Deck 7: Ð Bonds As Electrophiles
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Ð Bonds As Electrophiles
1
What is the hybridization of the intermediate in the following reaction? 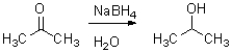
A)sp
B)sp2
C)sp3
D)s

A)sp
B)sp2
C)sp3
D)s
sp3
2
Which of the following best describes the carbon bound to magnesium in a Grignard reagent?
A)electropositive and nucleophilic
B)electropositive and electrophilic
C)electronegative and nucleophilic
D)electronegative and electrophilic
A)electropositive and nucleophilic
B)electropositive and electrophilic
C)electronegative and nucleophilic
D)electronegative and electrophilic
electronegative and nucleophilic
3
What does a nucleophilic attack on a carbonyl by a hydride result in?
A)ether
B)alcohol
C)ketone
D)carboxylic acid
A)ether
B)alcohol
C)ketone
D)carboxylic acid
alcohol
4
Which reaction scheme would accomplish the transformation shown below? 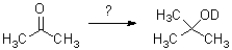
A)1)MgBrMe,Et2O 2)D2O
B)D2O
C)NaBD4,EtOH
D)NaBH4,EtOD

A)1)MgBrMe,Et2O 2)D2O
B)D2O
C)NaBD4,EtOH
D)NaBH4,EtOD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the functional group shown below? 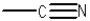
A)amine
B)imine
C)enamine
D)nitrile
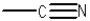
A)amine
B)imine
C)enamine
D)nitrile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the product of the following reaction (D = deuterium,an isotope of hydrogen)? 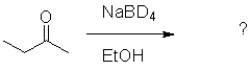
A)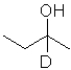
B)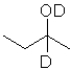
C)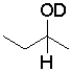
D)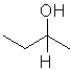

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the electrophilic reactant B in the following reaction scheme? 
A)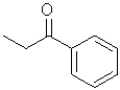
B)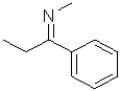
C)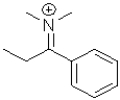
D)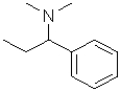

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following best describes a carbonyl ð bond?
A)The atoms are sp2 hybridized and the ð bond is parallel to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
B)The atoms are sp2 hybridized and the ð bond is perpendicular to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
C)The atoms are sp3 hybridized and the ð bond is parallel to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
D)The atoms are sp3 hybridized and the ð bond is perpendicular to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
A)The atoms are sp2 hybridized and the ð bond is parallel to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
B)The atoms are sp2 hybridized and the ð bond is perpendicular to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
C)The atoms are sp3 hybridized and the ð bond is parallel to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.
D)The atoms are sp3 hybridized and the ð bond is perpendicular to the plane of the carbonyl atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which resonance state contributes most to the observed electrophilic reactivity of imines? 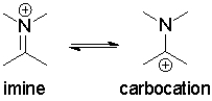
A)the imine,because it's the most stable resonance form
B)the imine,because the positive site contains a complete octet
C)the carbocation,because it's the least stable resonance form
D)the carbocation,because the positive site contains an open p orbital

A)the imine,because it's the most stable resonance form
B)the imine,because the positive site contains a complete octet
C)the carbocation,because it's the least stable resonance form
D)the carbocation,because the positive site contains an open p orbital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the role of ethanol in the following reaction? 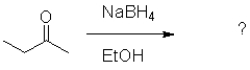
A)to activate the sodium borohydride reagent
B)to act solely as a solvent
C)to protonate the alkoxide formed during the reaction
D)to act as a nucleophile

A)to activate the sodium borohydride reagent
B)to act solely as a solvent
C)to protonate the alkoxide formed during the reaction
D)to act as a nucleophile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes the carbon atom in a carbonyl functional group?
A)It is electrophilic and has a partial positive charge.
B)It is electrophilic and has a partial negative charge.
C)It is nucleophilic and has a partial positive charge.
D)It is nucleophilic and has a partial negative charge.
A)It is electrophilic and has a partial positive charge.
B)It is electrophilic and has a partial negative charge.
C)It is nucleophilic and has a partial positive charge.
D)It is nucleophilic and has a partial negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which resonance is more heavily favoured and why? 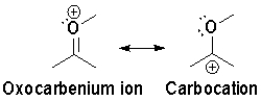
A)the oxocarbenium ion,because ð bonds are more stable than lone pairs
B)the oxocarbenium ion,because all atoms have a full octet
C)the carbocation,because the positive charge is on the least electronegative atom
D)the carbocation,because lone pair electrons are more stable than ð bonds

