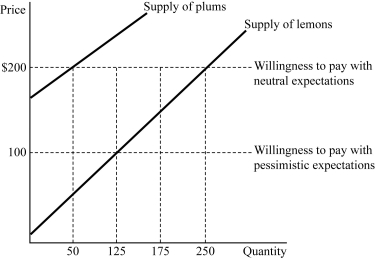 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of the used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), how much will they be willing to pay for a used refrigerator?
A) $100
B) $200
C) $250
D) $300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
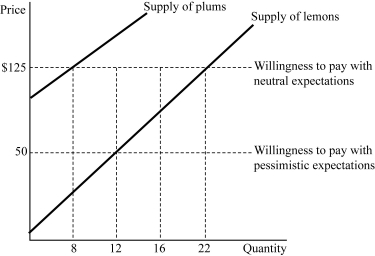 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers have pessimistic expectations about the used bikes in the market, how many used plums (high-quality used bikes) will be sold?
A) 0
B) 8
C) 12
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer cameras are sold in equilibrium?
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers believe that 50% of used bikes are lemons (low quality), how many lemons (low quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 8
B) 12
C) 16
D) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers have pessimistic expectations about the used bikes in the market, what number of used bikes sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A) 8
B) 12
C) 16
D) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
 Table 9.1
Table 9.1In Table 9.1, Market 1 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons accounted for
A) 60% of the market.
B) 55% of the market.
C) 45% of the market.
D) 40% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers believe that 50% of used bikes are lemons (low quality), how many plums (high quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 8
B) 12
C) 16
D) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), how many plums (high quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 50
B) 125
C) 175
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), how many lemons (low quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 50
B) 125
C) 175
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how many lemons (low quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used bikes sold will actually be plums (high quality)?
A) 8/30
B) 22/30
C) 8/22
D) 30/30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer bikes are sold in equilibrium?
A) 8
B) 12
C) 18
D) 22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers believe that 50% of used bikes in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used bikes sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A) 8/30
B) 22/30
C) 8/22
D) 30/30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
 Figure 9.1
Figure 9.1Figure 9.1 represents the market for used bikes. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $200 for a plum (high-quality) used bike and $50 for a lemon (low-quality) used bike. If buyers believe that 50% of the used bikes are lemons (low quality), how much will they be willing to pay for a used bike?
A) $50
B) $80
C) $125
D) $200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that all of the used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what number of used cameras sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how many plums (high quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 10
B) 15
C) 20
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
 Table 9.1
Table 9.1Refer to Table 9.1. In which market do buyers underestimate the chance of getting a lemon?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used cameras sold will actually be plums (high quality)?
A) 10/25
B) 10/35
C) 25/35
D) None of the cameras sold will be plums.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Figure 9.2 represents the market for used cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $125 for a plum (high-quality) used camera and $25 for a lemon (low-quality) used camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used cameras sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A) 10/25
B) 10/35
C) 25/35
D) All of the cameras sold will be lemons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used refrigerators sold will actually be plums (high quality)?
A) 50/250
B) 50/300
C) 250/300
D) None of the refrigerators sold will be plums.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
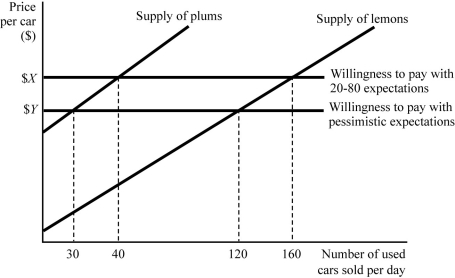 Figure 9.5
Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what is consumers' willingness to pay ($X)?
A) $5,000
B) $3,400
C) $3,000
D) $1,700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
 Figure 9.5
Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how many plums will be supplied in the market?
A) 30
B) 40
C) 70
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
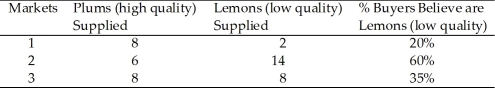 Table 9.2
Table 9.2In Table 9.2, Market 3 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed plums account for
A) 30% of the market.
B) 40% of the market.
C) 50% of the market.
D) 60% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
 Table 9.2
Table 9.2Table 9.2 represents 3 markets for used guitars. Which of the markets in Table 9.2 are NOT in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Table 9.2
Table 9.2In Table 9.2, Market 2 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for
A) 55% of the market.
