Deck 11: Transcription of the Genetic Code: Biosynthesis of Rna
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Transcription of the Genetic Code: Biosynthesis of Rna
1
At what point does the sigma (s) subunit of RNA polymerase released from the core enzyme?
A) Prior to the incorporation of any nucleotides into an RNA strand.
B) After transcription begins and about 10 nucleotides have been added to the RNA chain.
C) Just prior to chain termination.
D) Never; it is an intrinsic part of the core enzyme.
A) Prior to the incorporation of any nucleotides into an RNA strand.
B) After transcription begins and about 10 nucleotides have been added to the RNA chain.
C) Just prior to chain termination.
D) Never; it is an intrinsic part of the core enzyme.
B
2
The promoter site is
A) the start site for transcription in DNA
B) the binding site for regulatory proteins that stimulate transcription
C) the general region of DNA downstream from the start site
D) the site on DNA at which RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription
A) the start site for transcription in DNA
B) the binding site for regulatory proteins that stimulate transcription
C) the general region of DNA downstream from the start site
D) the site on DNA at which RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription
D
3
How do the core enzyme and the holoenzyme of RNA polymerase differ in
A) The holoenzyme includes the sigma (s) subunit, the core enzyme does not.
B) The core enzyme includes the sigma (s) subunit, the holoenzyme does not.
C) The holoenzyme transcribes from an RNA template, the core enzyme from a DNA template.
D) The core enzyme transcribes from an RNA template, the holoenzyme from a DNA template.
E) coli?
A) The holoenzyme includes the sigma (s) subunit, the core enzyme does not.
B) The core enzyme includes the sigma (s) subunit, the holoenzyme does not.
C) The holoenzyme transcribes from an RNA template, the core enzyme from a DNA template.
D) The core enzyme transcribes from an RNA template, the holoenzyme from a DNA template.
E) coli?
A
4
Which of the following correctly describes a difference between RNA & DNA polymerases?
A) RNA polymerases usually do not need a template, while DNA polymerases do.
B) DNA polymerases usually require a primer (i.e., they can only continue a strand, not start one), while most RNA polymerases do not.
C) RNA polymerases usually synthesize introns, while DNA polymerases synthesize cistrons.
D) RNA polymerases polymerize 5' 3', while DNA polymerases polymerize 3' 5'.
A) RNA polymerases usually do not need a template, while DNA polymerases do.
B) DNA polymerases usually require a primer (i.e., they can only continue a strand, not start one), while most RNA polymerases do not.
C) RNA polymerases usually synthesize introns, while DNA polymerases synthesize cistrons.
D) RNA polymerases polymerize 5' 3', while DNA polymerases polymerize 3' 5'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not a property of the sigma (s) subunit?
A) It tells the RNA Polymerase where to sit down.
B) It helps point the RNA Pol in the proper direction.
C) It causes the RNA Pol to bind tightly to the DNA.
D) It stays with the RNA Pol throughout synthesis.
A) It tells the RNA Polymerase where to sit down.
B) It helps point the RNA Pol in the proper direction.
C) It causes the RNA Pol to bind tightly to the DNA.
D) It stays with the RNA Pol throughout synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Initiation of RNA biosynthesis involves
A) recognition of the promoter region by the a subunit of RNA polymerase
B) conversion of the closed-promoter complex to the open-promoter complex
C) binding of one of the a subunits of RNA polymerase to each strand of DNA
D) incorporation of four pyrimidine nucleotides in succession
A) recognition of the promoter region by the a subunit of RNA polymerase
B) conversion of the closed-promoter complex to the open-promoter complex
C) binding of one of the a subunits of RNA polymerase to each strand of DNA
D) incorporation of four pyrimidine nucleotides in succession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The enzyme principally responsible for RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli
A) is a multisubunit enzyme
B) consists of a single polypeptide chain
C) requires Mn2+ for activity
D) requires a DNA primer
A) is a multisubunit enzyme
B) consists of a single polypeptide chain
C) requires Mn2+ for activity
D) requires a DNA primer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of following statements concerning RNA transcription is false?
A) The DNA strands become separated during synthesis.
B) Synthesis of RNA is as accurate as synthesis of DNA
C) The template strand is read in the 3' 5' direction.
