Deck 11: Displacement Reactions on Saturated Carbons
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Displacement Reactions on Saturated Carbons
1
Which of the following is the stronger nucleophile and why? 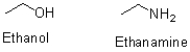
A)Ethanol is stronger because oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen.
B)Ethanamine is stronger because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen.
C)Ethanol is stronger because oxygen has a smaller atomic radius than nitrogen.
D)Ethanamine is stronger because nitrogen has a larger atomic radius than oxygen.
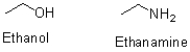
A)Ethanol is stronger because oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen.
B)Ethanamine is stronger because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen.
C)Ethanol is stronger because oxygen has a smaller atomic radius than nitrogen.
D)Ethanamine is stronger because nitrogen has a larger atomic radius than oxygen.
Ethanamine is stronger because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen.
2
Which of the following best describes an SN1 reaction?
A)It is unimolecular and occurs in a single step.
B)It is unimolecular and occurs in two steps.
C)It is bimolecular and occurs in a single step.
D)It is bimolecular and occurs in two steps.
A)It is unimolecular and occurs in a single step.
B)It is unimolecular and occurs in two steps.
C)It is bimolecular and occurs in a single step.
D)It is bimolecular and occurs in two steps.
It is unimolecular and occurs in two steps.
3
Which of the following equations best describes the rate of an SN2 reaction?
A)Rate = k[A]
B)Rate = k[A][B]
C)Rate = k[A]2
D)Rate = k
A)Rate = k[A]
B)Rate = k[A][B]
C)Rate = k[A]2
D)Rate = k
Rate = k[A][B]
4
How do polar protic solvents improve the rate of SN1 reactions?
A)They protonate the leaving group.
B)They stabilize the charge of the transition state.
C)They stabilize the charge of the nucleophile.
D)They stabilized the charge on the generated carbocation.
A)They protonate the leaving group.
B)They stabilize the charge of the transition state.
C)They stabilize the charge of the nucleophile.
D)They stabilized the charge on the generated carbocation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best describes an SN2 reaction?
A)It is unimolecular and occurs in a single step.
B)It is unimolecular and occurs in two steps.
C)It is bimolecular and occurs in a single step.
D)It is bimolecular and occurs in two steps.
A)It is unimolecular and occurs in a single step.
B)It is unimolecular and occurs in two steps.
C)It is bimolecular and occurs in a single step.
D)It is bimolecular and occurs in two steps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following has the smallest effect on an SN1 rate of reaction?
A)strength of the nucleophile
B)quality of leaving group
C)electrophile substituents
D)solvent
A)strength of the nucleophile
B)quality of leaving group
C)electrophile substituents
D)solvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following nucleophiles would have the greatest rate of reaction in an SN2 reaction?
A)(-NH2)
B)(-OH)
C)(-F)
D)(H2O)
A)(-NH2)
B)(-OH)
C)(-F)
D)(H2O)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In an SN2 reaction,what orbital of the electrophile is approached by the nucleophile?
A)ó
B)ó*
C)ð
D)ð*
A)ó
B)ó*
C)ð
D)ð*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following electrophiles would have the greatest rate in an SN2 reaction?
A)
B)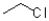
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of an SN2 reaction?
A)The nucleophile attacks and the leaving group leaves in a concerted fashion.
B)The nucleophile forms a bond with the electrophile first,followed by the loss of a leaving group.
C)The leaving group leaves first,followed by the attack of a nucleophile.
D)The electrophile attacks and the leaving group leaves in a concerted fashion.
A)The nucleophile attacks and the leaving group leaves in a concerted fashion.
B)The nucleophile forms a bond with the electrophile first,followed by the loss of a leaving group.
C)The leaving group leaves first,followed by the attack of a nucleophile.
D)The electrophile attacks and the leaving group leaves in a concerted fashion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of an SN2 reaction?
A)The LUMO of a nucleophile interacts with the HOMO of an electrophile.
B)The LUMO of a nucleophile interacts with the LUMO of an electrophile.
C)The HOMO of a nucleophile interacts with the HOMO of an electrophile.
D)The HOMO of a nucleophile interacts with the LUMO of an electrophile.
A)The LUMO of a nucleophile interacts with the HOMO of an electrophile.
B)The LUMO of a nucleophile interacts with the LUMO of an electrophile.
C)The HOMO of a nucleophile interacts with the HOMO of an electrophile.
D)The HOMO of a nucleophile interacts with the LUMO of an electrophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following conditions would most favour an SN2 reaction with a secondary á-carbon?
A)strong nucleophile and protic solvent
B)weak nucleophile and protic solvent
C)strong nucleophile and aprotic solvent
D)weak nucleophile and aprotic solvent
A)strong nucleophile and protic solvent
B)weak nucleophile and protic solvent
C)strong nucleophile and aprotic solvent
D)weak nucleophile and aprotic solvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Given the conditions provided in the reaction scheme below,what would be the expected product? 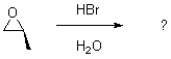
A)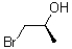
B)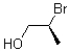
C)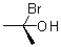
D)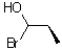