A)the oxocarbenium ion,because ð bonds are more stable than lone pairs
B)the oxocarbenium ion,because all atoms have a full octet
C)the carbocation,because the positive charge is on the least electronegative atom
D)the carbocation,because lone pair electrons are more stable than ð bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which functional group is more reactive as an electrophile and why?
A)Aldehydes are more reactive electrophiles because they experience more electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
B)Aldehydes are more reactive electrophiles because they experience less electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
C)Ketones are more reactive electrophiles because they experience more electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
D)Ketones are more reactive electrophiles because they experience less electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
A)Aldehydes are more reactive electrophiles because they experience more electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
B)Aldehydes are more reactive electrophiles because they experience less electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
C)Ketones are more reactive electrophiles because they experience more electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.
D)Ketones are more reactive electrophiles because they experience less electron induction from neighbouring alkyl chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following best describes the reduction of a ketone to an alcohol by lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4)?
A)A hydride nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon,followed by electrostatic stabilization of the alkoxide oxygen by lithium,followed by acidic protonation of the alkoxide.
B)Lithium aluminum hydride transfers a hydrogen to both the carbonyl carbon and oxygen,resulting in an alcohol.
C)A hydride nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon,followed by nucleophilic attack of AlH3 by the generated alkoxide,followed by acidic or basic conversion of the alkoyxaluminum hydride product to an alcohol.
D)Acidic protonation of the carbonyl,followed by neutralization of charge by the ð electrons,followed by nucleophilic attack by hydride.
A)A hydride nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon,followed by electrostatic stabilization of the alkoxide oxygen by lithium,followed by acidic protonation of the alkoxide.
B)Lithium aluminum hydride transfers a hydrogen to both the carbonyl carbon and oxygen,resulting in an alcohol.
C)A hydride nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon,followed by nucleophilic attack of AlH3 by the generated alkoxide,followed by acidic or basic conversion of the alkoyxaluminum hydride product to an alcohol.
D)Acidic protonation of the carbonyl,followed by neutralization of charge by the ð electrons,followed by nucleophilic attack by hydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the following Grignard reaction,what are the nucleophilic and electrophilic sites? 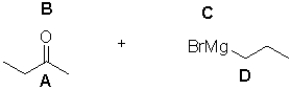
A)A is electrophilic;D is nucleophilic
B)A is nucleophilic;C is electrophilic
C)B is nucleophilic;C is electrophilic
D)B is electrophilic;D is nucleophilic
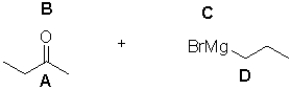
A)A is electrophilic;D is nucleophilic
B)A is nucleophilic;C is electrophilic
C)B is nucleophilic;C is electrophilic
D)B is electrophilic;D is nucleophilic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why is the oxocarbenium ion the more stabilized resonance state? 
A)because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and prefers to carry the charge as a result
B)because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and prefers ð bonds as a result
C)because all atoms have a full octet in this resonance state
D)because ketones are more stable than ethers

A)because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and prefers to carry the charge as a result
B)because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and prefers ð bonds as a result
C)because all atoms have a full octet in this resonance state
D)because ketones are more stable than ethers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the product of the following reaction (D = deuterium,an isotope of hydrogen)? 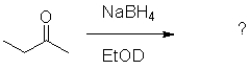
A)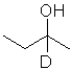
B)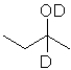
C)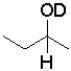
D)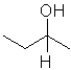

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the electrophilic reactant A in the following reaction scheme? 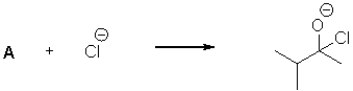
A)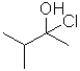
B)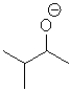
C)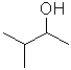
D)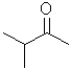

