Deck 15: Ð Bond Electrophiles Connected to Leaving Groups
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Ð Bond Electrophiles Connected to Leaving Groups
1
What is the best leaving group in an SNAr reaction?
A)fluoride
B)chloride
C)bromide
D)iodide
A)fluoride
B)chloride
C)bromide
D)iodide
fluoride
2
Which carboxylic acid derivative would you expect to be most reactive to a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction?
A)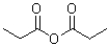
B)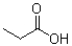
C)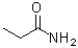
D)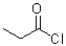
A)

B)

C)

D)


3
Which of the following best describes cyanate groups in SNAr reactions?
A)electron withdrawing and activating
B)electron withdrawing and deactivating
C)electron donating and activating
D)electron donating and deactivating
A)electron withdrawing and activating
B)electron withdrawing and deactivating
C)electron donating and activating
D)electron donating and deactivating
electron withdrawing and activating
4
Which of the following best describes the role of acid in acyl substitution reactions?
A)It activates electrophiles.
B)It activates electrophiles and nucleophiles.
C)It improves leaving group capability.
D)It activates electrophiles and improves leaving group capability.
A)It activates electrophiles.
B)It activates electrophiles and nucleophiles.
C)It improves leaving group capability.
D)It activates electrophiles and improves leaving group capability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best describes DIBAL in the reaction scheme shown below? 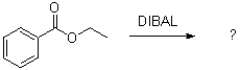
A)nucleophilic and oxidizing
B)nucleophilic and reducing
C)electrophilic and oxidizing
D)electrophilic and reducing

A)nucleophilic and oxidizing
B)nucleophilic and reducing
C)electrophilic and oxidizing
D)electrophilic and reducing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many equivalents of a Grignard reagent will an ester react with?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following best describes the conditions required to reduce an acid anhydride?
A)LiAlH4 will accomplish this transformation.
B)NaBH4 will accomplish this transformation.
C)NaCNBH3 will accomplish this transformation.
D)Both LiAlH4 and NaBH4 will accomplish this transformation.
A)LiAlH4 will accomplish this transformation.
B)NaBH4 will accomplish this transformation.
C)NaCNBH3 will accomplish this transformation.
D)Both LiAlH4 and NaBH4 will accomplish this transformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following reagents can reduce an ester?
A)LiAlH4
B)NaBH4
C)NaCNBH3
D)H2O
A)LiAlH4
B)NaBH4
C)NaCNBH3
D)H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What acts as the nucleophile in the first step of the following reaction? 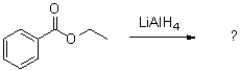
A)hydride
B)lithium
C)aluminum
D)ethyl benzoate

A)hydride
B)lithium
C)aluminum
D)ethyl benzoate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes the role of base in acyl substitution reactions?
A)It activates electrophiles.
B)It activates nucleophiles.
C)It improves leaving group capability.
D)It activates electrophiles and improves leaving group capability.
A)It activates electrophiles.
B)It activates nucleophiles.
C)It improves leaving group capability.
D)It activates electrophiles and improves leaving group capability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How many hydrides from LiAlH4 are required to reduce a carboxylic acid?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why is base added in excess when reacting an acid chloride with an amine?
A)to deprotonate the acid chloride and make it more nucleophilic
B)to deprotonate the amine and make it more nucleophilic
C)to form a salt with the formed HCl byproduct
D)to hydrogen bond with the amine and acid chloride to bring them together
A)to deprotonate the acid chloride and make it more nucleophilic
B)to deprotonate the amine and make it more nucleophilic
C)to form a salt with the formed HCl byproduct
D)to hydrogen bond with the amine and acid chloride to bring them together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When forming an amide from an acid chloride,how many equivalents of amine are required if no base is used?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)excess
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)excess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following best describes LiAlH4 in the reaction scheme shown below? 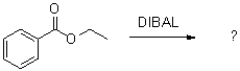
A)It is a reducing agent.
B)It is an oxidizing agent.
C)It is an acid.
D)It is a base.

