Deck 6: Decision Analysis and Expected Value
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Decision Analysis and Expected Value
1
The variance of a discrete distribution increases if we add a positive constant to each one of its value.
False
2
A variable that can take on values at any point over a given interval is called a discrete random variable.
False
3
Variables which take on values only at certain points over a given interval are called continuous random variables.
False
4
The mean or the expected value of a discrete distribution is the long-run average of the occurrences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The expected monetary payoff of perfect information is the value of perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
To compute the variance of a discrete distribution, it is necessary to know the mean of the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In a decision analysis problem, variables (such as general macroeconomic conditions) which are under the decision maker's control are called prior probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a decision-making scenario, if it is known which of the states of nature will occur and further if the probabilities of occurrence of the states are also unknown the scenario is called decision-making under double risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a decision-making under risk scenario, the expected monetary value of a decision alternative is the weighted average (using the probability of each state of nature as the weight) of the payoffs to the decision alternative in each state of the nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In decision-making under risk, the expected monetary payoff of perfect information is the weighted average of the best payoff for each state of nature (using the probability of the state of nature as the weight).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The amount of time a patient waits in a doctor's office is an example of a continuous random variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a decision-making under uncertainty scenario, the decision maker chooses the decision alternative that has the minimum expected (i.e., probability-weighted) payoff among all the available alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The number of visitors to a website each day is an example of a discrete random variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a decision analysis problem, variables (such as investing in common stocks or corporate bonds) which are under the decision maker's control are called decision alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a decision analysis problem, variables (such as benefits or rewards that result from investments in common stocks or corporate bonds and from a new product launch) which result from selecting a particular decision alternative are called posterior probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a decision-making scenario, if it is known which of the states of nature will occur but the probabilities of occurrence of the states are known the scenario is called decision-making under risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In a decision-making under risk scenario, the expected monetary value of a decision alternative is the arithmetic average of the payoffs to the decision alternative in each state of the nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a decision-making scenario, if the decision maker knows which state of nature will occur, the scenario is called decision-making under certainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In decision-making under risk, the expected monetary value without information is the largest of the expected monetary values for the various decision alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The value of perfect information is the difference between the monetary payoff with perfect information and the expected monetary payoff with no information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a decision analysis problem, variables (such as investing in common stocks or corporate bonds) which are under the decision maker's control are called ___.
A) payoffs
B) decision alternatives
C) states of nature
D) revised probabilities
E) prior probabilities
A) payoffs
B) decision alternatives
C) states of nature
D) revised probabilities
E) prior probabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A market research team compiled the following discrete probability distribution. In this distribution, x represents the number of automobiles owned by a family: 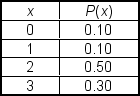 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A) This distribution is skewed to the right.
B) This is a binomial distribution.
C) This is a normal distribution.
D) This distribution is skewed to the left.
E) This distribution is bimodal.
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A) This distribution is skewed to the right.
B) This is a binomial distribution.
C) This is a normal distribution.
D) This distribution is skewed to the left.
E) This distribution is bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The speed at which a jet plane can fly is an example of ___.
A) neither discrete nor continuous random variable
B) both discrete and continuous random variable
C) a continuous random variable
D) a discrete random variable
E) a constant
A) neither discrete nor continuous random variable
B) both discrete and continuous random variable
C) a continuous random variable
D) a discrete random variable
E) a constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Dianna Ivy is evaluating a plan to expand the production facilities of International Compressors Company which manufactures natural gas compressors. Dianna feels that the price of coal is a significant factor in her decision, but she cannot control it. For her decision, the different prices of coal represent the ___.
A) payoffs
B) decision alternatives
C) states of nature
D) revised probabilities
E) prior probabilities
A) payoffs
B) decision alternatives
C) states of nature
D) revised probabilities
E) prior probabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Dan Hein owns the mineral and drilling rights to a 1,000 acre tract of land. If he drills a well and does strike oil his net loss will be $50,000, but if he drills a well and strikes oil his net gain will be $100,000. If he does drill, his loss is the cost of the mineral and drilling rights, which amount to $1000. For Dan's decision problem, the variable "oil in the tract" is one of the
A) payoffs.
B) decision alternatives.
C) states of nature.
D) revised probabilities.
E) prior probabilities.
A) payoffs.
B) decision alternatives.
C) states of nature.
D) revised probabilities.
E) prior probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In American Roulette, there are two zeroes and 36 non-zero numbers (18 red and 18 black). If a player bets 1 unit on red, his chance of winning 1 unit is therefore 18/38 and his chance of losing 1 unit (or winning -1) is 20/38. Let x be the player profit per game. The mean (average) value of x is approximately ___.
A) 0.0526
B) -0.0526
C) 1
D) -1
E) 0
A) 0.0526
B) -0.0526
C) 1
D) -1
E) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A market research team compiled the following discrete probability distribution on the number of soft drinks the average adult drinks each day. In this distribution, x represents the number of sodas which an adult drinks: 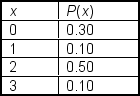 The standard deviation of x is ___.
The standard deviation of x is ___.
A) 1.04
B) 0.89
C) 1.40
D) 1.02
E) .588
 The standard deviation of x is ___.
The standard deviation of x is ___.A) 1.04
B) 0.89
C) 1.40
D) 1.02
E) .588

