Deck 20: Reactions Controlled by Orbital Interactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Reactions Controlled by Orbital Interactions
1
What number of ð electrons is possible in a thermal cycloaddition?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
6
2
Which of the following best describes the Cope rearrangement?
A)cycloaddition
B)sigmatropic rearrangement
C)electrocyclic reaction
D)dipolar cycloaddition
A)cycloaddition
B)sigmatropic rearrangement
C)electrocyclic reaction
D)dipolar cycloaddition
sigmatropic rearrangement
3
What is the product of a Claisen rearrangement?
A)a carbonyl
B)an ether
C)a vinylic ether
D)a 1,3-unsaturated carbonyl
A)a carbonyl
B)an ether
C)a vinylic ether
D)a 1,3-unsaturated carbonyl
a carbonyl
4
What are the reactants of the following reaction? 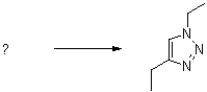
A)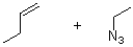
B)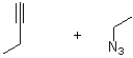
C)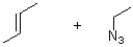
D)

A)
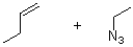
B)
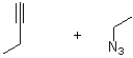
C)
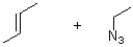
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the product of the following reaction? 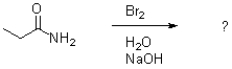
A)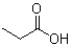
B)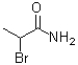
C)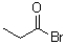
D)
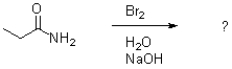
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following best describes a Diels-Alder cycloaddition?
A)loss of one ð bond and gain of one á bond
B)loss of one ð bond and gain of two á bonds
C)loss of two ð bonds and gain of one á bond
D)loss of two ð bonds and gain of two á bonds
A)loss of one ð bond and gain of one á bond
B)loss of one ð bond and gain of two á bonds
C)loss of two ð bonds and gain of one á bond
D)loss of two ð bonds and gain of two á bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the product of the following reaction? 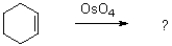
A)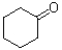
B)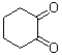
C)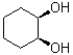
D)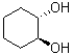
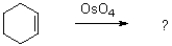
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following best describes the reaction shown below? 
A)cycloaddition
B)sigmatropic rearrangement
C)electrocyclic reaction
D)substitution

A)cycloaddition
B)sigmatropic rearrangement
C)electrocyclic reaction
D)substitution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following best describes the product of the reaction shown below? 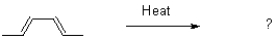
A)conrotatory movement of orbitals and a trans product
B)conrotatory movement of orbitals and a cis product
C)disrotatory movement of orbitals and a trans product
D)disrotatory movement of orbitals and a cis product
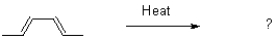
A)conrotatory movement of orbitals and a trans product
B)conrotatory movement of orbitals and a cis product
C)disrotatory movement of orbitals and a trans product
D)disrotatory movement of orbitals and a cis product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes the diene shown below? 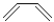
A)cis
B)trans
C)s-cis
D)s-trans

A)cis
B)trans
C)s-cis
D)s-trans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best describes the reaction of a [2+2] cycloaddition of two alkenes?
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following best describes A and B in the following Diels-Alder reaction? 
A)A and B are both electron withdrawing.
B)A and B are both electron donating.
C)A is electron withdrawing,and B is electron donating.
D)A is electron donating,and B is electron withdrawing.

A)A and B are both electron withdrawing.
B)A and B are both electron donating.
C)A is electron withdrawing,and B is electron donating.
D)A is electron donating,and B is electron withdrawing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following represents the product of the reaction shown below? 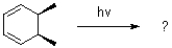
A)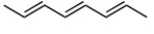
B)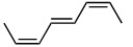
C)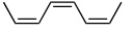
D)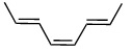
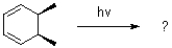
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following reactants are involved in a [4+2] cycloaddition?
A)an alkene and a diene
B)an alkene and a carbonyl
C)two alkenes
D)two dienes
A)an alkene and a diene
B)an alkene and a carbonyl
C)two alkenes
D)two dienes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following orbitals are involved a thermal [4+2] cycloaddition?
A)the dienophile HOMO and the diene HOMO
B)the dienophile HOMO and the diene LUMO
C)the dienophile LUMO and the diene HOMO
D)the dienophile LUMO and the diene LUMO
A)the dienophile HOMO and the diene HOMO
B)the dienophile HOMO and the diene LUMO
C)the dienophile LUMO and the diene HOMO
D)the dienophile LUMO and the diene LUMO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following reactions involves the breaking of a sigma bond?
A)cycloaddition
B)sigmatropic rearrangement
C)electrocyclic reaction
D)dipolar cycloaddition
A)cycloaddition
B)sigmatropic rearrangement
C)electrocyclic reaction
D)dipolar cycloaddition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following contains a SOMO?
A)diene
B)dienophile
C)radical
D)carbocation
A)diene
B)dienophile
C)radical
D)carbocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a reactant for the Cope rearrangement?
A)1,3-hexadiene
B)1,4-hexadiene
C)1,5-hexadiene
D)1-hexene
A)1,3-hexadiene
B)1,4-hexadiene
C)1,5-hexadiene
D)1-hexene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following represents the most reactive diene in a Diels-Alder cycloaddition?
A)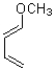
B)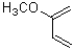
C)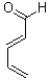
D)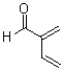
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the product of the following reaction? 
A)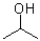
B)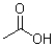
C)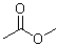
D)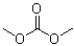

