Deck 12: The Capital Budgeting Decision
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Capital Budgeting Decision
1
Possibly the most overlooked part of the capital budgeting process is the search for new opportunities through innovation and creative thinking.
True
2
Using the payback method can be appropriate when the time value of money is considered.
False
3
It is not unusual for a corporate president to be as sensitive to after-tax income rather than cash flow.
True
4
Even though one project may have superior cash flows, top management may sometimes choose a project that inflates earnings instead of cash flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
With non-mutually exclusive events and no capital rationing, we will usually arrive at the same conclusions using either the net present value or internal rate of return methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The payback method is not really a theoretically correct approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The first administrative consideration in any capital budgeting process is collection of data.
The first step is the search for opportunities among alternatives.
The first step is the search for opportunities among alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The net present value primary advantage over the internal rate of return method is that it does not require the time value of money calculations that the internal rate of return requires.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Capital budgeting decisions involve a minimum time horizon of five years.
Project expenditures are planned for at least one year.
Project expenditures are planned for at least one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Capital budgeting is only a concern of finance and accounting personnel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A rapid payback may be important to firms having rapid technological development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Non-mutually exclusive alternatives can be accepted at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In most capital budgeting decisions, the emphasis should be on reported earnings rather than cash flows.
Cash flow is given more emphasis in capital budgeting decisions than earnings.
Cash flow is given more emphasis in capital budgeting decisions than earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The internal rate of return is the interest rate that equates the cash outflows of an investment with the subsequent cash inflows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The selection of a mutually exclusive project means that all other projects with a positive net present value may also be selected.
By definition, mutually exclusive means that the selection of one project precludes the selection of any other alternative.
By definition, mutually exclusive means that the selection of one project precludes the selection of any other alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The payback method is very basic but it gives the user an understanding of when the cost of the initial project will be completely paid off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A good capital budgeting program requires that a number of steps be taken in the decision-making process. The first step is the explanation of data.
The first step involves searching for investment opportunities.
The first step involves searching for investment opportunities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To find the exact internal rate of return for projects with uneven cash flows, we can interpolate between two factors from the time value of money table: present value of a $1.
Annuity can't be used for uneven cash flows
Annuity can't be used for uneven cash flows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Depreciation is important in calculating projected cash flows because it lowers the profits, but does not affect the cash account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
We add depreciation to net income to arrive at a true earnings picture.
Depreciation is re-added to net income to move closer to a "cash basis" earnings number, since it represents a "non-cash" expense.
Depreciation is re-added to net income to move closer to a "cash basis" earnings number, since it represents a "non-cash" expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
It is the difference in the reinvestment assumptions that can be significant in determining when to use the net present value or internal rate of return methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under MACRS depreciation, there are no tax credits for the purpose of calculating the base for depreciation expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Most real estate property is depreciated over a 10-year period.
Under the MACRS regulations, depreciation on real estate typically begins at no less than 27.5 years.
Under the MACRS regulations, depreciation on real estate typically begins at no less than 27.5 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The modified internal rate of return method assumes that inflows are reinvested at 80% of the internal rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a replacement decision, a book loss on an old asset can be a valuable feature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The net present value profile allows a firm to examine the project's net present value over time without any adjustments.
The method provides a comparison at the investment origin point between current cash flows and future discounted cash flows.
The method provides a comparison at the investment origin point between current cash flows and future discounted cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The net present values' weakness is that it does not provide a decision for mutually exclusive investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Under the "modified accelerated-cost-recovery system" (MACRS) of depreciation, cash flow tends to decline with the passage of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Although firms can elect to use straight-line depreciation for their external financial reporting, the MACRS depreciation schedules have exceeded in use over other depreciation methods for tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Under MACRS depreciation, the tax life of an asset and its economically useful life are assumed to be the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If an asset is sold for a price above its book value, the difference is considered taxable income to the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For a small business, it is possible for the purchase price of an asset to be expensed rather than depreciated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Under MACRS depreciation, taxes paid in the first year of an asset's life are subtracted from the base used to calculate depreciation expense.
