Deck 6: Acids and Bases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Acids and Bases
1
What hybridization best stabilizes the negative charge of conjugate bases?
A)p
B)sp
C)sp2
D)sp3
A)p
B)sp
C)sp2
D)sp3
sp
2
Figure 1
Figure 1 is a list of pKa values for various organic functional groups.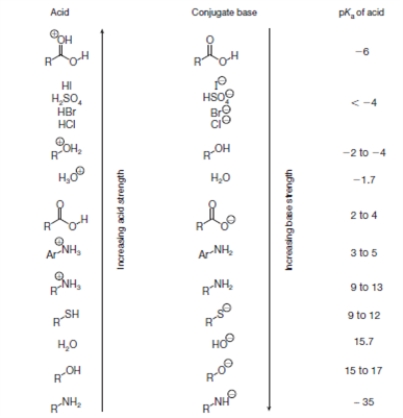
Referring to Figure 1,what is the most acidic proton in the following molecule?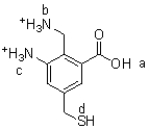
A)Choice a
B)Choice b
C)Choice c
D)Choice d
Figure 1 is a list of pKa values for various organic functional groups.

Referring to Figure 1,what is the most acidic proton in the following molecule?

A)Choice a
B)Choice b
C)Choice c
D)Choice d
Choice a
3
Given the structure and pKa of analine (shown below),what can be said about its protonation state at pH 4.9? 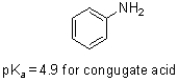
A)˜100%
B)˜100%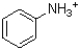
C)˜50%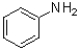 ,˜50%
,˜50%
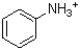
D)There is not enough data to evaluate.

A)˜100%

B)˜100%

C)˜50%
 ,˜50%
,˜50%
D)There is not enough data to evaluate.
˜50%  ,˜50%
,˜50%

 ,˜50%
,˜50%
4
What is the definition of a Lewis base?
A)a proton donor
B)a proton acceptor
C)an electron donor
D)an electron acceptor
A)a proton donor
B)a proton acceptor
C)an electron donor
D)an electron acceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the definition of a Brønsted acid?
A)proton donor
B)proton acceptor
C)electron donor
D)electron acceptor
A)proton donor
B)proton acceptor
C)electron donor
D)electron acceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given the structure and pKa of 2,2,2 trifluoroethanol (shown below),what can be said about its protonation state at pH 10? 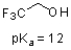
A)It will exist mostly in the protonated form.
B)It will exist mostly in the deprotonated form.
C)It will be 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
D)There is not enough data to evaluate.
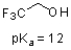
A)It will exist mostly in the protonated form.
B)It will exist mostly in the deprotonated form.
C)It will be 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
D)There is not enough data to evaluate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which acid shown below is stronger and why? 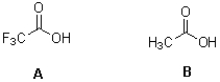
A)A due to charge delocalization
B)B due to charge delocalization
C)A due to induction
D)B due to induction
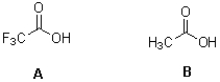
A)A due to charge delocalization
B)B due to charge delocalization
C)A due to induction
D)B due to induction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which acid shown below is stronger and why? 
A)A due to atomic size
B)B due to atomic size
C)A due to electronegativity
D)B due to electronegativity

A)A due to atomic size
B)B due to atomic size
C)A due to electronegativity
D)B due to electronegativity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which acid shown below is stronger and why? 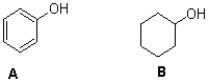
A)A due to charge delocalization
B)B due to charge delocalization
C)A due to hybridization
D)B due to hybridization

A)A due to charge delocalization
B)B due to charge delocalization
C)A due to hybridization
D)B due to hybridization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the role of induction in conjugate base stability?
A)Larger atoms are better capable of dispersing the negative charge of the conjugate base.
B)Electronegative atoms are better able to carry negative charge.
C)Neighbouring electronegative groups can help distribute charge over a wider area.
D)Higher s character helps stabilize negative charge.
A)Larger atoms are better capable of dispersing the negative charge of the conjugate base.
B)Electronegative atoms are better able to carry negative charge.
C)Neighbouring electronegative groups can help distribute charge over a wider area.
D)Higher s character helps stabilize negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Given the structure and pKa of pyridine (shown below),what can be said about its protonation state at pH 7? 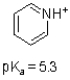
A)It will exist mostly in the protonated form.
B)It will exist mostly in the deprotonated form.
C)It will be 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
D)There is not enough data to evaluate.

