Deck 12: Inflation and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/163
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Inflation and Aggregate Supply
1
At a constant rate of exchange between currencies, higher inflation makes domestic goods sold abroad ____expensive and, hence, ____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) more; increases
B) less; increases
C) less; decreases
D) more; decreases
A) more; increases
B) less; increases
C) less; decreases
D) more; decreases
more; decreases
2
As inflation increases, households become _____ uncertain leading to _____ spending.
A) more; more
B) more; less
C) less; more
D) less; less
A) more; more
B) more; less
C) less; more
D) less; less
more; less
3
The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between inflation and:
A) the nominal interest rate.
B) the exchange rate.
C) the real interest rate.
D) short-run equilibrium output.
A) the nominal interest rate.
B) the exchange rate.
C) the real interest rate.
D) short-run equilibrium output.
short-run equilibrium output.
4
High levels of inflation ___ the real value of money and, hence, ____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) reduce; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) reduce; decrease
D) increase; increase
A) reduce; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) reduce; decrease
D) increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the Fed's monetary policy reaction function does not change, then when inflation increases the Fed responds by _____ the real interest rate, which _____ consumption and investment spending, which _____ output.
A) increasing; increases; increases
B) increasing; increases; decreases
C) increasing; decreases; decreases
D) decreasing; decreases; decreases
A) increasing; increases; increases
B) increasing; increases; decreases
C) increasing; decreases; decreases
D) decreasing; decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All else equal, a decrease in the rate of inflation ____ aggregate spending and ____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) increases; increases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; decreases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; decreases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Higher rates of inflation reduce spending because:
A) the Fed reacts to the higher inflation by lowering interest rates.
B) the reduction in wealth, resulting from the reduced real value of money, restricts spending.
C) resources are redistributed from low-spending households to high-spending households.
D) the real value of money increases.
A) the Fed reacts to the higher inflation by lowering interest rates.
B) the reduction in wealth, resulting from the reduced real value of money, restricts spending.
C) resources are redistributed from low-spending households to high-spending households.
D) the real value of money increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
For a fixed target real interest rate and target inflation rate, when inflation increases, the Fed ____ interest rates, hence _____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; increasing
C) increases; decreasing
D) decreases; decreasing
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; increasing
C) increases; decreasing
D) decreases; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Because increases in inflation reduce aggregate spending and short-run equilibrium output:
A) the short-run aggregate supply line is downward sloping.
B) the aggregate demand curve is horizontal.
C) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
D) the aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.
A) the short-run aggregate supply line is downward sloping.
B) the aggregate demand curve is horizontal.
C) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
D) the aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping for all of the following reasons EXCEPT for the:
A) response of the Fed to inflation through its policy reaction function.
B) effect of inflation on the value of money.
C) impact of inflation on the consumer price index (CPI).
D) distributional impact of inflation on spending.
A) response of the Fed to inflation through its policy reaction function.
B) effect of inflation on the value of money.
C) impact of inflation on the consumer price index (CPI).
D) distributional impact of inflation on spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Increases in inflation redistribute resources from _____-spending to ____-spending households and hence, _____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) high; low; increase
B) low; high; increase
C) high; low; decrease
D) low; high; decrease
A) high; low; increase
B) low; high; increase
C) high; low; decrease
D) low; high; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Lower rates of inflation increase planned spending because:
A) the Fed reacts to the lower inflation by lowering interest rates.
B) the reduction in wealth, resulting from the reduced real value of money, restrains spending.
C) resources are redistributed from high-spending households to low-spending households.
D) the prices of domestic goods sold abroad increase (with a constant exchange rate).
A) the Fed reacts to the lower inflation by lowering interest rates.
B) the reduction in wealth, resulting from the reduced real value of money, restrains spending.
C) resources are redistributed from high-spending households to low-spending households.
D) the prices of domestic goods sold abroad increase (with a constant exchange rate).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the Fed's monetary policy reaction function does not change, then when inflation decreases the Fed responds by _____ the real interest rate, which _____ consumption and investment spending, which _____ output.
