Deck 10: Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Replication
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids: Replication
1
Which of the following is not a function of DNA Polymerase III?
A) Polymerization.
B) Ligating the final products.
C) Proofreading.
D) Clamping on to the template.
E) All of these.
A) Polymerization.
B) Ligating the final products.
C) Proofreading.
D) Clamping on to the template.
E) All of these.
B
2
The duplication process of DNA is called
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) nucleation.
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) nucleation.
A
3
The flow of genetic information is RNA DNA in
A) all organisms.
B) all prokaryotes.
C) retroviruses.
D) no known organisms.
A) all organisms.
B) all prokaryotes.
C) retroviruses.
D) no known organisms.
C
4
When the synthesis of new DNA is directed by an original template DNA molecule
A) the DNA produced has two newly formed strands (no change in the original DNA)
B) two DNA molecules are formed, each with one new strand and one strand from the original DNA
C) there is random arrangement of newly formed and original DNA on the two strands of the DNA produced
D) no information is available on this subject
A) the DNA produced has two newly formed strands (no change in the original DNA)
B) two DNA molecules are formed, each with one new strand and one strand from the original DNA
C) there is random arrangement of newly formed and original DNA on the two strands of the DNA produced
D) no information is available on this subject

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose Meselson & Stahl had observed the following data in their famous experiment involving a switch from medium containing 15N to 14N.What would they have concluded about the nature of DNA replication? 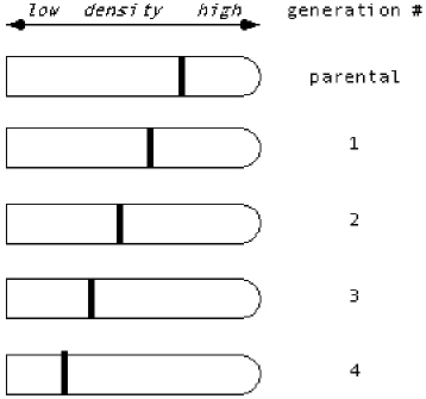
A) They still would have concluded that DNA replication is semiconservative, i.e., each double helix contains one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand.
B) They would have concluded that DNA replication is conservative, i.e., one double helix contains only the parental strands, while the other contains only newly synthesized DNA.
C) They would have concluded that DNA replication is dispersive/random, i.e., each strand of each double helix contains a mixture of parental and newly synthesized sequences.
D) They would have been unable to distinguish which is correct.

A) They still would have concluded that DNA replication is semiconservative, i.e., each double helix contains one parental strand and one newly synthesized strand.
B) They would have concluded that DNA replication is conservative, i.e., one double helix contains only the parental strands, while the other contains only newly synthesized DNA.
C) They would have concluded that DNA replication is dispersive/random, i.e., each strand of each double helix contains a mixture of parental and newly synthesized sequences.
D) They would have been unable to distinguish which is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following best describes the process of DNA replication in a prokaryote?
A) Replication begins at a unique site and proceeds in one direction all the way around a typically circular chromosome.
B) Replication begins at a unique site and proceeds in two directions, meeting about halfway around a typically circular chromosome.
C) Replication begins at multiple sites, spreading outward until the entire typically circular chromosome is replicated.
D) Replication begins at multiple sites, spreading outward until the entire typically linear chromosome is replicated.
A) Replication begins at a unique site and proceeds in one direction all the way around a typically circular chromosome.
B) Replication begins at a unique site and proceeds in two directions, meeting about halfway around a typically circular chromosome.
C) Replication begins at multiple sites, spreading outward until the entire typically circular chromosome is replicated.
D) Replication begins at multiple sites, spreading outward until the entire typically linear chromosome is replicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The direction of synthesis of a DNA strand is
A) from the 5' end to the 3' end on both strands.
B) from the 3' end to the 5' end on both strands.
C) from the 5' end to the 3' end on one strand and from the 3' end to the 5' end on the other strand.
D) none of the above.
A) from the 5' end to the 3' end on both strands.
B) from the 3' end to the 5' end on both strands.
C) from the 5' end to the 3' end on one strand and from the 3' end to the 5' end on the other strand.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The following enzyme is responsible for the bulk of DNA synthesis during replication.
A) DNA Polymerase I
B) DNA Polymerase II
C) DNA Polymerase III
D) DNA Polymerases IV
E) All four can make lots of DNA rapidly.