A)It will exist mostly in the protonated form.
B)It will exist mostly in the deprotonated form.
C)It will be 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
D)There is not enough data to evaluate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which side will the equilibrium of the following acid/base reaction lie and why? 
A)to the left because ethoxide is a stronger base than acetate
B)to the left because acetate is a stronger base than ethoxide
C)to the right because ethoxide is a stronger base than acetate
D)to the right because acetate is a stronger base than ethoxide

A)to the left because ethoxide is a stronger base than acetate
B)to the left because acetate is a stronger base than ethoxide
C)to the right because ethoxide is a stronger base than acetate
D)to the right because acetate is a stronger base than ethoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the role of atomic size in conjugate base stability?
A)Larger atoms can disperse developed charge better than smaller atoms,making them better acids.
B)Smaller atoms can disperse developed charge better than larger atoms,making them better acids.
C)Larger atoms can disperse developed charge better than smaller atoms,making them worse acids.
D)Smaller atoms can disperse developed charge better than larger atoms,making them worse acids.
A)Larger atoms can disperse developed charge better than smaller atoms,making them better acids.
B)Smaller atoms can disperse developed charge better than larger atoms,making them better acids.
C)Larger atoms can disperse developed charge better than smaller atoms,making them worse acids.
D)Smaller atoms can disperse developed charge better than larger atoms,making them worse acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following best describes BF3?
A)Brønsted acid
B)Brønsted base
C)Lewis acid
D)Lewis base
A)Brønsted acid
B)Brønsted base
C)Lewis acid
D)Lewis base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What characterizes weak acids in comparison to strong acids?
A)a larger Ka and a larger pKa
B)a larger Ka and a smaller pKa
C)a smaller Ka and a larger pKa
D)a smaller Ka and a smaller pKa
A)a larger Ka and a larger pKa
B)a larger Ka and a smaller pKa
C)a smaller Ka and a larger pKa
D)a smaller Ka and a smaller pKa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which acid shown below is stronger and why? 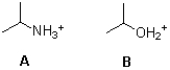
A)A because nitrogen is more electronegative
B)A because oxygen is more electronegative
C)B because nitrogen is more electronegative
D)B because oxygen is more electronegative
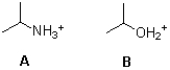
A)A because nitrogen is more electronegative
B)A because oxygen is more electronegative
C)B because nitrogen is more electronegative
D)B because oxygen is more electronegative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which is the most acidic proton in the molecule shown below? 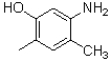
A)The methyl proton is the most acidic.
B)The amino proton is the most acidic.
C)The hydroxyl proton is the most acidic.
D)All groups are equally acidic is the most acidic.

A)The methyl proton is the most acidic.
B)The amino proton is the most acidic.
C)The hydroxyl proton is the most acidic.
D)All groups are equally acidic is the most acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the phenols shown below is the stronger acid,and why? 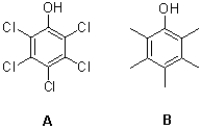
A)A,because the chloride groups are inductively electron donating
B)A,because the chloride groups are inductively electron withdrawing
C)B,because the methyl groups are inductively electron donating
D)B,because the methyl groups are inductively electron withdrawing

A)A,because the chloride groups are inductively electron donating
B)A,because the chloride groups are inductively electron withdrawing
C)B,because the methyl groups are inductively electron donating
D)B,because the methyl groups are inductively electron withdrawing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Rank these compounds in order of increasing basicity.(Least basic to most basic) 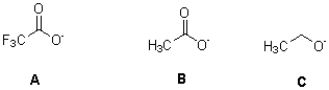
A)C,B,A
B)B,A,C
C)C,A,B
D)A,B,C

A)C,B,A
B)B,A,C
C)C,A,B
D)A,B,C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 1
Figure 1 is a list of pKa values for various organic functional groups.
Referring to Figure 1,on what side of the equilibrium will the following reaction lie?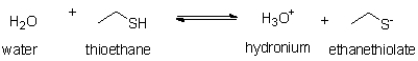
A)the left,because water has a higher pKa than thioethane
B)the right,because water has a higher pKa than thioethane
C)the left,because hydronium has a lower pKa than thioethane
D)the right,because hydronium has a lower pKa than thioethane
Figure 1 is a list of pKa values for various organic functional groups.

Referring to Figure 1,on what side of the equilibrium will the following reaction lie?

