Deck 3: Individual Demand Curves
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Individual Demand Curves
1
Suppose two goods coffee and creamer provide the consumer with utility but only if they are consumed in fixed proportions.An increase in the price of coffee will yield
A) a substitution effect and an income effect in opposite directions.
B) a substitution effect and an income effect in the same direction.
C) a substitution effect but no income effect.
D) an income effect but no substitution effect.
A) a substitution effect and an income effect in opposite directions.
B) a substitution effect and an income effect in the same direction.
C) a substitution effect but no income effect.
D) an income effect but no substitution effect.
D
2
With only two goods,if the income effect is in the opposite direction as the substitution effect but the income effect dominates then the good is
A) normal
B) inferior but not Giffen
C) Giffen
D) There is not enough information to answer.
A) normal
B) inferior but not Giffen
C) Giffen
D) There is not enough information to answer.
C
3
With only two goods,if the income effect is in the same direction as the substitution effect then the good is
A) normal
B) inferior but not Giffen
C) Giffen
D) There is not enough information to answer.
A) normal
B) inferior but not Giffen
C) Giffen
D) There is not enough information to answer.
A
4
If a good is normal and its price increases,
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a good is inferior and its price decreases,
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following functional forms for utility suggests the greatest substitution effect when starting at the point where PX = PY
A) U = min (X, Y)
B) U = X + Y
C) U = X1/2Y1/2
D) U = X1/4Y3/4
A) U = min (X, Y)
B) U = X + Y
C) U = X1/2Y1/2
D) U = X1/4Y3/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The lump sum principle suggests that the tax that reduces utility the least is
A) a tax on income
B) a tax on a good with many substitutes
C) an equal tax per-unit on all goods
D) a tax on a good with only a few substitutes
A) a tax on income
B) a tax on a good with many substitutes
C) an equal tax per-unit on all goods
D) a tax on a good with only a few substitutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The relationship between changes in income and purchase of a good indicates
A) whether the good is a luxury or necessity.
B) whether the good is normal or inferior.
C) whether the good is a complement or substitute.
D) Both a and b.
A) whether the good is a luxury or necessity.
B) whether the good is normal or inferior.
C) whether the good is a complement or substitute.
D) Both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose a person's utility is only a function of their consumption of diet soda and they do not care which brand,Diet Coke (DC)or Diet Pepsi (DP)they consume.Suppose further that PDC < PDP.If PDC rises but it remains less than PDP then the consumption of DC
A) Falls from a positive amount to zero
B) Falls from a positive amount to another positive amount.
C) rises.
D) stays at zero.
A) Falls from a positive amount to zero
B) Falls from a positive amount to another positive amount.
C) rises.
D) stays at zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a good is inferior and its price increases,
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the prices of all goods increase by the same proportion as income,the quantity demanded of good X will
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) remain unchanged.
D) change in a way that cannot be determined from the information given.
A) decrease.
B) increase.
C) remain unchanged.
D) change in a way that cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a good is normal and its price decreases,
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose 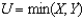 and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the income effect (in terms of units of X bought)is
and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the income effect (in terms of units of X bought)is
A) 2
B) -1
C) 0
D) -2
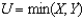 and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the income effect (in terms of units of X bought)is
and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the income effect (in terms of units of X bought)isA) 2
B) -1
C) 0
D) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose you were to believe that "money illusion" exists that is as prices and incomes both rise proportionally,people buy more.Which of the following characteristics of demand does that cause you to doubt?
A) demand functions are downward sloping
B) demand has a positive vertical intercept
C) demand has a positive horizontal intercept.
D) demand functions are homogeneous of degree zero.
A) demand functions are downward sloping
B) demand has a positive vertical intercept
C) demand has a positive horizontal intercept.
D) demand functions are homogeneous of degree zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a good is Giffen and its price increases,
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.
A) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be positive.
B) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be negative.
C) the income effect will be positive and the substitution effect will be negative.
