Deck 1: Economic Models
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Economic Models
1
For the function 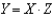 ,the equation
,the equation 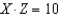 represents
represents
A) the X-intercept.
B) the Y-intercept.
C) a contour line.
D) a tangent line.
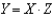 ,the equation
,the equation 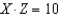 represents
representsA) the X-intercept.
B) the Y-intercept.
C) a contour line.
D) a tangent line.
C
2
The Y-intercept of Y = 3X + 8 is
A) 3/8.
B) 3.
C) 8.
D) −8/3.
A) 3/8.
B) 3.
C) 8.
D) −8/3.
C
3
In the equation Y = 13X + 38 where Y is a function of X
A) Y is the independent variable.
B) 38 is a variable.
C) the slope of the line is 38.
D) None of these.
A) Y is the independent variable.
B) 38 is a variable.
C) the slope of the line is 38.
D) None of these.
D
4
If Y = X2 + Z2,the contour lines
A) are concentric circles.
B) are parabolas.
C) are hyperbolas.
D) intersect whenever either X or Z is zero.
A) are concentric circles.
B) are parabolas.
C) are hyperbolas.
D) intersect whenever either X or Z is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Given Y = f(X,Z),which of the following are necessarily true?
A) Y is a linear function.
B) X, Z are dependent variables.
C) A contour line of this function would keep Y constant.
D) An increase in X would increase Y.
A) Y is a linear function.
B) X, Z are dependent variables.
C) A contour line of this function would keep Y constant.
D) An increase in X would increase Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A major problem that may occur with models that predict the values of economic variables in the future is that
A) researchers are pessimistic about the future.
B) the model may fail to acknowledge that economic actors will change their behavior in response to changing situations.
C) the model may make predictions that conflict with widely held opinions.
D) no one cares about these predictions.
A) researchers are pessimistic about the future.
B) the model may fail to acknowledge that economic actors will change their behavior in response to changing situations.
C) the model may make predictions that conflict with widely held opinions.
D) no one cares about these predictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The slope of a nonlinear function at some particular point
A) is the slope of the straight line that is tangent to the function at that point.
B) is the slope of the straight line connecting the origin and the point.
C) cannot be determined.
D) is constant for the entire function.
A) is the slope of the straight line that is tangent to the function at that point.
B) is the slope of the straight line connecting the origin and the point.
C) cannot be determined.
D) is constant for the entire function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Graphically,the solution to a system of two independent linear equations is usually
A) the average of the slopes.
B) the average of the intercepts.
C) a single point.
D) None of these.
A) the average of the slopes.
B) the average of the intercepts.
C) a single point.
D) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Positive economic analysis
A) involves the study of firms with positive profits.
B) involves how resources are actually used in an economy.
C) involves judgments on how resources should be used in an economy.
D) is usually thought to be a waste of time.
A) involves the study of firms with positive profits.
B) involves how resources are actually used in an economy.
C) involves judgments on how resources should be used in an economy.
D) is usually thought to be a waste of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Normative economic analysis
A) involves the study of what comprises a normal firm.
B) involves how resources are actually used in an economy.
C) involves judgments on how resources should be used in an economy.
D) is usually thought to be a waste of time.
A) involves the study of what comprises a normal firm.
B) involves how resources are actually used in an economy.
C) involves judgments on how resources should be used in an economy.
D) is usually thought to be a waste of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If society is producing a combination of goods on its production possibilities frontier
A) it must be employing all available resources.
B) it must be growing.
C) it is using all the available natural resources but may not be using all available labor resources.
D) Both a and b.
A) it must be employing all available resources.
B) it must be growing.
C) it is using all the available natural resources but may not be using all available labor resources.
D) Both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The solution to the simultaneous equations 5X - Y = 10 and 10X + Y = 35 is
A) X = 15, Y = 0.
B) X = 3, Y = 5.
C) X = 5, Y = 3.
D) None of these.
A) X = 15, Y = 0.
B) X = 3, Y = 5.
C) X = 5, Y = 3.
D) None of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The X-intercept of Y = 4X + 12 is
A) -3.
B) 3.
C) −1/3.
D) 12.
A) -3.
B) 3.
C) −1/3.
D) 12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The problem of scarcity
A) arises only in poor countries.
B) exists because the price of goods is too high.
C) exists because of limited resources.
D) will eventually be solved by better planning.
A) arises only in poor countries.
B) exists because the price of goods is too high.
C) exists because of limited resources.
D) will eventually be solved by better planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The slope of the production possibility frontier shows
A) how inputs must be changed to keep them fully employed.
B) the technically efficient combinations of the two goods.