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the predicted geometry of an SN2 reaction transition state?
A)trigonal planar
B)tetrahedral
C)trigonal bipyramidal
D)trigonal pyramidal
A)trigonal planar
B)tetrahedral
C)trigonal bipyramidal
D)trigonal pyramidal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following would NOT form a stabilized carbocation in an SN1 reaction mechanism?
A)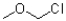
B)
C)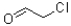
D)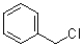
A)
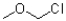
B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements best describes the nucleophilicity and leaving group capabilities of halogens?
A)I- is both a worse nucleophile and leaving group compared to Cl-.
B)I- is a worse nucleophile and a better leaving group compared to Cl-.
C)I- is a better nucleophile and a worse leaving group compared to Cl-.
D)I- is both a better nucleophile and leaving group compared to Cl-.
A)I- is both a worse nucleophile and leaving group compared to Cl-.
B)I- is a worse nucleophile and a better leaving group compared to Cl-.
C)I- is a better nucleophile and a worse leaving group compared to Cl-.
D)I- is both a better nucleophile and leaving group compared to Cl-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would act as the leaving group in the reaction shown below? 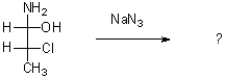
A)(-OH)
B)(-NH2)
C)(-CH3)
D)(-Cl)
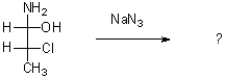
A)(-OH)
B)(-NH2)
C)(-CH3)
D)(-Cl)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is the stronger nucleophile shown below and why? 
A)Acetate is stronger because the charge is delocalized.
B)Ethanoate is stronger because the charge is not delocalized.
C)Ethanoate is stronger because it is less sterically hindered.
D)Both acetate and ethanoate are equally strong nucleophiles.

A)Acetate is stronger because the charge is delocalized.
B)Ethanoate is stronger because the charge is not delocalized.
C)Ethanoate is stronger because it is less sterically hindered.
D)Both acetate and ethanoate are equally strong nucleophiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In an SN1 reaction,what sort of stereochemistry is observed in the product?
A)inversion of stereochemistry
B)retention of stereochemistry
C)a racemic mixture
D)Stereochemistry plays no role in SN1 reactions.
A)inversion of stereochemistry
B)retention of stereochemistry
C)a racemic mixture
D)Stereochemistry plays no role in SN1 reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the predicted geometry of an SN2 reaction intermediate?
A)trigonal planar
B)tetrahedral
C)trigonal bipyramidal
D)trigonal pyramidal
A)trigonal planar
B)tetrahedral
C)trigonal bipyramidal
D)trigonal pyramidal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following would be the most stable carbocation?
A)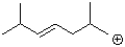
B)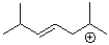
C)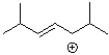
D)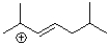
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is considered a polar solvent?
A)dimethylsulfoxide
B)dimethylformamide
C)ethanol
D)acetonitrile
A)dimethylsulfoxide
B)dimethylformamide
C)ethanol
D)acetonitrile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Polar protic solvents increase the rate of SN1 reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following would be the major product of the reaction shown below? 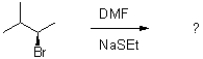
A)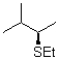
B)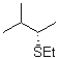
C)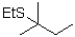
D)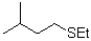

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How would you best describe the alkyl halide shown below? 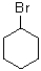
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary

A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following electrophiles would undergo the slowest rate of reaction?
A)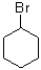
B)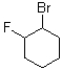
C)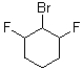
D)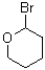
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the product of the epoxide opening reaction under basic conditions shown below? 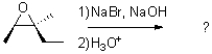
A)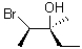
B)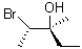
C)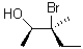
D)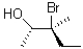
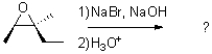
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Strength of a nucleophile has no effect in an SN1 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is the strongest nucleophile?
A)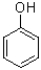
B)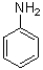
C)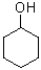
D)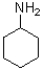
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following mechanisms is preferred for the electrophile shown below? 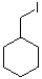
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)Both SN1 and SN2
D)Neither SN1 nor SN2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)Both SN1 and SN2
D)Neither SN1 nor SN2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
SN2 reactions lead to an inversion of stereochemistry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following equations best describes the rate of an SN2 reaction?
A)Rate = k[A]
B)Rate = k[A][B]
C)Rate = k[A]2
D)Rate = k
A)Rate = k[A]
B)Rate = k[A][B]
C)Rate = k[A]2
D)Rate = k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following mechanisms is preferred for the electrophile shown below? 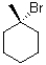
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)both SN1 and SN2
D)neither SN1 nor SN2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)both SN1 and SN2
D)neither SN1 nor SN2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following conditions would most favour an SN1 reaction with a secondary á-carbon?
A)strong nucleophile and protic solvent
B)weak nucleophile and protic solvent
C)strong nucleophile and aprotic solvent
D)weak nucleophile and aprotic solvent
A)strong nucleophile and protic solvent
B)weak nucleophile and protic solvent
C)strong nucleophile and aprotic solvent
D)weak nucleophile and aprotic solvent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is the best electrophile?
A)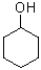
B)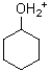
C)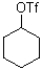
D)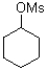
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following mechanisms is preferred for the electrophile shown below? 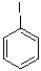
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)both SN1 and SN2
D)neither SN1 nor SN2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)both SN1 and SN2
D)neither SN1 nor SN2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
SN2 reactions lead to a racemic mixture of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Electrophiles act as electron donors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following electrophiles is most likely to go through an SN1 reaction?
A)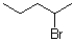
B)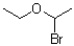
C)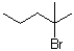
D)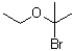
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following mechanisms is preferred for the electrophile shown below? 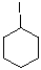
A)SN1
B)SN2
C)both SN1 and SN2
D)neither SN1 nor SN2

A)SN1
B)SN2
C)both SN1 and SN2
D)neither SN1 nor SN2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Primary substrates react faster than secondary substrates through the SN2 mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Delocalization of electrons increases the nucleophilicity of a molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The more electronegative an atom is,the better a leaving group it is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Identity of the leaving group is important in SN1 reactions but not SN2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Amines are more nucleophilic than alcohols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A thiol is a stronger nucleophile than an alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A benzylic halide is more electrophilic then an allylic halide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The higher the electronegativity of an atom,the more nucleophilic it is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Gabriel synthesis involves the use of an azide to make an amine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Basic conditions promote nucleophillic attack on the more substituted position of an epoxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Formation of a carbocation intermediate is the rate determining step in SN1 reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In substitution reactions,the leaving group always takes a pair of electrons with it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Concerted reactions are those whereupon the steps of a reaction occur separately from each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Increase in atomic size leads to decreased nucleophilicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Cl- is a better leaving group than I-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Acetate is a stronger nucleophile than hydroxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Weak nucleophiles will promote the SN1 mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An SN1 reaction goes through a carbocation intermediate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Neighbouring inductive electron withdrawing groups can speed up an SN2 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Delocalization can stabilize a carbocation in SN1 reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Another name for the electron donor in the substitution reaction is the _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Gabriel synthesis used _______________ as a source of nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
DMSO is an example of a(n)_______________ solvent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Provide a mechanism for the transformation shown below. 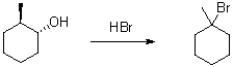


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Provide a mechanism for the transformation shown below. 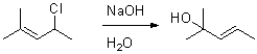


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Under the following reaction conditions,a mixture of three products were formed.Draw the three products. 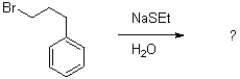


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Propose a mechanism for the transformation shown below. 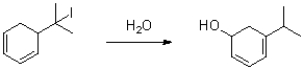


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
SN2 reactions lead to _______________ of stereochemistry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Nucleophilicity is _______________ in aprotic solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The transition state of an SN2 reaction has a(n)_______________ geometry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Substitution reactions that go through the _______________ run the risk of carbocation rearrangements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Provide a mechanism for the following transformation. 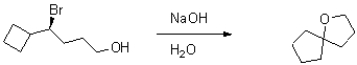


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A tertiary á carbon structure will more likely undergo a(n)_______________ reaction mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Neighbouring alkyl groups stabilize carbocations through _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The intermediate of an SN1 reaction has a(n)_______________ geometry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Draw two different sets of reactants that form the product in the following SN1 reaction.One should contain an aromatic nucleophile and one should contain an aromatic electrophile.Which set is a better set of electrophiles and why? 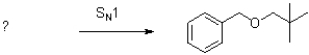


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Predict the product of the following reaction under both SN1 and SN2 conditions. 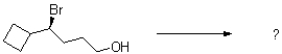
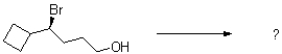

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



