Deck 25: Derivatives and Hedging Risk
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Derivatives and Hedging Risk
1
Futures contracts contrast with forward contracts by:
A) trading on an organized exchange.
B) marking to the market on a daily basis.
C) allowing the seller to deliver any day over the delivery month.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.
A) trading on an organized exchange.
B) marking to the market on a daily basis.
C) allowing the seller to deliver any day over the delivery month.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.
All of these.
2
A chocolate company which uses the futures market to lock in the price of cocoa to protect a profit is an example of:
A) a long hedge.
B) a short hedge.
C) purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
D) Both a long hedge; and purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
E) Both a short hedge; and purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
A) a long hedge.
B) a short hedge.
C) purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
D) Both a long hedge; and purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
E) Both a short hedge; and purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
Both a long hedge; and purchasing futures to guard against a potential loss.
3
A derivative is a financial instrument whose value is determined by:
A) a regulatory body such as the FTC.
B) a primitive or underlying asset.
C) hedging a risk.
D) hedging a speculation.
E) None of these.
A) a regulatory body such as the FTC.
B) a primitive or underlying asset.
C) hedging a risk.
D) hedging a speculation.
E) None of these.
a primitive or underlying asset.
4
LIBOR stands for:
A) Lausanne Interest Basis Offered Rate.
B) London International Offered Rate.
C) London Interbank Offered Rate.
D) London Interagency Offered Rate.
E) None of these.
A) Lausanne Interest Basis Offered Rate.
B) London International Offered Rate.
C) London Interbank Offered Rate.
D) London Interagency Offered Rate.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Two key features of futures contracts that make them more in demand than forward contracts are:
A) futures are traded on exchanges and must be marked to the market.
B) futures contracts allow flexibility in delivery dates and provide a liquid market for netting positions.
C) futures are marked to the market and allow delivery flexibility.
D) futures are traded in liquid markets and are marked to the market.
E) All of
A) futures are traded on exchanges and must be marked to the market.
B) futures contracts allow flexibility in delivery dates and provide a liquid market for netting positions.
C) futures are marked to the market and allow delivery flexibility.
D) futures are traded in liquid markets and are marked to the market.
E) All of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A potential disadvantage of forward contracts versus futures contracts is:
A) the extra liquidity required to cover the potential outflows that occur prior to delivery and caused by marking to market.
B) the incentive for a particular party to default.
C) that the buyers and sellers don't know each other and never meet.
D) All of these.
E) Both the extra liquidity required to cover the potential outflows that occur prior to delivery and caused by marking to market; and that the buyers and sellers don't know each other and never meet.
A) the extra liquidity required to cover the potential outflows that occur prior to delivery and caused by marking to market.
B) the incentive for a particular party to default.
C) that the buyers and sellers don't know each other and never meet.
D) All of these.
E) Both the extra liquidity required to cover the potential outflows that occur prior to delivery and caused by marking to market; and that the buyers and sellers don't know each other and never meet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The main difference between a forward contract and a cash transaction is:
A) only the cash transaction creates an obligation to perform.
B) a forward is performed at a later date while the cash transaction is performed immediately.
C) only one involves a deliverable instrument.
D) neither allows for hedging.
E) None of these.
A) only the cash transaction creates an obligation to perform.
B) a forward is performed at a later date while the cash transaction is performed immediately.
C) only one involves a deliverable instrument.
D) neither allows for hedging.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
You hold a forward contract to take delivery of U.S. Treasury bonds in 9 months. If the entire term structure of interest rates shifts down over the 9-month period,the value of the forward contract will have _____ on the date of delivery.
A) risen
B) fallen
C) not changed
D) either risen or fallen, depending on the maturity of the T-bond
E) collapsed
A) risen
B) fallen
C) not changed
D) either risen or fallen, depending on the maturity of the T-bond
E) collapsed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is true about the user of derivatives?
A) Derivatives usually appear explicitly in the financial statements.
B) Academic surveys account for much of our knowledge of corporate derivatives use.
C) Smaller firms are more likely to use derivatives than large firms.
D) The most frequently used derivatives are commodity and equity futures.
E) None of these. are truE.
A) Derivatives usually appear explicitly in the financial statements.