A) DNA Polymerase I
B) DNA Polymerase II
C) DNA Polymerase III
D) DNA Polymerases IV
E) All four can make lots of DNA rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the requirement for a template strand in DNA replication?
A) It serves as a guide in determining the next nucleotide to be added according to the Watson-Crick base pairing scheme.
B) It serves as the start point for the new DNA strand.
C) It allows the DNA polymerase to move along it easily.
D) It is a substrate for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity.
A) It serves as a guide in determining the next nucleotide to be added according to the Watson-Crick base pairing scheme.
B) It serves as the start point for the new DNA strand.
C) It allows the DNA polymerase to move along it easily.
D) It is a substrate for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The famous Meselson and Stahl experiment showed:
A) DNA is replicated by a semi-conservative mechanism.
B) The direction of DNA synthesis proceeds 5' 3'.
C) The isotope 15N is denser than 14N.
D) DNA replication is semi-conservative and 15N is denser than 14N.
E) All of these are correct.
A) DNA is replicated by a semi-conservative mechanism.
B) The direction of DNA synthesis proceeds 5' 3'.
C) The isotope 15N is denser than 14N.
D) DNA replication is semi-conservative and 15N is denser than 14N.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Semiconservative replication of DNA was established experimentally by
A) gel electrophoresis.
B) ultraviolet spectroscopy.
C) column chromatography.
D) density-gradient centrifugation.
A) gel electrophoresis.
B) ultraviolet spectroscopy.
C) column chromatography.
D) density-gradient centrifugation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The process by which an mRNA base sequence directs the amino acid sequence of a protein is called
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) nucleation.
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) nucleation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the original Central Dogma of biology,the ordinary flow of genetic information is:
A) DNA RNA Protein
B) RNA DNA Protein
C) Protein RNA DNA
D) DNA Protein RNA.
E) None of these
A) DNA RNA Protein
B) RNA DNA Protein
C) Protein RNA DNA
D) DNA Protein RNA.
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Semiconservative replication implies that
A) each of the new double stranded DNA molecules contains one of the original intact strands and one completely new strand.
B) one of the new double stranded DNA molecules contains both of the original strands, while the other contains two new strands.
C) each of the new double stranded DNA molecules contains strands that are composed of segments of original and newly synthesized material.
D) None of these.
A) each of the new double stranded DNA molecules contains one of the original intact strands and one completely new strand.
B) one of the new double stranded DNA molecules contains both of the original strands, while the other contains two new strands.
C) each of the new double stranded DNA molecules contains strands that are composed of segments of original and newly synthesized material.
D) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All the following describe the general mechanism of DNA synthesis,except:
A) From the perspective of the DNA template strands, one strand is made 5' 3' while the other strand is made 3' 5'.
B) The strands become separated during synthesis.
C) Synthesis occurs in both directions from the starting site of synthesis.
D) Synthesis of DNA is a very accurate process.
E) All of these are correct.
A) From the perspective of the DNA template strands, one strand is made 5' 3' while the other strand is made 3' 5'.
B) The strands become separated during synthesis.
C) Synthesis occurs in both directions from the starting site of synthesis.
D) Synthesis of DNA is a very accurate process.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The universal features of DNA replication include all the following,except:
A)Release of PPi from a nucleoside triphosphate.
B)Synthesis from the 5' end to the 3' end.
C)Base pairing of A to T and G to C.
D)Use of a primer.
E)All of these describe DNA synthesis.
A)Release of PPi from a nucleoside triphosphate.
B)Synthesis from the 5' end to the 3' end.
C)Base pairing of A to T and G to C.
D)Use of a primer.
E)All of these describe DNA synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The production of RNA on a DNA template is called
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) nucleation.
A) replication.
B) transcription.
C) translation.
D) nucleation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How do origins of replication differ in eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
A) Eukaryotes have several origins, while prokaryotes typically have one.
B) Prokaryotes have several origins, while eukaryotes typically have one.
C) Only prokaryotes have origins of replication.
D) None of these.
A) Eukaryotes have several origins, while prokaryotes typically have one.
B) Prokaryotes have several origins, while eukaryotes typically have one.
C) Only prokaryotes have origins of replication.
D) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An important process in the synthesis of new DNA is
A) proofreading and repair.