C) how demanders are willing to trade one good for another.
D) the opportunity cost of one good in terms of the other.
A) how inputs must be changed to keep them fully employed.
B) the technically efficient combinations of the two goods.
C) how demanders are willing to trade one good for another.
D) the opportunity cost of one good in terms of the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the prevailing price of shirts is $10 and at this price demanders demand 100 shirts while suppliers are willing to supply 110 shirts,there is a(n)
A) shortage at the $10 price.
B) surplus at the $10 price.
C) equilibrium in this market.
D) shortage if price were to rise above $10.
A) shortage at the $10 price.
B) surplus at the $10 price.
C) equilibrium in this market.
D) shortage if price were to rise above $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the Y-intercept of a linear function increases while the slope remains unchanged
A) the graph must shift down.
B) the graph must rotate to the left about the X intercept.
C) the graph must shift up.
D) the graph remains unchanged.
A) the graph must shift down.
B) the graph must rotate to the left about the X intercept.
C) the graph must shift up.
D) the graph remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
For the equation 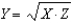 the point X = 20,Z = 5
the point X = 20,Z = 5
A) yields a value of Y = 10.
B) lies below the contour line that includes the point X = 15, Z = 7.
C) lies on the same contour line as the point X = 12, Z = 6.
D) Both a and b.
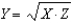 the point X = 20,Z = 5
the point X = 20,Z = 5A) yields a value of Y = 10.
B) lies below the contour line that includes the point X = 15, Z = 7.
C) lies on the same contour line as the point X = 12, Z = 6.
D) Both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the slope of a linear function changes with no change in the Y-intercept
A) the graph shifts either up or down.
B) the graph remains unchanged.
C) the graph rotates about its X-intercept.
D) the graph rotates about its Y-intercept.
A) the graph shifts either up or down.
B) the graph remains unchanged.
C) the graph rotates about its X-intercept.
D) the graph rotates about its Y-intercept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For the equation Y = X2 + Z2,which of the following points lie on the Y = 25 contour line?
A) X = 2, Z = 4.
B) X = 3. Z = 5.
C) X = 4, Z = 3.
D) Both a and c.
A) X = 2, Z = 4.
B) X = 3. Z = 5.
C) X = 4, Z = 3.
D) Both a and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 4X2 + Y2 = 16 then the point X = 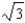 ; Y = 2 is
; Y = 2 is
A) outside the production possibilities frontier
B) on the production possibilities frontier
C) inside the production possibilities frontier
D) in the wrong quadrant to be on the graph
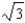 ; Y = 2 is
; Y = 2 isA) outside the production possibilities frontier
B) on the production possibilities frontier
C) inside the production possibilities frontier
D) in the wrong quadrant to be on the graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose a production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 9X2 + Y2 = 81 what is the opportunity cost of going from 2 units of X to 3 units of X (in terms of units of Y)?
A)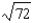
B)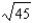
C) 1
D) 0
A)
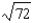
B)
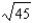
C) 1
D) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Let QD = -5P + 54 and QS = P - 6.Equilibrium can be found at
A) Q = 4; P = 10
B) Q = 6; P = 10
C) P = 6; Q = 0
D) Q =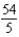 ; P = 2
; P = 2
A) Q = 4; P = 10
B) Q = 6; P = 10
C) P = 6; Q = 0
D) Q =
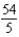 ; P = 2
; P = 2
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose you can write generic supply and demand curves such that QS = A + BP and QD = D + CP.If consumers demand less as price rises,C must be
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose a production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 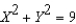 .The opportunity cost of going from 0 units of
.The opportunity cost of going from 0 units of 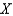 to 1 unit of
to 1 unit of 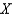 is approximately
is approximately
A) .17
B) .59
C) 2.24
D) 3
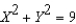 .The opportunity cost of going from 0 units of
.The opportunity cost of going from 0 units of 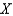 to 1 unit of
to 1 unit of 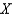 is approximately
is approximatelyA) .17
B) .59
C) 2.24
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose a production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 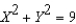 .The opportunity cost of going from 1 units of
.The opportunity cost of going from 1 units of 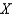 to 2 unit of
to 2 unit of 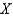 is approximately
is approximately
A) .17
B) .59
C) 2.24
D) 3
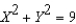 .The opportunity cost of going from 1 units of
.The opportunity cost of going from 1 units of 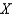 to 2 unit of
to 2 unit of 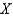 is approximately
is approximatelyA) .17
B) .59
C) 2.24
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose a production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 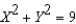 .The opportunity cost of going from 2 units of
.The opportunity cost of going from 2 units of 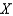 to 3 unit of
to 3 unit of 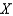 is approximately
is approximately
A) .17
B) .59
C) 2.24
D) 3
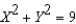 .The opportunity cost of going from 2 units of
.The opportunity cost of going from 2 units of 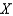 to 3 unit of
to 3 unit of 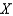 is approximately
is approximatelyA) .17
B) .59
C) 2.24
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose 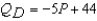 and
and 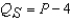 .The equilibrium price is
.The equilibrium price is
A) 7
B) 8
C) 9
D) 10
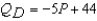 and
and 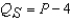 .The equilibrium price is
.The equilibrium price isA) 7
B) 8
C) 9
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose T = .02 .If taxes are regressive which of the following is true?
