Deck 12: Imperfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/27
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Imperfect Competition
1
Consider the market for nonalcoholic beers from the previous question.Which of the following is the Bertrand reaction function for Cudweiser?
A) PC = 1 + .033PB
B) PC = 1 - .033PB
C) PC = 1.5 + .075PB
D) PB = 1.5 + .075PC
A) PC = 1 + .033PB
B) PC = 1 - .033PB
C) PC = 1.5 + .075PB
D) PB = 1.5 + .075PC
A
2
In the cartel model
A) firms believe that price increases result in a very elastic demand, while price decreases result in an inelastic demand for their products.
B) each firm acts as a price taker.
C) one dominant firm takes the reactions of all other firms into account in its output and pricing decisions.
D) firms coordinate their decisions to act as a multiplant monopoly.
A) firms believe that price increases result in a very elastic demand, while price decreases result in an inelastic demand for their products.
B) each firm acts as a price taker.
C) one dominant firm takes the reactions of all other firms into account in its output and pricing decisions.
D) firms coordinate their decisions to act as a multiplant monopoly.
D
3
Consider the market for nonalcoholic beers from the previous question.Boors' price in a Nash equilibrium (assuming Bertrand competition in these differentiated beers)is about
A) 1.71
B) 2.55
C) 3.55
D) 4.29
A) 1.71
B) 2.55
C) 3.55
D) 4.29
B
4
Which game does the Cournot model most resemble and why?
A) the Battle of the Sexes because firms need to coordinate their outputs.
B) the Battle of the Sexes because firms disagree on which outcome is best.
C) the Prisoners Dilemma because firms don't maximize joint payoffs in equilibrium.
D) the Prisoners Dilemma because firms play dominant strategies.
A) the Battle of the Sexes because firms need to coordinate their outputs.
B) the Battle of the Sexes because firms disagree on which outcome is best.
C) the Prisoners Dilemma because firms don't maximize joint payoffs in equilibrium.
D) the Prisoners Dilemma because firms play dominant strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the same market for nonalcoholic beer as in the previous question.How many "units" of beer will Cudweiser produce?
A) 667
B) 1,667
C) 2,333
D) 3,000
A) 667
B) 1,667
C) 2,333
D) 3,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose there are two firms,Boors and Cudweiser,each selling identical-tasting nonalcoholic beer.Consumers of this beer have no brand loyalty so market demand can be expressed as 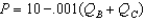 .Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$4 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $2 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,in the Nash equilibrium,Cudweiser will produce
.Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$4 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $2 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,in the Nash equilibrium,Cudweiser will produce
A) 1,333
B) 2,333
C) 3,333
D) 4,333
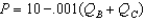 .Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$4 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $2 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,in the Nash equilibrium,Cudweiser will produce
.Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$4 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $2 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,in the Nash equilibrium,Cudweiser will produceA) 1,333
B) 2,333
C) 3,333
D) 4,333

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Two firms engage in Bertrand competition in differentiated products.After doing all the appropriate calculations,you find the best-response functions are 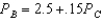 and
and 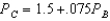 .Without doing any further calculations,can you determine the relationship between their Nash equilibrium prices?
.Without doing any further calculations,can you determine the relationship between their Nash equilibrium prices?
A) Yes,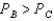
B) Yes,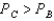
C) Yes,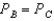 d. It cannot be determined.
d. It cannot be determined.
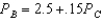 and
and 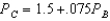 .Without doing any further calculations,can you determine the relationship between their Nash equilibrium prices?
.Without doing any further calculations,can you determine the relationship between their Nash equilibrium prices?A) Yes,
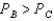
B) Yes,
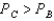
C) Yes,
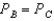 d. It cannot be determined.
d. It cannot be determined. 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose there are two firms,Boors and Cudweiser,each selling identical-tasting nonalcoholic beer.Consumers of this beer have no brand loyalty so market demand can be expressed as 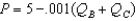 .Boors marginal revenue function can be written MRB = 5 - .001(2QB + QC)(and symmetrically for Cudweiser).Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$2 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $1 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,Boor's best-response function is
.Boors marginal revenue function can be written MRB = 5 - .001(2QB + QC)(and symmetrically for Cudweiser).Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$2 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $1 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,Boor's best-response function is
A)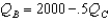
B)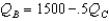
C)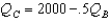
D)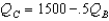
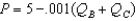 .Boors marginal revenue function can be written MRB = 5 - .001(2QB + QC)(and symmetrically for Cudweiser).Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$2 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $1 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,Boor's best-response function is
.Boors marginal revenue function can be written MRB = 5 - .001(2QB + QC)(and symmetrically for Cudweiser).Boors operates with out of date technology and has constant cost of (MC = AC)$2 per unit where as Cudweiser has constant cost of $1 per unit.Assuming the firms behave as Cournot competitors,Boor's best-response function isA)
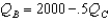
B)
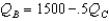
C)
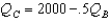
D)
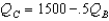