A)the left,because water has a higher pKa than thioethane
B)the right,because water has a higher pKa than thioethane
C)the left,because hydronium has a lower pKa than thioethane
D)the right,because hydronium has a lower pKa than thioethane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which molecule shown below would you expect to be most acidic and why? 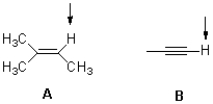
A)A,due to charge delocalization
B)B,due to charge delocalization
C)A,due to hybridization
D)B,due to hybridization

A)A,due to charge delocalization
B)B,due to charge delocalization
C)A,due to hybridization
D)B,due to hybridization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Given the following reaction scheme,what best describes ethanethiolate? 
A)It is an acid.
B)It is a base.
C)It is a conjugate acid.
D)It is a conjugate base.

A)It is an acid.
B)It is a base.
C)It is a conjugate acid.
D)It is a conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Electron withdrawing groups stabilize conjugate bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following best describes the molecules shown below? 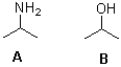
A)A is the stronger base;B is the stronger acid.
B)A is the stronger acid;B is the stronger base.
C)A is the stronger base and the stronger acid.
D)B is the stronger base and the stronger acid.

A)A is the stronger base;B is the stronger acid.
B)A is the stronger acid;B is the stronger base.
C)A is the stronger base and the stronger acid.
D)B is the stronger base and the stronger acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Rank the following molecules in terms of increasing acidity (from least to most). 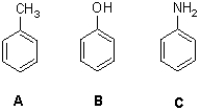
A)A,B,C
B)C,B,A
C)B,C,A
D)A,C,B

A)A,B,C
B)C,B,A
C)B,C,A
D)A,C,B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Given the following reaction scheme,what best describes water? 
A)It is an acid.
B)It is a base.
C)It is a conjugate acid.
D)It is a conjugate base.

A)It is an acid.
B)It is a base.
C)It is a conjugate acid.
D)It is a conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following molecules is the stronger acid and why? 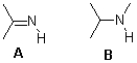
A)A,due to charge delocalization
B)B,due to charge delocalization
C)A,due to hybridization
D)B,due to hybridization
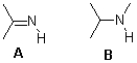
A)A,due to charge delocalization
B)B,due to charge delocalization
C)A,due to hybridization
D)B,due to hybridization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A Lewis acid is an electron acceptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Acidity increases going down the periodic table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Compound A has a pKa of 10 and compound B has a pKa of 5.How many times more acidic is compound B compared to A?
A)2 times more acidic
B)5 times more acidic
C)10 000 times more acidic
D)50 000 times more acidic
A)2 times more acidic
B)5 times more acidic
C)10 000 times more acidic
D)50 000 times more acidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Rank the labelled protons in the following molecule in order of increasing acidity (from least acidic to most acidic). 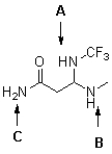
A)A,B,C
B)C,B,A
C)C,A,B
D)B,A,C

A)A,B,C
B)C,B,A
C)C,A,B
D)B,A,C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which proton is expected to be the most acidic in the molecule shown below? 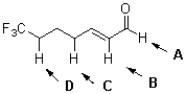
A)a!
B)b!
C)c!
D)d!

A)a!
B)b!
C)c!
D)d!

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which proton in the following molecule is more acidic and why? 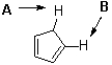
A)A,because of charge distribution
B)A,because of hybridization
C)B,because of charge distribution
D)B,because of hybridization

A)A,because of charge distribution
B)A,because of hybridization
C)B,because of charge distribution
D)B,because of hybridization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the indicated protons in the following molecule is more acidic and why? 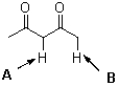
A)A,because of greater charge distribution
B)A,because of greater induction
C)B,because of greater charge distribution
D)B,because of greater induction

A)A,because of greater charge distribution
B)A,because of greater induction
C)B,because of greater charge distribution
D)B,because of greater induction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following best describes the molecules shown below? 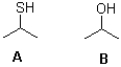
A)A is the stronger base;B is the stronger acid.
B)A is the stronger acid;B is the stronger base.
C)A is the stronger base and the stronger acid.
D)B is the stronger base and the stronger acid.