D) All 4 ribonucleotides are required.
A) The DNA strands become separated during synthesis.
B) Synthesis of RNA is as accurate as synthesis of DNA
C) The template strand is read in the 3' 5' direction.
D) All 4 ribonucleotides are required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of following statements concerning RNA transcription is false?
A) The release of pyrophosphate from a nucleoside triphosphate drives the reaction.
B) RNA is synthesized from the 5' end to the 3' end.
C)
C) DNA to RNA base pairing includes A to U and G to
D) Transcription requires the use of a primer.
A) The release of pyrophosphate from a nucleoside triphosphate drives the reaction.
B) RNA is synthesized from the 5' end to the 3' end.
C)
C) DNA to RNA base pairing includes A to U and G to
D) Transcription requires the use of a primer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Minor differences in the consensus sequence for RNA Polymerase
A) can be exploited to vary the amount of mRNA which is synthesized from that gene.
B) dictate the direction that RNA Pol proceeds from the promoter.
C) dictate whether sigma (s) factor is required.
D) never occur.
A) can be exploited to vary the amount of mRNA which is synthesized from that gene.
B) dictate the direction that RNA Pol proceeds from the promoter.
C) dictate whether sigma (s) factor is required.
D) never occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following offers the best description of a Pribnow box?
A) A promoter consensus sequence located at approximately -35.
B) A promoter consensus sequence located at approximately -10.
C) A sequence forming a hairpin loop signaling the termination of transcription.
D) A sequence immediately surrounding the start site of transcription.
A) A promoter consensus sequence located at approximately -35.
B) A promoter consensus sequence located at approximately -10.
C) A sequence forming a hairpin loop signaling the termination of transcription.
D) A sequence immediately surrounding the start site of transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What provides the energy for rho-dependent chain termination?
A) ATP hydrolysis distinct from any incorporation into the chain.
B) Nucleotide hydrolysis associated with incorporation into the chain.
C) Torsional stress built into the separating DNA strands.
D) There is no energy requirement.
A) ATP hydrolysis distinct from any incorporation into the chain.
B) Nucleotide hydrolysis associated with incorporation into the chain.
C) Torsional stress built into the separating DNA strands.
D) There is no energy requirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the function of the sigma (s) subunit of RNA polymerase in
A) It recognizes promoters where transcription should begin.
B) It contains the active site for synthesis of RNA.
C) It ensures proper processitvity of the polymerase, so it doesn't stop prematurely.
D) It is involved in chain termination.
E) coli?
A) It recognizes promoters where transcription should begin.
B) It contains the active site for synthesis of RNA.
C) It ensures proper processitvity of the polymerase, so it doesn't stop prematurely.
D) It is involved in chain termination.
E) coli?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following best describes the order of events at the promoter?
A) open complex closed complex transcription initiation
B) closed complex open complex transcription initiation
C) open complex transcription initiation closed complex
D) transcription initiation open complex closed complex
A) open complex closed complex transcription initiation
B) closed complex open complex transcription initiation
C) open complex transcription initiation closed complex
D) transcription initiation open complex closed complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not part of the core promoter?
A) the transcription start site
B) the Pribnow box (-10 region)
C) the -35 region
D) the UP element
A) the transcription start site
B) the Pribnow box (-10 region)
C) the -35 region
D) the UP element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
RNA synthesis begins at the base in the DNA sequence designated by the following number:
A) +1 (plus one)
B) 0 (zero)
C) -1 (minus one)
D) -10 region (minus ten)
E) It varies among genes.
A) +1 (plus one)
B) 0 (zero)
C) -1 (minus one)
D) -10 region (minus ten)
E) It varies among genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of following statements describes a difference between replication of DNA and transcription of RNA?
A) Nucleoside triphosphates are the precursors for replication, but nucleoside diphosphates are used for transcription.
B) Both strands of DNA are copied in replication, but usually only one is copied in transcription.
C) Base pairing is used to copy the sequence in replication, but not in transcription.
D) The chain grows from the 5' to the 3' end in replication, but 3' to 5' in transcription.
A) Nucleoside triphosphates are the precursors for replication, but nucleoside diphosphates are used for transcription.
B) Both strands of DNA are copied in replication, but usually only one is copied in transcription.