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the product of the following reaction? 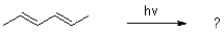
A)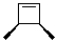
B)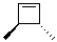
C)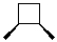
D)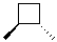
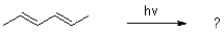
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following best describes the reaction shown below? 
A)loss of one ð bond and gain of one á bond
B)loss of one ð bond and gain of two á bonds
C)loss of two ð bonds and gain of one á bond
D)loss of two ð bonds and gain of two á bonds

A)loss of one ð bond and gain of one á bond
B)loss of one ð bond and gain of two á bonds
C)loss of two ð bonds and gain of one á bond
D)loss of two ð bonds and gain of two á bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What product is favoured in the following reaction and why? 
A)I because of aromaticity
B)I because of hyperconjugation
C)II because of aromaticity
D)II because of hyperconjugation

A)I because of aromaticity
B)I because of hyperconjugation
C)II because of aromaticity
D)II because of hyperconjugation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following best describes the electrocyclic rearrangement shown below? 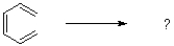
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed
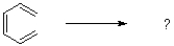
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the product of the following reaction? 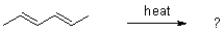
A)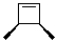
B)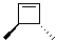
C)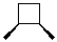
D)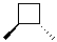
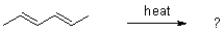
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following best describes a [4+2] cycloaddition?
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following cycloadditions is photochemically controlled?
A)[4+2]
B)[4+4]
C)[4+6]
D)[6+4]
A)[4+2]
B)[4+4]
C)[4+6]
D)[6+4]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the name of the following intermediate formed in the ozonolysis of an alkene? 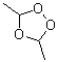
A)ozonide
B)molozonide
C)ozonate
D)molozonate

A)ozonide
B)molozonide
C)ozonate
D)molozonate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What conditions will generate the following product,and what best describes the rotation of orbitals in the electrocyclic reaction shown below? 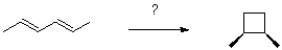
A)Heat is required to generate the product,and it is formed through a conrotatory movement of orbitals.
B)Hv is required to generate the product,and it is formed through a conrotatory movement of orbitals.
C)Heat is required to generate the product,and it is formed through a disrotatory movement of orbitals.
D)Hv is required to generate the product and it is formed through a disrotatory movement of orbitals.
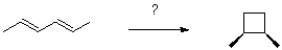
A)Heat is required to generate the product,and it is formed through a conrotatory movement of orbitals.
B)Hv is required to generate the product,and it is formed through a conrotatory movement of orbitals.
C)Heat is required to generate the product,and it is formed through a disrotatory movement of orbitals.
D)Hv is required to generate the product and it is formed through a disrotatory movement of orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is the favoured product in the reversible sigmatropic rearrangement shown below,and why? 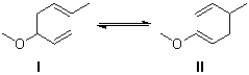
A)I because of conjugation
B)I because of hyperconjugation
C)II because of conjugation
D)II because of hyperconjugation
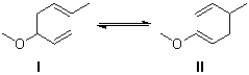
A)I because of conjugation
B)I because of hyperconjugation
C)II because of conjugation
D)II because of hyperconjugation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which orbital is considered the HOMO in a diene?
A)Ø1
B)Ø2
C)Ø3
D)Ø4
A)Ø1
B)Ø2
C)Ø3
D)Ø4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following terms involves opposing rotation of orbitals in electrocyclic reactions?
A)rotatory
B)counterrotatory
C)conrotatory
D)disrotatory
A)rotatory
B)counterrotatory
C)conrotatory
D)disrotatory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
[2+2] cycloadditions occur under thermal conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the product of the reaction shown below? 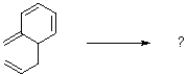
A)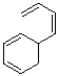
B)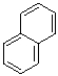
C)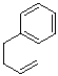
D)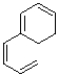
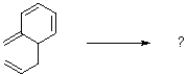
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the intermediate of the following reaction? 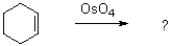
A)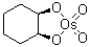
B)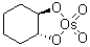
C)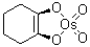
D)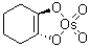
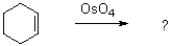
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A [4+2] cycloaddition is thermally allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
s-trans dienes are in equilibrium with s-cis dienes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What conditions will generate the following product? 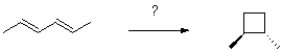
A)heat
B)hv
C)acid
D)both heat and hv
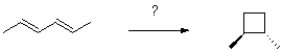
A)heat
B)hv
C)acid
D)both heat and hv

