Deck 21: International Financial Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: International Financial Management
1
The purchasing power parity theory of exchange rates suggests that exchange rates will adjust until the cost of equivalent goods is approximately equal in each country.
True
2
In recent years, fully owned foreign subsidiaries are experiencing increased political pressure from foreign governments.
True
3
During the global financial crisis that began in late 2008, the dollar fell in value relative to the British pound and the euro.
False
4
Companies such as Coca-Cola and McDonald's generate more than 50% of their sales revenues from foreign activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Multinational firms tend to have a lower level of portfolio risk than comparable U.S. firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One benefit in joining the "Eurozone" was to have easy access to borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Currency exchange rates may be either floating or fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A foreign affiliate lowers the portfolio risk of its parent company because the foreign and domestic economies tend to be fairly similar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
There is no guarantee that any currency will stay strong relative to other currencies, but the dollar is an exception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When a country has a weak currency relative to other countries, visiting that country is much more expensive for people that don't live in that country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A foreign affiliate may be an exporter, a joint venture, or a fully owned foreign subsidiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An exporter is able to satisfy foreign demand for a product while avoiding long-term investment in that foreign country, although this method is considered riskier than all other alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The North American Free Trade Association (NAFTA) continues to generate more foreign trade despite some negative political views.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A foreign exchange rate specifies how much a currency is worth in terms of another currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The purchasing power parity theory states that currency exchange rates tend to vary inversely with their respective purchasing powers in order to provide similar purchasing powers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Investors and firms who diversify their U.S. portfolios by buying foreign stocks or investing in foreign subsidiaries take on a much higher level of portfolio risk than if they had invested in domestic stocks or companies only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All of the countries that joined the "Eurozone" were able to enjoy economic benefits for various reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A joint venture with a private entrepreneur in a host country exposes the multinational corporation to the least amount of political risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A forward exchange rate can be used to help establish the value of a currency at a future point in time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a free market, the exchange rate between two currencies is determined by the supply of and demand for those currencies with the influence of the central bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
"Balance of payments" is a method of keeping the foreign exchange market in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Political risk and labor unrest will tend to strengthen a country's currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A "bear market" (declining stock prices) will tend to exert a depressing effect on the value of a country's currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A money market hedge does not require the use of a futures exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When a bank issues a "letter of credit," the bank absorbs ALL of the credit risk of the exporter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The future rates of currency tend to increase for dates further in the future because of the increasing uncertainty over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Translation exposure occurs because of changes in foreign exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Forward contracts tend to be created on organized exchanges like the International Money Market of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A fronting loan disguises the identity of a parent multinational corporation that infuses money into a foreign subsidiary. This technique is intended to reduce the political risk of operating a subsidiary in a foreign country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Transaction exposure results in foreign exchange gains and losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The expected future value of a currency is reflected in its spot rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Political risks include the possibility that a government may expropriate a firm's profits, or worse, repatriate all of the firm's assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the financing of a foreign affiliate, the simplest and most common arrangement is a direct loan from the parent company to the subsidiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Foreign exchange risk is the risk that a person or business will not be able to exchange currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a fronting loan arrangement, the intermediary bank extends a risk-free loan to the foreign affiliate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Transaction exposure associated with changes in the exchange rate between countries can be hedged with a currency futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In Germany, restrictions limiting labor layoffs have encouraged companies to reduce investment there. Thus, in the long run, these labor protection laws actually can be expected to result in higher unemployment in Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The term balance of payments refers to the flow of economic transactions between the residents of one country and the residents of another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
According to the interest rate parity theory, interest rates along with exchange rates adjust until the foreign exchange market and the money market are in equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A firm that perhaps suffers a loss as a result of a decline in the value of the Japanese yen could offset part of that risk by selling Japanese yen futures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An example of comparing cross rates for countries is like comparing the U.S. dollar to the Japanese yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The possibility of political risk may be excluded when an investor considers maximizing expected returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A licensing agreement provides a U.S. multinational corporation with a guarantee that it will be able to export the product to the foreign market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Multinational corporations (MNC) may take several forms. An exporter could be described as
A) a MNC that produces a product within its own borders, but sells in a foreign market.