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Dan Hein owns the mineral and drilling rights to a 1,000 acre tract of land. If he drills a well and does strike oil his net loss will be $50,000, but if he drills a well and strikes oil his net gain will be $100,000. If he does drill, his loss is the cost of the mineral and drilling rights, which amount to $1000. For Dan's decision problem, the variable "drill the well" is one of the ___.
A) payoffs
B) decision alternatives
C) states of nature
D) revised probabilities
E) prior probabilities
A) payoffs
B) decision alternatives
C) states of nature
D) revised probabilities
E) prior probabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You are offered an investment opportunity. Its outcomes and probabilities are presented in the following table: 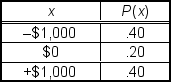 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A) This distribution is skewed to the right.
B) This is a binomial distribution.
C) This distribution is symmetric.
D) This distribution is skewed to the left.
E) This is a Poisson distribution.
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A) This distribution is skewed to the right.
B) This is a binomial distribution.
C) This distribution is symmetric.
D) This distribution is skewed to the left.
E) This is a Poisson distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The volume of liquid in an unopened 5.68 litre can of paint is an example of ___.
A) the binomial distribution
B) both discrete and continuous variable
C) a continuous random variable
D) a discrete random variable
E) a constant
A) the binomial distribution
B) both discrete and continuous variable
C) a continuous random variable
D) a discrete random variable
E) a constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A market research team compiled the following discrete probability distribution for families residing in Pictou County. In this distribution, x represents the number of evenings the family dines outside their home during a week: 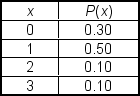 The standard deviation of x is ___.
The standard deviation of x is ___.
A) 1.00
B) 2.00
C) 0.80
D) 0.89
E) 1.09
 The standard deviation of x is ___.
The standard deviation of x is ___.A) 1.00
B) 2.00
C) 0.80
D) 0.89
E) 1.09

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A recent analysis of the number of rainy days per month found the following outcomes and probabilities: 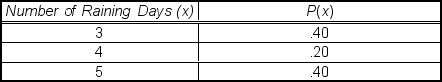 The standard deviation of this distribution is ___.
The standard deviation of this distribution is ___.
A) .800
B) .894
C) .400
D) 4.00
E) .457
 The standard deviation of this distribution is ___.
The standard deviation of this distribution is ___.A) .800
B) .894
C) .400
D) 4.00
E) .457

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A market research team compiled the following discrete probability distribution on the number of soft drinks the average adult drinks each day. In this distribution, x represents the number of sodas which an adult drinks: 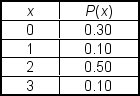 The mean (average) value of x is ___.
The mean (average) value of x is ___.
A) 1.4
B) 1.75
C) 2.10
D) 2.55
E) 3.02
 The mean (average) value of x is ___.
The mean (average) value of x is ___.A) 1.4
B) 1.75
C) 2.10
D) 2.55
E) 3.02

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Dan Hein owns the mineral and drilling rights to a 1,000 acre tract of land. If he drills a well and does strike oil his net loss will be $50,000, but if he drills a well and strikes oil his net gain will be $100,000. If he does drill, his loss is the cost of the mineral and drilling rights, which amount to $1000. For Dan's decision problem, the variable "net loss of $50,000" is one of the
A) payoffs.
B) decision alternatives.
C) states of nature.
D) revised probabilities.
E) prior probabilities.
A) payoffs.
B) decision alternatives.
C) states of nature.
D) revised probabilities.
E) prior probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The A-Life Corporation has 320 employees. The Human Resource manager of the corporation documents the frequency with which employees call in sick. In the month of December, 16 employees called in sick 3 times, 48 employees called in sick 2 times, 64 employees called in sick once, and 160 did not call in sick at all.
a) What type of variable is x = 'the number of times employees called in sick'?
b) Develop a probability distribution for the x.
a) What type of variable is x = 'the number of times employees called in sick'?
b) Develop a probability distribution for the x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The number of finance majors within the School of Business is an example of ___.
A) a discrete random variable
B) a continuous random variable
C) the Poisson distribution
D) the normal distribution
E) a constant
A) a discrete random variable
B) a continuous random variable
C) the Poisson distribution
D) the normal distribution
E) a constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A recent analysis of the number of rainy days per month found the following outcomes and probabilities: 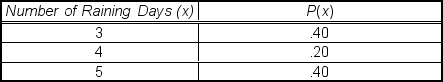 The mean of this distribution is ___.
The mean of this distribution is ___.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) <1
 The mean of this distribution is ___.
The mean of this distribution is ___.A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) <1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The expected monetary value without information is $60, and the expected monetary payoff with perfect information is $120. The expected value of perfect information is
A) $60.
B) $2.
C) $180.
D) $0.50.
E) $120.
A) $60.
B) $2.
C) $180.
D) $0.50.
E) $120.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A market research team compiled the following discrete probability distribution for families residing in Pictou County. In this distribution, x represents the number of evenings the family dines outside their home during a week: 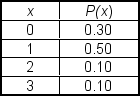 The mean (average) value of x is ___.
The mean (average) value of x is ___.
A) 1.0
B) 1.5
C) 2.0
D) 2.5
E) 3.0
 The mean (average) value of x is ___.
The mean (average) value of x is ___.A) 1.0
B) 1.5
C) 2.0
D) 2.5
E) 3.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The expected monetary value without information is $2,500, and the expected monetary payoff with perfect information is $5,000. The expected value of perfect information is
A) $7,500.
B) $2,500.
C) $1,500.
D) $2,000.
E) $1,250.
A) $7,500.
B) $2,500.
C) $1,500.
D) $2,000.
E) $1,250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A market research team compiled the following discrete probability distribution for families residing in Randolph County. In this distribution, x represents the number of evenings the family dines outside their home during a week:
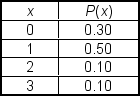 Determine the mean (average) value and standard deviation of x.
Determine the mean (average) value and standard deviation of x.
 Determine the mean (average) value and standard deviation of x.
Determine the mean (average) value and standard deviation of x. 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A dream car lottery is valued at $100,000. The probability of winning the car is 0.001. What is the expected value of the lottery if it costs $50 to play?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