B) Academic surveys account for much of our knowledge of corporate derivatives use.
C) Smaller firms are more likely to use derivatives than large firms.
D) The most frequently used derivatives are commodity and equity futures.
E) None of these. are truE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A farmer with wheat in the fields and who uses the futures market to protect a profit is an example of:
A) a long hedge.
B) a short hedge.
C) selling futures to guard against a potential loss.
D) Both a long hedge and selling futures to guard against a potential loss.
E) Both a short hedge and selling futures to guard against a potential loss.
A) a long hedge.
B) a short hedge.
C) selling futures to guard against a potential loss.
D) Both a long hedge and selling futures to guard against a potential loss.
E) Both a short hedge and selling futures to guard against a potential loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following terms is not part of a forward contract?
A) Making delivery
B) Taking delivery
C) Delivery instrument
D) Cash transaction
E) None of these.
A) Making delivery
B) Taking delivery
C) Delivery instrument
D) Cash transaction
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A miller who needs wheat to mill to flour uses the futures market to protect a profit by:
A) a long hedge to take delivery.
B) a short hedge to deliver.
C) buying futures to guard against a potential loss.
D) Both a long hedge to take delivery; and buying futures to guard against a potential loss.
E) Both a short hedge to deliver; and buying futures to guard against a potential loss.
A) a long hedge to take delivery.
B) a short hedge to deliver.
C) buying futures to guard against a potential loss.
D) Both a long hedge to take delivery; and buying futures to guard against a potential loss.
E) Both a short hedge to deliver; and buying futures to guard against a potential loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Derivatives can be used to either hedge or speculate. These actions:
A) increase risk in both cases.
B) decrease risk in both cases.
C) spread or minimize risk in both cases.
D) offset risk by hedging and increase risk by speculating.
E) offset risks by speculating and increase risk by hedging.
A) increase risk in both cases.
B) decrease risk in both cases.
C) spread or minimize risk in both cases.
D) offset risk by hedging and increase risk by speculating.
E) offset risks by speculating and increase risk by hedging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The buyer of a forward contract:
A) will be taking delivery of the good(s) today at today's price.
B) will be making delivery of the good(s) at a later date at that date's price.
C) will be making delivery of the good(s) today at today's price.
D) will be taking delivery of the good(s) at a later date at pre-specified price.
E) Both will be taking delivery of the good(s) today at today's price or will be taking delivery of the good(s) at a later date at pre-specified pricE.
A) will be taking delivery of the good(s) today at today's price.
B) will be making delivery of the good(s) at a later date at that date's price.
C) will be making delivery of the good(s) today at today's price.
D) will be taking delivery of the good(s) at a later date at pre-specified price.
E) Both will be taking delivery of the good(s) today at today's price or will be taking delivery of the good(s) at a later date at pre-specified pricE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the producer of a product has entered into a fixed price sale agreement for that output,the producer faces:
A) a nice steady profit because the output price is fixed.
B) an uncertain profit if the input prices are volatile. This risk can be reduced by a short hedge.
C) an uncertain profit if the input prices are volatile. This risk can be reduced by a long hedge.
D) a modest profit if the input prices are stable. This risk can be reduced by a long hedge.
E) a modest profit if the input prices are stablE. This risk can be reduced by a short hedgE.
A) a nice steady profit because the output price is fixed.
B) an uncertain profit if the input prices are volatile. This risk can be reduced by a short hedge.
C) an uncertain profit if the input prices are volatile. This risk can be reduced by a long hedge.
D) a modest profit if the input prices are stable. This risk can be reduced by a long hedge.
E) a modest profit if the input prices are stablE. This risk can be reduced by a short hedgE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A swap is an arrangement for two counterparties to:
A) exchange cash flows over time.
B) permit fluctuation in interest rates.
C) help exchange markets clear.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.
A) exchange cash flows over time.
B) permit fluctuation in interest rates.
C) help exchange markets clear.
D) All of these.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If rates in the market fall between now and one month from now,the mortgage banker:
A) loses as the mortgages are sold at a discount.
B) gains as the mortgages are sold at a discount.
C) loses as the mortgages are sold at a premium.
D) gains as the mortgages are sold at a premium.
E) neither gains nor loses.