B) the least risky political arrangement.
C) a MNC willing to commit itself to long-term foreign investment.
D) More than one of the options is correct.
A) a MNC that produces a product within its own borders, but sells in a foreign market.
B) the least risky political arrangement.
C) a MNC willing to commit itself to long-term foreign investment.
D) More than one of the options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A form of multinational corporation (MNC) that exposes the firm to the least amount of political risk, and is therefore the preferred arrangement by both business and foreign governments, is called
A) an exporter.
B) a licensing agreement.
C) a joint venture.
D) a fully owned foreign subsidiary.
A) an exporter.
B) a licensing agreement.
C) a joint venture.
D) a fully owned foreign subsidiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
As inflation in any "Eurozone" country increases, while the U.S. experiences no change in inflation, the exchange rate of the euro to the dollar will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Selling common stock to residents of foreign countries is illegal in most countries, although it minimizes risk for any multinational corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For a U.S. company, foreign business operations are more complex because the
A) host country's economy may be different from the domestic economy.
B) rules of taxation are different.
C) structure and operations of financial markets vary.
D) all of these options are true.
A) host country's economy may be different from the domestic economy.
B) rules of taxation are different.
C) structure and operations of financial markets vary.
D) all of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In a licensing agreement, the multinational corporation will very likely
A) be able to compete with the local domestic manufacturers.
B) experience import restrictions imposed by the foreign government.
C) allow a foreign firm to use its technology in exchange for a fee.
D) none of these options are true.
A) be able to compete with the local domestic manufacturers.
B) experience import restrictions imposed by the foreign government.
C) allow a foreign firm to use its technology in exchange for a fee.
D) none of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A fully owned foreign subsidiary is a form of MNC (multinational corporation) in which
A) a local entrepreneur buys the firm in its own foreign country.
B) the MNC owns and operates the firm by itself.
C) the foreign government gives its full cooperation.
D) none of these options are true.
A) a local entrepreneur buys the firm in its own foreign country.
B) the MNC owns and operates the firm by itself.
C) the foreign government gives its full cooperation.
D) none of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A multinational corporation may be defined as
A) a company that owns property in a foreign country.
B) a company that hires foreign laborers.
C) a company that carries on some business activity outside of its own national borders.
D) all of the options are true.
A) a company that owns property in a foreign country.
B) a company that hires foreign laborers.
C) a company that carries on some business activity outside of its own national borders.
D) all of the options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When the euro rises and the dollar falls, foreign travel to Europe becomes cheaper for Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Eurobond issues are sold simultaneously in several national capital markets, but denominated in a currency different from that of the nation in which the bonds are issued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Because of political risk, it is generally disadvantageous for U.S. firms to list their stocks on the world stock exchanges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The most widely used currency in the Eurobond market is the euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Legal, political, and economic factors are most conducive to which form of multinational corporation (MNC) organization?
A) Exporter/importer
B) Licensing agreements
C) Joint ventures
D) Fully owned foreign subsidiaries
A) Exporter/importer
B) Licensing agreements
C) Joint ventures
D) Fully owned foreign subsidiaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The lending rate for borrowers in the Eurodollar market is based on the prime lending rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is NOT an accusation made against multinational corporations (MNCs) by foreign countries?
A) MNCs cause instability in their currencies in international money and foreign exchange markets.
B) MNCs contribute to unemployment and avoid taxes.
C) MNCs exploit local labor with low wages.
D) All of these options are accusations made by critics of MNCs.
A) MNCs cause instability in their currencies in international money and foreign exchange markets.
B) MNCs contribute to unemployment and avoid taxes.