B) unwinding of the double helix.
C) protection of single-stranded regions from nuclease action.
D) all of these
A) proofreading and repair.
B) unwinding of the double helix.
C) protection of single-stranded regions from nuclease action.
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
DNA replication is a challenging process because:
A) DNA strands must be separated
B) New DNA is always synthesized from the 5' 3' direction but the two template strands run in opposite directions
C) The cell must guard against replication errors
D) All of these
A) DNA strands must be separated
B) New DNA is always synthesized from the 5' 3' direction but the two template strands run in opposite directions
C) The cell must guard against replication errors
D) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following activities does
A)5' 3' polymerase
B)5' 3' exonuclease
C)3' 5' exonuclease
D)E.coli DNA polymerase III has ALL of the above activities.
A)5' 3' polymerase
B)5' 3' exonuclease
C)3' 5' exonuclease
D)E.coli DNA polymerase III has ALL of the above activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The mechanism for all template-directed synthesis of any type of nucleic acid involves the following:
A) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi.
B) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi.
C) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing Pi.
D) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing Pi.
E) More than one of these would work, since the mechanism is not universal.
A) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi.
B) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi.
C) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing Pi.
D) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing Pi.
E) More than one of these would work, since the mechanism is not universal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The primer for in vivo DNA replication is:
A) The 3' hydroxyl of the preceding Okazaki fragment.
B) A short piece of RNA.
C) A nick made in the DNA template.
D) A primer is not always required for DNA replication.
E) All of these are true.
A) The 3' hydroxyl of the preceding Okazaki fragment.
B) A short piece of RNA.
C) A nick made in the DNA template.
D) A primer is not always required for DNA replication.
E) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In prokaryotic replication,all DNA polymerases are capable of all of the following tasks except:
A) Reading a template strand and putting the complementary base in the correct position
B) Polymerizing DNA in the 5' to 3' direction
C) Excising DNA in the 3' to 5' direction
D) Excising DNA in the 5' to 3' direction
E) All of these are capabilities of all DNA polymerases
A) Reading a template strand and putting the complementary base in the correct position
B) Polymerizing DNA in the 5' to 3' direction
C) Excising DNA in the 3' to 5' direction
D) Excising DNA in the 5' to 3' direction
E) All of these are capabilities of all DNA polymerases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In Escherichia coli,the enzyme principally responsible for the synthesis of new DNA strands is
A) DNA polymerase I
B) DNA polymerase III
C) DNA ligase
D) primase
A) DNA polymerase I
B) DNA polymerase III
C) DNA ligase
D) primase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In E.coli,
A) the leading strand is synthesized in one piece while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously.
B) the leading strand is synthesized discontinuously while the lagging strand is synthesized in one piece.
C) both the leading and lagging strands are synthesized in one piece.
D) both the leading and lagging strands are synthesized discontinuously.
A) the leading strand is synthesized in one piece while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously.
B) the leading strand is synthesized discontinuously while the lagging strand is synthesized in one piece.
C) both the leading and lagging strands are synthesized in one piece.
D) both the leading and lagging strands are synthesized discontinuously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the synthesis of DNA in Escherichia coli
A) a single-strand nick in the template DNA gives rise to a swivel point just in advance of the replication fork
B) Mn2+ is required
C) all enzymes involved are single polypeptide chains
D) neither the template DNA nor the daughter DNA molecules exhibit supercoiling
A) a single-strand nick in the template DNA gives rise to a swivel point just in advance of the replication fork
B) Mn2+ is required
C) all enzymes involved are single polypeptide chains
D) neither the template DNA nor the daughter DNA molecules exhibit supercoiling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The energetic driving force for nucleic acid synthesis is
A) removal of pyrophosphate from the incoming nucleotide.
B) removal of pyrophosphate from the growing strand.
C) removal of inorganic phosphate from the incoming nucleotide.
D) removal of inorganic phosphate from the growing strand.
A) removal of pyrophosphate from the incoming nucleotide.
B) removal of pyrophosphate from the growing strand.
C) removal of inorganic phosphate from the incoming nucleotide.
D) removal of inorganic phosphate from the growing strand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not a function of DNA polymerase I from E.coli?
