Deck 19: Radicals
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Radicals
1
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 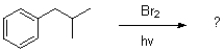
A)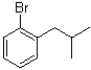
B)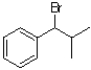
C)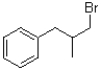
D)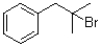
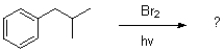
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
What reagent or condition is missing in the following reaction scheme? 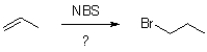
A)ROOR
B)H3O+
C)Heat
D)hv

A)ROOR
B)H3O+
C)Heat
D)hv
hv
3
What accounts for the regioselectivity of radical halogen?
A)More substituted carbons have lower C-H bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons.
B)More substituted carbons have higher C-H bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons.
C)More substituted carbons have lower C-X bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons,where X represents a halide.
D)More substituted carbons have higher C-X bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons,where X represents a halide.
A)More substituted carbons have lower C-H bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons.
B)More substituted carbons have higher C-H bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons.
C)More substituted carbons have lower C-X bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons,where X represents a halide.
D)More substituted carbons have higher C-X bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons,where X represents a halide.
More substituted carbons have lower C-H bond disassociation energies than less substituted carbons.
4
What kind of polymerization reaction is shown below? 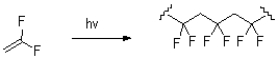
A)alkenyl
B)polar
C)addition
D)condensation

A)alkenyl
B)polar
C)addition
D)condensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following terms best describes radical bond breakage?
A)homolytic cleavage
B)heterolytic cleavage
C)polar cleavage
D)non-polar cleavage
A)homolytic cleavage
B)heterolytic cleavage
C)polar cleavage
D)non-polar cleavage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What monomer subunit would form the addition polymer shown below? 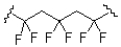
A)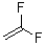
B)
C)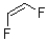
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following conditions would accomplish the transformation shown below? 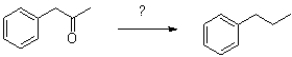
A)Zn/Hg,HCl
B)Zn/Hg,NaOH
C)1)LiAlH4,2)H3O+
D)1)LiAlH4,2)NaOH

A)Zn/Hg,HCl
B)Zn/Hg,NaOH
C)1)LiAlH4,2)H3O+
D)1)LiAlH4,2)NaOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following represents a radical propagation step?
A)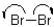
B)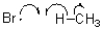
C)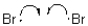
D)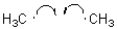
A)
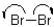
B)
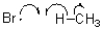
C)
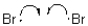
D)
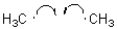

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the major product of the transformation shown below? 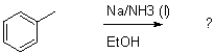
A)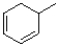
B)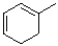
C)
D)
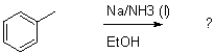
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following represents a radical termination step?
A)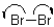
B)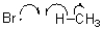
C)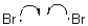
D)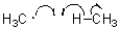
A)
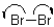
B)
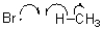
C)
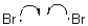
D)
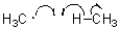

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following represents a radical initiation step?
A)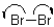
B)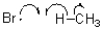
C)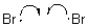
D)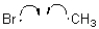
A)
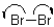
B)
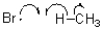
C)
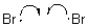
D)
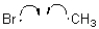