D) the income effect will be negative and the substitution effect will be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
With only two goods,if the income effect is in the opposite direction as the substitution effect but the substitution effect dominates then the good is
A) normal
B) inferior but not Giffen
C) Giffen
D) There is not enough information to answer.
A) normal
B) inferior but not Giffen
C) Giffen
D) There is not enough information to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose a person's utility is only a function of their consumption of diet soda and they do not care which brand,Diet Coke (DC)or Diet Pepsi (DP)they consume.Suppose further that PDC < PDP.If PDC rises to a point where PDC > PDP then the consumption of DC
A) Falls from a positive amount to zero
B) Falls from a positive amount to another positive amount.
C) rises.
D) stays at zero.
A) Falls from a positive amount to zero
B) Falls from a positive amount to another positive amount.
C) rises.
D) stays at zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose 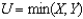 and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the substitution effect is
and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the substitution effect is
A) 2
B) -1
C) 0
D) -2
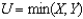 and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the substitution effect is
and the price of X is 1,the price of Y is 1 and income is $12.If the price of X increases to 2,the substitution effect isA) 2
B) -1
C) 0
D) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Demand functions are "homogeneous of degree zero in all prices and income." This means
A) a proportional increase in all prices and income will leave quantities demanded unchanged.
B) a doubling of all prices will not alter consumption decisions.
C) prices directly enter individuals' utility functions.
D) an increase in income will cause all quantities demanded to increase proportionately.
A) a proportional increase in all prices and income will leave quantities demanded unchanged.
B) a doubling of all prices will not alter consumption decisions.
C) prices directly enter individuals' utility functions.
D) an increase in income will cause all quantities demanded to increase proportionately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose there are two goods (X and Y).On a traditional graph of a budget line a tripling of all prices and incomes will
A) alter the slope of the budget line only.
B) alter the slope of the budget line as well as the Y-intercept.
C) alter the slope of the budget line as well as the X-intercept.
D) leave the budget line unaltered.
A) alter the slope of the budget line only.
B) alter the slope of the budget line as well as the Y-intercept.
C) alter the slope of the budget line as well as the X-intercept.
D) leave the budget line unaltered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If income doubles and the quantity demanded of good X more than doubles,then good X can be described as a
A) substitute good.
B) complement good.
C) necessity.
D) luxury.
A) substitute good.
B) complement good.
C) necessity.
D) luxury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Two goods,X and Y,are called complements if
A) an increase in PX causes more Y to be bought.
B) an increase in PX causes less Y to be bought.
C) an increase in PY causes less Y to be bought.
D) an increase in income causes more of both X and Y to be bought.
A) an increase in PX causes more Y to be bought.
B) an increase in PX causes less Y to be bought.
C) an increase in PY causes less Y to be bought.
D) an increase in income causes more of both X and Y to be bought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 2 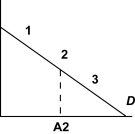
In Figure 2,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "2" is
A) 0
B) between - and -1
C) -1
D) between -1 and 0

In Figure 2,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "2" is
A) 0
B) between - and -1
C) -1
D) between -1 and 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If an individual's housing purchases are always a constant fraction of income,then the income elasticity of demand for housing is
A) greater than one.
B) equal to one.
C) less than one.
D) Cannot be determined from the available information.
A) greater than one.
B) equal to one.
C) less than one.
D) Cannot be determined from the available information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 1 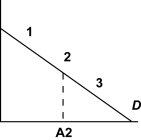
In Figure 1,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "1" is
A) 0
B) between - and -1
C) -1
D) between -1 and 0

In Figure 1,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "1" is
A) 0
B) between - and -1
C) -1
D) between -1 and 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An increase in quantity demanded is represented by
A) a shift outward of the entire demand curve.
B) a shift inward of the entire demand curve.
C) a movement along the demand curve in a southeasterly direction in response to a decline in the good's price.
D) a movement along the demand curve in a northwesterly direction in response to a decline in the good's price.
A) a shift outward of the entire demand curve.
B) a shift inward of the entire demand curve.