A) adding nucleotides to the primer strand
B) 3' 5' exonuclease activity
C) 5' 3' exonuclease activity
D) proofreading
A) adding nucleotides to the primer strand
B) 3' 5' exonuclease activity
C) 5' 3' exonuclease activity
D) proofreading

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In order to replicate both strands,E.coli
A) displaces one of the strands and folds it back so both strands face in the same direction, so they can be synthesized at once.
B) synthesizes each strand in the opposite direction (one 5' 3', one 3' 5'), so they can be synthesized at once.
C) only synthesizes one strand at a time.
A) displaces one of the strands and folds it back so both strands face in the same direction, so they can be synthesized at once.
B) synthesizes each strand in the opposite direction (one 5' 3', one 3' 5'), so they can be synthesized at once.
C) only synthesizes one strand at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
DNA polymerase III from E.coli
A) is a large, multisubunit protein
B) has a sliding clamp portion that anchors it to DNA
C) has a polymerization site separate from the DNA binding site
D) all of these
A) is a large, multisubunit protein
B) has a sliding clamp portion that anchors it to DNA
C) has a polymerization site separate from the DNA binding site
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Exhibit 10A 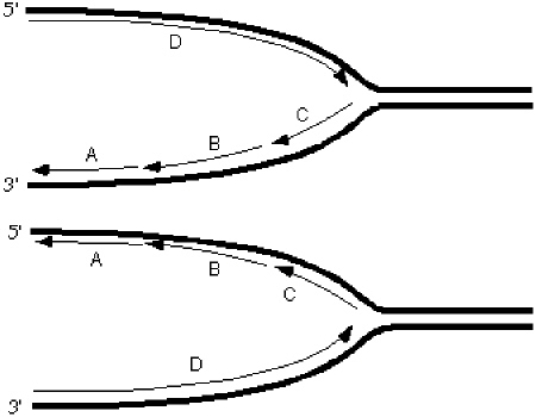 Consider the following diagrams showing a replication fork moving from left to right.The thick lines represent the template/parental strands.The 5' and 3' represent the ends of those template/parental strands.
Consider the following diagrams showing a replication fork moving from left to right.The thick lines represent the template/parental strands.The 5' and 3' represent the ends of those template/parental strands.
Refer to Exhibit 10A.Which diagram correctly depicts the orientation of the lagging and leading strands on the parentals?
A) The top
B) The bottom
C) Neither is fully accurate.
D) Either would be accurate dependent on the organism being studied.
 Consider the following diagrams showing a replication fork moving from left to right.The thick lines represent the template/parental strands.The 5' and 3' represent the ends of those template/parental strands.
Consider the following diagrams showing a replication fork moving from left to right.The thick lines represent the template/parental strands.The 5' and 3' represent the ends of those template/parental strands.Refer to Exhibit 10A.Which diagram correctly depicts the orientation of the lagging and leading strands on the parentals?
A) The top
B) The bottom
C) Neither is fully accurate.
D) Either would be accurate dependent on the organism being studied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
AZT,used in treating AIDS,is an effective inhibitor of nucleic acid synthesis because:
A) It has a nitrogen group instead of a 3' OH.
B) It is a 2', 3' dideoxy compound.
C) It doesn't form good base pairs.
D) It inhibits RNA Polymerase needed to make RNA for new HIV virus particles.
E) More than one of these is correct.
A) It has a nitrogen group instead of a 3' OH.
B) It is a 2', 3' dideoxy compound.
C) It doesn't form good base pairs.
D) It inhibits RNA Polymerase needed to make RNA for new HIV virus particles.
E) More than one of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 10A Consider the following diagrams showing a replication fork moving from left to right.The thick lines represent the template/parental strands.The 5' and 3' represent the ends of those template/parental strands.
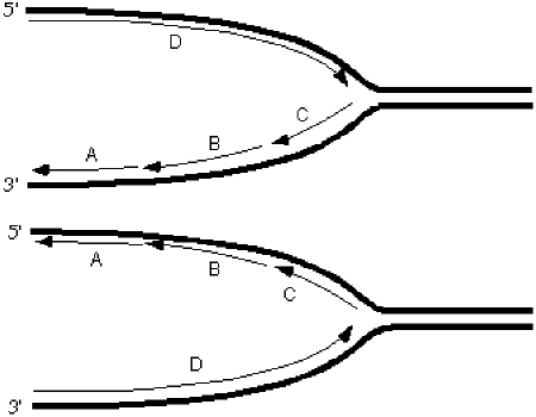 Refer to Exhibit 10A.Which Okazaki fragment was synthesized earliest?
