Deck 17: Effects of Positive Pressure Ventilation on the Pulmonary System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/28
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Effects of Positive Pressure Ventilation on the Pulmonary System
1
In what areas of the lung are ventilation and perfusion best matched during spontaneous ventilation in the supine position?
A) Apices of the lungs
B) Nondependent anterior lung areas
C) Dependent posterior lung areas
D) Basilar segments of lower lobes
A) Apices of the lungs
B) Nondependent anterior lung areas
C) Dependent posterior lung areas
D) Basilar segments of lower lobes
Dependent posterior lung areas
2
Lung injury is more likely to occur with which of the following with normal lung tissue?
A) PA = 25 cm H2O;Ppl = 18 cm H2O
B) PA = 29 cm H2O;Ppl = 10 cm H2O
C) PA = 30 cm H2O;Ppl = 21 cm H2O
D) PA = 45 cm H2O;Ppl = 34 cm H2O
A) PA = 25 cm H2O;Ppl = 18 cm H2O
B) PA = 29 cm H2O;Ppl = 10 cm H2O
C) PA = 30 cm H2O;Ppl = 21 cm H2O
D) PA = 45 cm H2O;Ppl = 34 cm H2O
PA = 29 cm H2O;Ppl = 10 cm H2O
3
Which of the following mechanically ventilated patients shows clinical signs of hypoventilation?
A) A patient who is cool to the touch and has negative T waves on the ECG.
B) A patient who has twitchy extremities and also atrial flutter on the ECG.
C) A patient who is anxious and hypertensive and has elevated T waves on the ECG.
D) A patient who has cool,twitchy extremities and also low,rounded T waves on the ECG.
A) A patient who is cool to the touch and has negative T waves on the ECG.
B) A patient who has twitchy extremities and also atrial flutter on the ECG.
C) A patient who is anxious and hypertensive and has elevated T waves on the ECG.
D) A patient who has cool,twitchy extremities and also low,rounded T waves on the ECG.
A patient who is anxious and hypertensive and has elevated T waves on the ECG.
4
The RT performs a patient-ventilator system check on a 24-year-old,5-foot,10-inch male patient who has been intubated because of a drug overdose.The RT notices what appears to be swelling around the patient's upper anterior chest and neck area.Palpation elicits a tissue paper feeling.The ventilator settings are: VC-CMV,rate 12/min with no patient assist,VT 900 mL,PEEP 5 cm H2O,FIO2 0.4,TI 1.2 sec.The most appropriate action for the RT to take is which of the following?
A) Increase the set flow rate.
B) Decrease the set tidal volume.
C) Reduce the set respiratory rate.
D) Perform emergency needle decompression.
A) Increase the set flow rate.
B) Decrease the set tidal volume.
C) Reduce the set respiratory rate.
D) Perform emergency needle decompression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a mechanically ventilated patient who is receiving lorazepam and succinylcholine,the diaphragm moves in which of the following ways?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Shear stress is most likely to affect a patient with which of the following?
A) PA = 35 cm H2O;Ppl = 21 cm H2O
B) PA = 35 cm H2O;Ppl = 12 cm H2O
C) PA = 45 cm H2O;Ppl = 33 cm H2O
D) PA = 50 cm H2O;Ppl = 38 cm H2O
A) PA = 35 cm H2O;Ppl = 21 cm H2O
B) PA = 35 cm H2O;Ppl = 12 cm H2O
C) PA = 45 cm H2O;Ppl = 33 cm H2O
D) PA = 50 cm H2O;Ppl = 38 cm H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The RT assesses the flow-time scalar from an apneic patient mechanically ventilated in the VC-CMV mode.The most appropriate action for this patient is to do which of the following? 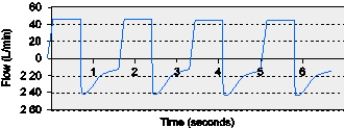
A) Decrease the set flow rate.
B) Reduce the set ventilator rate.
C) Increase the inspiratory time.
D) Decrease the set tidal volume.

