Deck 4: Extensions of Mendelian Inheritance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Extensions of Mendelian Inheritance
1
In rabbits, full coat color (c) is the dominant trait. A second allele, chinchilla (cch) is recessive to full coat color. Himalayan coat color (ch) is recessive to chinchilla and full coat colors and albino (c) is recessive to all coat colors. If two chinchilla rabbits mate, what coat color is not possible in their offspring?
A) Full coat color
B) Chinchilla coat color
C) Himalayan coat color
D) Albino coat color
E) All coat colors are possible
A) Full coat color
B) Chinchilla coat color
C) Himalayan coat color
D) Albino coat color
E) All coat colors are possible
A
2
An individual with type A blood and an individual with type B blood mate and have offspring. What blood type is not possible in their offspring?
A)Type O blood
B)Type A blood
C)Type B blood
D)Type AB blood
E)All blood types are possible
A)Type O blood
B)Type A blood
C)Type B blood
D)Type AB blood
E)All blood types are possible
E
3
Huntington disease in humans is an example of a(n) ____________.
A)essential gene
B)lethal allele
C)semilethal allele
D)nonessential gene
E) conditional lethal allele
A)essential gene
B)lethal allele
C)semilethal allele
D)nonessential gene
E) conditional lethal allele
A
4
A paralog ____________.
A) is found for every gene in mammals
B) is only found on the X but not the Y chromosome
C) can explain the lack of phenotype for a gene knockout
D) cannot be mutated
E) has the same DNA sequence as the original duplicated gene
A) is found for every gene in mammals
B) is only found on the X but not the Y chromosome
C) can explain the lack of phenotype for a gene knockout
D) cannot be mutated
E) has the same DNA sequence as the original duplicated gene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For a certain trait, a heterozygous individual has a selective advantage as compared to a homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive individual. This is called ________.
A) codominance
B) incomplete dominance
C) overdominance
D) incomplete penetrance
E) multiple allele systems
A) codominance
B) incomplete dominance
C) overdominance
D) incomplete penetrance
E) multiple allele systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At the molecular level, which of the following best explain heterozygous advantage and overdominance?
A) A heterozygous individual can produce more varieties of homodimer proteins
B) The alleles produce two different proteins with slightly different functions
C) The proteins produced by the alleles may provide a broader range of environmental tolerance, such as temperature ranges
D) Infectious organisms may recognize only a specific functional protein
E) All of the answers are possibilities
A) A heterozygous individual can produce more varieties of homodimer proteins
B) The alleles produce two different proteins with slightly different functions
C) The proteins produced by the alleles may provide a broader range of environmental tolerance, such as temperature ranges
D) Infectious organisms may recognize only a specific functional protein
E) All of the answers are possibilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a geneticist describes a trait as being 70% penetrant, what would they mean?
A)Individuals with the trait show variation in expression
B)It is lethal in 30% of the individuals who have the trait
C)Only 70% of the individuals who carry the allele(s) for a trait express the trait
D)The trait is present in 70% of the population
A)Individuals with the trait show variation in expression
B)It is lethal in 30% of the individuals who have the trait
C)Only 70% of the individuals who carry the allele(s) for a trait express the trait
D)The trait is present in 70% of the population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Male-pattern baldness is only an autosomal dominant trait in humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In four-o'clock plants, red flower color is dominant to white flower color. However, heterozygous plants have a pink color. If a pink-flowered plant is crossed with a white-flowered plant, what will be the phenotypic ratios of their offspring?
A) ¼ red, ½ pink, ¼ white
B) All pink
C) All white
D) ½ pink, ½ white
E) ½ red, ½ pink
A) ¼ red, ½ pink, ¼ white
B) All pink
C) All white
D) ½ pink, ½ white
E) ½ red, ½ pink

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At the molecular level, type A and type B blood differ in which of the following characteristics?
A)The antigens present on the surface of the red blood cells
B)The type of sugar found in each type
C)The antibodies that are generated against the other type of blood
D)All of the answers are correct
A)The antigens present on the surface of the red blood cells
B)The type of sugar found in each type
C)The antibodies that are generated against the other type of blood
D)All of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An individual carries the allele for polydactyly, but is normal. This is an example of __________.
A) simple Mendelian inheritance
B) incomplete dominance
C) incomplete penetrance
D) codominance
E) gene dosage
A) simple Mendelian inheritance
B) incomplete dominance
C) incomplete penetrance
D) codominance
E) gene dosage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If an allele is dominant in one sex and recessive in another, it is an example of ___________.
A)sex-limited inheritance
B)sex-influenced inheritance
C)incomplete dominance
D)simple Mendelian inheritance
A)sex-limited inheritance
B)sex-influenced inheritance
C)incomplete dominance
D)simple Mendelian inheritance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The coat characteristics of arctic foxes and Siamese cats, where proteins in the extremities function differently than in other parts of the body, is an example of _________.
A) incomplete dominance
B) multiple allele systems
C) semilethal alleles
D) temperature-sensitive allele
E) None of the answers are correct
A) incomplete dominance
B) multiple allele systems
C) semilethal alleles
D) temperature-sensitive allele
E) None of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In human blood groups, the fact that an individual can have an AB blood type is an example of ___________.
A)incomplete dominance
B)incomplete penetrance
C)sex-influenced trait
D)temperature-sensitive conditional allele
E) codominance
A)incomplete dominance
B)incomplete penetrance
C)sex-influenced trait
D)temperature-sensitive conditional allele
E) codominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A woman who is heterozygous for an allele that results in X-linked pattern baldness marries a man who is nonbald. Which of the following would be true of their offspring?
A)All would be bald
B)All of the females would be nonbald, all males would be bald
C)All of the females would be nonbald, ½ of the males would be bald
D)½ of females would be bald, and ½ of the males would be bald
E)All would be nonbald
A)All would be bald
B)All of the females would be nonbald, all males would be bald
C)All of the females would be nonbald, ½ of the males would be bald
D)½ of females would be bald, and ½ of the males would be bald
E)All would be nonbald