A) decreasing; increases; increases
B) increasing; increases; decreases
C) increasing; decreases; decreases
D) decreasing; decreases; decreases
A) decreasing; increases; increases
B) increasing; increases; decreases
C) increasing; decreases; decreases
D) decreasing; decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Because decreases in inflation increase aggregate spending and short-run equilibrium output:
A) the short-run aggregate supply line is downward sloping.
B) the aggregate demand curve is horizontal.
C) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
D) the aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.
A) the short-run aggregate supply line is downward sloping.
B) the aggregate demand curve is horizontal.
C) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
D) the aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Changes in aggregate spending not caused by changes in output or the inflation rate, also known as exogenous changes in spending, will shift the:
A) short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) potential output line.
D) aggregate demand curve.
A) short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) potential output line.
D) aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All else equal, an increase in the rate of inflation ____ aggregate spending and ____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) increases; increases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; decreases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) decreases; increases
C) increases; decreases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The aggregate demand curve shows the relationship between short-run equilibrium output and the:
A) nominal interest rate.
B) real interest rate.
C) unemployment rate.
D) inflation rate.
A) nominal interest rate.
B) real interest rate.
C) unemployment rate.
D) inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As inflation decreases, households become _____ uncertain leading to _____ spending.
A) more; more
B) more; less
C) less; more
D) less; less
A) more; more
B) more; less
C) less; more
D) less; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The aggregate demand curve shifts when there are changes in:
A) inflation inertia and aggregate supply shocks.
B) exogenous spending and the Fed's reaction function.
C) exogenous spending and inflation inertia.
D) potential output and exogenous spending.
A) inflation inertia and aggregate supply shocks.
B) exogenous spending and the Fed's reaction function.
C) exogenous spending and inflation inertia.
D) potential output and exogenous spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For a fixed target real interest rate and target inflation rate, when inflation decreases, the Fed ____ interest rates, hence _____ short-run equilibrium output.
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; increasing
C) increases; decreasing
D) decreases; decreasing
A) increases; increasing
B) decreases; increasing
C) increases; decreasing
D) decreases; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
A) Income taxes are raised.
B) The government increases spending on education.
C) Consumers become pessimistic about the future.
D) Business managers become pessimistic about the future.
A) Income taxes are raised.
B) The government increases spending on education.
C) Consumers become pessimistic about the future.
D) Business managers become pessimistic about the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function is a _____ of monetary policy, and the aggregate demand curve _______.
A) tightening; shifts right
B) easing; shifts right
C) tightening; shifts left
D) easing; shifts left
A) tightening; shifts right
B) easing; shifts right
C) tightening; shifts left
D) easing; shifts left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left?
A) Income taxes are lowered.
B) The government increases spending on education.
C) Consumers become optimistic about the future.
D) Foreign economies fall into recession, reducing their demand for domestic exports.
A) Income taxes are lowered.
B) The government increases spending on education.
C) Consumers become optimistic about the future.
D) Foreign economies fall into recession, reducing their demand for domestic exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Based on the figure below, the economy is initially at point A on the monetary policy reaction function (RF1) and the aggregate demand curve (AD1). The actual rate of inflation is ' and the Federal Reserve's target inflation rate is *1. 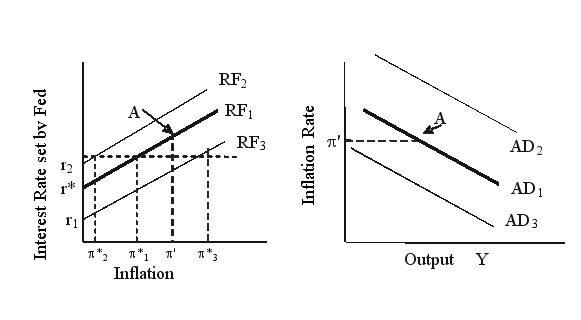 If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to *2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to *2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
A) shift to RF3; shift to AD2
B) shift to RF2; shift to AD2
C) shift to RF3: shift to AD3
D) shift to RF2: shift to AD3
 If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to *2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to *2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.A) shift to RF3; shift to AD2
B) shift to RF2; shift to AD2
C) shift to RF3: shift to AD3
D) shift to RF2: shift to AD3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
A) Income taxes are raised.