A) loses as the mortgages are sold at a discount.
B) gains as the mortgages are sold at a discount.
C) loses as the mortgages are sold at a premium.
D) gains as the mortgages are sold at a premium.
E) neither gains nor loses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A futures contract on gold states that buyers and sellers agree to make or take delivery of an ounce of gold for $400 per ounce. The contract expires in 3 months. The current price of gold is $400 per ounce. If the price of gold rises and continues to rise every day over the 3 month period,then when the contract is settled,the buyer will _____ and the seller will _____.
A) lose; gain
B) gain; lose
C) gain; break even
D) gain; gain
E) lose; lose
A) lose; gain
B) gain; lose
C) gain; break even
D) gain; gain
E) lose; lose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A forward contract is described by:
A) agreeing today to buy a product at a later date at a price to be set in the future.
B) agreeing today to buy a product today at its current price.
C) agreeing today to buy a product at a later date at a price set today.
D) agreeing today to buy a product if and only if its price rises above the exercise price today at its current price.
E) None of these.
A) agreeing today to buy a product at a later date at a price to be set in the future.
B) agreeing today to buy a product today at its current price.
C) agreeing today to buy a product at a later date at a price set today.
D) agreeing today to buy a product if and only if its price rises above the exercise price today at its current price.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Duration is a measure of the:
A) yield to maturity of a bond.
B) coupon yield of a bond.
C) price of a bond.
D) effective maturity of a bond.
E) All of
A) yield to maturity of a bond.
B) coupon yield of a bond.
C) price of a bond.
D) effective maturity of a bond.
E) All of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Interest rate and currency swaps allow one party to exchange a:
A) floating interest rate or currency value for a fixed value over the contract term.
B) fixed interest rate or currency value for a lower fixed value over the contract term.
C) floating interest rate or currency value for a lower floating value over the contract term.
D) fixed interest rate position for a currency position over the contract term.
E) None of these.
A) floating interest rate or currency value for a fixed value over the contract term.
B) fixed interest rate or currency value for a lower fixed value over the contract term.
C) floating interest rate or currency value for a lower floating value over the contract term.
D) fixed interest rate position for a currency position over the contract term.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a firm purchases a cap at 10% this will:
A) limit the amount of borrowing to 10% of assets.
B) pay the firm 10% on their purchase.
C) pay the holder the LIBOR interest above 10%.
D) pay the holder the LIBOR interest below the 10%.
E) None of these.
A) limit the amount of borrowing to 10% of assets.
B) pay the firm 10% on their purchase.
C) pay the holder the LIBOR interest above 10%.
D) pay the holder the LIBOR interest below the 10%.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A pure discount bond pays:
A) no coupons, therefore its duration is equal to its maturity.
B) discounted coupons, therefore its duration is greater than its maturity.
C) level coupons, therefore its duration is equal to its maturity.
D) declining coupons, therefore its duration is less than its maturity.
E) None of these.
A) no coupons, therefore its duration is equal to its maturity.
B) discounted coupons, therefore its duration is greater than its maturity.
C) level coupons, therefore its duration is equal to its maturity.
D) declining coupons, therefore its duration is less than its maturity.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A savings and loan has extremely long-term assets that are currently matched against extremely short-term liabilities. For this S&L:
A) falling interest rates will decrease the value of its equity.
B) falling interest rates will increase the value of its equity.
C) rising interest rates will increase the value of its equity.
D) rising interest rates will decrease the value of its equity.
E) Both falling interest rates will increase the value of its equity; and rising interest rates will decrease the value of its equity.
A) falling interest rates will decrease the value of its equity.
B) falling interest rates will increase the value of its equity.
C) rising interest rates will increase the value of its equity.
D) rising interest rates will decrease the value of its equity.
E) Both falling interest rates will increase the value of its equity; and rising interest rates will decrease the value of its equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Duration of a coupon paying bond is:
A) equal to its number of payments.
B) less than a zero coupon bond.
C) equal to the zero coupon bond.
D) equal to its maturity.
E) None of these.
A) equal to its number of payments.
B) less than a zero coupon bond.
C) equal to the zero coupon bond.
D) equal to its maturity.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
To protect against interest rate risk,the mortgage banker should:
A) buy futures, as this position will hedge losses if rates rise.