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the expected product of the following transformation? 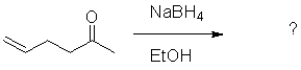
A)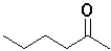
B)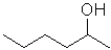
C)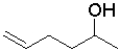
D)
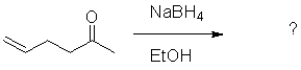
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the product of the following transformation? 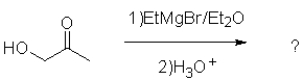
A)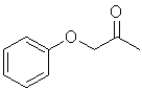
B)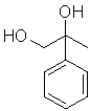
C)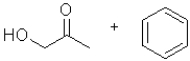
D)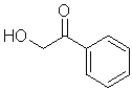
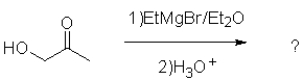
A)

B)

C)
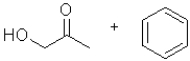
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What would be the most likely product from the reaction scheme below? 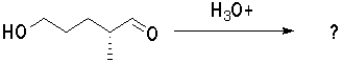
A)
B)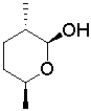
C)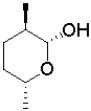
D)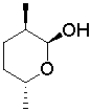
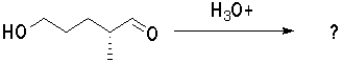
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following molecules will undergo intramolecular hemiacetal formation under acidic conditions the fastest?
A)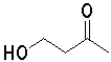
B)
C)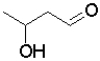
D)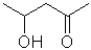
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the expected major product of the following transformation? 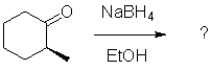
A)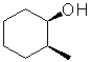
B)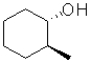
C)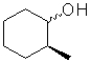
D)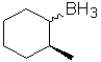
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is a major difference between acid and base catalyzed hydration of a carbonyl?
A)Base deprotonates water and acid protonates the carbonyl in the first step of the mechanism.
B)Base deprotonates water and acid protonates the alkoxide in the second step of the mechanism.
C)Base deprotonates the carbonyl and acid protonates water in the first step of the mechanism.
D)Base deprotonates the carbonyl and acid protonates water in the second step of the mechanism.
A)Base deprotonates water and acid protonates the carbonyl in the first step of the mechanism.
B)Base deprotonates water and acid protonates the alkoxide in the second step of the mechanism.
C)Base deprotonates the carbonyl and acid protonates water in the first step of the mechanism.
D)Base deprotonates the carbonyl and acid protonates water in the second step of the mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which orbital of a carbonyl group accepts electrons from an incoming nucleophile?
A)ó
B)ð
C)ð*
D)ó*
A)ó
B)ð
C)ð*
D)ó*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What would be the most likely product from the reaction scheme below? 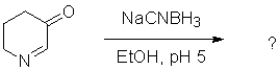
A)
B)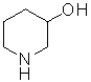
C)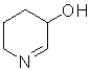
D)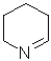

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the role of acid in the following reaction? 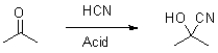
A)to protonate the negatively charged cyanide
B)to stabilize the ketone
C)to protonate the formed alkoxide
D)to form hydrogen bonds with the nitrogen in the cyanide ion

A)to protonate the negatively charged cyanide
B)to stabilize the ketone
C)to protonate the formed alkoxide
D)to form hydrogen bonds with the nitrogen in the cyanide ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which molecule would undergo the fastest reduction with sodium borohydride (NaBH4)and why?
A)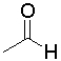 because it is the least sterically hindered
because it is the least sterically hindered
B)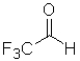 because it is the least sterically hindered
because it is the least sterically hindered
C)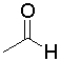 because it contains the most electropositive carbonyl due to induction
because it contains the most electropositive carbonyl due to induction
D)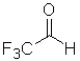
A)
 because it is the least sterically hindered
because it is the least sterically hinderedB)
 because it is the least sterically hindered
because it is the least sterically hinderedC)
 because it contains the most electropositive carbonyl due to induction
because it contains the most electropositive carbonyl due to inductionD)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the functional group shown below? 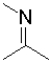
A)amine
B)imine
C)enamine
D)nitrile