C) Base pairing is used to copy the sequence in replication, but not in transcription.
D) The chain grows from the 5' to the 3' end in replication, but 3' to 5' in transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these terms does not describe the DNA strand used to direct RNA synthesis?
A) Template strand
B) Coding strand
C) Antisense strand
D) Negative or "-" strand
E) All these terms describe the complementary DNA strand
A) Template strand
B) Coding strand
C) Antisense strand
D) Negative or "-" strand
E) All these terms describe the complementary DNA strand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The end of the new mRNA molecule in E.coli.usually terminates in a string of A's

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consensus sequences are
A) sequences that are invariant throughout the DNA.
B) sequences required for transcription to occur
C) sequences that have many bases in common
D) sequences that lie far upstream of the core promoter.
A) sequences that are invariant throughout the DNA.
B) sequences required for transcription to occur
C) sequences that have many bases in common
D) sequences that lie far upstream of the core promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What provides the energy for the conversion from the open complex to chain elongation?
A) ATP hydrolysis distinct from any incorporation into the chain.
B) Nucleotide hydrolysis associated with incorporation into the chain.
C) Torsional stress built into the separating DNA strands.
D) Binding of rho (r) factor to the holoenzyme.
A) ATP hydrolysis distinct from any incorporation into the chain.
B) Nucleotide hydrolysis associated with incorporation into the chain.
C) Torsional stress built into the separating DNA strands.
D) Binding of rho (r) factor to the holoenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true concerning the first nucleotide incorporated into an RNA chain?
A) The first nucleotide incorporated into the RNA chain retains its 5'-triphosphate
B) The first nucleotide is always GMP
C) The first nucleotide is always cleaved off post-transcriptionally
D) The first nucleotide is always modified after transcription
A) The first nucleotide incorporated into the RNA chain retains its 5'-triphosphate
B) The first nucleotide is always GMP
C) The first nucleotide is always cleaved off post-transcriptionally
D) The first nucleotide is always modified after transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which is not associated with bacterial promoters?
A) the transcription start site
B) the Pribnow box
C) the -35 element
D) 3' antiterminator
A) the transcription start site
B) the Pribnow box
C) the -35 element
D) 3' antiterminator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A mutation in the lac A gene would result in
A) continuous production of the proteins encoded by the three structural genes
B) continuous production of the lac repressor
C) normal operation of the lac operon, but with an alteration in the proteins encoded by the lac A gene
D) no transcription from the lac operon
A) continuous production of the proteins encoded by the three structural genes
B) continuous production of the lac repressor
C) normal operation of the lac operon, but with an alteration in the proteins encoded by the lac A gene
D) no transcription from the lac operon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
There is only one sigma subunit,since the same RNA Polymerase must bind to all genes in E.coli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In prokaryotic RNA synthesis
A) the rate of incorporation of nucleotides is constant throughout the elongation process
B) the r (rho) protein is always required for termination
C) a unique series of three bases leads to termination
D) inverted-repeat sequences in the DNA being transcribed can lead to termination
A) the rate of incorporation of nucleotides is constant throughout the elongation process
B) the r (rho) protein is always required for termination
C) a unique series of three bases leads to termination
D) inverted-repeat sequences in the DNA being transcribed can lead to termination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Chain termination occurs,in vivo,when:
A) RNA Pol gets to the end of the DNA.
B) The factor called rho (r) binds to the DNA.
C) A hairpin loop forms in the template.
D) Either a hairpin loop forms or rho (r) is involved.
A) RNA Pol gets to the end of the DNA.
B) The factor called rho (r) binds to the DNA.
C) A hairpin loop forms in the template.
D) Either a hairpin loop forms or rho (r) is involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How do enhancers differ from promoters?
A) Enhancers do not bind RNA polymerase.
B) Enhancers include the UP element.
C) Enhancers bind the sigma (s) factor.
D) There is no difference; these terms are synonymous.
A) Enhancers do not bind RNA polymerase.
B) Enhancers include the UP element.
C) Enhancers bind the sigma (s) factor.