C) MNCs exploit local labor with low wages.
D) All of these options are accusations made by critics of MNCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A rising euro and a falling dollar will cause an increase in U.S. exports to Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A particular country's pattern of importing more than is being exported is likely to
A) depress that country's currency.
B) depress other countries' currencies.
C) increase the value of that country's currency.
D) more than one of the options is correct.
A) depress that country's currency.
B) depress other countries' currencies.
C) increase the value of that country's currency.
D) more than one of the options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The following are the prices in the foreign exchange market between the U.S. dollar and another local currency (LC). 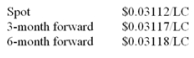 What was the approximate discount or premium on a three-month forward for LC?
What was the approximate discount or premium on a three-month forward for LC?
A) 0.643% premium
B) .013% premium
C) .013% discount
D) 0.643% discount
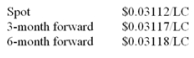 What was the approximate discount or premium on a three-month forward for LC?
What was the approximate discount or premium on a three-month forward for LC?A) 0.643% premium
B) .013% premium
C) .013% discount
D) 0.643% discount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The value of a country's currency may increase by
A) continuous excessive government spending.
B) a stock market rally in that country.
C) an increase in that country's money supply.
D) More than one of the options is correct.
A) continuous excessive government spending.
B) a stock market rally in that country.
C) an increase in that country's money supply.
D) More than one of the options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Assume that you had U.S. dollar quotes for the Japanese yen and the British pound. If you want to know the yen/pound exchange rate, you would rely on
A) forward rates.
B) cross rates.
C) The Wall Street Journal.
D) hedge ratios.
A) forward rates.
B) cross rates.
C) The Wall Street Journal.
D) hedge ratios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Swiss franc is selling for $.9412 and the British pound is selling for $1.5119. The cross rate between the franc and the pound (the number of Swiss francs that would buy one British pound) is approximately:
A) .161
B) 1.61
C) .0322
D) 3.22
A) .161
B) 1.61
C) .0322
D) 3.22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
As exchange rates change, the rates
A) change the relative purchasing power between countries.
B) can affect imports and exports between those two countries.
C) will affect the flow of funds between the countries.
D) all of these options are true.
A) change the relative purchasing power between countries.
B) can affect imports and exports between those two countries.
C) will affect the flow of funds between the countries.
D) all of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the past, the U.S. dollar's exchange rate with the Iceland krona was .0008 dollars per krona. If today the exchange rate is .0006 dollars per krona, the dollar
A) strengthened against the krona.
B) weakened against the krona.
C) is not highly correlated to the krona.
D) The answer cannot be determined without knowing the number of kronas needed to buy a dollar.
A) strengthened against the krona.
B) weakened against the krona.
C) is not highly correlated to the krona.
D) The answer cannot be determined without knowing the number of kronas needed to buy a dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The belief that shifts in exchange rates result from increasing or decreasing demand for a country's exports (or the corresponding opposite movements in supply of a country's imports) forms the basis for the
A) purchasing power theory of exchange rates.
B) interest rate parity theory of exchange rates.
C) balance of payments theory of exchange rates.
D) government intervention theory of exchange rates.
A) purchasing power theory of exchange rates.
B) interest rate parity theory of exchange rates.
C) balance of payments theory of exchange rates.
D) government intervention theory of exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If one Czech crown is equal to $.05 U.S. dollar, the U.S. dollar is equal to how many Czech crowns?
A) 25.00
B) 4.00
C) 20.00
D) 400.00
A) 25.00
B) 4.00
C) 20.00
D) 400.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The possibility of experiencing a drop in revenue or an increase in cost in an international transaction due to a change in foreign exchange rates is called
A) foreign exchange risk.
B) political risk.
C) translation exposure.
D) hedging risk.
A) foreign exchange risk.
B) political risk.
C) translation exposure.