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the major product of the transformation shown below? 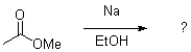
A)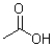
B)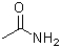
C)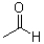
D)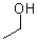
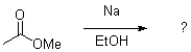
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the product of the reaction shown below? 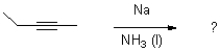
A)
B)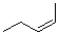
C)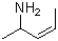
D)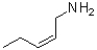
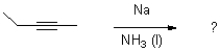
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the major product of the transformation shown below? 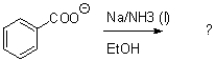
A)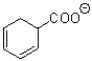
B)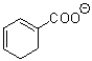
C)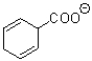
D)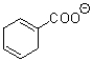
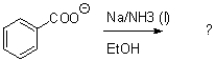
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following best describes a radical bromination reaction?
A)Markovnikov regiochemistry
B)anti-Markovnikov regiochemistry
C)Markovnikov stereochemistry
D)anti-Markovnikov stereochemistry
A)Markovnikov regiochemistry
B)anti-Markovnikov regiochemistry
C)Markovnikov stereochemistry
D)anti-Markovnikov stereochemistry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following represents the most stable radical?
A)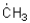
B)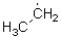
C)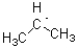
D)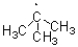
A)
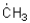
B)
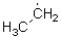
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following represents the most stable radical?
A)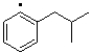
B)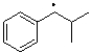
C)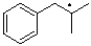
D)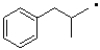
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following represents the most stable radical?
A)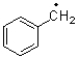
B)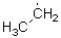
C)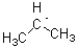
D)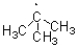
A)

B)
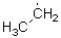
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the role of ammonia in the mechanism of the Birch reduction shown below? 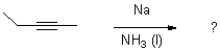
A)stoichiometric acid
B)stoichiometric base
C)catalytic acid
D)catalytic base
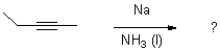
A)stoichiometric acid
B)stoichiometric base
C)catalytic acid
D)catalytic base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Birch reduction of an alkyne results in a cis-alkene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would produce the least stable radical?
A)
B)
C)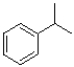
D)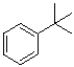
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following hydrocarbons would produce the most stable radical?
A)
B)
C)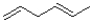
D)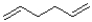
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following reagents would achieve the transformation shown below? 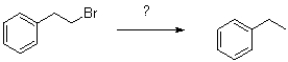
A)Na/NH3 (l)
B)AlBN,HSnBu3
C)Zn/Hg,HCl
D)hv ROOR
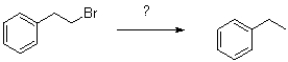
A)Na/NH3 (l)
B)AlBN,HSnBu3
C)Zn/Hg,HCl
D)hv ROOR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What role do radicals play in a radical initiation reaction?
A)They are reactants only.
B)They are products only.
C)They are both reactants and products.
D)They are neither reactants nor products.
A)They are reactants only.
B)They are products only.
C)They are both reactants and products.
D)They are neither reactants nor products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following would produce the most stable radical?
A)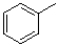
B)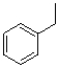
C)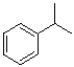
D)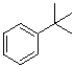
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What monomer subunit would form the addition polymer shown below? 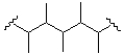
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following represents the first mechanistic step of the aromatic reduction shown below? 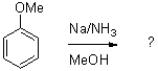
A)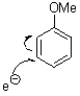
B)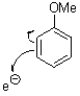
C)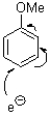
D)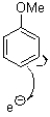
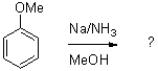
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following reagents would achieve the transformation shown below? 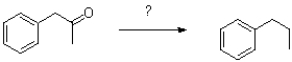
A)Na/NH3 (l)
B)AlBN,HSnBu3
C)Zn/Hg,HCl
D)hv,ROOR
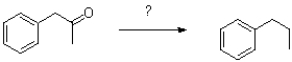
A)Na/NH3 (l)
B)AlBN,HSnBu3
C)Zn/Hg,HCl
D)hv,ROOR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What monomer subunit would form the addition polymer shown below? 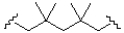
A)
B)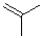
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Radical propagation reactions involve radical reactants and products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What role do radicals play in a radical termination reaction?
A)They are reactants only.
B)They are products only.
C)They are both reactants and products.
D)They are neither reactants nor products.
A)They are reactants only.
B)They are products only.
C)They are both reactants and products.
D)They are neither reactants nor products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Termination of a radical cycle involves a bond being formed from two radicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What role do radicals play in a radical propagation reaction?
A)They are reactants only.
B)They are products only.
C)They are both reactants and products.
D)They are neither reactants nor products.
A)They are reactants only.
B)They are products only.
C)They are both reactants and products.
D)They are neither reactants nor products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Radical chlorination is more regioselective than radical bromination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following best describes the conditions required to generate radicals?
A)heat
B)UV light
C)rigorous mixing
D)both heat and UV light
A)heat
B)UV light
C)rigorous mixing
D)both heat and UV light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Tertiary radicals are less stable than secondary radicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following best describes stabilization of radicals?
A)Radicals are stabilized by electron delocalization but not hyperconjugation.
B)Radicals are stabilized by hyperconjugation but not electron delocalization.
C)Radicals are stabilized by both electron delocalization and hyperconjugation.
D)Radicals are stabilized by neither electron delocalization nor hyperconjugation.
A)Radicals are stabilized by electron delocalization but not hyperconjugation.
B)Radicals are stabilized by hyperconjugation but not electron delocalization.
C)Radicals are stabilized by both electron delocalization and hyperconjugation.
D)Radicals are stabilized by neither electron delocalization nor hyperconjugation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A stochiometric amount of radical imitator is required for radical reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Adjacent electronegative atom with lone pair electrons help stabilize radicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Electron-withdrawing groups affect the regiochemistry of the Birch reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Birch reduction involves the transformation of aromatic species into a 1,3-cyclohexadienes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Radical bromination has _______________ regiochemistry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In radical additions of HBr with alkenes,peroxides act as a radical initiator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Secondary alkyl halides are formed preferentially over primary alkyl halides in radical halogenations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Fishhook arrows are representative of homolytic cleavage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Electrons solvated in ammonia have a characteristic blue colour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the Birch reduction,magnesium metal is oxidized to produce solvated electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Carbon radicals are sp2 hybridized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Radicals are stabilized by delocalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
AIBN is used as a radical initiator in dehalogenation of alkyl halides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Reduction of an alkyne with dissolved sodium metal in ammonia results in a(n)_______________ geometry alkene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A zinc/mercury alloy is used in the reduction of carbonyls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Electrons are solvated in aqueous solutions for their use in metal reduction reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Clemmensen reduction results in the reduction of a ketone to an alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Dissolving metal reduction of alkynes results in a trans alkene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Primary radicals are less stable than tertiary radicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Radical addition of hydrogen bromide to an alkene leads to a Markovnikov product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
NBS is used for allylic halogenation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Tributyl tin hydride is used as a radical initiator in dehalogenation of alkyl halides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Show the mechanism for the three stages (initiation,propagation,and termination)of the following radical reaction. 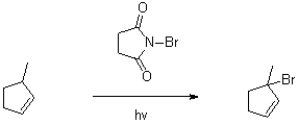