A)A is the stronger base;B is the stronger acid.
B)A is the stronger acid;B is the stronger base.
C)A is the stronger base and the stronger acid.
D)B is the stronger base and the stronger acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A Brønsted base is a molecule that contains hydroxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Rank the labelled amines in the following molecule in order of increasing basicity (from least basic to most basic). 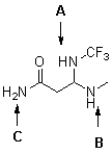
A)A,C,B
B)C,B,A
C)C,A,B
D)B,A,C

A)A,C,B
B)C,B,A
C)C,A,B
D)B,A,C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given the following reaction scheme,which molecule is the base? 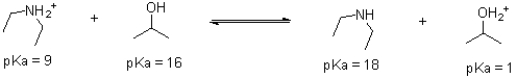
A)
B)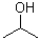
C)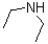
D)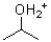

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Given the following reaction scheme,which molecule is the conjugate acid? 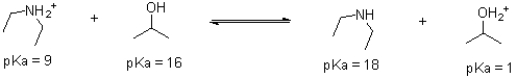
A)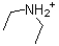
B)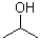
C)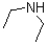
D)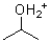

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Atoms with greater s character are better able to stabilize negative charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Electronegativity is used to compare the acidity of atoms in the same row on the periodic table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Atomic size is used to compare the acidity of atoms in the same row on the periodic table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Atoms with greater electronegativity are better electron withdrawers through induction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The strength of a neutral acid is dependent on how well the charge is stabilized in the conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Neighbouring electron withdrawing groups will destabilize a positively charged atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Reactions proceed in the direction of weak acid to strong conjugate acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
HClO2 is a stronger acid then HClO3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Strong acids tend to have negative ÄG values,whereas weak acids tend to have positive ÄG values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Alcohols are stronger bases than amines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Most organic acids are considered strong acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The equilibrium of an acid/base reaction will favour the side with the higher acid pKa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols due to their enhanced ability to delocalize positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Brønsted bases are not considered Lewis bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Thiols are stronger acids than alcohols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Higher pKa values lead to stronger acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Alcohols are stronger acids than amines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The protonated state of a molecule dominates if the pH is less than the pKa of a molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The strength of a base is independent of its conjugate acid's pKa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Neighbouring alkyl groups will destabilize a positively charged atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A carbocation is an example of a Lewis acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A carbanion is an example of a Lewis _______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Neighbouring _______________ groups stabilize a conjugate base through induction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Electronegative atoms are _______________ capable of carrying positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Given the following reaction equilibrium and pKa values,determine which direction is favoured.Identify each molecule as acid,base,conjugate acid,or conjugate base. 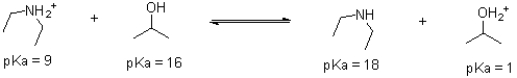


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Substituents on phenol can modulate its pKa values.Explain the differences in pKa seen in the three different phenol molecules shown below.Draw resonance structures to justify your answers. 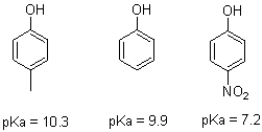


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Sulfur is better at stabilizing negative charge compared to oxygen due to its _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A molecule with an empty p orbital is an example of a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Determine which side of the equilibrium is favoured in the following acid/base reaction shown below.Justify your answer.Indicate which is the acid,base,conjugate acid,and conjugate base. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A molecule will be deprotonated If the pH is _______________ the pKa of an acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Tert-butanol is 100 times less acidic then ethanol (shown below).Explain why this is the case. 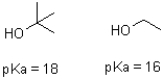


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A chemist mixes propanoic acid with one equivalent of a strong base,hoping to produce the following anion.Explain the error in the chemist's logic and show what product will actually be produced. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Predict the products of the following acid/base reaction shown below. 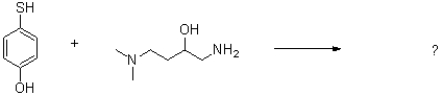


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When considering atomic size,_______________ atoms are better able to handle positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Would water be a suitable solvent for the following reaction? Why or why not.Water has a pK35 of 14. 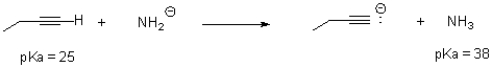


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Alkyl groups are considered inductively electron _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Although similar constitutional isomers,salicylic acid is 50 times more acidic than p-hydroxybenzoic acid (shown below).Come up with a reason why this is the case,and draw a structure that verifies your hypothesis. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use resonance structures to explain the differences in pKa of the two structures shown below. 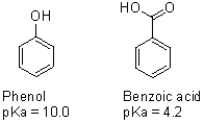


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Oxygen is better able to stabilize negative charge compared to nitrogen due to its _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The hydrogen atoms on the sp3-hybridized carbon are much more acidic then their sp2-hybridized counterparts in 1,3-cyclopentandiene,seemingly violating the rule that atoms with more s character are more acidic.Explain why this is the case.Draw a picture of the molecule to justify your answer. 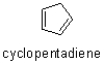


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The stronger the acid,the _______________ the conjugate base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