B) 65% of the market.
C) 70% of the market.
D) 80% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
 Figure 9.5
Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. Initially buyers believe that 80% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with these initial expectations, how many fewer cars are sold in equilibrium?
A) 50
B) 80
C) 110
D) The number of cars sold in equilibrium is the same as the outcome with neutral expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
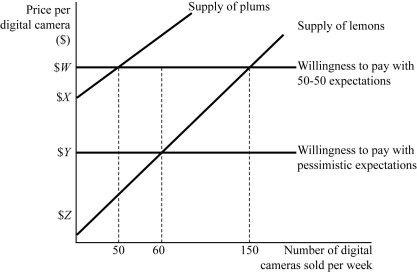 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how many plums (high quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A) 50
B) 60
C) 150
D) 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that all of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what number of used digital cameras sold will actually be lemons?
A) 50
B) 60
C) 110
D) 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer refrigerators are sold in equilibrium?
A) 50
B) 125
C) 175
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that all of the used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what number of used refrigerators sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A) 50
B) 125
C) 175
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. Compared to the situation when buyers have neutral expectations, if buyers believed that fewer than 50% of used refrigerators are lemons (low-quality)
A) more plums (high-quality) used refrigerators would be on the market.
B) fewer plums (high-quality) used refrigerators would be on the market.
C) fewer lemons (low-quality) used refrigerators would be on the market.
D) the same total number of used refrigerators would be on the market, but more of them would be plums (high-quality) used refrigerators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Figure 9.5
Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 represents the market for used cars. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $5,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $3,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 80% of used cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what percent of used cars sold will actually be plums?
A) 20%
B) 25%
C) 33.33%
D) 75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Table 9.2
Table 9.2Table 9.2 represents 3 markets for used guitars. Which of the markets in Table 9.2 are in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what is consumers' willingness to pay ($W)?
A) $100
B) $200
C) $300
D) $400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), how many lemons will be supplied by sellers?
A) 50
B) 60
C) 150
D) 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. At any price between $X and $Z
A) only plums will be supplied.
B) only lemons will be supplied.
C) both plums and lemons will be supplied
D) neither plums nor lemons will be supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Figure 9.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what fraction of used refrigerators sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A) 50/250
B) 50/300
C) 250/300
D) All of the refrigerators sold will be lemons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. Initially buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality). Compared to the outcome with neutral expectations, how many fewer digital cameras are sold in equilibrium?
A) 90
B) 110
C) 140
D) The number of cameras sold in equilibrium is the same as the outcome with neutral expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Figure 9.4 represents the market for used 12 megapixel digital cameras. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $400 for a plum (high-quality) used digital camera and $200 for a lemon (low-quality) used digital camera. If buyers believe that 50% of used digital cameras in the market are lemons (low quality), what percent of used digital cameras sold will actually be lemons?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
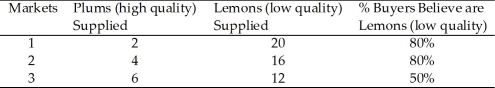 Table 9.4
Table 9.4In Table 9.4, Market 3 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed plums accounted for
A) 11.11% of the market.
B) 22.22% of the market.
C) 33.33% of the market.
D) 66.67% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
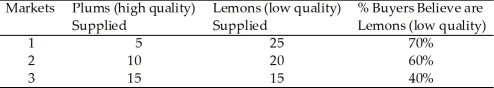 Table 9.3
Table 9.3In Table 9.3, Market 2 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed plums account for
A) about 16.67% of the market.
B) about 33.33% of the market.
C) about 66.67% of the market.
D) about 88.89% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When sellers have more information about the quality of a good than buyers do, a relatively large share of the goods in the market will be low-quality goods. This is the ________ problem.
A) free-rider
B) law of diminishing returns
C) adverse selection
D) moral hazard
A) free-rider
B) law of diminishing returns
C) adverse selection
D) moral hazard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
 Table 9.4
Table 9.4Table 9.4 represents 3 markets for used motorcycles. Which of the markets in Table 9.4 are in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose buyers in the used car market are willing to pay $3,500 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $1,500 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 30% of the used cars on the market are lemons (low quality), what would they be willing to pay for a used car?
