Deck 3: Interdependence and the Gains From Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Interdependence and the Gains From Trade
1
Table 3-1
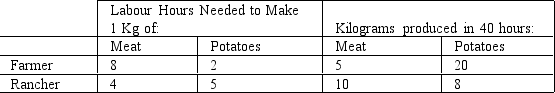
Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in potatoes.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods.

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in potatoes.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods.
B
2
A rancher can produce only hamburgers, while a farmer can produce only French fries. If the rancher and the farmer like both foods, which of the following is most likely?
A)They cannot gain from trade.
B)They could gain from trade under certain circumstances, but not always.
C)They could gain from trade because each would enjoy a greater variety of food.
D)They could gain from trade only if each were indifferent between hamburgers and French fries.
A)They cannot gain from trade.
B)They could gain from trade under certain circumstances, but not always.
C)They could gain from trade because each would enjoy a greater variety of food.
D)They could gain from trade only if each were indifferent between hamburgers and French fries.
C
3
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of potatoes for the Farmer?
A)8 hours of labour.
B)2 hours of labour.
C)4 kg of meat.
D)1/4 kg of meat.

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of potatoes for the Farmer?
A)8 hours of labour.
B)2 hours of labour.
C)4 kg of meat.
D)1/4 kg of meat.
D
4
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pound of meat for the Farmer?
A)1/4 hour of labour.
B)4 hours of labour.
C)4 kg of potatoes.
D)1/4 kg of potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pound of meat for the Farmer?
A)1/4 hour of labour.
B)4 hours of labour.
C)4 kg of potatoes.
D)1/4 kg of potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If there is trade, which of the following is most likely?
A)A country is worse off because it becomes dependent on other countries.
B)A country will produce a greater variety of goods and services to trade.
C)A country's consumption possibilities frontier can be outside its production possibilities frontier.
D)A country will experience a lower unemployment rate.
A)A country is worse off because it becomes dependent on other countries.
B)A country will produce a greater variety of goods and services to trade.
C)A country's consumption possibilities frontier can be outside its production possibilities frontier.
D)A country will experience a lower unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If labour in Mexico is less productive than labour in the United States in all areas of production, which of the following is correct?
A)Neither nation can benefit from trade.
B)Mexico can benefit from trade but the United States cannot.
C)Mexico will not have a comparative advantage in any good.
D)Both nations can benefit from trade.
A)Neither nation can benefit from trade.
B)Mexico can benefit from trade but the United States cannot.
C)Mexico will not have a comparative advantage in any good.
D)Both nations can benefit from trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the difference between production possibilities frontiers that are bowed out and those that are linear?
A)Bowed out production possibilities frontiers illustrate tradeoffs where linear production possibilities frontiers do not.
B)Bowed out production possibilities frontiers show increasing opportunity cost where linear ones show constant opportunity cost.
C)Bowed out production possibilities frontiers are the result of perfectly shiftable resources where linear production possibilities frontiers are not.
D)Linear production possibilities frontiers illustrate real world conditions more than bowed out production possibilities frontiers.
A)Bowed out production possibilities frontiers illustrate tradeoffs where linear production possibilities frontiers do not.
B)Bowed out production possibilities frontiers show increasing opportunity cost where linear ones show constant opportunity cost.
C)Bowed out production possibilities frontiers are the result of perfectly shiftable resources where linear production possibilities frontiers are not.
D)Linear production possibilities frontiers illustrate real world conditions more than bowed out production possibilities frontiers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is NOT correct?
A)Trade allows for specialization.
B)Trade is good for nations.
C)Trade is based on absolute advantage.
D)Trade allows individuals to consume outside of their individual production possibilities curve.
A)Trade allows for specialization.
B)Trade is good for nations.
C)Trade is based on absolute advantage.
D)Trade allows individuals to consume outside of their individual production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table 3-2
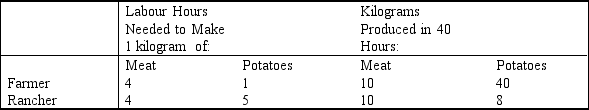
Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of meat for the Farmer?
A)1/4 hour of labour.
B)4 hours of labour.
C)4 kilograms of potatoes.
D)1/4 kilogram of potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of meat for the Farmer?
A)1/4 hour of labour.
B)4 hours of labour.
C)4 kilograms of potatoes.
D)1/4 kilogram of potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When will a production possibilities frontier be linear and not bowed out?
A)If no tradeoffs exist.
B)If the tradeoff between the two goods is always at a constant rate.
C)If unemployment is zero.
D)If resources are allocated efficiently.
A)If no tradeoffs exist.
B)If the tradeoff between the two goods is always at a constant rate.
C)If unemployment is zero.
D)If resources are allocated efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When can a country's consumption possibilities frontier be outside its production possibilities frontier?
A)If additional resources become available.
B)If there is an increase in the level of technology.
C)If the country engages in trade.
D)If resources are shiftable.
A)If additional resources become available.
B)If there is an increase in the level of technology.
C)If the country engages in trade.
D)If resources are shiftable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of meat for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 kg of potatoes.
D)4/5 kg of potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of meat for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 kg of potatoes.
D)4/5 kg of potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in neither good, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in both goods, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
D)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in meat.