C) a movement along the demand curve in a southeasterly direction in response to a decline in the good's price.
D) a movement along the demand curve in a northwesterly direction in response to a decline in the good's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 3 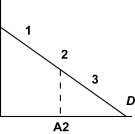 In Figure 3,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "3" is
In Figure 3,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "3" is
A) 0
B) between - and -1
C) -1
D) between -1 and 0
 In Figure 3,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "3" is
In Figure 3,the point A2 is half way between the origin and the quantity intercept of the demand curve.The price elasticity at point "3" isA) 0
B) between - and -1
C) -1
D) between -1 and 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose demand can be written as PQ = 1000.The price elasticity of demand is)
A) increasing as price rises.
B) decreasing as price rises.
C) constant regardless of prices and perfectly elastic.
D) constant regardless of prices and unit elastic.
A) increasing as price rises.
B) decreasing as price rises.
C) constant regardless of prices and perfectly elastic.
D) constant regardless of prices and unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Two goods,X and Y,are called substitutes if
A) an increase in PX causes more Y to be bought.
B) an increase in PX causes less Y to be bought.
C) an increase in PY causes less Y to be bought.
D) an increase in income causes more of both X and Y to be bought.
A) an increase in PX causes more Y to be bought.
B) an increase in PX causes less Y to be bought.
C) an increase in PY causes less Y to be bought.
D) an increase in income causes more of both X and Y to be bought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Assume X and Y are the only two goods a person consumes.If after a rise in 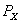 the quantity demanded of Y increases,one could say
the quantity demanded of Y increases,one could say
A) the income effect dominates the substitution effect for Y.
B) the substitution effect dominates the income effect for Y.
C) it is impossible to determine whether the substitution or income effect dominates for Y.
D) None of the above.
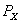 the quantity demanded of Y increases,one could say
the quantity demanded of Y increases,one could sayA) the income effect dominates the substitution effect for Y.
B) the substitution effect dominates the income effect for Y.
C) it is impossible to determine whether the substitution or income effect dominates for Y.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose there are two people who demand apples.Suppose one considers apples and oranges complements and another considers them substitutes.An increase in the price of oranges will
A) increase the market demand for oranges.
B) decrease the market demand for apples
C) increase the market demand for apples.
D) have an uncertain impact on the market demand for apples.
A) increase the market demand for oranges.
B) decrease the market demand for apples
C) increase the market demand for apples.
D) have an uncertain impact on the market demand for apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If good X is a normal good and its price rises,then quantity demanded
A) may or may not fall.
B) will always fall.
C) will always rise.
D) will remain unchanged.
A) may or may not fall.
B) will always fall.
C) will always rise.
D) will remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The inelasticity of demand for gasoline in the short run
A) makes no theoretical sense.
B) makes sense because there are very few substitutes.
C) makes little sense because there are very few substitutes.
D) is more pronounced in the long run.
A) makes no theoretical sense.
B) makes sense because there are very few substitutes.
C) makes little sense because there are very few substitutes.
D) is more pronounced in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At any price,the market demand curve
A) is flatter than the flattest individual demand curve.
B) has a slope that is the average of the individual demand curve slopes.
C) is steeper than the steepest individual demand curve.
D) has a horizontal intercept equal to the average of the individual demand curve horizontal intercepts.
A) is flatter than the flattest individual demand curve.
B) has a slope that is the average of the individual demand curve slopes.
C) is steeper than the steepest individual demand curve.
D) has a horizontal intercept equal to the average of the individual demand curve horizontal intercepts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An individual's demand curve
A) represents the various quantities that a consumer is willing to purchase of a good at various price levels.
B) is derived from an individual's indifference curve map.
C) will shift if preferences, prices of other goods, or income change.
D) all of the above.
A) represents the various quantities that a consumer is willing to purchase of a good at various price levels.
B) is derived from an individual's indifference curve map.
C) will shift if preferences, prices of other goods, or income change.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose demand can be written as Q = 5.The elasticity of demand is)
A) increasing as price rises.