Refer to Exhibit 10A.Which Okazaki fragment was synthesized earliest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
 Refer to Exhibit 10A.Which Okazaki fragment was synthesized earliest?
Refer to Exhibit 10A.Which Okazaki fragment was synthesized earliest?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following characteristics is not associated with
A) it synthesizes the RNA primer in DNA replication
B) it synthesizes a primer with a free 3'-OH end
C) it is essential for DNA replication
D) it is essential for RNA replication
E) coli primase?
A) it synthesizes the RNA primer in DNA replication
B) it synthesizes a primer with a free 3'-OH end
C) it is essential for DNA replication
D) it is essential for RNA replication
E) coli primase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
E.coli replication on the lagging strand
A) is carried out by DNA polymerase I
B) is initially synthesized as Okazaki fragments
C) is synthesized continuously
D) has this DNA strand synthesized in a 3' 5' direction
A) is carried out by DNA polymerase I
B) is initially synthesized as Okazaki fragments
C) is synthesized continuously
D) has this DNA strand synthesized in a 3' 5' direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Why is thymine used in DNA rather than uracil?
A) Thymine is more hydrophobic, so it stacks better in the helix.
B) If cytosine is deaminated, it forms uracil, which can be easily distinguished from thymine.
C) Thymine is not capable of wobbling, so it pairs more accurately than uracil.
D) All of these are correct.
A) Thymine is more hydrophobic, so it stacks better in the helix.
B) If cytosine is deaminated, it forms uracil, which can be easily distinguished from thymine.
C) Thymine is not capable of wobbling, so it pairs more accurately than uracil.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Okazaki fragments are
A) short DNA pieces that explain how DNA is synthesized on the lagging strand.
B) short DNA pieces that explain how DNA is synthesized on the leading strand.
C) the remnants of the original strands that are dispersed in the new double stranded DNA molecules
D) RNA primers used for DNA replication.
A) short DNA pieces that explain how DNA is synthesized on the lagging strand.
B) short DNA pieces that explain how DNA is synthesized on the leading strand.
C) the remnants of the original strands that are dispersed in the new double stranded DNA molecules
D) RNA primers used for DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A prokaryotic replisome typically contains two molecules of DNA pol III,but only one molecule of DNA pol I.Why?
A) The DNA pol I works on the leading strand, while DNA pol IIIs work on the Okazaki fragments. since there are several of those, it takes more proteins to keep up.
B) DNA pol I has a built-in proofreading exonuclease; DNA pol III does not. The second DNA pol III is needed to follow the first to accomplish the necessary proofreading.
C) The DNA pol IIIs do most of the work. DNA pol I only has to work on the telomers.
D) DNA pol I replaces the RNA primers with DNA, which really only needs to be done repetitively on one strand, while both strands are worked on by the DNA pol IIIs.
A) The DNA pol I works on the leading strand, while DNA pol IIIs work on the Okazaki fragments. since there are several of those, it takes more proteins to keep up.
B) DNA pol I has a built-in proofreading exonuclease; DNA pol III does not. The second DNA pol III is needed to follow the first to accomplish the necessary proofreading.
C) The DNA pol IIIs do most of the work. DNA pol I only has to work on the telomers.
D) DNA pol I replaces the RNA primers with DNA, which really only needs to be done repetitively on one strand, while both strands are worked on by the DNA pol IIIs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the need for a primer strand in DNA replication?
A) it ensures the fidelity of the newly synthesized DNA strand
B) the DNA polymerases require a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 3'-OH
C) the DNA polymerases require a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 5'-OH
D) it ensures the integrity of the new DNA
A) it ensures the fidelity of the newly synthesized DNA strand
B) the DNA polymerases require a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 3'-OH
C) the DNA polymerases require a preexisting strand with a nucleotide having a 5'-OH
D) it ensures the integrity of the new DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
It is so important to keep the DNA molecule fully connected that some repair mechanisms will actually allow mismatches or deletions from the DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true about the so-called "MUT" (for "mutation") repair mechanisms?
A) Depend on the methylation of old strands of DNA to determine which strand to repair.
B) Often remove hundreds or even thousands of bases during the repair process.
C) Can only repair mismatches that occur during the normal replication process.