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Fishhook arrows are involved in _______________ cleavage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In radical reactions,peroxides tend to act as _______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the major product of the reaction shown below? 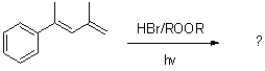


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the radical addition of HBr to an alkene,a peroxide acts as a(n)_______________ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Draw the mechanism of the following dissolving metal transformation. 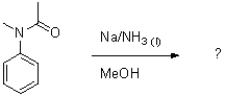


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the product of the following reaction? 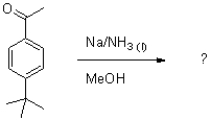


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
_______________ cleavage represents a bond-breaking reaction where both electrons migrate to one atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The formation of a sigma bond from two radicals represents a(n)_______________ step in a radical chain reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Predict the product of the following addition polymerization reaction. 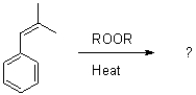


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Propose a mechanism for the following transformation. 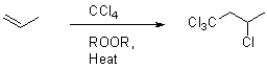


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The Birch reduction involves transforming a(n)_______________ into a 1,4-cyclohexadiene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Draw the possible products of the reaction shown below.Indicate the major product. 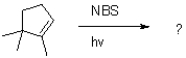


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Solvated electrons in ammonia result in a deep _______________ colour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The three phases of a radical chain reaction are initiation,_______________ ,and termination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What reactant would form the product shown below? 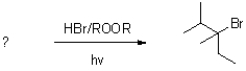


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