B) The government reduces purchases to balance the budget.
C) Consumers become more optimistic about the future.
D) Foreign economies fall into recession, reducing their demand for domestic exports.
A) Income taxes are raised.
B) The government reduces purchases to balance the budget.
C) Consumers become more optimistic about the future.
D) Foreign economies fall into recession, reducing their demand for domestic exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For a given level of inflation, if a rise in the stock market makes consumers more willing to spend, known as the wealth effect, then the _____ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For a given level of inflation, if a resolution of international disputes leads to a cutback in government military spending, then the _____ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For a given level of inflation, if concerns about future weakness in the economy cause businesses to reduce their spending on new capital, then the _____ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The AD curve can be shifted by:
A) both fiscal and monetary policy.
B) neither fiscal nor monetary policy.
C) fiscal policy only.
D) monetary policy only.
A) both fiscal and monetary policy.
B) neither fiscal nor monetary policy.
C) fiscal policy only.
D) monetary policy only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For a given inflation rate, if increasing threats to domestic security cause the government to increase military spending, then the ______ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the Federal Reserve reduces its target rate of inflation, it will set a _____ real interest rate at every inflation rate and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
A) higher; shift to the right
B) lower; shift to the right
C) higher; shift to the left
D) lower; shift to the left
A) higher; shift to the right
B) lower; shift to the right
C) higher; shift to the left
D) lower; shift to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function is a _____ of monetary policy, and the aggregate demand curve _______.
A) tightening; shifts right
B) easing; shifts right
C) tightening; shifts left
D) easing; shifts left
A) tightening; shifts right
B) easing; shifts right
C) tightening; shifts left
D) easing; shifts left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the Federal Reserve raises its target inflation rate, the monetary policy reaction function _____ and the aggregate demand curve _____.
A) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the right
B) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the right
C) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the left
D) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the left
A) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the right
B) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the right
C) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the left
D) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For a given level of inflation, if there is a greater reluctance by foreigners to purchase domestic goods, then the _____ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate, the monetary policy reaction function _____ and the aggregate demand curve _____.
A) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the right
B) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the right
C) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the left
D) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the left
A) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the right
B) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the right
C) shifts upward to the left; shifts to the left
D) shifts downward to the right; shifts to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exogenous changes in spending refer to changes in planned spending:
A) caused by changes in output.
B) caused by changes in the inflation rate.
C) caused by changes in the real interest rate.
D) not caused by changes in output or changes in the inflation rate.
A) caused by changes in output.
B) caused by changes in the inflation rate.
C) caused by changes in the real interest rate.
D) not caused by changes in output or changes in the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left?
A) Income taxes are raised.
B) The government increases spending on education.
C) Consumers become optimistic about the future.
D) A new technology is developed that will increase profits.
A) Income taxes are raised.
B) The government increases spending on education.
C) Consumers become optimistic about the future.
D) A new technology is developed that will increase profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For a given level of inflation, if bright prospects for the future of the economy cause businesses to increase their investment in new capital, then the _____ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When the Federal Reserve increases its target rate of inflation, it will set a _____ real interest rate at every inflation rate and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
A) higher; shift to the right
B) lower; shift to the right
C) higher; shift to the left
D) lower; shift to the left
A) higher; shift to the right
B) lower; shift to the right
C) higher; shift to the left
D) lower; shift to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For a given level of inflation, if there is a greater willingness by foreigners to purchase domestic goods, then the _____ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) short-run aggregate supply line; downward
C) aggregate demand curve; left
D) short-run aggregate supply line; upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When actual output equals potential output there is ____ output gap and the rate of inflation will tend to ____.