B) sell futures, as this position will hedge losses if rates rise.
C) sell futures, as this position will add to his gains if rates rise.
D) buy futures, as this position will add to his gains if rates rise.
E) None of these.
A) buy futures, as this position will hedge losses if rates rise.
B) sell futures, as this position will hedge losses if rates rise.
C) sell futures, as this position will add to his gains if rates rise.
D) buy futures, as this position will add to his gains if rates rise.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A set of bonds all have the same maturity. Which one has the least percentage price change for given shifts in interest rates:
A) zero coupon bonds.
B) high coupon bonds.
C) low coupon bonds.
D) pure discount bonds.
E) not enough information to determinE.
A) zero coupon bonds.
B) high coupon bonds.
C) low coupon bonds.
D) pure discount bonds.
E) not enough information to determinE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When interest rates shift,the price of zero coupon bonds:
A) are more volatile as compared with short-term bonds of the same maturity.
B) are less volatile as compared with short-term bonds of the same maturity.
C) are more volatile as compared with long-term bonds of the same maturity.
D) are less volatile as compared with long-term bonds of the same maturity.
E) Both are more volatile as compared with short-term bonds of the same maturity; and are more volatile as compared with long-term bonds of the same maturity.
A) are more volatile as compared with short-term bonds of the same maturity.
B) are less volatile as compared with short-term bonds of the same maturity.
C) are more volatile as compared with long-term bonds of the same maturity.
D) are less volatile as compared with long-term bonds of the same maturity.
E) Both are more volatile as compared with short-term bonds of the same maturity; and are more volatile as compared with long-term bonds of the same maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The duration of a 15 year zero coupon bond priced at $182.70 is:
A) 2.74 years.
B) 15 years.
C) 17.74 years.
D) cannot determine without the interest rate.
E) None of these.
A) 2.74 years.
B) 15 years.
C) 17.74 years.
D) cannot determine without the interest rate.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a financial institution has equated the dollar effects of interest rate risk on its assets with the dollar effects on its liabilities,it has engaged in:
A) a long hedge.
B) a short hedge.
C) a protected swap.
D) immunizing interest rate risk.
E) None of these.
A) a long hedge.
B) a short hedge.
C) a protected swap.
D) immunizing interest rate risk.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A bond manager who wishes to hold the bond with the greatest potential volatility would be wise to hold:
A) short-term, high-coupon bonds.
B) long-term, low-coupon bonds.
C) long-term, zero-coupon bonds.
D) short-term, zero-coupon bonds.
E) short-term, low-coupon bonds.
A) short-term, high-coupon bonds.
B) long-term, low-coupon bonds.
C) long-term, zero-coupon bonds.
D) short-term, zero-coupon bonds.
E) short-term, low-coupon bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A financial institution can hedge its interest rate risk by:
A) matching the duration of its assets to the duration of its liabilities.
B) setting the duration of its assets equal to half that of the duration of its liabilities.
C) matching the duration of its assets, weighted by the market value of its assets with the duration of its liabilities, weighted by the market value of its liabilities.
D) setting the duration of its assets, weighted by the market value of its assets to one half that of the duration of the liabilities, weighted by the market value of the liabilities.
A) matching the duration of its assets to the duration of its liabilities.
B) setting the duration of its assets equal to half that of the duration of its liabilities.
C) matching the duration of its assets, weighted by the market value of its assets with the duration of its liabilities, weighted by the market value of its liabilities.
D) setting the duration of its assets, weighted by the market value of its assets to one half that of the duration of the liabilities, weighted by the market value of the liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An inverse floater and a super-inverse floater are more valuable to a purchaser if:
A) interest rates stay the same.
B) interest rates fall.
C) interest rates rise.
D) held for a long time.
E) None of these.
A) interest rates stay the same.
B) interest rates fall.
C) interest rates rise.
D) held for a long time.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exotic derivatives are complicated blends of other derivatives. Some exotics are:
A) inverse floaters.
B) cap and floors.
C) futures.
D) Both inverse floaters; and cap and floors.
E) Both cap and floors; and futures.
A) inverse floaters.
B) cap and floors.
C) futures.
D) Both inverse floaters; and cap and floors.