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Temperature-sensitive alleles are examples of _________.
A)essential genes
B)lethal alleles
C)semilethal alleles
D)nonessential genes
E) conditional lethal alleles
A)essential genes
B)lethal alleles
C)semilethal alleles
D)nonessential genes
E) conditional lethal alleles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Humans homozygous for the sickle cell allele have sickle cell anemia. A human that is heterozygous for the sickle cell allele is an example of _____________.
A) codominance
B) incomplete penetrance
C) heterozygous advantage
D) multiple allele systems
A) codominance
B) incomplete penetrance
C) heterozygous advantage
D) multiple allele systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A heterozygote possesses a phenotype that is intermediate between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. This is most likely an example of ________.
A)lethal alleles
B)incomplete dominance
C)gene dosage
D)sex-influenced inheritance
A)lethal alleles
B)incomplete dominance
C)gene dosage
D)sex-influenced inheritance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Genes that are not required for survival, but are likely to be beneficial to the organism, are called _________.
A)essential genes
B)lethal alleles
C)semilethal alleles
D)nonessential genes
E) conditional lethal alleles
A)essential genes
B)lethal alleles
C)semilethal alleles
D)nonessential genes
E) conditional lethal alleles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Phenylketonuria in humans is an example of __________.
A)incomplete penetrance
B)codominance
C)an environmentally-influenced trait
D)incomplete dominance
A)incomplete penetrance
B)codominance
C)an environmentally-influenced trait
D)incomplete dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How did Bateson and Punnett's work with comb morphology in chickens differ from the dihybrid work of Mendel?
A)They were working with sex-limited traits.
B)Their F2 offspring displayed 4 unique phenotypes, not the four combinations of two phenotypes expected in a Mendelian cross.
C)½ of their combinations were lethal.
D)The expression of their trait varied by the environment in which the chickens were raised.
A)They were working with sex-limited traits.
B)Their F2 offspring displayed 4 unique phenotypes, not the four combinations of two phenotypes expected in a Mendelian cross.
C)½ of their combinations were lethal.
D)The expression of their trait varied by the environment in which the chickens were raised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A _______ allele encodes a protein that is made in the proper amount and functions normally.
A) loss-of-function
B) mutant
C) wild-type
D) gain-of-function
E) lethal
A) loss-of-function
B) mutant
C) wild-type
D) gain-of-function
E) lethal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a dihybrid cross of two heterozygous individuals, you expect a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in the offspring, but observe a ratio of 9:7. What is the most likely explantation?
A)Codominance
B)It is a sex-limited trait
C)Simple Mendelian inheritance
D)Incomplete penetrance
E) Epistatic interaction of the two genes
A)Codominance
B)It is a sex-limited trait
C)Simple Mendelian inheritance
D)Incomplete penetrance
E) Epistatic interaction of the two genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In overdominance, the _______ genotype is beneficial over the _______ genotypes.
A)heterozygous, homozygous
B)homozygous, heterozygous
C)homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive
D)homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant
E)incomplete dominant, codominant
A)heterozygous, homozygous
B)homozygous, heterozygous
C)homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive
D)homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant
E)incomplete dominant, codominant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a combination of two or more genes is required to produce a specific trait, it is called a(n) _______.
A) overdominance
B) simple mendelian trait
C) sex-influenced trait
D) sex-linked trait
E) gene interaction
A) overdominance
B) simple mendelian trait
C) sex-influenced trait
D) sex-linked trait
E) gene interaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In an epistatic interaction, the genes must be located on the same chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Human blood groups are determined by antigens on the surface of red blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The presence of a group of antigens that determine blood type is an example of a(n) ____________.
A) semilethal allele
B) sex-linked trait
C) multiple allele system
D) incomplete dominance
A) semilethal allele
B) sex-linked trait
C) multiple allele system
D) incomplete dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The trait of cream-colored eyes in Drosophila is an example of ________.
A)simple recessive alleles
B)incomplete penetrance of red eyes
C)a gene modifier effect in eye color
D)gene dosage
E) a spontaneous mutation
A)simple recessive alleles
B)incomplete penetrance of red eyes
C)a gene modifier effect in eye color
D)gene dosage
E) a spontaneous mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The interaction of two genes to produce a phenotype was first described by __________.
A)Morgan and Bridges
B)Mendel
C)Darwin
D)Bateson and Punnett
E)None of the answers are correct
A)Morgan and Bridges
B)Mendel
C)Darwin
D)Bateson and Punnett
E)None of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Variable expressivity means that the phenotype of a trait can vary between individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not correct concerning epistatic interactions?
A)They can be associated with enzymatic pathways.
B)They produce variations in the expected 9:3:3:1 ratio of a dihybrid cross.
C)They can result when a gene at one locus masks the expression of a gene at a different locus.
D)They always result in a 9:7 ratio of a dihybrid cross.
E) They are due to gene interactions.
A)They can be associated with enzymatic pathways.
B)They produce variations in the expected 9:3:3:1 ratio of a dihybrid cross.
C)They can result when a gene at one locus masks the expression of a gene at a different locus.
D)They always result in a 9:7 ratio of a dihybrid cross.
E) They are due to gene interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Incomplete dominance is an example of blending of phenotypes, not genotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Typically, a recessive allele increases the expression of a functional protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Incomplete penetrance indicates that individuals who possess a dominant trait always express the trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Epistasis is _______________.
A)another term for overdominance
B)when one gene can mask the expression of a second gene
C)a trait that is only expressed in one sex of the species
D)when two dominant alleles can be expressed in the same individual
E)None of the answers are correct
A)another term for overdominance
B)when one gene can mask the expression of a second gene
C)a trait that is only expressed in one sex of the species
D)when two dominant alleles can be expressed in the same individual
E)None of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When wild-type offspring are produced from a cross between parents that both display the same recessive phenotype, this illustrates the genetic phenomenon of _______.
A) simple recessive alleles
B) incomplete penetrance
C) complementation
D) gene dosage
E) a spontaneous mutation
A) simple recessive alleles
B) incomplete penetrance
C) complementation
D) gene dosage
E) a spontaneous mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In cattle, the presence or absence of scurs follows a sex-influenced pattern of inheritance. A heterozygous male has _______ and a heterozygous female has _______ .
A) Y-linked, X-linked
B) no scurs, scurs
C) X-linked, Y-linked
D) scurs, no scurs
A) Y-linked, X-linked
B) no scurs, scurs
C) X-linked, Y-linked
D) scurs, no scurs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Paralogs are often functionally redundant and can compensate for the loss of either of the paralogs in a set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The multiple effects of a single gene on the phenotype of an organism is called _______.
A)epistasis
B)penetrance
C)expressivity
D)overdominance
E) pleiotropy
A)epistasis
B)penetrance
C)expressivity
D)overdominance
E) pleiotropy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Heavy metals, such as copper, are required for proper development. However, if too much copper is present it can lead to developmental defects. A scientist was interested in studying the developmental defects that could occur at various concentrations of copper. Genetically identical organisms were grown in 6 different concentrations of copper. This experiment evaluates a(n) _____________.
A) epistasis
B) dominant trait
C) recessive trait
D) norm of reaction
A) epistasis
B) dominant trait
C) recessive trait
D) norm of reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The pedigree below shows the inheritance pattern of a rare allele for one family. The filled in circles and square show affected individuals. What is the probability of individual III-2 being born female and affected? 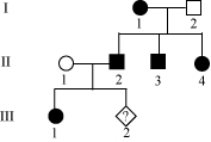
A) 1/2
B) 1/3
C) 1/4
D) 0