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in neither good, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in both goods, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
D)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in neither good.
D)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in neither good.
D)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the best reason for people to provide you with goods and services?
A)They are acting out of generosity.
B)They are acting because they like you.
C)They do so because they get something in return.
D)They are required to do so by government.
A)They are acting out of generosity.
B)They are acting because they like you.
C)They do so because they get something in return.
D)They are required to do so by government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Regan grows flowers and makes vases. Jayson also grows flowers and makes vases, but Regan is better at producing both. In this case, who could benefit from trade?
A)Both Jayson and Regan.
B)Jayson, but not Regan.
C)Regan, but not Jayson.
D)Neither Jayson nor Regan.
A)Both Jayson and Regan.
B)Jayson, but not Regan.
C)Regan, but not Jayson.
D)Neither Jayson nor Regan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of potatoes for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 kg of meat.
D)4/5 kg of meat.

Refer to Table 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of potatoes for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 kg of meat.
D)4/5 kg of meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.

Refer to Table 3-1. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Table 3-1

Refer to Table 3-1. How could the Farmer and Rancher both benefit?
A)By the Farmer specializing in meat and the Rancher specializing in potatoes.
B)By the Farmer specializing in potatoes and the Rancher specializing in meat.
C)By the Farmer specializing in neither good and the Rancher specializing in both goods.
D)They cannot benefit by specialization and trade.

Refer to Table 3-1. How could the Farmer and Rancher both benefit?
A)By the Farmer specializing in meat and the Rancher specializing in potatoes.
B)By the Farmer specializing in potatoes and the Rancher specializing in meat.
C)By the Farmer specializing in neither good and the Rancher specializing in both goods.
D)They cannot benefit by specialization and trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If there is no trade, which of the following is most likely?
A)A country is better off because it will become self-sufficient.
B)A country's production possibilities frontier is also its consumption possibilities frontier.
C)A country can still benefit from international specialization.
D)More product variety is available in a country.
A)A country is better off because it will become self-sufficient.
B)A country's production possibilities frontier is also its consumption possibilities frontier.
C)A country can still benefit from international specialization.
D)More product variety is available in a country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
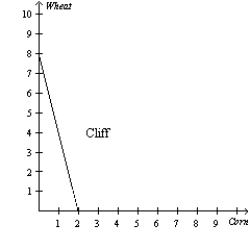
Figure 3-1 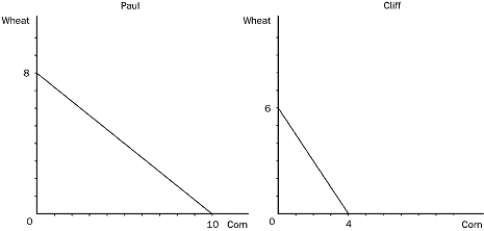
Refer to Figure 3-1. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and each was dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product they have a comparative advantage in. What would happen to the total production of corn?
A)Increase by 1 bushel.
B)Increase by 3 bushels.
C)Increase by 5 bushels.
D)Decrease by 2 bushels.

Refer to Figure 3-1. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and each was dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product they have a comparative advantage in. What would happen to the total production of corn?
A)Increase by 1 bushel.
B)Increase by 3 bushels.
C)Increase by 5 bushels.
D)Decrease by 2 bushels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-62. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in potatoes.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Refer to Table 3-62. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in potatoes.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 3-1 
Refer to Figure 3-1. If Paul divides his time equally between corn and wheat, what will he be able to produce?
A)2 bushels of wheat and 2 bushels of corn.
B)3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
C)4 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.
D)4 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn.

Refer to Figure 3-1. If Paul divides his time equally between corn and wheat, what will he be able to produce?
A)2 bushels of wheat and 2 bushels of corn.
B)3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
C)4 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.
D)4 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of potatoes for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 pounds of meat.
D)4/5 pound of meat.