A)It is a reducing agent.
B)It is an oxidizing agent.
C)It is an acid.
D)It is a base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the product of the transformation shown below? 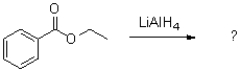
A)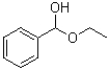
B)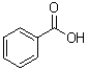
C)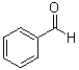
D)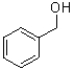

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What would be the product of the following reaction? 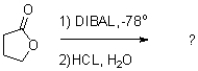
A)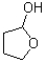
B)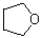
C)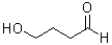
D)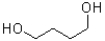
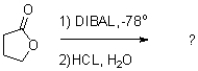
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following best describes the relationship between borane and DIBAL?
A)Borane is more electrophilic and more reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
B)Borane is more electrophilic and less reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
C)Borane is less electrophilic and more reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
D)Borane is less electrophilic and less reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
A)Borane is more electrophilic and more reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
B)Borane is more electrophilic and less reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
C)Borane is less electrophilic and more reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.
D)Borane is less electrophilic and less reactive towards carbonyls than DIBAL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the role of acid in acid-catalyzed acyl substitution reactions?
A)It protonates the carbonyl oxygen,making the carbon more electrophilic.
B)It protonates the nucleophile,making it more nucleophilic.
C)It protonates the carbonyl oxygen,making the carbon more negatively charged.
D)It makes the solvent more polar,improving the rate of substitution reactions.
A)It protonates the carbonyl oxygen,making the carbon more electrophilic.
B)It protonates the nucleophile,making it more nucleophilic.
C)It protonates the carbonyl oxygen,making the carbon more negatively charged.
D)It makes the solvent more polar,improving the rate of substitution reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the rate determining step in an SNAr reaction?
A)deprotonation of the nucleophile
B)nucleophilic attack of the aromatic ring
C)resonance stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate
D)loss of leaving group
A)deprotonation of the nucleophile
B)nucleophilic attack of the aromatic ring
C)resonance stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate
D)loss of leaving group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the major product of the following reaction scheme? 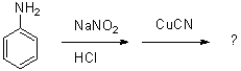
A)
B)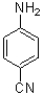
C)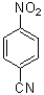
D)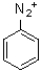

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the major product of the following reaction? 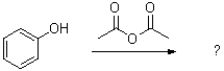
A)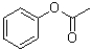
B)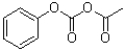
C)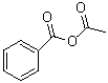
D)No reaction would occur.

A)

B)

C)

D)No reaction would occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT an intermediate of the reaction shown below? 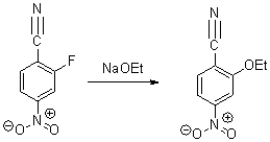
A)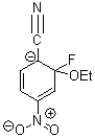
B)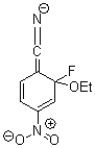
C)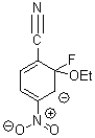
D)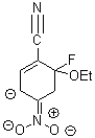

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the product of the following reaction? 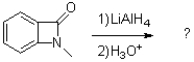
A)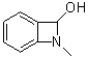
B)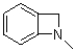
C)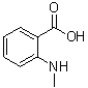
D)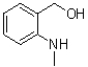

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 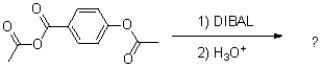
A)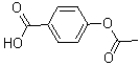
B)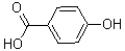
C)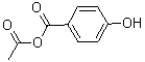
D)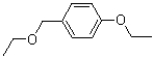

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 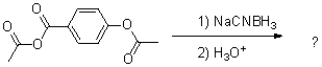
A)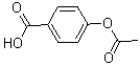
B)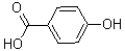
C)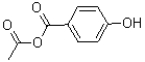
D)No reaction will occur.

A)

B)

C)

D)No reaction will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following best describes the set of conditions that can accomplish the transformation shown below? 
A)H3O+.propylamine
B)DCC,propylamine
C)1)SOCl2 2)excess propylamine
D)Both DCC,propylamine and 1)SOCl2 2)excess propylamine will accomplish this transformation.