It would be inaccurate and inappropriate to adjust for tax savings in calculating a depreciable base.
It would be inaccurate and inappropriate to adjust for tax savings in calculating a depreciable base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Under the net present value method, cash flows are assumed to be reinvested at the firm's weighted average cost of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For high-internal rate of return investments, it is perfectly acceptable to assume that reinvestment will occur at an equally high, if not higher, rate.
Under the IRR assumption, it may be unrealistic to assume reinvestment at that high resulting rate can occur.
Under the IRR assumption, it may be unrealistic to assume reinvestment at that high resulting rate can occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The profitability index is calculated by dividing the project's net present value by the present value of the projected cash outflows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Under capital rationing, a firm will maximize profitability.
Capital rationing is a management-imposed constraint, rather than a result of marginal analysis.
Capital rationing is a management-imposed constraint, rather than a result of marginal analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In most cases, asset lives are shorter under MACRS depreciation than they would be with straight-line depreciation.
Asset lives will be generally comparable under alternative methods.
Asset lives will be generally comparable under alternative methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When using accelerated depreciation, the present value of future cash flows increases.
By moving greater tax deductions into earlier years that carry a greater PV effect, with all other things being equal, the PV of cash inflows in earlier years is then amplified.
By moving greater tax deductions into earlier years that carry a greater PV effect, with all other things being equal, the PV of cash inflows in earlier years is then amplified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A tax loss on the sale of a depreciable asset used in business or trade may be written off against income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
It is more likely for financial managers to focus on cash flow and corporate executives to focus on earnings of the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The first step in the capital budgeting process is
A) collection of data.
B) idea development.
C) assign probabilities.
D) determine cash flows.
A) collection of data.
B) idea development.
C) assign probabilities.
D) determine cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The reinvestment assumption is a downside of the internal rate of return method of analysis because it assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the cost of capital.
It actually assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR rate, which can sometimes be excessively high, rendering this assumption unrealistic.
It actually assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR rate, which can sometimes be excessively high, rendering this assumption unrealistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The dollar amount of losses incurred when an old asset is sold below book value is added to the purchase price of a new asset in calculating the base for depreciation.
All else being equal, the new asset is typically depreciated separately, although the tax benefits of writing off losses on older assets might provide a net benefit to the company.
All else being equal, the new asset is typically depreciated separately, although the tax benefits of writing off losses on older assets might provide a net benefit to the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Capital rationing is generally a positive action for a firm because it prevents rapid growth, which can drive up the cost of capital.
Capital rationing is used for "macromanagement" purposes, including debt constraints or economic concerns. It is generally considered a negative action since it can impede achieving maximum profitability.
Capital rationing is used for "macromanagement" purposes, including debt constraints or economic concerns. It is generally considered a negative action since it can impede achieving maximum profitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The payback method has several disadvantages, among them:
A) Payback fails to choose the optimum or most economic solution to a capital budgeting problem.
B) Payback ignores cash inflows after the payback period.
C) Payback fails to choose the optimum or most economic solution to a capital budgeting problem, and it ignores cash inflows after the payback period.
D) None of these options are disadvantages.
A) Payback fails to choose the optimum or most economic solution to a capital budgeting problem.
B) Payback ignores cash inflows after the payback period.
C) Payback fails to choose the optimum or most economic solution to a capital budgeting problem, and it ignores cash inflows after the payback period.
D) None of these options are disadvantages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When net present value and internal rate of return analysis provide inconsistent rankings of projects, the financial manager should generally move forward with the project that has the highest internal rate of return.
In the event of such a conflict, all facts must be reconsidered, including the discount rate.
In the event of such a conflict, all facts must be reconsidered, including the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Investors discount the later years of a long-term project at a lower rate because they are generally less precise.
While uncertainty increases as the time horizon increases of course, later years are discounted at a lower TVM factor primarily because of the time over which the discounting rate works.
While uncertainty increases as the time horizon increases of course, later years are discounted at a lower TVM factor primarily because of the time over which the discounting rate works.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The reason cash flow is used in capital budgeting is because
A) cash rather than income is used to purchase new machines.