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of potatoes for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 pounds of meat.
D)4/5 pound of meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 3-1 
Refer to Figure 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of wheat for Cliff?
A)1/3 bushel of corn.
B)2/3 bushel of corn.
C)1 bushel of corn.
D)3/2 bushels of corn.

Refer to Figure 3-1. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of wheat for Cliff?
A)1/3 bushel of corn.
B)2/3 bushel of corn.
C)1 bushel of corn.
D)3/2 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 3-2 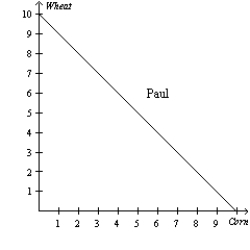
Refer to Figure 3-2. Assume that both Paul and Cliff divide their time equally between the production of corn and wheat, and they do not trade. If they were the only producers of corn and wheat, what would the total production of wheat and corn be?
A)7 bushels of wheat and 8 bushels of corn.
B)8 bushels of wheat and 7 bushels of corn.
C)9 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn.
D)18 bushels of wheat and 12 bushels of corn.


Refer to Figure 3-2. Assume that both Paul and Cliff divide their time equally between the production of corn and wheat, and they do not trade. If they were the only producers of corn and wheat, what would the total production of wheat and corn be?
A)7 bushels of wheat and 8 bushels of corn.
B)8 bushels of wheat and 7 bushels of corn.
C)9 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn.
D)18 bushels of wheat and 12 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in neither good, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in both goods, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
D)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in meat.

Refer to Table 3-2. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in neither good, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in both goods.
B)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in both goods, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
D)The Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. How could the Farmer and Rancher both benefit?
A)By the Farmer specializing in meat and the Rancher specializing in potatoes.
B)By the Farmer specializing in potatoes and the Rancher specializing in meat.
C)By the Farmer specializing in neither good and the Rancher specializing in both goods.
D)They cannot benefit by specialization and trade.

Refer to Table 3-2. How could the Farmer and Rancher both benefit?
A)By the Farmer specializing in meat and the Rancher specializing in potatoes.
B)By the Farmer specializing in potatoes and the Rancher specializing in meat.
C)By the Farmer specializing in neither good and the Rancher specializing in both goods.
D)They cannot benefit by specialization and trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 3-2 

Refer to Figure 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of wheat for Cliff?
A)1/4 bushel of corn.
B)1/2 bushel of corn.
C)1 bushel of corn.
D)4 bushels of corn.


Refer to Figure 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 bushel of wheat for Cliff?
A)1/4 bushel of corn.
B)1/2 bushel of corn.
C)1 bushel of corn.
D)4 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 3-1 
Refer to Figure 3-1. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has an absolute advantage in wheat and Cliff has an absolute advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has an absolute advantage in wheat and Paul has an absolute advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.

Refer to Figure 3-1. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has an absolute advantage in wheat and Cliff has an absolute advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has an absolute advantage in wheat and Paul has an absolute advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 3-2 

Refer to Figure 3-2. If Paul divides his time equally between corn and wheat, what will he be able to produce?
A)4 bushels of wheat and 1 bushel of corn.
B)4 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.
C)5 bushels of wheat and 4 bushels of corn.
D)5 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.


Refer to Figure 3-2. If Paul divides his time equally between corn and wheat, what will he be able to produce?
A)4 bushels of wheat and 1 bushel of corn.
B)4 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.
C)5 bushels of wheat and 4 bushels of corn.
D)5 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in neither good.
D)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-2. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in both goods, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in neither good.
D)The Rancher has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Farmer has a comparative advantage in potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of meat for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 kilograms of potatoes.
D)4/5 kilogram of potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of meat for the Rancher?
A)4 hours of labour.
B)5 hours of labour.
C)5/4 kilograms of potatoes.
D)4/5 kilogram of potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 3-2 

Refer to Figure 3-2. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and both were dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product for which they have a comparative advantage. What would happen to the production of corn?
A)Increase by 1 bushel.
B)Increase by 2 bushels.
C)Increase by 3 bushels.
D)Increase by 4 bushels.