A) > 1
B) 0 < < 1
C) = 1
D) = 0
A) > 1
B) 0 < < 1
C) = 1
D) = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose you can write generic supply and demand curves such that QS = A + BP and QD = D + CP.If firms produce more when price rises,B must be
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose you can write generic supply and demand curves such that QS = A + BP and QD = D + CP.
A)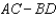
B)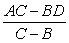
C)
D) B
A)
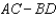
B)
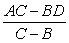
C)

D) B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose T = .02 .If taxes are proportional which of the following is true?
A) > 1
B) 0 < < 1
C) = 1
D) = 0
A) > 1
B) 0 < < 1
C) = 1
D) = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 4X2 + Y2 = 16 then the point X = 1; Y = 4 is
A) outside the production possibilities frontier
B) on the production possibilities frontier
C) inside the production possibilities frontier
D) in the wrong quadrant to be on the graph
A) outside the production possibilities frontier
B) on the production possibilities frontier
C) inside the production possibilities frontier
D) in the wrong quadrant to be on the graph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An increase in the technology used in the production of only one of the two goods in a society will
A) eliminate scarcity
B) move the production possibilities frontier out in all directions
C) move the production possibilities frontier in all directions
D) leave one corner of the production possibilities frontier fixed and swing out from the other
A) eliminate scarcity
B) move the production possibilities frontier out in all directions
C) move the production possibilities frontier in all directions
D) leave one corner of the production possibilities frontier fixed and swing out from the other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose a production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 9X2 + Y2 = 81 what is the opportunity cost of going from 1 unit of X to 2 units of X (in terms of units of Y)?
A) 45
B)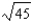
C)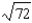 -
- 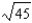
D) 1
A) 45
B)
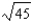
C)
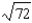 -
- 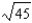
D) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose you can write generic supply and demand curves such that QS = A + BP and QD = D + CP.If price must reach a certain level before firms supply anything,,A must be
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose right (R)and left (L)shoes are only useful if produced in equal proportion and societal happiness is expressed as min(R,L).The contour lines would be
A) downward sloping lines
B) upward sloping lines
C) L-shaped
D) backward L-shaped
A) downward sloping lines
B) upward sloping lines
C) L-shaped
D) backward L-shaped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose you can write generic supply and demand curves such that QS = A + BP and QD = D + CP.Equilibrium price is given by
A)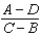
B)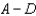
C)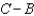
D)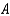
A)
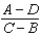
B)
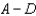
C)
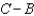
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose 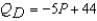 and
and 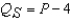 .The equilibrium quantity is
.The equilibrium quantity is
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
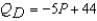 and
and 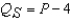 .The equilibrium quantity is
.The equilibrium quantity isA) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose T = .02S1 .If taxes are progressive which of the following is true?
A) > 1
B) 0 < < 1
C) = 1
D) = 0
A) > 1
B) 0 < < 1
C) = 1
D) = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Ricardian notion that of diminishing returns implies that
A) as more input is used more output will be made.
B) as more input is used less output will be made.
C) as more input is used the increase in output will increase.
D) as more input is used the increase in output will decrease.
A) as more input is used more output will be made.
B) as more input is used less output will be made.
C) as more input is used the increase in output will increase.
D) as more input is used the increase in output will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose you can write generic supply and demand curves such that QS = A + BP and QD = D + CP.In the usual supply-demand configuration,D must be
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0
A) positive
B) negative
C) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Economists typically use ____ analysis,whereas clergy members typically use ____ analysis.
A) positive; positive
B) normative; normative
C) positive; normative
D) normative; positive
A) positive; positive
B) normative; normative
C) positive; normative
D) normative; positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The underlying reason early economists believed a (short-run)supply curve would be upward sloping is because of
A) decreasing average costs
B) increasing average cost
C) decreasing marginal costs
D) increasing marginal costs
A) decreasing average costs
B) increasing average cost
C) decreasing marginal costs
D) increasing marginal costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