B) cash outlays need to be evaluated in terms of the present value of the resultant cash inflows.
C) to ignore the tax shield provided from depreciation would ignore the cash flow provided by the machine, which should be reinvested to replace older machines.
D) All of these options are true.
A) cash rather than income is used to purchase new machines.
B) cash outlays need to be evaluated in terms of the present value of the resultant cash inflows.
C) to ignore the tax shield provided from depreciation would ignore the cash flow provided by the machine, which should be reinvested to replace older machines.
D) All of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Cash flow is used for a net present value analysis, while earnings are used for the internal rate of return and payback analysis.
Cash flow is used for all such analyses.
Cash flow is used for all such analyses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a general sense, "cash flow" can be said to equal
A) operating income less taxes plus depreciation.
B) operating income less taxes.
C) operating income before depreciation and taxes plus depreciation.
D) operating income after taxes minus depreciation.
A) operating income less taxes plus depreciation.
B) operating income less taxes.
C) operating income before depreciation and taxes plus depreciation.
D) operating income after taxes minus depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
There are several disadvantages to the payback method, among them:
A) Payback ignores the interest that is earned during the period of time the project is in place.
B) Payback emphasizes receiving money back as fast as possible for reinvestment.
C) Payback is basic to use and understand.
D) Payback can be used in conjunction with time-adjusted methods of evaluation.
A) Payback ignores the interest that is earned during the period of time the project is in place.
B) Payback emphasizes receiving money back as fast as possible for reinvestment.
C) Payback is basic to use and understand.
D) Payback can be used in conjunction with time-adjusted methods of evaluation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Dammon Corp. has the following investment opportunities:  Under the payback method and assuming these machines are mutually exclusive, which machine(s) would Dammon Corp. choose?
Under the payback method and assuming these machines are mutually exclusive, which machine(s) would Dammon Corp. choose?
A) Machine A
B) Machine B
C) Machine C
D) Machine A and B
 Under the payback method and assuming these machines are mutually exclusive, which machine(s) would Dammon Corp. choose?
Under the payback method and assuming these machines are mutually exclusive, which machine(s) would Dammon Corp. choose?A) Machine A
B) Machine B
C) Machine C
D) Machine A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Assume a $6,500 investment and the following cash flows for two alternatives. 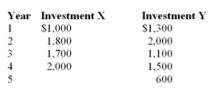 Under the payback method, which of the following could be concluded?
Under the payback method, which of the following could be concluded?
A) Investment X should be selected.
B) Investment Y should be selected.
C) Investment X and Y provide the same payback period.
D) The investments are not comparable since they have different time frames.
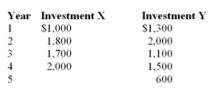 Under the payback method, which of the following could be concluded?
Under the payback method, which of the following could be concluded?A) Investment X should be selected.
B) Investment Y should be selected.
C) Investment X and Y provide the same payback period.
D) The investments are not comparable since they have different time frames.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Assume a corporation has earnings before depreciation and taxes of $82,000, depreciation of $45,000, and that it has a 30% tax bracket. What are the after-tax cash flows for the company?
A) $70,900
B) $82,000
C) $42,000
D) $127,000
A) $70,900
B) $82,000
C) $42,000
D) $127,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is not a time-adjusted method for ranking investment proposals?
A) The net present value method
B) The payback method
C) The internal rate of return method
D) All of these options are time-adjusted methods.
A) The net present value method
B) The payback method
C) The internal rate of return method
D) All of these options are time-adjusted methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Assume a project has earnings before depreciation and taxes of $15,000, depreciation of $25,000, and that the firm has a 30% tax bracket. What are the after-tax cash flows for the project?
A) A positive $18,000
B) A positive $19,000
C) A loss of $21,000
D) A positive $28,000
A) A positive $18,000
B) A positive $19,000
C) A loss of $21,000
D) A positive $28,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Capital budgeting is primarily concerned with
A) capital formation in the economy.