Refer to Figure 3-2. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and both were dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product for which they have a comparative advantage. What would happen to the production of corn?
A)Increase by 1 bushel.
B)Increase by 2 bushels.
C)Increase by 3 bushels.
D)Increase by 4 bushels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 3-1 
Refer to Figure 3-1. Assume that both Paul and Cliff divide their time equally between the production of corn and wheat, and they do not trade. If they were the only producers of corn and wheat, what would the total production of wheat and corn be?
A)8 bushels of wheat and 7 bushels of corn.
B)7 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn.
C)6 bushels of wheat and 8 bushels of corn.
D)7 bushels of wheat and 7 bushels of corn.

Refer to Figure 3-1. Assume that both Paul and Cliff divide their time equally between the production of corn and wheat, and they do not trade. If they were the only producers of corn and wheat, what would the total production of wheat and corn be?
A)8 bushels of wheat and 7 bushels of corn.
B)7 bushels of wheat and 6 bushels of corn.
C)6 bushels of wheat and 8 bushels of corn.
D)7 bushels of wheat and 7 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of potatoes for the Farmer?
A)8 hours of labour.
B)2 hours of labour.
C)4 kilograms of meat.
D)1/4 kilogram of meat.

Refer to Table 3-2. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kilogram of potatoes for the Farmer?
A)8 hours of labour.
B)2 hours of labour.
C)4 kilograms of meat.
D)1/4 kilogram of meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 3-1 
Refer to Figure 3-1. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has a comparative advantage in wheat and Cliff has a comparative advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has a comparative advantage in wheat and Paul has a comparative advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.

Refer to Figure 3-1. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has a comparative advantage in wheat and Cliff has a comparative advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has a comparative advantage in wheat and Paul has a comparative advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Table 3-2

Refer to Table 3-2. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.

Refer to Table 3-2. Which of the following is correct?
A)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
B)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in meat, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.
C)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in potatoes, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in meat.
D)The Farmer has an absolute advantage in neither good, and the Rancher has a comparative advantage in potatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 3-1 
Refer to Figure 3-1. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and each was dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product they have a comparative advantage in and trade 3 bushels of wheat for 3 bushels of corn. What would Cliff now be able to consume?
A)4 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
B)3 bushels of wheat and 4 bushels of corn.
C)3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
D)2 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.

Refer to Figure 3-1. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and each was dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product they have a comparative advantage in and trade 3 bushels of wheat for 3 bushels of corn. What would Cliff now be able to consume?
A)4 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
B)3 bushels of wheat and 4 bushels of corn.
C)3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
D)2 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 3-2 

Refer to Figure 3-2. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and both were dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product for which they have a comparative advantage and trade 3 bushels of wheat for 3 bushels of corn. What would Cliff now be able to consume?
A)5 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
B)4 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
C)3 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.
D)3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.


Refer to Figure 3-2. Assume that Cliff and Paul were both producing wheat and corn, and both were dividing their time equally between the two. Then they decide to specialize in the product for which they have a comparative advantage and trade 3 bushels of wheat for 3 bushels of corn. What would Cliff now be able to consume?
A)5 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
B)4 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.
C)3 bushels of wheat and 5 bushels of corn.
D)3 bushels of wheat and 3 bushels of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.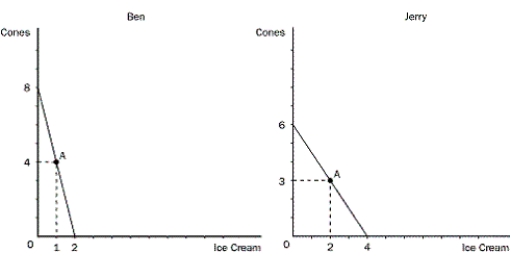
Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in cones and Jerry has an absolute advantage in ice cream.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in neither good.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in cones.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in cones and Jerry has an absolute advantage in ice cream.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in neither good.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in cones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 pound of ice cream?
A)3/2 kg of cones.
B)1/3 kg of cones.
C)1 kg of cones.
D)2 kg of cones.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 pound of ice cream?
A)3/2 kg of cones.
B)1/3 kg of cones.
C)1 kg of cones.
D)2 kg of cones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 3-4 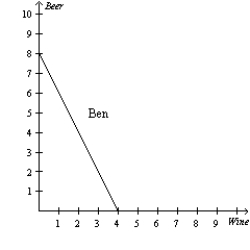
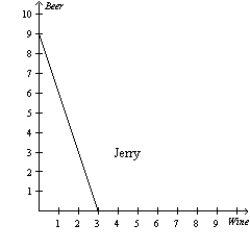
Refer to Figure 3-4. For Ben, what is the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of wine?
A)1/4 bottle of beer.
B)1/2 bottle of beer.
C)2 bottles of beer.
D)4 bottles of beer.