D) All of these are true.
A) Depend on the methylation of old strands of DNA to determine which strand to repair.
B) Often remove hundreds or even thousands of bases during the repair process.
C) Can only repair mismatches that occur during the normal replication process.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Ultra-violet light principally causes which of the following damages to DNA?
A) mismatches between stands
B) breaks in the phosphodiester backbone of the DNA strand
C) thymine dimerization
D) methylation of specific bases
A) mismatches between stands
B) breaks in the phosphodiester backbone of the DNA strand
C) thymine dimerization
D) methylation of specific bases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of these proteins is used less for leading strand replication than for lagging strand replication?
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA-binding protein
C) DNA ligase
D) DNA gyrase
A) DNA polymerase
B) DNA-binding protein
C) DNA ligase
D) DNA gyrase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Repair of DNA is usually carried out by
A) hydrolysis of the entire damaged DNA molecule and synthesis of new DNA
B) hydrolysis of one strand of the damaged DNA molecule and synthesis of a new strand
C) a cut-and patch process
D) introducing additional supercoiling in the molecule
A) hydrolysis of the entire damaged DNA molecule and synthesis of new DNA
B) hydrolysis of one strand of the damaged DNA molecule and synthesis of a new strand
C) a cut-and patch process
D) introducing additional supercoiling in the molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the activities of DNA Polymerase I is most important in its role of proofreading?
A) Polymerase activity.
B) Ability to nick intact double stranded DNA.
C) 5' 3' exonuclease.
D) 3' 5' exonuclease.
E) None of these is used for proofreading.
A) Polymerase activity.
B) Ability to nick intact double stranded DNA.
C) 5' 3' exonuclease.
D) 3' 5' exonuclease.
E) None of these is used for proofreading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following enzymes is used to create AP sites?
A) primase
B) helicase
C) ligase
D) glycosylase
A) primase
B) helicase
C) ligase
D) glycosylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following repair mechanisms would most likely be used to repair a G in DNA damaged by oxidation?
A) Base Excision:
B) Nucleotide Excision
C) Pol III Proofreading
D) Mismatch Repair
A) Base Excision:
B) Nucleotide Excision
C) Pol III Proofreading
D) Mismatch Repair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following mechanisms allow repair enzymes to distinguish incorrect bases in DNA?
A) The newly synthesized strand of DNA lacks methylated bases and other modifications.
B) Deamination of A and C lead to improper bases for DNA.
C) Thymine dimers and other cross links kink the DNA and are easy to find.
D) All of these mechanisms allow repair enzymes to distinguish which base is incorrect.
A) The newly synthesized strand of DNA lacks methylated bases and other modifications.
B) Deamination of A and C lead to improper bases for DNA.
C) Thymine dimers and other cross links kink the DNA and are easy to find.
D) All of these mechanisms allow repair enzymes to distinguish which base is incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
One of the most important ways in which DNA is modified after synthesis is
A) methylation of bases
B) covalent binding of proteins to the sugar moieties
C) splicing of RNA "leaders"
D) electrostatic binding of negatively charged counterions
A) methylation of bases
B) covalent binding of proteins to the sugar moieties
C) splicing of RNA "leaders"
D) electrostatic binding of negatively charged counterions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The enzyme that attaches the Okazaki fragments together is called
A) ligase.
B) primase.
C) DNA polymerase I
D) DNA polymerase III
A) ligase.
B) primase.
C) DNA polymerase I
D) DNA polymerase III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
DNA repair mechanisms are essentially the same whether the DNA has minor damage or major damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is not required for optimal DNA replication?
A) Primase
B) DNA Polymerase II.
C) Single strand binding proteins.
D) Gyrase
E) All of these are necessary.
A) Primase
B) DNA Polymerase II.
C) Single strand binding proteins.
D) Gyrase
E) All of these are necessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The proofreading of DNA is especially good because "the identity of each base pair is checked before the enzyme moves on to the next base pair."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which is most likely to have a high processivity?
A) a DNA polymerase that is primarily a repair enzyme
B) a primase
C) a DNA ligase
D) a DNA polymerase that is a main polymerizing enzyme
A) a DNA polymerase that is primarily a repair enzyme
B) a primase
C) a DNA ligase
D) a DNA polymerase that is a main polymerizing enzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Since DNA Polymerase II has endonuclease activity,it is able to proofread its product when it is used in DNA repair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is not an activity of DNA Polymerase I?