B) planning future financing needs.
C) evaluating investment alternatives.
D) minimizing the cost of capital.
A) capital formation in the economy.
B) planning future financing needs.
C) evaluating investment alternatives.
D) minimizing the cost of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An appropriate capital budgeting process requires that the following steps be taken in which order? a) Collection of data
B) Re evaluation and adjustment
C) Evaluation and decision making
D) Search for and discovery of investment opportunities
A) d, a, c, b
B) d, a, b, c
C) d, b, a, c
D) b, d, a, c
B) Re evaluation and adjustment
C) Evaluation and decision making
D) Search for and discovery of investment opportunities
A) d, a, c, b
B) d, a, b, c
C) d, b, a, c
D) b, d, a, c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements about the "payback method" is true?
A) The payback method considers cash flows after the payback has been reached.
B) The payback method does not consider the time value of money.
C) The payback method uses discounted cash-flow techniques.
D) The payback method generally leads to the same decision as other investment selection methods.
A) The payback method considers cash flows after the payback has been reached.
B) The payback method does not consider the time value of money.
C) The payback method uses discounted cash-flow techniques.
D) The payback method generally leads to the same decision as other investment selection methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For acceptable investments, the reinvestment assumption under the internal rate of return is generally
A) higher acceptance than under the net present value method.
B) lower acceptance than under the net present value method.
C) at the cost of capital.
D) below the cost of capital.
A) higher acceptance than under the net present value method.
B) lower acceptance than under the net present value method.
C) at the cost of capital.
D) below the cost of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The internal rate of return assumes that funds are reinvested at the
A) cost of capital.
B) yield on the investment.
C) minimal acceptable rate to the corporation.
D) yield to maturity.
A) cost of capital.
B) yield on the investment.
C) minimal acceptable rate to the corporation.
D) yield to maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The internal rate of return and net present value methods
A) always give the same investment decision answer.
B) never give the same investment decision answer.
C) usually give the same investment decision answer.
D) always give conclusions different from the payback method.
A) always give the same investment decision answer.
B) never give the same investment decision answer.
C) usually give the same investment decision answer.
D) always give conclusions different from the payback method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The net present value (NPV) method is considered to be a better method of evaluation than the internal rate of return (IRR) method because the NPV method
A) uses time value of money while IRR does not.
B) is a more liberal method of analysis.
C) assumes that cash flows can be reinvested at the firm's more conservative cost of capital.
D) None of these options are true.
A) uses time value of money while IRR does not.
B) is a more liberal method of analysis.
C) assumes that cash flows can be reinvested at the firm's more conservative cost of capital.
D) None of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If projects are mutually exclusive
A) they can only be accepted under capital rationing.
B) the selection of one alternative precludes the selection of other alternatives.
C) the payback method should be used.
D) only the net present value method can be used.
A) they can only be accepted under capital rationing.
B) the selection of one alternative precludes the selection of other alternatives.
C) the payback method should be used.
D) only the net present value method can be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
You require an internal rate of return of 8% to accept a project. If the project will yield $10,000 per year for 10 years, what is the maximum amount that you would be willing to invest in the project?
A) $51,400
B) $67,100
C) $100,000
D) $144,870
A) $51,400
B) $67,100
C) $100,000
D) $144,870

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As the cost of capital increases
A) fewer projects are accepted.
B) more projects are accepted.
C) project selection remains unchanged.
D) None of these options
A) fewer projects are accepted.
B) more projects are accepted.
C) project selection remains unchanged.
D) None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How would the salvage value be treated in a net present value calculation?
A) Disregard the salvage
B) As a positive cash flow in the final year that the asset is used
C) As a negative cash flow in the final year that the asset is used
D) As a negative cash flow in the first year that the asset is used
A) Disregard the salvage
B) As a positive cash flow in the final year that the asset is used
C) As a negative cash flow in the final year that the asset is used
D) As a negative cash flow in the first year that the asset is used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If an investment project has a positive net present value, then the internal rate of return is
A) less than the cost of capital.