A)H3O+.propylamine
B)DCC,propylamine
C)1)SOCl2 2)excess propylamine
D)Both DCC,propylamine and 1)SOCl2 2)excess propylamine will accomplish this transformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following reagents will accomplish the transformation shown below? 
A)BH3
B)DIBAL
C)LiAlH4
D)H3O+/H2O

A)BH3
B)DIBAL
C)LiAlH4
D)H3O+/H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 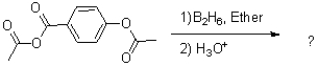
A)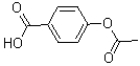
B)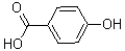
C)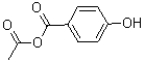
D)No reaction would occur.

A)

B)

C)

D)No reaction would occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the rate-determining step of an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester?
A)protonation of the electrophile
B)breaking of the ð bond and formation of the tetrahedral intermediate
C)breaking of the ó bond and loss of the leaving group
D)protonation of the leaving group
A)protonation of the electrophile
B)breaking of the ð bond and formation of the tetrahedral intermediate
C)breaking of the ó bond and loss of the leaving group
D)protonation of the leaving group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the major product of the following reaction? 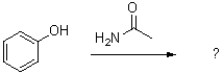
A)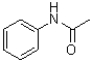
B)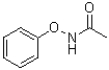
C)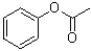
D)No reaction would occur.

A)

B)

C)

D)No reaction would occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the product (or products)of the transformation shown below? 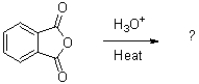
A)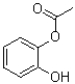
B)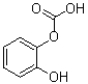
C)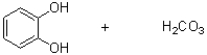
D)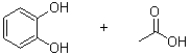

A)

B)

C)
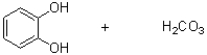
D)
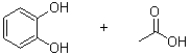

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 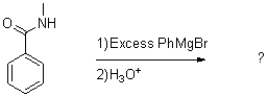
A)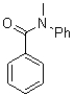
B)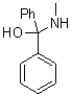
C)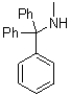
D)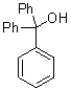
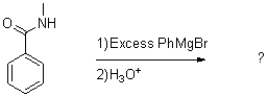
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which aromatic ring will react faster to an SNAr reaction and why? 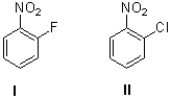
A)I because fluoride is a better leaving group
B)I because fluoride makes the ring more electrophilic
C)II because chloride is a better leaving group
D)II because chloride makes the ring more electrophilic

A)I because fluoride is a better leaving group
B)I because fluoride makes the ring more electrophilic
C)II because chloride is a better leaving group
D)II because chloride makes the ring more electrophilic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the product of the transformation shown below? 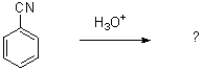
A)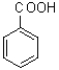
B)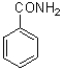
C)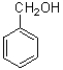
D)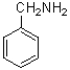

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following would be the most reactive in an SNAr reaction?
A)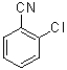
B)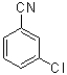
C)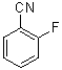
D)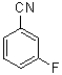
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the product of the following reaction? 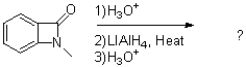
A)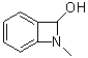
B)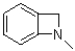
C)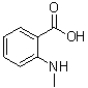
D)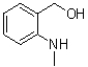
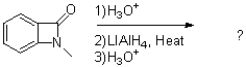
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 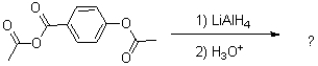
A)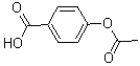
B)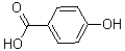
C)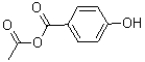
D)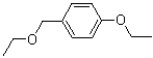

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the product of the following reaction? 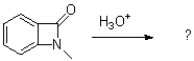
A)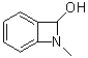
B)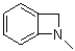
C)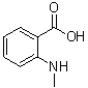
D)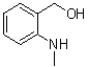