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the market for nonalcoholic beers from the previous question.Which of the following is the Bertrand reaction function for Boors?
A) PB = -2.5 + .05PC
B) PB = 2.5 + .05PC
C) PC = 2.5 - .05PB
D) PB = 2.5 - .15PC
A) PB = -2.5 + .05PC
B) PB = 2.5 + .05PC
C) PC = 2.5 - .05PB
D) PB = 2.5 - .15PC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the same market for nonalcoholic beer as in the previous question.Cudweiser's response function is
A)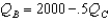
B)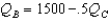
C)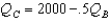
D)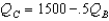
A)
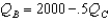
B)
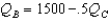
C)
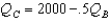
D)
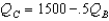

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose there are two firms,Boors and Cudweiser,each selling nonalcoholic beer.Suppose Boors and Cudweiser are not viewed as perfect substitutes but rather demand for Boors is 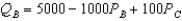 and demand for Cudweiser is
and demand for Cudweiser is 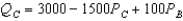 .For simplicity,assume zero marginal costs.Which is the more preferred beer?
.For simplicity,assume zero marginal costs.Which is the more preferred beer?
A) Boor's
B) Cudweiser
C) they are equally preferred
D) neither are preferred
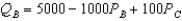 and demand for Cudweiser is
and demand for Cudweiser is 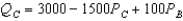 .For simplicity,assume zero marginal costs.Which is the more preferred beer?
.For simplicity,assume zero marginal costs.Which is the more preferred beer?A) Boor's
B) Cudweiser
C) they are equally preferred
D) neither are preferred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Under the cartel model,each firm produces where
A) marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B) price equals marginal cost.
C) the average cost curve is at a minimum.
D) price exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.
A) marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B) price equals marginal cost.
C) the average cost curve is at a minimum.
D) price exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the same market for nonalcoholic beer as in the previous question.How many units will Boors produce in the Nash equilibrium?
A) 1,333
B) 2,333
C) 3,333
D) 4,333
A) 1,333
B) 2,333
C) 3,333
D) 4,333