D) There is no difference; these terms are synonymous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The weakness of A-U base pairs at the end of the RNA molecule may help in dissociation of the new RNA product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Attenuation mechanisms rely on alternative secondary structures forming in the mRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the conditions would result in the greatest amount of transcription of the lac operon? 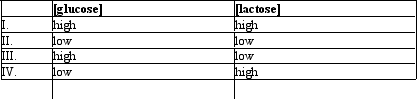
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a characteristic of catabolite activator protein (CAP)?
A) it is a positive regulator of the lac operon
B) when the cell has sufficient glucose and lactose, CAP will not be bound to the CAP binding site
C) CAP binding near the promoter site depends on CAP complexation with cAMP
D) the binding of CAP to DNA requires ATP hydrolysis
A) it is a positive regulator of the lac operon
B) when the cell has sufficient glucose and lactose, CAP will not be bound to the CAP binding site
C) CAP binding near the promoter site depends on CAP complexation with cAMP
D) the binding of CAP to DNA requires ATP hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following influence the amount of expression of an operon?
A) Availability of the specific sigma factor for that operon.
B) How well the Pribnow box conforms to the consensus sequence.
C) Attenuation mechanisms.
D) Presence of 3' 5' cyclic AMP.
E) All of these.
A) Availability of the specific sigma factor for that operon.
B) How well the Pribnow box conforms to the consensus sequence.
C) Attenuation mechanisms.
D) Presence of 3' 5' cyclic AMP.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cyclic AMP affects transcription by
A) triggering the action of several protein factors
B) phosphorylating a subunit of RNA polymerase
C) phosphorylating a transcription factor
D) inhibiting DNA looping
A) triggering the action of several protein factors
B) phosphorylating a subunit of RNA polymerase
C) phosphorylating a transcription factor
D) inhibiting DNA looping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the following apply to attenuation mechanisms,except:
A) They are used most often for operons for amino acid synthesis.
B) They involve the synthesis of proteins in the regulation of RNA synthesis.
C) The rate of RNA synthesis is regulated by the conformation of the protein being synthesized.
D) They require the presence of partially completed mRNA molecules.
E) All of these apply to attenuation mechanisms.
A) They are used most often for operons for amino acid synthesis.
B) They involve the synthesis of proteins in the regulation of RNA synthesis.
C) The rate of RNA synthesis is regulated by the conformation of the protein being synthesized.
D) They require the presence of partially completed mRNA molecules.
E) All of these apply to attenuation mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A single operon
A) usually contains all the enzymes which are specific for the synthesis of a special biomolecule.
B) usually does not contain all the enzymes which are specific for the synthesis of a special biomolecule.
C) usually contains only a single structural gene for a critical enzyme.
D) usually contains only a gene for a repressor.
A) usually contains all the enzymes which are specific for the synthesis of a special biomolecule.
B) usually does not contain all the enzymes which are specific for the synthesis of a special biomolecule.
C) usually contains only a single structural gene for a critical enzyme.
D) usually contains only a gene for a repressor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the need for a primer strand in transcription?
A) It ensures the fidelity of the newly synthesized RNA strand.
B) There is none.
C) RNA polymerases requires a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 3'-OH.
D) RNA polymerase requires a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 5'-OH.
A) It ensures the fidelity of the newly synthesized RNA strand.
B) There is none.
C) RNA polymerases requires a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 3'-OH.
D) RNA polymerase requires a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 5'-OH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Operons
A) control the expression of constitutive genes.
B) are subject to positive or to negative control.
C) are not affected by mutations in the genes for repressors or inducers.
D) occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
A) control the expression of constitutive genes.
B) are subject to positive or to negative control.
C) are not affected by mutations in the genes for repressors or inducers.
D) occur in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following does not influence the timing of expression of an operon?
A) Repressors
B) Co-repressors
C) Presence of substrates of the operon which need to be degraded
D) Inducers
E) All of these influence the timing of expression
A) Repressors
B) Co-repressors
C) Presence of substrates of the operon which need to be degraded
D) Inducers
E) All of these influence the timing of expression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is the best description of an operon?
A) An enhancer that positively regulates gene expression.
B) An silencer that negatively regulates gene expression.
C) A binding element for the sigma (s) factor.
D) A group of genes under the control of a common promoter.
A) An enhancer that positively regulates gene expression.
B) An silencer that negatively regulates gene expression.
C) A binding element for the sigma (s) factor.