E) Both cap and floors; and futures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In percentage terms,higher coupon bonds experience a _______ price change compared with lower coupon bonds of the same maturity given a change in yield to maturity.
A) greater
B) smaller
C) similar
D) smaller or greater
E) None of these.
A) greater
B) smaller
C) similar
D) smaller or greater
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A financial institution has equity equal to one-tenth of its assets. If its asset duration is currently equal to its liability duration,then to immunize,the firm needs to:
A) decrease the duration of its assets.
B) increase the duration of its assets.
C) decrease the duration of its liabilities.
D) do nothing, i.e., keep the duration of its liabilities equal to the duration of its assets.
A) decrease the duration of its assets.
B) increase the duration of its assets.
C) decrease the duration of its liabilities.
D) do nothing, i.e., keep the duration of its liabilities equal to the duration of its assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Comparing long-term bonds with short-term bonds,long-term bonds are _____ volatile and therefore experience _____ price change than short-term bonds for the same interest rate shift.
A) less; less
B) less; more
C) more; more
D) more; less
E) more; the same
A) less; less
B) less; more
C) more; more
D) more; less
E) more; the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Futures market transactions are used to reduce risk. Risk may not be totally offset if:
A) the two instruments have different maturities.
B) payoff schedules of the two instruments are different.
C) the volatility of the two instruments are different.
D) the price movements are not perfectly correlated.
E) All of
A) the two instruments have different maturities.
B) payoff schedules of the two instruments are different.
C) the volatility of the two instruments are different.
D) the price movements are not perfectly correlated.
E) All of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Duration of a pure discount bond:
A) is equal to its half-life.
B) is less than a zero coupon bond.
C) is equal to the liabilities hedged.
D) is equal to its maturity.
E) None of these.
A) is equal to its half-life.
B) is less than a zero coupon bond.
C) is equal to the liabilities hedged.
D) is equal to its maturity.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Hedging in the futures markets can reduce all risk if:
A) price movements in both the cash and futures markets are perfectly correlated.
B) price movements in both the cash and futures markets have zero correlation.
C) price movements in both the cash and futures markets are less than perfectly correlated.
D) the hedge is a short hedge, but not a long hedge.
E) the hedge is a long hedge, but not a short hedgE.
A) price movements in both the cash and futures markets are perfectly correlated.
B) price movements in both the cash and futures markets have zero correlation.
C) price movements in both the cash and futures markets are less than perfectly correlated.
D) the hedge is a short hedge, but not a long hedge.
E) the hedge is a long hedge, but not a short hedgE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
There are always ___ counterparties in a credit default swap:
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) more than three
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) more than three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the practical use of credit default swaps there:
A) is not an organized exchange or template for the agreement.
B) is an organized exchange or template for the agreement.
C) are laws making them illegal in the United States.
D) are limits to the amount of borrowing of both parties.
E) None of these.
A) is not an organized exchange or template for the agreement.
B) is an organized exchange or template for the agreement.
C) are laws making them illegal in the United States.
D) are limits to the amount of borrowing of both parties.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A bank has a $80 million mortgage bond risk position which it hedges in the Treasury bond futures markets at the Chicago Board of Trade. Approximately how many contracts are needed to be held in the hedge?
A) 8
B) 80
C) 800
D) 8,000
E) 80,000
A) 8
B) 80
C) 800
D) 8,000
E) 80,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Calculate the duration of a 4-year $1,000 face value bond,which pays 8% coupons annually throughout maturity and has a yield to maturity of 9%.
A) 3.29 years
B) 3.57 years
C) 3.69 years
D) 3.89 years
E) 4.00 years
A) 3.29 years
B) 3.57 years
C) 3.69 years
D) 3.89 years
E) 4.00 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
On June 1,you contract to take delivery of 1 ounce of gold for $965. The agreement is good for any day up to July 1. Throughout June,the price of gold hit a low of $960 and hit a high of $990. The price settled on June 30 at $980,and on July 1st you settle your futures agreement at that price. Your net cash flow is:
A) -$20.
B) -$15.
C) -$5
D) $15.
E) $20.
A) -$20.
B) -$15.
C) -$5
D) $15.