B) decreasing as price rises.
C) constant regardless of prices and perfectly inelastic.
D) constant regardless of prices and unit elastic.
A) increasing as price rises.
B) decreasing as price rises.
C) constant regardless of prices and perfectly inelastic.
D) constant regardless of prices and unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following will not cause a demand curve to shift position?
A) A doubling of the good's price.
B) A doubling of the price of a closely substitutable good.
C) A shift in preferences.
D) A doubling of both the price of X and the price of Y.
A) A doubling of the good's price.
B) A doubling of the price of a closely substitutable good.
C) A shift in preferences.
D) A doubling of both the price of X and the price of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If an individual buys only two goods and these must be used in a fixed relationship with one another (e.g.,coffee and cream for a coffee drinker who never varies the amount of cream used in each cup),then
A) there is no substitution effect from a change in the price of coffee.
B) there is no income effect from a change in the price of coffee.
C) Giffen's Paradox must occur if both coffee and cream are inferior goods.
D) an increase in income will not affect cream purchases.
A) there is no substitution effect from a change in the price of coffee.
B) there is no income effect from a change in the price of coffee.
C) Giffen's Paradox must occur if both coffee and cream are inferior goods.
D) an increase in income will not affect cream purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A decrease in demand is represented by
A) a shift outward of the entire demand curve.
B) a shift inward of the entire demand curve.
C) a movement along the demand curve in a southeasterly direction.
D) a movement along the demand curve in a northwesterly direction.
A) a shift outward of the entire demand curve.
B) a shift inward of the entire demand curve.
C) a movement along the demand curve in a southeasterly direction.
D) a movement along the demand curve in a northwesterly direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose demand can be written as P = 5.The elasticity of demand is)
A) increasing as price rises.
B) decreasing as price rises.
C) constant regardless of prices and perfectly elastic.
D) constant regardless of prices and unit elastic.
A) increasing as price rises.
B) decreasing as price rises.
C) constant regardless of prices and perfectly elastic.
D) constant regardless of prices and unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the cross price elasticity of demand equals -1,then the two goods are
A) both normal.
B) both inferior.
C) complements to one another.
D) substitutes to one another.
A) both normal.
B) both inferior.
C) complements to one another.
D) substitutes to one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the demand for a product is elastic,then a rise in price will
A) cause total spending on the good to increase.
B) cause total spending on the good to decrease.
C) keep total spending the same, but reduce the quantity demanded.
D) keep total spending the same, but increase the quantity demanded.
A) cause total spending on the good to increase.
B) cause total spending on the good to decrease.
C) keep total spending the same, but reduce the quantity demanded.
D) keep total spending the same, but increase the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The price elasticity of demand for a linear demand curve follows the pattern (moving from high prices to low prices)
A) elastic, unit elastic, inelastic.
B) unit elastic, inelastic, elastic.
C) inelastic, unit elastic, elastic.
D) elastic, inelastic, unit elastic.
A) elastic, unit elastic, inelastic.
B) unit elastic, inelastic, elastic.
C) inelastic, unit elastic, elastic.
D) elastic, inelastic, unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A change in the distribution of income which leaves total income constant will not shift the market demand curve for a product providing
A) everyone has an income elasticity of demand of zero for the product.
B) everyone has the same income elasticity of demand for the product.
C) individuals have differing income elasticities for the product, but the average income elasticity for income gainers is equal to the average income elasticity for income losers.
D) any of the above conditions occur.
A) everyone has an income elasticity of demand of zero for the product.
B) everyone has the same income elasticity of demand for the product.
C) individuals have differing income elasticities for the product, but the average income elasticity for income gainers is equal to the average income elasticity for income losers.
D) any of the above conditions occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The price elasticity of demand for any good must be less than or equal to zero unless
A) the good is a necessity.
B) the good is a luxury.
C) the good is a Giffen good.
D) the good is a substitute.
A) the good is a necessity.
B) the good is a luxury.
C) the good is a Giffen good.