D) A group of genes under the control of a common promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Phosphorylation of the CTD of RNA polymerase II occurs during which phase of transcription?
A) initial binding to the promoter
B) conversion from the closed complex to the open complex
C) termination of transcription
D) None of these
A) initial binding to the promoter
B) conversion from the closed complex to the open complex
C) termination of transcription
D) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Initiation of transcription in eukaryotes is primarily controlled
A) by two transcription factors
B) by keeping the TATA-binding protein physically separated from other transcription factors
C) by the order of binding of TFIIA and TFIIB
D) in the formation of the preinitiation complex
A) by two transcription factors
B) by keeping the TATA-binding protein physically separated from other transcription factors
C) by the order of binding of TFIIA and TFIIB
D) in the formation of the preinitiation complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements about eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases,is false?
A) There are 3 different RNA polymerases in eukaryotes, instead of just one.
B) Eukaryotic polymerases have the same number of subunits as prokaryotic ones.
C) Only prokaryotic polymerases use sigma factor.
D) The enzymatic mechanism is the same for both types of organisms.
A) There are 3 different RNA polymerases in eukaryotes, instead of just one.
B) Eukaryotic polymerases have the same number of subunits as prokaryotic ones.
C) Only prokaryotic polymerases use sigma factor.
D) The enzymatic mechanism is the same for both types of organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements about the various RNA Polymerases in eukaryotes is false?
A) Permanent RNAs, such as tRNA and rRNA use different RNA Polymerases.
B) The different RNA Polymerases share some subunits.
C) The RNA Polymerase for mRNA is designated RNA Pol II.
D) Eukaryotic RNA polymerases are generally monomeric.
A) Permanent RNAs, such as tRNA and rRNA use different RNA Polymerases.
B) The different RNA Polymerases share some subunits.
C) The RNA Polymerase for mRNA is designated RNA Pol II.
D) Eukaryotic RNA polymerases are generally monomeric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which enzyme transcribes genes encoding tRNA in eukaryotes?
A) RNA polymerase I
B) RNA polymerase II
C) RNA polymerase III
D) Different tRNAs are transcribed by different RNA polymerases.
A) RNA polymerase I
B) RNA polymerase II
C) RNA polymerase III
D) Different tRNAs are transcribed by different RNA polymerases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
RNA polymerases from prokaryotes and eukaryotes
A) have sequence homology in catalytic subunits
B) have identical s factors
C) differ because there is no analogue to the prokaryotic a subunit in eukaryotes
D) have the same number and kind of subunits
A) have sequence homology in catalytic subunits
B) have identical s factors
C) differ because there is no analogue to the prokaryotic a subunit in eukaryotes
D) have the same number and kind of subunits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Inducers for operons are often structurally related to the enzyme substrates of that operon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Control of transcription in prokaryotes does not involve
A) enhancers.
B) silencers.
C) leucine zipper proteins.
D) alternative s factors.
A) enhancers.
B) silencers.
C) leucine zipper proteins.
D) alternative s factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How do eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases compare?
A) Since eukaryotic RNA polymerases are more complex, little homology has been found between the actual protein sequences in the catalytic subunits.
B) Since eukaryotic transcription is less complex than in prokaryotes, monomeric RNA polymerases are used.
C) Despite their added complexity, eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases are generally homologous.
D) Eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases are virtually identical.
A) Since eukaryotic RNA polymerases are more complex, little homology has been found between the actual protein sequences in the catalytic subunits.
B) Since eukaryotic transcription is less complex than in prokaryotes, monomeric RNA polymerases are used.
C) Despite their added complexity, eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases are generally homologous.
D) Eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases are virtually identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The catabolite activator protein can overcome the effect of a repressor binding to the operon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Inducers allow for a system in which an enzyme is not made unless it is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following transcription factors is involved in the elongation phase of eukaryotic transcription?
A) TFIIA
B) TFIID
C) TFIIF
D) There are no transcription factors associated with elongation.