D) hedging risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
You are leaving Mexico and have 290 pesos to change into dollars. The exchange rate is now 12 pesos to the dollar. Approximately how many dollars will you receive?
A) $3025.00
B) $24.16
C) $264.00
D) $3,480.00
A) $3025.00
B) $24.16
C) $264.00
D) $3,480.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following factors will NOT increase the value of a currency in foreign markets?
A) High interest rates in that country
B) High inflation in that country
C) A positive balance of payments with that country
D) A strong stock market rally in that country
A) High interest rates in that country
B) High inflation in that country
C) A positive balance of payments with that country
D) A strong stock market rally in that country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The interplay between interest rate differentials and exchange rates such that each adjusts until the foreign exchange market and the money market reach equilibrium is called the
A) purchasing power parity theory.
B) balance of payments.
C) interest rate parity theory.
D) multinational corporation.
A) purchasing power parity theory.
B) balance of payments.
C) interest rate parity theory.
D) multinational corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements about forward exchange rates is false?
A) They reduce uncertainty about the future value of currencies.
B) They reflect expectations about the future value of currencies.
C) They are usually slightly lower than the spot rate.
D) All of these options are true.
A) They reduce uncertainty about the future value of currencies.
B) They reflect expectations about the future value of currencies.
C) They are usually slightly lower than the spot rate.
D) All of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following kinds of risk is NOT uniquely associated with multinational corporations (MNCs)?
A) Exchange rate risk
B) Business risk
C) Political risk
D) None of these options are uniquely associated with MNCs.
A) Exchange rate risk
B) Business risk
C) Political risk
D) None of these options are uniquely associated with MNCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
While shopping in the Mexican market, you find that limes cost 11 pesos each. You remember that back in the U.S., they cost 80 cents each. If the purchasing power parity theory holds, the rate of exchange is
A) 13.75 pesos/dollar or 7.3 cents/peso.
B) 80 pesos/dollar or 1.25 cents/peso.
C) 7.3 pesos/dollar or 13.75 cents/peso.
D) 11 pesos/dollar or .80 cents/peso.
A) 13.75 pesos/dollar or 7.3 cents/peso.
B) 80 pesos/dollar or 1.25 cents/peso.
C) 7.3 pesos/dollar or 13.75 cents/peso.
D) 11 pesos/dollar or .80 cents/peso.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The spot rate of the British pound to the dollar is $1.15. The 180-day forward rate is $1.17. Thus, the approximate annualized forward premium is _________.
A) 1.018%
B) 3.571%
C) 7.273%
D) 3.478%
A) 1.018%
B) 3.571%
C) 7.273%
D) 3.478%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
You travel to Cancun Mexico for spring break. The current exchange rate is 13 pesos to the dollar. When you arrive, you convert $1,000 into how many pesos?
A) 1,300 pesos
B) 80 pesos
C) 13,000 pesos
D) 77 pesos
A) 1,300 pesos
B) 80 pesos
C) 13,000 pesos
D) 77 pesos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When Country A's currency strengthens against Country B's, citizens of Country A will
A) pay less to buy Country B's products.
B) pay more to buy Country B's products.
C) pay more to buy domestically produced products.
D) not be affected by the change in their currency's value.
A) pay less to buy Country B's products.
B) pay more to buy Country B's products.
C) pay more to buy domestically produced products.
D) not be affected by the change in their currency's value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following hedging strategies is not used to minimize transaction exposure?
A) The Eurobond market
B) The forward exchange market
C) The money market
D) The currency futures market
A) The Eurobond market
B) The forward exchange market
C) The money market
D) The currency futures market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If prices double in New York while the prices in Germany remain the same, the purchasing power of the dollar relative to the euro
A) should increase by 50%.
B) should increase by 100%.
C) should decrease by 50%.
D) should decrease by 100%.
A) should increase by 50%.
B) should increase by 100%.
C) should decrease by 50%.
D) should decrease by 100%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