B) greater than the cost of capital.
C) equal to the cost of capital.
D) indeterminate, because it depends on the length of the project.
A) less than the cost of capital.
B) greater than the cost of capital.
C) equal to the cost of capital.
D) indeterminate, because it depends on the length of the project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
With non-mutually exclusive projects,
A) the payback method will select the best project.
B) only one project can be accepted.
C) the IRR, NPV, and payback methods are all treated equally in the decision making process.
D) the net present value and the internal rate of return methods will usually accept or reject the same project.
A) the payback method will select the best project.
B) only one project can be accepted.
C) the IRR, NPV, and payback methods are all treated equally in the decision making process.
D) the net present value and the internal rate of return methods will usually accept or reject the same project.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A characteristic of capital budgeting is that
A) a large amount of money is always involved.
B) the net present value must be positive to be accepted.
C) the internal rate of return must be greater than the cost of capital.
D) the time horizon is at least five years.
A) a large amount of money is always involved.
B) the net present value must be positive to be accepted.
C) the internal rate of return must be greater than the cost of capital.
D) the time horizon is at least five years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The _________ assumes returns are reinvested at the cost of capital.
A) payback method
B) internal rate of return method
C) net present value method
D) capital rationing procedure
A) payback method
B) internal rate of return method
C) net present value method
D) capital rationing procedure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Assuming that a firm has no capital rationing constraint and that a firm's investment alternatives are not mutually exclusive, the firm should accept all investment proposals
A) for which it can obtain financing.
B) that have a positive net present value.
C) that have positive cash flows.
D) that provide returns greater than the after-tax cost of debt.
A) for which it can obtain financing.
B) that have a positive net present value.
C) that have positive cash flows.
D) that provide returns greater than the after-tax cost of debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
You buy a new piece of equipment for $7,360, and you receive a cash inflow of $1,000 per year for 10 years. What is the internal rate of return?
A) 4%
B) 6%
C) 8%
D) 10%
A) 4%
B) 6%
C) 8%
D) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The longer the life of an investment
A) the more significant the discount rate.
B) the less significant the discount rate.
C) the more it can initially cost.
D) the less it can initially cost.
A) the more significant the discount rate.
B) the less significant the discount rate.
C) the more it can initially cost.
D) the less it can initially cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose that interest rates (and, therefore, the firm's weighted average cost of capital) increase. This WOULD NOT CHANGE the capital budgeting choices a firm would make if it
A) uses payback method analysis.
B) uses net present value analysis.
C) uses internal rate of return analysis.
D) uses profitability indices.
A) uses payback method analysis.
B) uses net present value analysis.
C) uses internal rate of return analysis.
D) uses profitability indices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In using the internal rate of return method, it is assumed that cash flows can be reinvested at
A) the cost of equity.
B) the cost of capital.
C) the internal rate of return.
D) the prevailing interest rate.
A) the cost of equity.
B) the cost of capital.
C) the internal rate of return.
D) the prevailing interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A project requires an investment of $2,500 and has a net present value of $430. If the internal rate of return is 10%, what is the profitability index for the project?
A) 0.25
B) 2.33
C) 0.70
D) 1.17
A) 0.25
B) 2.33
C) 0.70
D) 1.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The net present value method (NPV) is a more conservative technique for selecting investment projects than the internal rate of return method because the NPV method
A) assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the project's internal rate of return.
B) concentrates on the liquidity aspects of investment projects.
C) assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the firm's weighted average cost of capital.
D) None of these options are true.
A) assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the project's internal rate of return.
B) concentrates on the liquidity aspects of investment projects.
C) assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the firm's weighted average cost of capital.
D) None of these options are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Stone Inc. is evaluating a project with an initial cost of $9,500. Cash inflows are expected to be $1,500, $1,500, and $10,000 in the three years over which the project will produce cash flows. If the discount rate is 6%, what is the net present value of the project?
A) $11,150
B) $26,930
C) $8,430
D) $1,650
A) $11,150
B) $26,930
C) $8,430
D) $1,650

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