A) TFIIA
B) TFIID
C) TFIIF
D) There are no transcription factors associated with elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is true about riboswitches:
A) They have a molecule sensing domain called an aptamer
B) There are known pathogens that use riboswitches as part of their mechanism
C) They respond to specific molecules and control translation in a way that is often similar to transcription attenuation
D) They contain a sensing domain and a decision making domain
E) All of these
A) They have a molecule sensing domain called an aptamer
B) There are known pathogens that use riboswitches as part of their mechanism
C) They respond to specific molecules and control translation in a way that is often similar to transcription attenuation
D) They contain a sensing domain and a decision making domain
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Where is the TATA box located?
A) At the transcription start site (+1).
B) -10 region.
C) -25 region.
D) -40 region.
A) At the transcription start site (+1).
B) -10 region.
C) -25 region.
D) -40 region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A transcription factor is
A) a subunit of RNA polymerase II that does not have a prokaryotic analogue.
B) the part of the promoter sequence closest to the start of transcription.
C) a protein other than RNA polymerase that is involved in transcription.
D) a sequence that determines whether an upstream element will be an enhancer or silencer.
A) a subunit of RNA polymerase II that does not have a prokaryotic analogue.
B) the part of the promoter sequence closest to the start of transcription.
C) a protein other than RNA polymerase that is involved in transcription.
D) a sequence that determines whether an upstream element will be an enhancer or silencer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The eukaryotic TATA-binding protein (TBP) functions in a manner similar to
A)sigma (s) factor in E.coli.
B)rho (r) factor in E.coli.
C)lac I in E.coli.
D)CAP in E.coli.
A)sigma (s) factor in E.coli.
B)rho (r) factor in E.coli.
C)lac I in E.coli.
D)CAP in E.coli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Transcription in eukaryotes differs from RNA synthesis in prokaryotes
A) by requiring a primer.
B) by simplifying the process with multifunctional enzymes.
C) in using more complex s factors.
D) by having multiple RNA polymerases rather than one.
A) by requiring a primer.
B) by simplifying the process with multifunctional enzymes.
C) in using more complex s factors.
D) by having multiple RNA polymerases rather than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the conditions would result in the least amount of transcription of the lac operon? 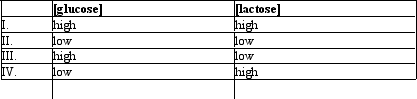
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
TATA-binding protein (TBP) is required for transcription by
A) Pol I.
B) Pol II.
C) Pol III.
D) all of these polymerases.
A) Pol I.
B) Pol II.
C) Pol III.
D) all of these polymerases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is not a key step in the activation of mRNA synthesis in eukaryotes?
A) Binding of TBP to the DNA.
B) Binding of other transcription factors.
C) Binding of RNA Pol I.
D) Phosphorylation of the RNA Pol.
E) All of these are necessary to initiate RNA synthesis in eukaryotes.
A) Binding of TBP to the DNA.
B) Binding of other transcription factors.
C) Binding of RNA Pol I.
D) Phosphorylation of the RNA Pol.
E) All of these are necessary to initiate RNA synthesis in eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One rather unusual transcription factor in eukaryotes halts RNA synthesis to allow for repair of damaged DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The major difference between RNA initiation in eukaryotes and prokaryotes is the number of factors involved in the process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Polyadenylation of eukaryotic mRNA
A) occurs at the 5' end.
B) occurs at the 3' end.
C) occurs at both ends.
D) doesn't occur at all.
A) occurs at the 5' end.
B) occurs at the 3' end.
C) occurs at both ends.
D) doesn't occur at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The elongation and termination phases of eukaryotic transcription
A) require several protein factors
B) are better understood than the initiation phase
C) are not subject to control mechanisms, only the initiation phase
D) proceed at a constant rate and always stop at the same termination sequence
A) require several protein factors
B) are better understood than the initiation phase
C) are not subject to control mechanisms, only the initiation phase
D) proceed at a constant rate and always stop at the same termination sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Intracellular levels of cyclic AMP can affect the phosphorylation of proteins and enzymes as a secondary messenger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Response elements
A) are similar to operons in that they are controlled by a single promoter
B) are enhancers of transcription activated by metabolic factors
C) are not affected by steroids
D) are silencers of transcription triggered by the presence of metal ions
A) are similar to operons in that they are controlled by a single promoter
B) are enhancers of transcription activated by metabolic factors
C) are not affected by steroids
D) are silencers of transcription triggered by the presence of metal ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
RNA transcribed from the coding strand instead of the template strand
A) is called antisense RNA.