A) $2,000
B) $2,500
C) $2,900
D) $3,500
A) $2,000
B) $2,500
C) $2,900
D) $3,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
 Table 9.4
Table 9.4In Table 9.4, Market 1 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons accounted for
A) about 90.91% of the market.
B) about 74.5% of the market.
C) about 63.25% of the market.
D) about 57.65% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
 Table 9.4
Table 9.4Table 9.4 represents 3 markets for used motorcycles. Which of the markets in Table 9.4 are NOT in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 Table 9.2
Table 9.2Refer to Table 9.2. In which market do buyers underestimate the chance of getting a lemon?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
 Table 9.3
Table 9.3In Table 9.3, Market 1 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for
A) about 83.33% of the market.
B) about 71.43% of the market.
C) about 66.67%% of the market.
D) about 42.86% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is NOT an example of the adverse selection problem?
A) Buyers in a market for used cars must choose from an undesirable selection of used cars.
B) An insurance company must choose one price for its coverage for both high-cost and low-cost people.
C) Commercial banks would rather use credit rationing than raising interest rates in the presence of excess demand for loans.
D) An insured motorist drives more recklessly.
A) Buyers in a market for used cars must choose from an undesirable selection of used cars.
B) An insurance company must choose one price for its coverage for both high-cost and low-cost people.
C) Commercial banks would rather use credit rationing than raising interest rates in the presence of excess demand for loans.
D) An insured motorist drives more recklessly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
 Table 9.3
Table 9.3In Table 9.3, Market 3 would be in equilibrium if buyers believed lemons account for
A) 45% of the market.
B) 50% of the market.
C) 55% of the market.
D) 60% of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 Table 9.3
Table 9.3Table 9.3 represents 3 markets for used stereos. Which of the markets in Table 9.3 are NOT in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose you notice that the market for used bikes is dominated by lemons (low-quality bikes). In such a situation, if you are a buyer of used bikes, you are faced with
A) a positive externality.
B) perfect information.
C) an adverse selection problem.
D) symmetric information.
A) a positive externality.
B) perfect information.
C) an adverse selection problem.
D) symmetric information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If the market for used computers has only lemons (low-quality computers) then the market
A) is an example of a thick market.
B) suffers from an adverse selection problem.
C) is a type of monopoly.
D) must be monopolistically competitive.
A) is an example of a thick market.
B) suffers from an adverse selection problem.
C) is a type of monopoly.
D) must be monopolistically competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
You are responsible for purchasing 20 used computers for your company. Red brand computers cost $1,250 and green brand computers cost $1,800. Based on experience, you believe that 60% of red brand computers are lemons (low quality) while 20% of green brand computers are lemons (low quality). You are willing to pay $1,000 for a known lemon and $2,000 for a known plum. Which brand do you purchase?
A) red
B) green
C) You are indifferent between brands.
D) You don't buy either brand.
A) red
B) green
C) You are indifferent between brands.
D) You don't buy either brand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
 Table 9.3
Table 9.3Table 9.3 represents 3 markets for used stereos. Which of the markets in Table 9.3 are in equilibrium?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a market with an adverse selection problem
A) one side of the market has better information about the goods than the other.
B) the uninformed side of the market must choose from an undesirable selection of goods.
C) some high-quality goods are sold but fewer than would be sold in a market with perfect information.
D) all of the above
A) one side of the market has better information about the goods than the other.
B) the uninformed side of the market must choose from an undesirable selection of goods.
C) some high-quality goods are sold but fewer than would be sold in a market with perfect information.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
You are responsible for purchasing 25 used cars for your company. Star Brand cars costs $7,500 and Diamond Brand cars cost $6,000. Based on experience, you believe that 20% of Star Brand cars are lemons (low quality) while 40% of Diamond Brand cars are lemons (low quality). You are willing to pay $5,000 for a known lemon and $12,000 for a known plum. Which brand do you purchase?
A) Star
B) Diamond
C) You are indifferent between brands.
D) You don't buy either brand.
A) Star
B) Diamond
C) You are indifferent between brands.
D) You don't buy either brand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 Table 9.4
Table 9.4Refer to Table 9.4. In which market do buyers underestimate the chance of getting a lemon?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
 Table 9.3
Table 9.3Refer to Table 9.3. In which market do buyers underestimate the chance of getting a lemon?
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 416 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