A)amine
B)imine
C)enamine
D)nitrile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best describes the formation of a hemiacetal?
A)The presence of an acid speeds up the rate of formation on a hemiacetal,whereas the presence of a base has no influence in the rate of formation of a hemiacetal.
B)The presence of an acid has no influence in the rate of formation on a hemiacetal,whereas the presence of a base speeds up the rate of formation of a hemiacetal.
C)Both the presence of an acid and a base speed up the rate of formation on a hemiacetal.
D)The presence of either an acid or a base have no influence in the rate of formation of a hemiacetal.
A)The presence of an acid speeds up the rate of formation on a hemiacetal,whereas the presence of a base has no influence in the rate of formation of a hemiacetal.
B)The presence of an acid has no influence in the rate of formation on a hemiacetal,whereas the presence of a base speeds up the rate of formation of a hemiacetal.
C)Both the presence of an acid and a base speed up the rate of formation on a hemiacetal.
D)The presence of either an acid or a base have no influence in the rate of formation of a hemiacetal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following reactants would most readily form an aldehyde under basic conditions?
A)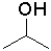
B)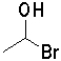
C)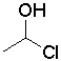
D)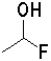
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following best describes the nucleophilic attack of a carbonyl?
A)The nucleophile donates electrons into the LUMO of an electrophile,which is the ð* orbital.
B)The nucleophile donates electrons into the LUMO of an electrophile,which is the ó* orbital.
C)The nucleophile donates electrons into the HOMO of an electrophile,which is the ð* orbital.
D)The nucleophile donates electrons into the HOMO of an electrophile,which is the ó* orbital.
A)The nucleophile donates electrons into the LUMO of an electrophile,which is the ð* orbital.
B)The nucleophile donates electrons into the LUMO of an electrophile,which is the ó* orbital.
C)The nucleophile donates electrons into the HOMO of an electrophile,which is the ð* orbital.
D)The nucleophile donates electrons into the HOMO of an electrophile,which is the ó* orbital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which reagent best reduces an imine to an amine and why?
A)NaBH4 because it contains the most nucleophilic hydride
B)NaBH4 because it is unreactive with acid
C)NaCNBH3 because it contains the most nucleophilic hydride
D)NaCNBH3 because it is unreactive with acid
A)NaBH4 because it contains the most nucleophilic hydride
B)NaBH4 because it is unreactive with acid
C)NaCNBH3 because it contains the most nucleophilic hydride
D)NaCNBH3 because it is unreactive with acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What would be the most likely product from the reaction scheme below? 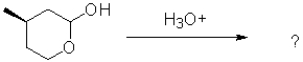
A)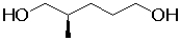
B)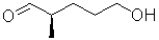
C)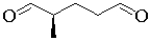
D)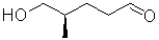
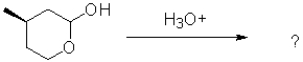
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following equilibrium of a ketone hydration shown below.Which reactant would have the largest equilibrium constant for this reaction? 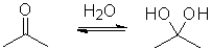
A)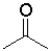
B)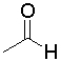
C)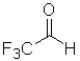
D)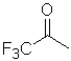
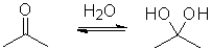
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the expected major product of the following transformation? 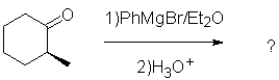
A)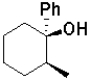
B)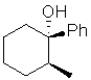
C)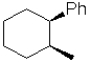
D)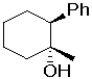
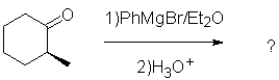
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the functional group shown below? 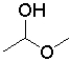
A)ether
B)alcohol
C)acetal
D)hemiacetal

A)ether
B)alcohol
C)acetal
D)hemiacetal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Considering the cyanide ion CN-,which atom acts as a nucleophile and why?
A)carbon because it bears the only lone pair
B)nitrogen because it bears the only lone pair
C)carbon because it has a formal charge of -1
D)nitrogen because it has a formal charge of -1
A)carbon because it bears the only lone pair
B)nitrogen because it bears the only lone pair
C)carbon because it has a formal charge of -1
D)nitrogen because it has a formal charge of -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What are the partial charges at each site shown? 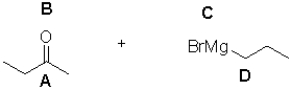
A)A: ä+ B: ä- C: ä+ D:ä-
B)A: ä+ B: ä- C: ä- D:ä+
C)A: ä- B: ä+ C: ä+ D:ä-
D)A: ä- B: ä+ C: ä- D:ä+
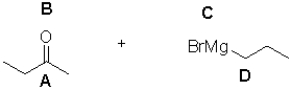
A)A: ä+ B: ä- C: ä+ D:ä-
B)A: ä+ B: ä- C: ä- D:ä+
C)A: ä- B: ä+ C: ä+ D:ä-
D)A: ä- B: ä+ C: ä- D:ä+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following molecules will undergo intramolecular hemiacetal formation under acidic conditions the fastest?
A)
B)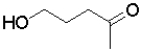
C)
D)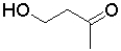
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An aldehyde functional group is more oxidized than an alcohol functional group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An imine functional group is more oxidized than a ketone functional group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the product of the following transformation? 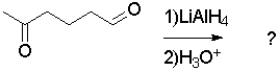
A)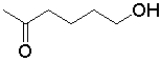
B)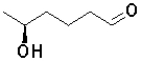
C)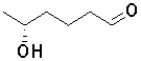
D)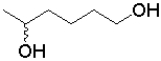