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following best describes the role of the chloride atom in the nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction of an acid chloride?
A)Its high electronegativity draws electron density away from the carbonyl,making it more electrophilic.
B)Its high electronegativity makes it effective at carrying negative charge and makes it a good leaving group.
C)Its easily protonated by acid makes it an effective electrophile for acid catalyzed reactions.
D)Its high electronegativity draws electron density away from the carbonyl and makes it effective at carrying negative charge,making it more electrophilic.
A)Its high electronegativity draws electron density away from the carbonyl,making it more electrophilic.
B)Its high electronegativity makes it effective at carrying negative charge and makes it a good leaving group.
C)Its easily protonated by acid makes it an effective electrophile for acid catalyzed reactions.
D)Its high electronegativity draws electron density away from the carbonyl and makes it effective at carrying negative charge,making it more electrophilic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The position of an electron withdrawing substituent has no effect on the reactivity of an aromatic ring in an SNAr reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sodium cyanoborohydride acts as a nucleophile,whereas sodium borohydride acts as a nucleophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Lithium aluminum hydride coverts an ester to a secondary alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Aryl fluorides are more reactive then aryl chlorides in SNAr reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Reaction of one equivalent of a Grignard reagent with an ester results in a ketone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Borane converts carboxylic acids into aldehydes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Borane acts as a nucleophile,whereas sodium borohydride acts as a nucleophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Acid protonates the carboxylic acid derivative in nucleophillic acyl substitutions making it more electrophilic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An alkoxide is a better leaving group then a halide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Dimethylaminopyridine is a better catalyst than pyridine in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is a reagent used to form amides and esters from carboxylic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A Grignard reaction will reduce an ester to a tertiary alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Acid chlorides are less electrophilic then acid anhydrides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Electron withdrawing groups make an aromatic ring more reactive to SNAr reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Nucleophillic acyl substitutions go through a trigonal planar intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The tetrahedral intermediate is the result of nucleophilic attack on a carbonyl carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
DIBAL can reduce acid anhydrides into both aldehydes and alcohols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Borane can reduce an amide to either an amine or an aldehyde.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An acyl chloride can be reduced by sodium cyanoborohydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Esters are more electrophilic then amides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Aldehydes and ketones are more reactive to Grignard reagents than esters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
DMAP acts as a(n)_______________ in the reaction of an acid chloride with an amine in excess pyridine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In acid catalyzed hydrolysis of an amide,the acid role in the first mechanistic step is to activate the_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Draw the mechanism for the following nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.Show the role of DMAP (p-dimethylaminopyridine)in the mechanism along with a resonance state that makes it a better catalyst than pyridine. 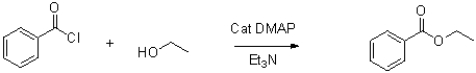


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester in _______________ conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Predict the product of the following reaction scheme and draw a mechanism to support it. 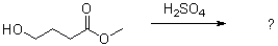
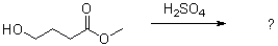

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
NaNO2 forms a diazonium salt from a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
DIBAL reduction of an ester maintained at warm temperature produces a alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In an SNAr reaction,a cyanate substituent acts as an electron _______________ group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
DIBAL reduction of an ester maintained at low temperature produces a ketone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Determine a multistep synthetic scheme to produce the following aromatic product from benzene.Show all intermediates. 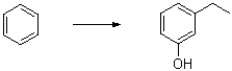


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Reduction of an amide with lithium aluminum hydride results in a(n)_______________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The rate-determining step of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction is the formation of the tetrahedral intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Nucleophilic attack on a carbonyl carbon forms a(n)_______________ intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Determine a multistep synthetic scheme to produce the following aromatic product from benzene. 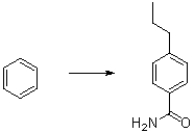


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Predict the product of the following reaction scheme and draw a mechanism to support it. 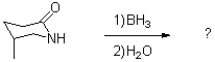
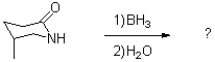

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When undergoing a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction,an acid anhydride leaving group is an alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the reaction of DIBAL with a carboxylic acid,DIBAL acts as a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In an SNAr reaction,the aromatic ð bond acts as a(n)_______________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An acid chloride can be formed from a carboxylic acid along with _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