A) Polymerase activity.
B) Ability to nick intact double stranded DNA.
C) 5' 3' exonuclease.
D) 3' 5' exonuclease.
E) All of these are present in DNA Pol I.
A) Polymerase activity.
B) Ability to nick intact double stranded DNA.
C) 5' 3' exonuclease.
D) 3' 5' exonuclease.
E) All of these are present in DNA Pol I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which repair mechanism has an intermediate wherein a region of single-stranded DNA is temporarily created?
A) Base Excision
B) Nucleotide Excision
C) Pol III Proofreading
D) Mismatch Repair
A) Base Excision
B) Nucleotide Excision
C) Pol III Proofreading
D) Mismatch Repair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the activities of DNA Polymerase I is most important in removing the primer?
A) Polymerase activity.
B) Ability to nick intact double stranded DNA.
C) 5' 3' exonuclease.
D) 3' 5' exonuclease.
E) None of these is used for primer removal.
A) Polymerase activity.
B) Ability to nick intact double stranded DNA.
C) 5' 3' exonuclease.
D) 3' 5' exonuclease.
E) None of these is used for primer removal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Single strand binding proteins are important for this activity:
A) Prevent single-stranded DNA from rewinding.
B) Protect single-stranded DNA from enzymatic degradation.
C) Prevent double helical DNA from unwinding.
D) Prevent double helical DNA from becoming a triple helix.
E) Prevent single-stranded DNA from rewinding and protect it from degradation.
A) Prevent single-stranded DNA from rewinding.
B) Protect single-stranded DNA from enzymatic degradation.
C) Prevent double helical DNA from unwinding.
D) Prevent double helical DNA from becoming a triple helix.
E) Prevent single-stranded DNA from rewinding and protect it from degradation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How do the Okazaki fragments of eukaryotes and prokaryotes compare?
A) The Okazaki fragments are much longer in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes.
B) The Okazaki fragments are much shorter in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes.
C) The Okazaki fragments of eukaryotes are on the leading strand, rather than the lagging strand.
D) There is little to no difference between the Okazaki fragments of eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
A) The Okazaki fragments are much longer in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes.
B) The Okazaki fragments are much shorter in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes.
C) The Okazaki fragments of eukaryotes are on the leading strand, rather than the lagging strand.
D) There is little to no difference between the Okazaki fragments of eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Linear eukaryotic DNA molecules
A) have many origins of synthesis, while circular bacterial DNA usually have only one.
B) have only one origin of synthesis, while circular bacterial DNA usually have many.
C) are synthesized fully conservatively, while circular bacterial DNA is synthesized semi-conservatively.
D) are synthesized dispersively, while circular bacterial DNA is synthesized semi-conservatively.
A) have many origins of synthesis, while circular bacterial DNA usually have only one.
B) have only one origin of synthesis, while circular bacterial DNA usually have many.
C) are synthesized fully conservatively, while circular bacterial DNA is synthesized semi-conservatively.
D) are synthesized dispersively, while circular bacterial DNA is synthesized semi-conservatively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The enzyme telomerase uses mechanisms that involve:
A) Repeating sequences at the telomeres.
B) Having RNA oligonucleotides to act as templates as part of the enzyme.
C) Allowing the end of the chromosome to get a little shorter each time a cell divides.
D) Both repeating sequences at the end of chromosomes and RNA oligonucleotides to act as templates as part of the enzyme.
E) All of these.
A) Repeating sequences at the telomeres.
B) Having RNA oligonucleotides to act as templates as part of the enzyme.
C) Allowing the end of the chromosome to get a little shorter each time a cell divides.
D) Both repeating sequences at the end of chromosomes and RNA oligonucleotides to act as templates as part of the enzyme.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Telomerase activity may decline with old age and this could explain why cells lose their ability to divide after many replications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Telomerase activity in cancer cells may explain their longevity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Eukaryotes need more types of DNA polymerases than bacteria because
A) the DNA-containing organelles have their own DNA polymerases.
B) they have linear DNA , which is harder to replicate than circular DNA.
C) because they have more kinds of bases in their DNA than the four used by prokaryotes.
D) That's not true; eukaryotes do not have more types of DNA polymerases.