A) an expansionary; increase
B) an expansionary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; increase
A) an expansionary; increase
B) an expansionary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If households and firms expect higher rates of inflation, the ______ curve will shift _____.
A) AD; rightward
B) SRAS; upward
C) SRAS; downward
D) AD; until it becomes vertical
A) AD; rightward
B) SRAS; upward
C) SRAS; downward
D) AD; until it becomes vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right when the Fed:
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Based on the figure below, the economy is initially at point A on the monetary policy reaction function (RF1) and the aggregate demand curve (AD1). The actual rate of inflation is ' and the Federal Reserve's target inflation rate is *1. 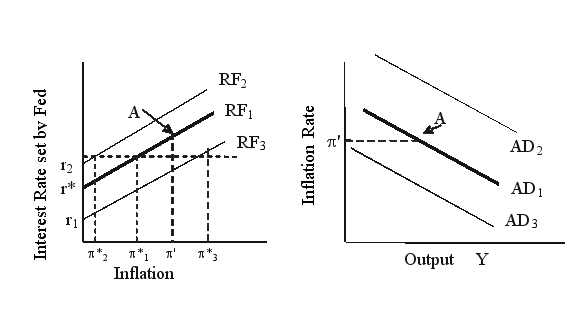 If the Federal Reserve raises its target inflation rate to *3, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
If the Federal Reserve raises its target inflation rate to *3, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
A) shift to RF3; shift to AD2
B) shift to RF2; shift to AD2
C) shift to RF3: shift to AD3
D) shift to RF2: shift to AD3
 If the Federal Reserve raises its target inflation rate to *3, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.
If the Federal Reserve raises its target inflation rate to *3, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will _____ and the aggregate demand curve will _____.A) shift to RF3; shift to AD2
B) shift to RF2; shift to AD2
C) shift to RF3: shift to AD3
D) shift to RF2: shift to AD3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For a fixed inflation rate target, an increase in the inflation rate corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve and an increase in exogenous spending corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) shift left of; movement up
B) movement up; shift right of
C) shift left of; shift right of
D) movement up; movement down
A) shift left of; movement up
B) movement up; shift right of
C) shift left of; shift right of
D) movement up; movement down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Inflation inertia is the result of the behavior of ____ and the existence of ______.
A) the central bank; automatic stabilizers
B) real and nominal interest rates; an output gap
C) autonomous aggregate demand; the Fed's policy reaction function
D) inflation expectations; long-term wage and price contracts
A) the central bank; automatic stabilizers
B) real and nominal interest rates; an output gap
C) autonomous aggregate demand; the Fed's policy reaction function
D) inflation expectations; long-term wage and price contracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Inflation inertia is the tendency for inflation to:
A) equal zero.
B) change relatively slowly from year to year.
C) decrease when the Fed increases interest rates.
D) increase when the Fed decreases interest rates.
A) equal zero.
B) change relatively slowly from year to year.
C) decrease when the Fed increases interest rates.
D) increase when the Fed decreases interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The economy moves down a stationary aggregate demand curve when the Fed:
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the left when the Fed:
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
High expected inflation leads to ____ increases in wages and costs and to ____ actual inflation.
A) large; high
B) large; low
C) small; low
D) small; high
A) large; high
B) large; low
C) small; low
D) small; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For a fixed inflation rate target, a decrease in the inflation rate corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve and a decrease in exogenous spending corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) shift left of; movement up
B) movement up; shift right of
C) shift left of; shift right of
D) movement down; shift left of
A) shift left of; movement up
B) movement up; shift right of
C) shift left of; shift right of
D) movement down; shift left of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The economy moves up a stationary aggregate demand curve when the Fed:
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
A) increases its target inflation rate, reflected by a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
B) decreases its target inflation rate, reflected by an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function.
C) increases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.