E) $20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You have taken a short position in a futures contract on corn at $2.60 per bushel. Over the next 5 days the contract settled at 2.52,2.57,2.62,2.68,and 2.70. You then decide to reverse your position in the futures market on the fifth day at close. What is the net amount you receive at the end of 5 days?
A) $0.00
B) $2.60
C) $2.70
D) $2.80
E) Must know the number of contracts
A) $0.00
B) $2.60
C) $2.70
D) $2.80
E) Must know the number of contracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Calculate the duration of a 7-year $1,000 zero-coupon bond with a current price of $399.63 and a yield to maturity of 14%.
A) 5 years
B) 6 years
C) 7 years
D) 8 years
E) 9 years
A) 5 years
B) 6 years
C) 7 years
D) 8 years
E) 9 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
On March 1,you contract to take delivery of 1 ounce of gold for $415. The agreement is good for any day up to April 1. Throughout March,the price of gold hit a low of $385 and hit a high of $435. The price settled on March 31 at $420,and on April 1st you settle your futures agreement at that price. Your net cash flow is:
A) -$30.
B) -$20.
C) -$15.
D) $5.
E) $20.
A) -$30.
B) -$20.
C) -$15.
D) $5.
E) $20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A bank has a $50 million mortgage bond risk position which it hedges in the Treasury bond futures markets at the Chicago Board of Trade. Approximately how many contracts are needed to be held in the hedge?
A) 5
B) 50
C) 500
D) 5,000
E) 50,000
A) 5
B) 50
C) 500
D) 5,000
E) 50,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Credit default swaps:
A) will pay the holder the LIBOR interest rate.
B) pay the borrower the LIBOR interest rate.
C) are like insurance against a loss of value if the firm defaults on a bond.
D) limit the amount of borrowing of all parties in the credit default swap.
E) None of these.
A) will pay the holder the LIBOR interest rate.
B) pay the borrower the LIBOR interest rate.
C) are like insurance against a loss of value if the firm defaults on a bond.
D) limit the amount of borrowing of all parties in the credit default swap.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A Treasury note with a maturity of 2 years pays interest semi-annually on a 9 percent annual coupon rate. The $1,000 face value is returned at maturity. If the effective annual yield for all maturities is 7 percent annually,what is the current price of the Treasury note?
A) $960.68
B) $986.69
C) $1,010.35
D) $1,034.40
E) $1,038.99
A) $960.68
B) $986.69
C) $1,010.35
D) $1,034.40
E) $1,038.99

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Firm A is paying $750,000 in interest payments a year while Firm B is paying LIBOR plus 75 basis points on $10,000,000 loans. The current LIBOR rate is 6.5%. Firm A and B have agreed to swap interest payments. What is the net payment this year?
A) Firm A pays $750,000 to Firm B
B) Firm B pays $725,000 to Firm A
C) Firm B pays $25,000 to Firm A
D) Firm A pays $25,000 to Firm B
E) None of these.
A) Firm A pays $750,000 to Firm B
B) Firm B pays $725,000 to Firm A
C) Firm B pays $25,000 to Firm A
D) Firm A pays $25,000 to Firm B
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The duration of a 2 year annual 10% bond that is selling for par is:
A) 1.00 years.
B) 1.91 years.
C) 2.00 years.
D) 2.09 years.
E) None of these.
A) 1.00 years.
B) 1.91 years.
C) 2.00 years.
D) 2.09 years.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
On March 1,you contract to take delivery of 1 ounce of gold for $495. The agreement is good for any day up to April 1. Throughout March,the price of gold hit a low of $425 and hit a high of $535. The price settled on March 31 at $505,and on April 1st you settle your futures agreement at that price. Your net cash flow is:
A) -$30.
B) -$20.
C) -$15.
D) $10.
E) $20.
A) -$30.
B) -$20.
C) -$15.
D) $10.
E) $20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose you agree to purchase one ounce of gold for $382 any time over the next month. The current price of gold is $380. The spot price of gold then falls to $377 the next day. If the agreement is represented by a futures contract marking to market on a daily basis as the price changes,what is your cash flow at the end of the next business day?