A) Decrease the set flow rate.
B) Reduce the set ventilator rate.
C) Increase the inspiratory time.
D) Decrease the set tidal volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The RT responds to the high pressure,high respiratory rate,low exhaled volume,and low exhaled minute volume alarms of a mechanically ventilated patient in the ICU.Upon entering the room,the RT notices that the patient,who is still attached to the ventilator,appears diaphoretic,tachypneic,tachycardic,and hypertensive.Breath sounds are absent on the left and distant on the right.The patient's trachea is deviated to the left,and jugular vein distention is present.The endotracheal tube is 24 cm at the teeth.Immediate action should include which of the following?
A) Order a chest radiograph in the upright position.
B) Administer intravenous etomidate and succinylcholine.
C) Pull back the endotracheal tube to 22 cm at the teeth.
D) Insert a 14-gauage needle into the second intercostal space right midclavicular line.
A) Order a chest radiograph in the upright position.
B) Administer intravenous etomidate and succinylcholine.
C) Pull back the endotracheal tube to 22 cm at the teeth.
D) Insert a 14-gauage needle into the second intercostal space right midclavicular line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Alveolar tissue and pulmonary capillary injury is caused by which of the following?
A) Barotrauma
B) Biotrauma
C) Shear stress
D) Overdistention
A) Barotrauma
B) Biotrauma
C) Shear stress
D) Overdistention

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Biotrauma is caused directly by which of the following?
A) High oxygen levels
B) Overdistention of alveoli
C) Long expiratory times
D) Fast respiratory rates
A) High oxygen levels
B) Overdistention of alveoli
C) Long expiratory times
D) Fast respiratory rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the minimum transpulmonary pressure that has been associated with lung injury in animals?
A) 30 cm H2O
B) 40 cm H2O
C) 50 cm H2O
D) 60 cm H2O
A) 30 cm H2O
B) 40 cm H2O
C) 50 cm H2O
D) 60 cm H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Shear stress injury and loss of surfactant from the resulting unstable lung units result in a loss of surfactant.This type of pulmonary trauma is known as _____________.
A) atelectrauma
B) barotrauma
C) biotrauma
D) volutrauma
A) atelectrauma
B) barotrauma
C) biotrauma
D) volutrauma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the minimum range of time constants necessary for the lungs to empty 98% of the inspired volume?
A) 1 to 2
B) 2 to 3
C) 3 to 4
D) 4 to 5
A) 1 to 2
B) 2 to 3
C) 3 to 4
D) 4 to 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Healthy areas of lung tissue in a patient with ARDS can be protected from lung injury caused by overdistention by which of the following?
A) Increasing FIO2.
B) Decreasing PEEP.
C) Using the prone position.
D) Using a VT of 10 to 12 mL/kg.
A) Increasing FIO2.
B) Decreasing PEEP.
C) Using the prone position.
D) Using a VT of 10 to 12 mL/kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Inappropriate ventilator settings can cause the release of inflammatory mediators within _______.
A) 1 to 3 hours
B) 5 to 10 hours
C) 10 to 12 hours
D) 24 hours
A) 1 to 3 hours
B) 5 to 10 hours
C) 10 to 12 hours
D) 24 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Overdistention of the lungs causes the release of which inflammatory mediators?
A) Tumor necrosis factor
B) Alpha-1 antitrypsin
C) Histamine
D) Macrophages
A) Tumor necrosis factor
B) Alpha-1 antitrypsin
C) Histamine
D) Macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Preservation of spontaneous breathing during mechanical ventilation favors the distribution of gas to which areas of the lung?
A) Peribronchial area
B) Upper airway
C) Lung periphery
D) Central airways
A) Peribronchial area
B) Upper airway
C) Lung periphery
D) Central airways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following mechanically ventilated patients shows clinical signs of hyperventilation?
A) A patient who has hot skin and also long P-R intervals on the ECG.
B) A patient who has cool skin and also shows paroxysmal tachycardia on the ECG.
C) A patient who is hypertensive and agitated and has S-T segment depression on the ECG.
D) A patient who is hypotensive and dyspneic and has widened QRS complexes on the ECG.
A) A patient who has hot skin and also long P-R intervals on the ECG.
B) A patient who has cool skin and also shows paroxysmal tachycardia on the ECG.
C) A patient who is hypertensive and agitated and has S-T segment depression on the ECG.
D) A patient who is hypotensive and dyspneic and has widened QRS complexes on the ECG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI)is associated with which of the following?
A) Air trapping
B) Biotrauma
C) Patient-ventilator asynchrony
D) Ventilator-associated pneumonia
A) Air trapping
B) Biotrauma
C) Patient-ventilator asynchrony
D) Ventilator-associated pneumonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Prolonged ventilator-induced hyperventilation can lead to which of the following?
A) Hypokalemia
B) Hyperkalemia
C) Increased ICP
D) Headaches
A) Hypokalemia
B) Hyperkalemia
C) Increased ICP
D) Headaches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The acceptable lower limit of PaO2 for a mechanically ventilated patient with ARDS is which of the following?
A) 50 mm Hg
B) 60 mm Hg
C) 70 mm Hg
D) 80 mm Hg
A) 50 mm Hg
B) 60 mm Hg
C) 70 mm Hg
D) 80 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The pressure-time scalar of a patient with COPD who is receiving PSV shows positive deflection toward the end of inspiration.The most appropriate way to alleviate this is to do which of the following?
A) Increase the PSV level.
B) Decrease the PSV level.
C) Increase the flow cycle percentage.
D) Decrease the flow cycle percentage.
A) Increase the PSV level.
B) Decrease the PSV level.
C) Increase the flow cycle percentage.
D) Decrease the flow cycle percentage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate the static compliance for a patient who has the following: auto PEEP = 8 cm H2O,set PEEP = 12 cm H2O,VT = 425 mL,PIP = 45 cm H2O,and Pplateau = 36 cm H2O.
A) 15 mL/cm H2O
B) 18 mL/cm H2O
C) 21 mL/cm H2O
D) 27 mL/cm H2O
A) 15 mL/cm H2O
B) 18 mL/cm H2O
C) 21 mL/cm H2O
D) 27 mL/cm H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A patient with asthma is being ventilated in PSV,5 cm H2O,with CPAP of 5 cm H2O.The patient has chest wall retractions on most breaths and appears to have an increased WOB.The following graphic occurred the entire time the respiratory therapist was assessing the patient.What does this graphic demonstrate? 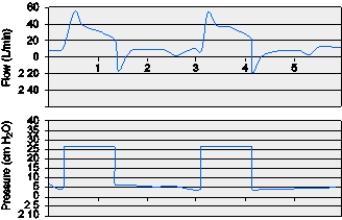
A) Trigger asynchrony
B) Mode asynchrony
C) PEEP asynchrony
D) Cycle asynchrony