B) produces histones.
C) is tRNA.
D) never occurs.
A) is called antisense RNA.
B) produces histones.
C) is tRNA.
D) never occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
As in prokaryotes,the regulatory regions for eukaryotic genes:
A) may be close to the genes they control
B) may be upstream of the genes they control
C) may be downstream of the genes they control
D) All of these are true
A) may be close to the genes they control
B) may be upstream of the genes they control
C) may be downstream of the genes they control
D) All of these are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The leucine zipper is different from other DNA binding domains,since it requires the DNA-binding protein to form a dimer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Proteins that recognize DNA with specific base sequences are
A) more likely to bind to the major groove.
B) more likely to bind to the minor groove.
C) equally likely to bind to the major or minor grooves.
D) never occur.
A) more likely to bind to the major groove.
B) more likely to bind to the minor groove.
C) equally likely to bind to the major or minor grooves.
D) never occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is not true?
A) The mechanism of activation of eukaryotic genes involves addition and removal of phosphate residues from some of the transcription factors.
B) In plants, there are 5 RNA polymerases.
C) RNA Pol IV is the primary RNA synthesizer in plants
D) Of the RNA Polymerases in eukaryotes, Pol II is the most extensively studied.
A) The mechanism of activation of eukaryotic genes involves addition and removal of phosphate residues from some of the transcription factors.
B) In plants, there are 5 RNA polymerases.
C) RNA Pol IV is the primary RNA synthesizer in plants
D) Of the RNA Polymerases in eukaryotes, Pol II is the most extensively studied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Alternative removal of exons from mRNA is important in which of the following?
A) Troponins and other contractile proteins.
B) Different types of collagen.
C) The disease lupus.
D) Alzheimer's disease.
E) All of these.
A) Troponins and other contractile proteins.
B) Different types of collagen.
C) The disease lupus.
D) Alzheimer's disease.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is not a common modification occurring after polymerization of RNA?
A) Methylation of bases.
B) Addition of phosphate to the bases.
C) Removal of bases from the polymer.
D) Addition of bases to the polymer.
E) All of these changes are common.
A) Methylation of bases.
B) Addition of phosphate to the bases.
C) Removal of bases from the polymer.
D) Addition of bases to the polymer.
E) All of these changes are common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is not a structural motif encountered in DNA-binding proteins?
A) helix-turn-helix
B) leucine zipper
C) zinc finger
D) b-barrel
A) helix-turn-helix
B) leucine zipper
C) zinc finger
D) b-barrel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
DNA binding domains are distinct from transcription-activation domains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In eukaryotes,which of the following types of RNA undergo some base modification after polymerization of the monomers?
A.mRNA
B.tRNA
C.rRNA
D.mRNA and tRNA
E.mRNA and rRNA
F.all of these
A.mRNA
B.tRNA
C.rRNA
D.mRNA and tRNA
E.mRNA and rRNA
F.all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following RNAs is noted for having a "cloverleaf" structure?
A) mRNA
B) rRNA
C) tRNA
D) All of these
A) mRNA
B) rRNA
C) tRNA
D) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
CREB contains the following structural motif:
A) Helix-turn-helix
B) b-barrel
C) Zinc finger
D) Leucine zipper
A) Helix-turn-helix
B) b-barrel
C) Zinc finger
D) Leucine zipper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following best describes leucine zipper motifs?
A) They allow protein-protein interactions via hydrophobic bonds.
B) They allow protein-protein interactions via hydrogen bonds.
C) They allow protein-protein interactions via electrostatic interactions.
D) They allow protein-DNA interactions by fitting into the major groove of DNA.
A) They allow protein-protein interactions via hydrophobic bonds.
B) They allow protein-protein interactions via hydrogen bonds.
C) They allow protein-protein interactions via electrostatic interactions.
D) They allow protein-DNA interactions by fitting into the major groove of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Capping of eukaryotic mRNA
A) occurs at the 5' end.
B) occurs at the 3' end.
C) occurs at both ends.
D) doesn't occur at all.
A) occurs at the 5' end.
B) occurs at the 3' end.
C) occurs at both ends.
D) doesn't occur at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