A) $0
B) $3
C) $5
D) -$3
E) -$5
A) $0
B) $3
C) $5
D) -$3
E) -$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
You have taken a short position in a futures contract on corn at $2.60 per bushel. Over the next 5 days the contract settled at 2.52,2.57,2.62,2.68,and 2.70. Before you can reverse your position in the futures market on the fifth day you are notified to complete delivery. What will you receive on delivery and what is the net amount you receive in total?
A) $2.60; $-0.10
B) $2.60; $0.10
C) $2.60; $2.70
D) $2.70; $-0.10
E) $2.70; $2.60
A) $2.60; $-0.10
B) $2.60; $0.10
C) $2.60; $2.70
D) $2.70; $-0.10
E) $2.70; $2.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose you agree to purchase one ounce of gold for $984 any time over the next month. The current price of gold is $970. The spot price of gold then falls to $960 the next day. If the agreement is represented by a futures contract marking to market on a daily basis as the price changes,what is your cash flow at the end of the next business day?
A) $10
B) $5
C) $0
D) -$5
E) -$10
A) $10
B) $5
C) $0
D) -$5
E) -$10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
You bought a futures contract for $2.60 per bushel and the contract ended at $2.70 after several days of trading with the following close prices each day: $2.52,$2.57,$2.62,$2.68,and $2.70. What would the mark to market sequence be?
A) -.08, .05, .05, .06, .02
B) .08, -.05, -.05, -.06, -.02
C) .08, .03, -.02, -.06, -.10
D) -.08, -.03, .02, .06, .10
E) .10, .06, .02, -.03, -.08
A) -.08, .05, .05, .06, .02
B) .08, -.05, -.05, -.06, -.02
C) .08, .03, -.02, -.06, -.10
D) -.08, -.03, .02, .06, .10
E) .10, .06, .02, -.03, -.08

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a firm sells a floor at 6% this will:
A) pay the holder the LIBOR interest below the 6%.
B) pay the firm 6% on their purchase.
C) pay the holder the LIBOR interest above 6%.
D) limit the amount of borrowing to 6% of assets.
E) None of these.
A) pay the holder the LIBOR interest below the 6%.
B) pay the firm 6% on their purchase.
C) pay the holder the LIBOR interest above 6%.
D) limit the amount of borrowing to 6% of assets.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A mortgage banker had made loan commitments for $10 million in 3 months. How many contracts on Treasury bonds futures must the banker write or buy?
A) Go short 10.
B) Go short 100.
C) Go long 10.
D) Go long 100.
E) None of these.
A) Go short 10.
B) Go short 100.
C) Go long 10.
D) Go long 100.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The futures markets are labeled as pure speculation and even gambling. Why is this an inaccurate portrayal of the market's function?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A bank has a $100 million mortgage bond risk position which it hedges in the Treasury bond futures markets at the Chicago Board of Trade. Approximately how many contracts are needed to be held in the hedge?
A) 10
B) 100
C) 1,000
D) 10,000
E) 100,000
A) 10
B) 100
C) 1,000
D) 10,000
E) 100,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Duration is defined as the weighted average time to maturity of a financial instrument. Explain how this knowledge can help protect against interest rate risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
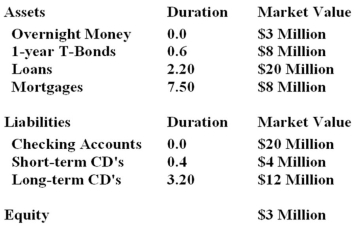 Calculate the duration of Tiger State Bank's assets and liabilities.
Calculate the duration of Tiger State Bank's assets and liabilities.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A mortgage banker had made loan commitments for $20 million in 3 months. How many contracts on Treasury bonds futures must the banker write or buy?
A) Go short 20.
B) Go short 200.
C) Go long 20.
D) Go long 200.
E) None of these.
A) Go short 20.
B) Go short 200.
C) Go long 20.
D) Go long 200.
E) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
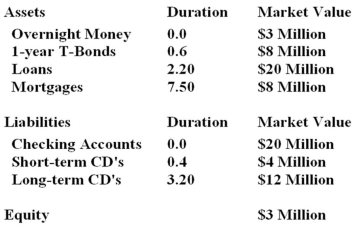 What new asset duration will immunize the balance sheet?
What new asset duration will immunize the balance sheet?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