Refer to Figure 3-4. For Ben, what is the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of wine?
A)1/4 bottle of beer.
B)1/2 bottle of beer.
C)2 bottles of beer.
D)4 bottles of beer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in cones and Jerry has a comparative advantage in ice cream.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in both goods and Jerry has a comparative advantage in cones.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in ice cream and Jerry has a comparative advantage in cones.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in neither good and Jerry has a comparative advantage in ice cream.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in cones and Jerry has a comparative advantage in ice cream.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in both goods and Jerry has a comparative advantage in cones.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in ice cream and Jerry has a comparative advantage in cones.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in neither good and Jerry has a comparative advantage in ice cream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in neither good.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in beer, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in wine.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in beer.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in neither good, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.


Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in neither good.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in beer, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in wine.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in beer.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in neither good, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of wine?
A)1 bottle of beer.
B)1/2 bottle of beer.
C)1/3 bottle of beer.
D)3 bottles of beer.


Refer to Figure 3-4. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of wine?
A)1 bottle of beer.
B)1/2 bottle of beer.
C)1/3 bottle of beer.
D)3 bottles of beer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 3-2 

Refer to Figure 3-2. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has an absolute advantage in wheat and Cliff has an absolute advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has an absolute advantage in wheat and Paul has an absolute advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.


Refer to Figure 3-2. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has an absolute advantage in wheat and Cliff has an absolute advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has an absolute advantage in wheat and Paul has an absolute advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has an absolute advantage in both wheat and corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. For Ben, what is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of ice cream?
A)1/4 kg of cones.
B)1/2 kg of cones.
C)2 kg of cones.
D)4 kg of cones.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. For Ben, what is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of ice cream?
A)1/4 kg of cones.
B)1/2 kg of cones.
C)2 kg of cones.
D)4 kg of cones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. For Ben, what is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of cones?
A)2 kg of ice cream.
B)1/2 kg of ice cream.
C)4 kg of ice cream.
D)1/4 kg of ice cream.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. For Ben, what is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of cones?
A)2 kg of ice cream.
B)1/2 kg of ice cream.
C)4 kg of ice cream.
D)1/4 kg of ice cream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of cones?
A)2/3 kg of ice cream.
B)3 kg of ice cream.
C)1 kg of ice cream.
D)2 kg of ice cream.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 kg of cones?
A)2/3 kg of ice cream.
B)3 kg of ice cream.
C)1 kg of ice cream.
D)2 kg of ice cream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in cones and Jerry has a comparative advantage in ice cream.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has a comparative advantage in cones.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in neither good and Jerry has a comparative advantage in both goods.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in both goods and Jerry has a comparative advantage in neither good.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in cones and Jerry has a comparative advantage in ice cream.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in ice cream and Jerry has a comparative advantage in cones.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in neither good and Jerry has a comparative advantage in both goods.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in both goods and Jerry has a comparative advantage in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in cones.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in cones and Jerry has an absolute advantage in ice cream.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in neither good and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in both goods and Jerry has an absolute advantage in neither good.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in ice cream and Jerry has an absolute advantage in cones.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in cones and Jerry has an absolute advantage in ice cream.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in neither good and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in both goods and Jerry has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. Ben and Jerry were currently both producing at point A on their production possibilities frontier and then Ben decided he would be willing to trade 4 pounds of cones to get 2 pounds of ice cream from Jerry. If both decided to specialize in what they had a comparative advantage in and trade, what would be the gains from trade?
A)1 pound of cones for Ben and 1 pound of ice cream for Jerry.
B)1 pound of ice cream for Ben and 1 pound of cones for Jerry.
C)2 pounds of ice cream for Ben and 2 pounds of cones for Jerry.
D)2 pounds of ice cream for Ben and 1 pound of cones for Jerry.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. Ben and Jerry were currently both producing at point A on their production possibilities frontier and then Ben decided he would be willing to trade 4 pounds of cones to get 2 pounds of ice cream from Jerry. If both decided to specialize in what they had a comparative advantage in and trade, what would be the gains from trade?
A)1 pound of cones for Ben and 1 pound of ice cream for Jerry.
B)1 pound of ice cream for Ben and 1 pound of cones for Jerry.
C)2 pounds of ice cream for Ben and 2 pounds of cones for Jerry.
D)2 pounds of ice cream for Ben and 1 pound of cones for Jerry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in beer, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in beer, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in wine.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in beer.


Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in beer, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in both goods.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in beer, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in wine.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in wine, and Jerry has an absolute advantage in beer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. For Ben, the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of beer is
A)1/2 bottle of wine.
B)1/4 bottle of wine.
C)2 bottles of wine.
D)4 bottles of wine.


Refer to Figure 3-4. For Ben, the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of beer is
A)1/2 bottle of wine.
B)1/4 bottle of wine.
C)2 bottles of wine.
D)4 bottles of wine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in neither good.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in both goods, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in beer.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in beer.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in beer, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in wine.


Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in neither good.
B)Ben has an absolute advantage in both goods, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in beer.
C)Ben has an absolute advantage in wine, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in beer.
D)Ben has an absolute advantage in beer, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in wine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 3-3
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.
Refer to Figure 3-3. Suppose that Ben and Jerry have both decided to produce at point A on their production possibilities frontiers. What do we know?
A)This is not an efficient combination for either Ben or Jerry.
B)Ben and Jerry are both allocating 1/2 their time to the production of each good.
C)no other production point is as efficient for both Ben and Jerry to produce as point A.
D)Both should always attempt to produce an equal number of cones and ice cream.
Ice cream is measured in kilograms.

Refer to Figure 3-3. Suppose that Ben and Jerry have both decided to produce at point A on their production possibilities frontiers. What do we know?
A)This is not an efficient combination for either Ben or Jerry.
B)Ben and Jerry are both allocating 1/2 their time to the production of each good.
C)no other production point is as efficient for both Ben and Jerry to produce as point A.
D)Both should always attempt to produce an equal number of cones and ice cream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in beer, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in wine.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in wine, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in beer.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in neither good, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in wine.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in both goods, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in neither.


Refer to Figure 3-4. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ben has a comparative advantage in beer, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in wine.
B)Ben has a comparative advantage in wine, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in beer.
C)Ben has a comparative advantage in neither good, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in wine.
D)Ben has a comparative advantage in both goods, and Jerry has a comparative advantage in neither.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 3-2 

Refer to Figure 3-2. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has an absolute advantage in wheat and Cliff has a comparative advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has a comparative advantage in wheat and Paul has a comparative advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.


Refer to Figure 3-2. Which of the following is true for Cliff and Paul?
A)Paul has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.
B)Paul has an absolute advantage in wheat and Cliff has a comparative advantage in corn.
C)Cliff has a comparative advantage in wheat and Paul has a comparative advantage in corn.
D)Cliff has a comparative advantage in both wheat and corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of beer?
A)1 bottle of wine.
B)1/2 bottle of wine.
C)1/3 bottle of wine.
D)3 bottles of wine.


Refer to Figure 3-4. For Jerry, what is the opportunity cost of 1 bottle of beer?
A)1 bottle of wine.
B)1/2 bottle of wine.
C)1/3 bottle of wine.
D)3 bottles of wine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Table 3-3
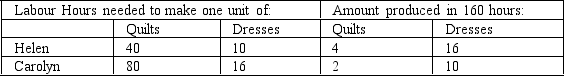
Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 quilt for Carolyn?
A)2 dresses.
B)3 dresses.
C)4 dresses.
D)5 dresses.

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 quilt for Carolyn?
A)2 dresses.
B)3 dresses.
C)4 dresses.
D)5 dresses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has a comparative advantage in dresses and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in quilts.
B)Helen has a comparative advantage in quilts and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in dresses.
C)Helen has a comparative advantage in neither good and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in both goods.
D)Helen has a comparative advantage in both goods and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in neither good.

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has a comparative advantage in dresses and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in quilts.
B)Helen has a comparative advantage in quilts and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in dresses.
C)Helen has a comparative advantage in neither good and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in both goods.
D)Helen has a comparative advantage in both goods and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 3-5 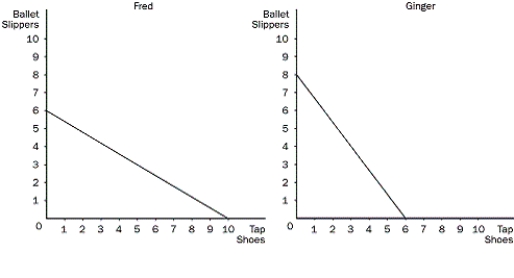
Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of tap shoes for Ginger?
A)1/4 pair of ballet slippers.
B)1/3 pair of ballet slippers.
C)3/4 pair of ballet slippers.
D)4/3 pairs of ballet slippers.

Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of tap shoes for Ginger?
A)1/4 pair of ballet slippers.
B)1/3 pair of ballet slippers.
C)3/4 pair of ballet slippers.
D)4/3 pairs of ballet slippers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 dress for Helen?
A)1 quilt.
B)1/2 quilt.
C)1/4 quilt.
D)4 quilts.

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 dress for Helen?
A)1 quilt.
B)1/2 quilt.
C)1/4 quilt.
D)4 quilts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ginger has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers and Fred has an absolute advantage in tap shoes.
B)Ginger has an absolute advantage in tap shoes and Fred has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers.
C)Ginger has an absolute advantage in neither good and Fred has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)Ginger has an absolute advantage in both goods and Fred has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Refer to Figure 3-5. Which of the following is correct?
A)Ginger has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers and Fred has an absolute advantage in tap shoes.
B)Ginger has an absolute advantage in tap shoes and Fred has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers.
C)Ginger has an absolute advantage in neither good and Fred has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)Ginger has an absolute advantage in both goods and Fred has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. How could Helen and Carolyn both benefit?
A)By Helen specializing in dresses and Carolyn specializing in quilts.
B)By Helen specializing in neither good and Carolyn specializing in both goods.
C)By Helen specializing in quilts and Carolyn specializing in dresses.
D)By Helen specializing in both goods and Carolyn specializing in neither good.

Refer to Table 3-3. How could Helen and Carolyn both benefit?
A)By Helen specializing in dresses and Carolyn specializing in quilts.
B)By Helen specializing in neither good and Carolyn specializing in both goods.
C)By Helen specializing in quilts and Carolyn specializing in dresses.
D)By Helen specializing in both goods and Carolyn specializing in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has a comparative advantage in quilts and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in neither good.
B)Helen has a comparative advantage in dresses and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in quilts.
C)Helen has a comparative advantage in quilts and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in dresses.
D)Helen has a comparative advantage in dresses and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in both goods.

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has a comparative advantage in quilts and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in neither good.
B)Helen has a comparative advantage in dresses and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in quilts.
C)Helen has a comparative advantage in quilts and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in dresses.
D)Helen has a comparative advantage in dresses and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Figure 3-4 

Refer to Figure 3-4. Suppose Ben and Jerry both spend half their time producing beer and half their time producing wine. What do we know?
A)This is not an efficient allocation of time for either Ben or Jerry.
B)Ben will produce 4 bottles of beer and 2 bottles of wine.
C)Jerry will produce 1.5 bottles of beer and 4.5 bottles of wine.
D)Ben will produce 8 bottles of beer and 4 bottles of wine.


Refer to Figure 3-4. Suppose Ben and Jerry both spend half their time producing beer and half their time producing wine. What do we know?
A)This is not an efficient allocation of time for either Ben or Jerry.
B)Ben will produce 4 bottles of beer and 2 bottles of wine.
C)Jerry will produce 1.5 bottles of beer and 4.5 bottles of wine.
D)Ben will produce 8 bottles of beer and 4 bottles of wine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has an absolute advantage in dresses and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in quilts.
B)Helen has an absolute advantage in both goods and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in dresses.
C)Helen has an absolute advantage in quilts and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in dresses.
D)Helen has an absolute advantage in both goods and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in quilts.

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has an absolute advantage in dresses and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in quilts.
B)Helen has an absolute advantage in both goods and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in dresses.
C)Helen has an absolute advantage in quilts and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in dresses.
D)Helen has an absolute advantage in both goods and Carolyn has a comparative advantage in quilts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. Ginger should specialize in
A)Ginger should specialize in tap shoes and Fred should specialize in ballet slippers.
B)Ginger should specialize in both goods and Fred should specialize in neither good.
C)Ginger should specialize in ballet slippers and Fred should specialize in tap shoes.
D)Ginger should specialize in neither good and Fred should specialize in both goods.

Refer to Figure 3-5. Ginger should specialize in
A)Ginger should specialize in tap shoes and Fred should specialize in ballet slippers.
B)Ginger should specialize in both goods and Fred should specialize in neither good.
C)Ginger should specialize in ballet slippers and Fred should specialize in tap shoes.
D)Ginger should specialize in neither good and Fred should specialize in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. If Fred and Ginger devote 1/2 of their time (20 hours) to the production of each good, what would the total production be?
A)7 ballet slippers and 8 tap shoes.
B)8 ballet slippers and 8 tap shoes.
C)9 ballet slippers and 6 tap shoes.
D)10 ballet slippers and 8 tap shoes.