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following best describes the sigmatropic rearrangement shown below? 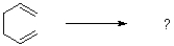
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed
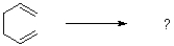
A)thermally and photochemically forbidden
B)thermally and photochemically allowed
C)thermally allowed and photochemically forbidden
D)thermally forbidden and photochemically allowed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which orbital is considered the LUMO in a diene?
A)Ø1
B)Ø2
C)Ø3
D)Ø4
A)Ø1
B)Ø2
C)Ø3
D)Ø4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
SUMO orbitals are formed by heating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Dipolar cycloadditions requires a zwitterionic compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A sigmatropic rearrangement involves the loss and gain of one sigma bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Photochemical electrocyclic reactions always involve disrotatory movement of orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Hoffman rearrangement transforms an amide into amines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Sigmatropic rearrangements are photochemically forbidden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
OsO4 transforms an alkene into a trans-diol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Ketenes are capable of [2+2] thermal cycloadditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Ozone transforms an alkene into carbonyls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A dieneophile is activated with electron withdrawing groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A reaction of an alkyne and an azide is termed a [3+2] cycloaddition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
[6+4] cycloadditions are thermally forbidden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Electrocyclic ring closures involve the loss of a ð bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A diene is activated with electron withdrawing groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A [2+2] cycloaddition is thermally allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
SUMO orbitals are involved in photochemical cycloadditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The sigmatropic rearrangement involves the overlap of two LUMO orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
[4+2] cycloadditions are photochemically forbidden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Electrocyclic rearrangements are photochemically forbidden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Baeyer-Villiger oxidation converts ketones into esters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Propose a mechanism for the following transformation. 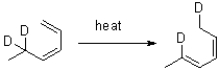


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Predict the reactants of the following cycloaddition reaction. 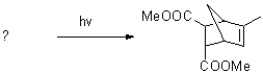


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A [2+2] cycloaddition occurs under _______________ conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Draw the product of the following reaction under both thermal and photochemical conditions. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The Claisen rearrangement is an example of a(n)_______________ rearrangement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Electron _______________ groups activate dienophiles in the Diels-Alder reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Diels-Alder cycloadditions are irreversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Draw the product and mechanism of the following transformation.Show using molecular orbitals. 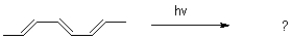
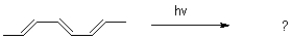

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Two orbitals rotating in the same direction are referred to as _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The conversion of a ketone to an ester involves the use of a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Two orbitals rotating in opposite directions are referred to as _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Determine the product and show the mechanism of the following transformation. 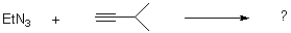


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A [2+2] cycloaddition is thermally_______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Predict the product of the following reaction and show the transition state. 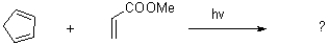
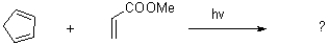

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The _______________ orbital of a diene is the reactive orbital in the Diels-Alder reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A [4+2] cycloaddition is _______________ forbidden.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Draw the product and the mechanism of the following reaction. 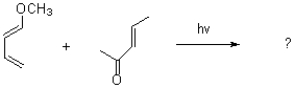


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Draw the product and mechanism of the following transformation.Show using molecular orbitals. 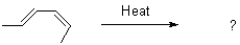
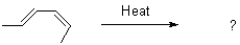

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Bromine is a reagent in the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A [4+2] cycloaddition occurs under _______________ conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