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the market for nonalcoholic beers from the previous question.Cudweisers' price in a Nash equilibrium (assuming Bertrand competition in these differentiated beers)is about
A) 0.99
B) 1.09
C) 1.71
D) 2.55
A) 0.99
B) 1.09
C) 1.71
D) 2.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which factor would make tacit collusion among firms in a market easier?
A) an increase in the number of firms.
B) a decrease in the probability the market will continue into future periods.
C) a decrease in the interest rate.
D) none of these.
A) an increase in the number of firms.
B) a decrease in the probability the market will continue into future periods.
C) a decrease in the interest rate.
D) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the long run,in the model of monopolistic competition,for a typical firm,price is
A) above average cost but equal to marginal cost.
B) above marginal cost but equal to average cost.
C) above marginal cost.
D) equal to marginal cost and equal to or greater than average cost.
A) above average cost but equal to marginal cost.
B) above marginal cost but equal to average cost.
C) above marginal cost.
D) equal to marginal cost and equal to or greater than average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which assumptions of the Bertrand model be altered to avoid the Bertrand Paradox (that an outcome resembling perfect competition may arise with even as few as two firms)?
A) assuming firms have limited capacities.
B) assuming firms produce differentiated rather than homogeneous products.
C) assuming firms play repeatedly and thus may collude.
D) all of the above.
A) assuming firms have limited capacities.
B) assuming firms produce differentiated rather than homogeneous products.
C) assuming firms play repeatedly and thus may collude.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Relative to the case in which two identical firms choose quantities simultaneously in a Cournot model,if one of the two moves first and is observed by the other,how would this affect its output?
A) it would increase its output, more so if it could deter the other from entering the market at all.
B) it would increase its output, but would moderate this increase if it were concerned about entry deterrence.
C) it would decrease its output if it couldn't deter entry and increase it otherwise.
D) it would decrease its output whether or not it wanted to deter entry.
A) it would increase its output, more so if it could deter the other from entering the market at all.
B) it would increase its output, but would moderate this increase if it were concerned about entry deterrence.
C) it would decrease its output if it couldn't deter entry and increase it otherwise.
D) it would decrease its output whether or not it wanted to deter entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the monopolistic competition model
A) firms are price takers
B) barriers to entry maintain some monopoly "rents" in the long run.
C) one dominant firm acts as the monopolist that is followed by the fringe of competitors.
D) none of these.
A) firms are price takers
B) barriers to entry maintain some monopoly "rents" in the long run.
C) one dominant firm acts as the monopolist that is followed by the fringe of competitors.
D) none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the same market for nonalcoholic beer as in the previous question.How many "units" of beer will Boors produce in the Nash equilibrium?
A) 667
B) 1,667
C) 2,333
D) 3,000
A) 667
B) 1,667
C) 2,333
D) 3,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the price leadership model,
A) firms believe that price increases result in a very elastic demand, while price decreases result in an inelastic demand for their product.
B) each firm acts as a price taker.
C) one dominant firm takes the reactions of all other firms into account in its output and pricing decisions.
D) firms coordinate their decisions to act as multiplant monopolies.
A) firms believe that price increases result in a very elastic demand, while price decreases result in an inelastic demand for their product.
B) each firm acts as a price taker.
C) one dominant firm takes the reactions of all other firms into account in its output and pricing decisions.
D) firms coordinate their decisions to act as multiplant monopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Product differentiation complicates the study of oligopolies because such markets may not
A) be efficient.
B) have prices equal to marginal cost.
C) have free entry and exit.
D) obey the law of one price.
A) be efficient.
B) have prices equal to marginal cost.
C) have free entry and exit.
D) obey the law of one price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a Cournot equilibrium each firm chooses an output level that
A) maximizes joint profits.
B) maximizes the price received.
C) maximizes profits given what the other firm produces.
D) maximizes revenue given what the other firm produces.
A) maximizes joint profits.
B) maximizes the price received.
C) maximizes profits given what the other firm produces.
D) maximizes revenue given what the other firm produces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the Cournot model,each firm assumes that its rival will ____ its output when the firm adjusts its own output.Which word best completes the sentence?
A) increase
B) not change
C) decrease
D) adjust
A) increase
B) not change
C) decrease
D) adjust

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A profit-maximizing firm should spend an additional dollar on advertising so long as this expenditure results in more than one dollar of
A) additional sales.
B) reduced costs.
C) increased profits.
D) demand.
A) additional sales.
B) reduced costs.
C) increased profits.
D) demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All of the following are problems associated with maintaining a cartel except
A) cartels are illegal.
B) a large amount of information is needed to coordinate a cartel.
C) profits are not maximized by a cartel so it will evolve into a monopoly.
D) each member of the cartel has an incentive to "chisel" by expanding output.
A) cartels are illegal.
B) a large amount of information is needed to coordinate a cartel.
C) profits are not maximized by a cartel so it will evolve into a monopoly.
D) each member of the cartel has an incentive to "chisel" by expanding output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Each firm in a cartel has an incentive to chisel because market price exceeds
A) marginal cost.
B) average cost.
C) average variable cost.
D) average fixed cost.
A) marginal cost.
B) average cost.
C) average variable cost.
D) average fixed cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 27 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