A) Trigger asynchrony
B) Mode asynchrony
C) PEEP asynchrony
D) Cycle asynchrony

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The combination of __________________ and ____________________ increases the risk of absorption atelectasis.
A) high tidal volumes,FIO2 >0.4
B) high tidal volumes,FIO2 >=0.7
C) low tidal volumes,FIOs >0.5
D) low tidal volumes,FIO2 >0.7
A) high tidal volumes,FIO2 >0.4
B) high tidal volumes,FIO2 >=0.7
C) low tidal volumes,FIOs >0.5
D) low tidal volumes,FIO2 >0.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When setting up a patient on volume ventilation with constant flow,the initial flow setting should be ________.
A) 50 L/min
B) 60 L/min
C) 70 L/min
D) 80 L/min
A) 50 L/min
B) 60 L/min
C) 70 L/min
D) 80 L/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A patient with a size 8 ET tube has a spontaneous minute ventilation of 20 L/min.Use the figure below to find the imposed WOB through the ET tube. 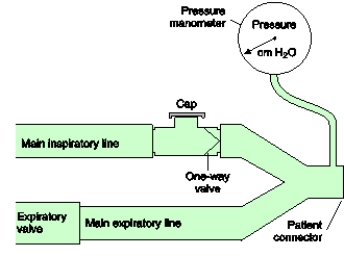
A) 5 J/min
B) 18 J/min
C) 22 J/min
D) 40 J/min

A) 5 J/min
B) 18 J/min
C) 22 J/min
D) 40 J/min

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Assessment of a mechanically ventilated patient reveals use of accessory muscles and a respiratory rate of 26 breaths/min.The mode is CPAP with 5 cm H2O and an FIO2 of 0.4.The most appropriate action is which of the following?
A) Return the patient to full ventilatory support.
B) Add pressure support to the CPAP.
C) Increase the CPAP to 8 cm H2O.
D) Deflate the cuff of the ET tube.
A) Return the patient to full ventilatory support.
B) Add pressure support to the CPAP.
C) Increase the CPAP to 8 cm H2O.
D) Deflate the cuff of the ET tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 28 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