A) the DNA-containing organelles have their own DNA polymerases.
B) they have linear DNA , which is harder to replicate than circular DNA.
C) because they have more kinds of bases in their DNA than the four used by prokaryotes.
D) That's not true; eukaryotes do not have more types of DNA polymerases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is a characteristic of eukaryotic,but not prokaryotic,DNA replication?
A) Topoisomerases are required.
B) A primer is needed on the lagging strand only.
C) Histone biosynthesis must take place.
D) There is only one origin of replication.
A) Topoisomerases are required.
B) A primer is needed on the lagging strand only.
C) Histone biosynthesis must take place.
D) There is only one origin of replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes use a dimeric DNA Polymerase for DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Recombination:
A) occurs randomly throughout a chromosome
B) occurs more often in areas called hot spots
C) is a process that only happens under controlled laboratory conditions
D) is a spontaneous process that requires no enzymes
A) occurs randomly throughout a chromosome
B) occurs more often in areas called hot spots
C) is a process that only happens under controlled laboratory conditions
D) is a spontaneous process that requires no enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A special protein called proliferating cell nuclear antigen serves the purpose of the clamp in eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following describes a difference between DNA polymerases in eukaryotes and bacteria?
A) Some eukaryotic polymerases include a primase.
B) All the eukaryotic enzymes are polymeric.
C) Eukaryotes require a special enzyme to remove the RNA primer.
D) Some eukaryotic polymerases include a primase and all are polymeric.
E) All of these are correct.
A) Some eukaryotic polymerases include a primase.
B) All the eukaryotic enzymes are polymeric.
C) Eukaryotes require a special enzyme to remove the RNA primer.
D) Some eukaryotic polymerases include a primase and all are polymeric.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
One of the most important ways in which eukaryotic DNA differs from that of prokaryotes is
A) prokaryotic DNA is complexed to proteins whereas eukaryotic DNA is not
B) eukaryotic DNA is complexed to proteins whereas prokaryotic DNA is not
C) DNA synthesis in eukaryotes takes place in the opposite direction from that in prokaryotes
D) there is no requirement for a primer in the synthesis of eukaryotic DNA
A) prokaryotic DNA is complexed to proteins whereas eukaryotic DNA is not
B) eukaryotic DNA is complexed to proteins whereas prokaryotic DNA is not
C) DNA synthesis in eukaryotes takes place in the opposite direction from that in prokaryotes
D) there is no requirement for a primer in the synthesis of eukaryotic DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following play a role in DNA replication in eukaryotes?
A) cyclin-dependent kinases
B) origin recognition complex
C) replication licensing factors
D) all of these
A) cyclin-dependent kinases
B) origin recognition complex
C) replication licensing factors
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The mechanism of breakage and reunion of DNA strands during recombination was proposed by:
A) Messelson and Stahl
B) Messelson and Weigle
C) Robin Holliday
D) Francis Crick
A) Messelson and Stahl
B) Messelson and Weigle
C) Robin Holliday
D) Francis Crick

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
One major difficulty in replicating linear DNA molecules is replacing the segment of DNA occupied by the RNA primer on the telomeres at the ends of the DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The DNA polymerases in eukaryotes have similar functions to those found in bacteria,but they are not identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Replication of eukaryotic DNA
A) must occur faster than replication of prokaryotic DNA
B) must be controlled to coordinate with the cell cycle
C) takes place during mitosis
D) takes place twice during each cell cycle
A) must occur faster than replication of prokaryotic DNA
B) must be controlled to coordinate with the cell cycle
C) takes place during mitosis
D) takes place twice during each cell cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In eukaryotic replication,the RNA primers are degraded by:
A) the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of pol ä
B) DNA ligase
C) Helicase
D) FEN-1 and RNase H1
A) the 5' to 3' exonuclease activity of pol ä
B) DNA ligase
C) Helicase
D) FEN-1 and RNase H1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Eukaryotic DNA polymerases differ from those of prokaryotes in that
A) they do not require a primer
B) they do not always have exonuclease activity
C) there is no equivalent to the sliding clamp in prokaryotic replication
D) they produce longer Okazaki fragments
A) they do not require a primer
B) they do not always have exonuclease activity
C) there is no equivalent to the sliding clamp in prokaryotic replication
D) they produce longer Okazaki fragments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 79 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