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A leaving group always takes a pair of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following best represents the change in oxidation state from reactant to product in the transformation below? 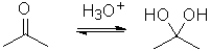
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)There is no change.
D)There is not enough information to determine change.
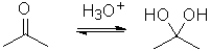
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)There is no change.
D)There is not enough information to determine change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Grignard reagents are prepared from elemental magnesium and an alkyl halide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following best represents the change in oxidation state from reactant to product in the transformation below? 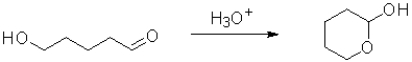
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)There is no change.
D)There is not enough information to determine change.
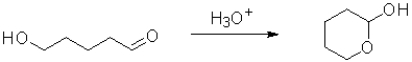
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)There is no change.
D)There is not enough information to determine change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Sodium borohydride reductions of aldehydes can be performed in protic solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Good leaving groups tend to be strong bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Aldehydes form hydrates faster than ketones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The carbonyl ð* orbital accepts electrons from the incoming nucleophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements best reflects the roles of acids and bases in the catalysis of carbonyl reactions?
A)Acids activate nucleophiles;bases activate electrophiles.
B)Acids activate electrophiles;bases activate nucleophiles.
C)Acids and bases both activate nucleophiles.
D)Acids and bases both activate electrophiles.
A)Acids activate nucleophiles;bases activate electrophiles.
B)Acids activate electrophiles;bases activate nucleophiles.
C)Acids and bases both activate nucleophiles.
D)Acids and bases both activate electrophiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following molecules represents the most oxidized state?
A)
B)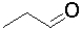
C)
D)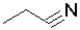
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Basic conditions are required for the reduction of an imine to an amine using sodium cyanoborohydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following best represents the change in oxidation state from reactant to product in the transformation below? 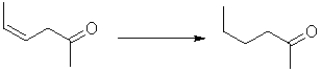
A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)There is no change.
D)There is not enough information to determine change.

A)It increases.
B)It decreases.
C)There is no change.
D)There is not enough information to determine change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Protonation of an imine makes it a better electrophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Lithium aluminum hydride reductions of ketones can be performed in protic solvents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Acetylides act as electrophiles in the presence of a ketone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Grignard reactions are performed in ethereal solutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Grignard reagents act as nucleophiles in the presence of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Positively charged imines are worse electrophiles than neutral imines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Nucleophilic attack of a nitrile on a carbonyl results in a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Lithium aluminum hydride is more reactive than sodium borohydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The LUMO orbital in the carbonyl bond is the _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Aldehydes are in fast equilibrium with their hydrated form in aqueous solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The nucleophilic attack of an alcohol on a ketone in acidic conditions forms a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A ketone must contain neighbouring electron withdrawing CF3 groups for a hydrate to form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Acid acts to protonate the alkoxide in the cyanohydrin formation reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Neighbouring _______________ groups shift the equilibrium from ketones towards hydrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
One molecule of lithium aluminum hydride can react with up to four carbonyl groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Going from a ketone to an alcohol is an example of a(n)_______________ reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Grignard reagents are compatible with all functional groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Intramolecular reactions occur most readily when they form _______________ membered rings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Hydrogen acts as a nucleophile in borohydride since it is less electronegative than boron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Lithium aluminum hydride is _______________ reactive then sodium borohydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Aldehydes are less electrophilic than ketones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
_______________ is used in lieu of NaBH4 to reduce imines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Intramolecular reactions are favoured when five- and six-membered rings are formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Aldehydes form hydrates in aqueous solution whereas ketones do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The Grignard reagents acts as a(n)_______________ in its reaction with a carbonyl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