D) the good is a substitute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The market demand curve for any good is
A) independent of individuals' demand curves for the good.
B) the vertical summation of individuals' demand curves.
C) the horizontal summation of individuals' demand curves.
D) derived from the firm's marginal cost of production.
A) independent of individuals' demand curves for the good.
B) the vertical summation of individuals' demand curves.
C) the horizontal summation of individuals' demand curves.
D) derived from the firm's marginal cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An increase in the price of good X will be accompanied by
A) a shift in the market demand curve for good X.
B) a shift in the market demand curve for good Y (a substitute for good X).
C) a movement along the market demand curve for good X.
D) Both b and c.
A) a shift in the market demand curve for good X.
B) a shift in the market demand curve for good Y (a substitute for good X).
C) a movement along the market demand curve for good X.
D) Both b and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose the "poor" and "rich" have identical demand functions for good X but only differ in income (I).
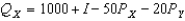 At a given price of X,the price elasticity of their individual demand curves is such that
At a given price of X,the price elasticity of their individual demand curves is such that
A) the rich person's demand is more elastic than the poor person's.
B) the poor person's demand is more elastic than the rich person's.
C) the poor person's demand is as elastic as the rich person's.
D) the rich person's demand is as elastic as the poor person's.
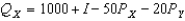 At a given price of X,the price elasticity of their individual demand curves is such that
At a given price of X,the price elasticity of their individual demand curves is such thatA) the rich person's demand is more elastic than the poor person's.
B) the poor person's demand is more elastic than the rich person's.
C) the poor person's demand is as elastic as the rich person's.
D) the rich person's demand is as elastic as the poor person's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If goods X and Y are complements,then the cross price elasticity of demand between them will be
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) infinity.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) zero.
D) infinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In Homogenia everyone is the same.Demand for apples is P = A - Bq for each of its 1 million citizens.Market demand for apples in Homogenia is given by the equation
A)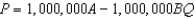
B)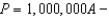
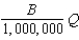
C)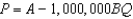
D)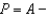
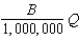
A)
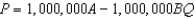
B)
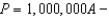
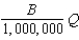
C)
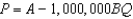
D)
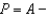
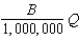

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In Sameslopia (all N people)have a different price at which they will start buying apples,but their reaction to a price change is the same so for each person i,individual demand is P = Ai - Bq.At a price where they are all buying a positive amount,the slope of the market demand curve (with P as a function of Q)will be
A) −B
B)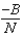
C) −BN
D) −N
A) −B
B)
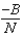
C) −BN
D) −N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the income elasticity of demand is 2,the good is
A) a luxury.
B) a normal good (but not a luxury).
C) an inferior good.
D) a Giffen good.
A) a luxury.
B) a normal good (but not a luxury).
C) an inferior good.
D) a Giffen good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the income elasticity of demand is 0.5,the good is
A) a luxury.
B) a normal good (but not a luxury).
C) an inferior good.
D) a Giffen good.
A) a luxury.
B) a normal good (but not a luxury).
C) an inferior good.
D) a Giffen good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If a consumer purchases only two goods (X and Y )and the demand for X is elastic,then a rise in the price of X
A) will cause total spending on good Y to rise.
B) will cause total spending on good Y to fall.
C) will cause total spending on good Y to remain unchanged.
D) will have an indeterminate effect on total spending on good Y.
A) will cause total spending on good Y to rise.
B) will cause total spending on good Y to fall.
C) will cause total spending on good Y to remain unchanged.
D) will have an indeterminate effect on total spending on good Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If there are only two goods and these are consumed in fixed proportions,the price elasticities of demand for these two goods will sum to
A) 0.0
B) -0.5
C) -1.0
D) a number between 0 and -1.
A) 0.0
B) -0.5
C) -1.0
D) a number between 0 and -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If demand is elastic,a decrease in quantity will cause the total spending (P * Q)to
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain unchanged.
D) change in a way that cannot be determined.
A) rise.
B) fall.
C) remain unchanged.
D) change in a way that cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