Refer to Figure 3-5. If Fred and Ginger devote 1/2 of their time (20 hours) to the production of each good, what would the total production be?
A)7 ballet slippers and 8 tap shoes.
B)8 ballet slippers and 8 tap shoes.
C)9 ballet slippers and 6 tap shoes.
D)10 ballet slippers and 8 tap shoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of tap shoes for Fred?
A)1/3 pair of ballet slippers.
B)1/5 pair of ballet slippers.
C)3/5 pair of ballet slippers.
D)5/3 pairs of ballet slippers.

Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of tap shoes for Fred?
A)1/3 pair of ballet slippers.
B)1/5 pair of ballet slippers.
C)3/5 pair of ballet slippers.
D)5/3 pairs of ballet slippers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 quilt for Helen?
A)2 dresses.
B)3 dresses.
C)4 dresses.
D)5 dresses.

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 quilt for Helen?
A)2 dresses.
B)3 dresses.
C)4 dresses.
D)5 dresses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of ballet slippers for Ginger?
A)1/4 pair of tap shoes.
B)1/3 pair of tap shoes.
C)3/4 pair of tap shoes.
D)4/3 pairs of tap shoes.

Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of ballet slippers for Ginger?
A)1/4 pair of tap shoes.
B)1/3 pair of tap shoes.
C)3/4 pair of tap shoes.
D)4/3 pairs of tap shoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. Ginger has an absolute advantage in
A)Ginger has an absolute advantage in tap shoes and Fred has a comparative advantage in ballet slippers.
B)Ginger has an absolute advantage in both goods and Fred has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)Ginger has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers and Fred has a comparative advantage in tap shoes.
D)Ginger has an absolute advantage in neither good and Fred has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Refer to Figure 3-5. Ginger has an absolute advantage in
A)Ginger has an absolute advantage in tap shoes and Fred has a comparative advantage in ballet slippers.
B)Ginger has an absolute advantage in both goods and Fred has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)Ginger has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers and Fred has a comparative advantage in tap shoes.
D)Ginger has an absolute advantage in neither good and Fred has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has an absolute advantage in dresses and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in quilts.
B)Helen has an absolute advantage in quilts and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in dresses.
C)Helen has an absolute advantage in neither good and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)Helen has an absolute advantage in both goods and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Refer to Table 3-3. Which of the following is correct?
A)Helen has an absolute advantage in dresses and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in quilts.
B)Helen has an absolute advantage in quilts and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in dresses.
C)Helen has an absolute advantage in neither good and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in both goods.
D)Helen has an absolute advantage in both goods and Carolyn has an absolute advantage in neither good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Table 3-3

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 dress for Carolyn?
A)5 quilts.
B)1 quilt.
C)1/5 quilt.
D)4 quilts.

Refer to Table 3-3. What is the opportunity cost of 1 dress for Carolyn?
A)5 quilts.
B)1 quilt.
C)1/5 quilt.
D)4 quilts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of ballet slippers for Fred?
A)1/3 pair of tap shoes.
B)1/5 pair of tap shoes.
C)3/5 pair of tap shoes.
D)5/3 pairs of tap shoes.

Refer to Figure 3-5. What is the opportunity cost of 1 pair of ballet slippers for Fred?
A)1/3 pair of tap shoes.
B)1/5 pair of tap shoes.
C)3/5 pair of tap shoes.
D)5/3 pairs of tap shoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. What should Fred produce?
A)Only tap shoes.
B)Only ballet slippers.
C)Both ballet slippers and tap shoes.
D)Neither ballet slippers nor tap shoes.

Refer to Figure 3-5. What should Fred produce?
A)Only tap shoes.
B)Only ballet slippers.
C)Both ballet slippers and tap shoes.
D)Neither ballet slippers nor tap shoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Figure 3-5 
Refer to Figure 3-5. Ginger has a comparative advantage in
A)Ginger has a comparative advantage in tap shoes and Fred has a comparative advantage in ballet slippers.
B)Ginger has a comparative advantage in both goods and Fred has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)Ginger has a comparative advantage in ballet slippers and Fred has a comparative advantage in tap shoes.
D)Ginger has a comparative advantage in neither good and Fred has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Refer to Figure 3-5. Ginger has a comparative advantage in
A)Ginger has a comparative advantage in tap shoes and Fred has a comparative advantage in ballet slippers.
B)Ginger has a comparative advantage in both goods and Fred has a comparative advantage in neither good.
C)Ginger has a comparative advantage in ballet slippers and Fred has a comparative advantage in tap shoes.
D)Ginger has a comparative advantage in neither good and Fred has a comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