A) 1/2
B) 1/3
C) 1/4
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The pedigree below shows the inheritance pattern of a rare allele for one family. The filled in circles and square show affected individuals. What is the probability of individual III-2 being born male and affected? 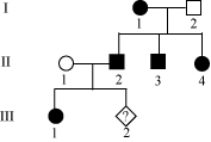
A) 1/2
B) 1/3
C) 1/4
D) 0

A) 1/2
B) 1/3
C) 1/4
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a light-eosin eye male Drosophila is crossed to a homozygous red eyed female, what will be the phenotype of their offspring?
A)All offspring will have red eyes.
B)All males will have light-eosin eyes and all females will have eosin eye
C)All females will have red eyes, all males will have light-eosin eyes.
D)All flies will have white eyes.
A)All offspring will have red eyes.
B)All males will have light-eosin eyes and all females will have eosin eye
C)All females will have red eyes, all males will have light-eosin eyes.
D)All flies will have white eyes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Filled in circles and square show affected individuals. Select the mode of inheritance for individual III-3 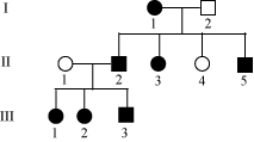
A) Incomplete dominance
B) Codominance
C) Pseudoautosomal inheritance
D) X-linked inheritance

A) Incomplete dominance
B) Codominance
C) Pseudoautosomal inheritance
D) X-linked inheritance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A male Manx cat and a female Manx cat produce kitten. What is the probability that kitten has a non-manx tail?
A) 1/3
B) 1/2
C) 1/4
D) 2/3
A) 1/3
B) 1/2
C) 1/4
D) 2/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