D) decreases real interest rates in response to inflation, but does not change its target inflation rate or the Fed's policy reaction function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Low expected inflation leads to ____ increases in wages and costs and to ____ actual inflation.
A) large; high
B) large; low
C) small; low
D) small; high
A) large; high
B) large; low
C) small; low
D) small; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Changes in the expected rate of inflation will:
A) not shift but create a movement along the SRAS curve.
B) shift the SRAS curve downward or upward.
C) cause the SRAS curve to become vertical.
D) cause the SRAS curve to become upward-sloping.
A) not shift but create a movement along the SRAS curve.
B) shift the SRAS curve downward or upward.
C) cause the SRAS curve to become vertical.
D) cause the SRAS curve to become upward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve and a decrease in exogenous spending corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) shift left of; movement up
B) shift left of; shift right of
C) shift right of; shift left of
D) movement up; shift right of
A) shift left of; movement up
B) shift left of; shift right of
C) shift right of; shift left of
D) movement up; shift right of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve and an increase in exogenous spending corresponds to a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) shift left of; movement up
B) shift left of; shift right of
C) shift right of; shift left of
D) movement up; shift right of
A) shift left of; movement up
B) shift left of; shift right of
C) shift right of; shift left of
D) movement up; shift right of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A low rate of expected inflation tends to lead to a ___ rate of actual inflation and a high rate of expected inflation tends to lead to a ____ rate of actual inflation.
A) high; high
B) high; low
C) low; low
D) low; high
A) high; high
B) high; low
C) low; low
D) low; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A decrease in interest rates by the Fed based on a given and unchanged policy reaction function represents a ____ the aggregate demand curve, and lower interest rates resulting from a downward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function represents a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) shift left of; movement up
B) shift left of; shift right of
C) movement up; movement down
D) movement down; shift right of
A) shift left of; movement up
B) shift left of; shift right of
C) movement up; movement down
D) movement down; shift right of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An increase in interest rates by the Fed based on a given and unchanged policy reaction function represents a ____ the aggregate demand curve, and higher interest rates resulting from an upward shift in the Fed's policy reaction function represents a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) shift left of; movement up
B) movement up; shift left of
C) shift left of; shift right of
D) movement up; shift right
A) shift left of; movement up
B) movement up; shift left of
C) shift left of; shift right of
D) movement up; shift right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The tendency for inflation to change relatively slowly from year to year in industrial countries is called:
A) the inflation gap
B) inflation expectations.
C) inflation inertia.
D) potential inflation.
A) the inflation gap
B) inflation expectations.
C) inflation inertia.
D) potential inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When inflation equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions and output equals the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation, the economy is said to be in ____ equilibrium.
A) potential
B) short-run
C) long-run
D) full-employment
A) potential
B) short-run
C) long-run
D) full-employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When no output gap exists actual output _____ potential output and the rate of inflation will tend to ______.
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) is less than; decrease
D) equals; remain the same
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) is less than; decrease
D) equals; remain the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The long-run aggregate supply line is:
A) downward sloping.
B) vertical at the economy's potential output.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical at the economy's actual output.
A) downward sloping.
B) vertical at the economy's potential output.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical at the economy's actual output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When a recessionary gap exists, actual output _____ potential output and the rate of inflation will tend to ______.
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) is less than; decrease
D) is less than; increase
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) is less than; decrease
D) is less than; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When an expansionary gap exists, actual output _____ potential output and the rate of inflation will tend to ______.
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) is less than; decrease
D) is less than; increase
A) exceeds; increase
B) exceeds; decrease
C) is less than; decrease
D) is less than; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The short-run aggregate supply line is:
A) downward sloping.
B) vertical at the economy's potential output.
C) upward sloping.
D) horizontal at the current rate of inflation.
A) downward sloping.
B) vertical at the economy's potential output.
C) upward sloping.
D) horizontal at the current rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Starting from potential output, if firms become less optimistic about the future and decide to decrease their investment in new capital, then this will generate a(n) _____ gap and inflation will _____.
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A vertical line showing the economy's potential is called the:
A) aggregate demand curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply line.
C) short-run equilibrium output line.
D) short-run aggregate supply line.
A) aggregate demand curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply line.
C) short-run equilibrium output line.
D) short-run aggregate supply line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When actual output is less than potential output, there is ____ output gap and the rate of inflation will tend to ____.
A) an expansionary; increase
B) an expansionary; decrease
C) a recessionary; decrease
D) a recessionary; increase
A) an expansionary; increase
B) an expansionary; decrease
C) a recessionary; decrease
D) a recessionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A vertical line showing an economy's potential output is called the _____, while a horizontal line showing the current rate of inflation is called the ____.
A) long-run aggregate supply; short-run aggregate supply
B) short-run aggregate supply; long-run aggregate supply
C) long-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
D) short-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
A) long-run aggregate supply; short-run aggregate supply
B) short-run aggregate supply; long-run aggregate supply
C) long-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
D) short-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Starting from potential output, if consumer confidence increases and consumers decide to spend more, then this will generate a(n) _____ gap and inflation will _____.
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Starting from potential output, if consumer confidence decreases and consumers decide to spend less, then this will generate a(n) _____ gap and inflation will _____.
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Graphically the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply line determines:
A) potential output.
B) short-run equilibrium.
C) long-run equilibrium.
D) exogenous spending.
A) potential output.
B) short-run equilibrium.
C) long-run equilibrium.
D) exogenous spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
At long-run equilibrium inflation _______ and output equals ______.
A) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; potential
B) equals the value determined by part expectations and pricing decisions; the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation rate
C) equals the value consistent with potential output; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
D) is stable; potential
A) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; potential
B) equals the value determined by part expectations and pricing decisions; the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation rate
C) equals the value consistent with potential output; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
D) is stable; potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Starting from potential output, if firms become more optimistic about the future and decide to increase their investment in new capital, then this will generate a(n) _____ gap and inflation will _____.
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase
A) recessionary; increase
B) recessionary; decrease
C) expansionary; decrease
D) expansionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The short-run aggregate supply curve shows _____ while the long-run aggregate supply curve shows _____.
A) potential output; the current inflation rate
B) output; aggregate spending
C) potential output; aggregate spending
D) the current inflation rate; potential output
A) potential output; the current inflation rate
B) output; aggregate spending
C) potential output; aggregate spending
D) the current inflation rate; potential output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A horizontal line showing the current rate of inflation, as determined by past expectations and pricing decisions is called the:
A) aggregate demand curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply line.
C) short-run equilibrium output line.
D) short-run aggregate supply line.
A) aggregate demand curve.
B) long-run aggregate supply line.
C) short-run equilibrium output line.
D) short-run aggregate supply line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
At short-run equilibrium inflation _______ and output equals ______.
A) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; potential
B) equals the value determined by part expectations and pricing decisions; the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation rate
C) equals the value consistent with potential output; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
D) is stable; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
A) equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions; potential
B) equals the value determined by part expectations and pricing decisions; the level of short-run equilibrium output consistent with that inflation rate
C) equals the value consistent with potential output; the level of output consistent with zero inflation
D) is stable; the level of output consistent with zero inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When actual output exceeds potential output there is ____ output gap and the rate of inflation will tend to ____.
A) an expansionary; increase
B) an expansionary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; increase
A) an expansionary; increase
B) an expansionary; decrease
C) no; remain the same
D) a recessionary; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Graphically short-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the:
A) short-run aggregate supply line and the long-run aggregate supply line
B) the aggregate expenditure line.
C) short-run aggregate supply line.
D) long-run aggregate supply line.
A) short-run aggregate supply line and the long-run aggregate supply line
B) the aggregate expenditure line.
C) short-run aggregate supply line.
D) long-run aggregate supply line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 163 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



