Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/142
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
1
The equilibrium constant is given for one of the reactions below.Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)Kc = 1.7 × 106
SO3(g)⇌ 1/2 O2(g)+ SO2(g)Kc = ?
A) 3.4 × 102
B) 8.5
C) 1.3 × 103
D) 1.2 × 10-6
E) 7.7 × 10-4
SO3(g)⇌ 1/2 O2(g)+ SO2(g)Kc = ?
A) 3.4 × 102
B) 8.5
C) 1.3 × 103
D) 1.2 × 10-6
E) 7.7 × 10-4
7.7 × 10-4
2
In which of the following reactions will Kc = Kp?
A) 4 NH3(g) + 3 O2(g) ⇌ 2 N2(g) + 6 H2O(g)
B) SO3(g) + NO(g) ⇌ SO2(g) + NO2(g)
C) 2 N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 N2O(g)
D) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 SO3(g)
E) None of the above reactions have Kc = Kp.
A) 4 NH3(g) + 3 O2(g) ⇌ 2 N2(g) + 6 H2O(g)
B) SO3(g) + NO(g) ⇌ SO2(g) + NO2(g)
C) 2 N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 N2O(g)
D) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 SO3(g)
E) None of the above reactions have Kc = Kp.
SO3(g) + NO(g) ⇌ SO2(g) + NO2(g)
3
What is Δn for the following equation in relating Kc to Kp?
N2O4(g)⇌ 2NO2(g)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1
N2O4(g)⇌ 2NO2(g)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1
1
4
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) When K >> 1, the forward reaction is favored and essentially goes to completion.
B) When K << 1, the reverse reaction is favored and the forward reaction does not proceed to a great extent.
C) When K ≈ 1, neither the forward or reverse reaction is strongly favored, and about the same amount of reactants and products exist at equilibrium.
D) K >> 1 implies that the reaction is very fast at producing products.
E) None of the above
A) When K >> 1, the forward reaction is favored and essentially goes to completion.
B) When K << 1, the reverse reaction is favored and the forward reaction does not proceed to a great extent.
C) When K ≈ 1, neither the forward or reverse reaction is strongly favored, and about the same amount of reactants and products exist at equilibrium.
D) K >> 1 implies that the reaction is very fast at producing products.
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Chemical equilibrium is the result of
A) all of the reactants being converted into products.
B) stoppage of further reaction.
C) formation of products equal in mass to the mass of the reactants.
D) opposing reactions attaining equal rates.
E) a loss of pressure in the system.
A) all of the reactants being converted into products.
B) stoppage of further reaction.
C) formation of products equal in mass to the mass of the reactants.
D) opposing reactions attaining equal rates.
E) a loss of pressure in the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Equilibrium in which rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction is
A) dynamic.
B) temperature independent.
C) concentration independent.
D) volume independent.
E) impossible.
A) dynamic.
B) temperature independent.
C) concentration independent.
D) volume independent.
E) impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The equilibrium constant is given for two of the reactions below.Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. A(g)+ 2B(g)⇌ AB2(g)Kc = 59
AB2(g)+ B(g)⇌ AB3(g)Kc = ?
A(g)+ 3B(g)⇌ AB3(g)Kc = 478
A) 3.5 × 10-5
B) 2.8 × 104
C) 8.1
D) 0.12
E) 89
AB2(g)+ B(g)⇌ AB3(g)Kc = ?
A(g)+ 3B(g)⇌ AB3(g)Kc = 478
A) 3.5 × 10-5
B) 2.8 × 104
C) 8.1
D) 0.12
E) 89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. 16 CH3Cl(g)+ 8 Cl2(g)⇔ 16 CH2Cl2(g)+ 8 H2(g)
A) K =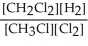
B) K =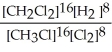
C) K =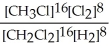
D) K =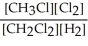
E) K =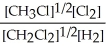
A) K =
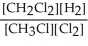
B) K =
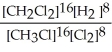
C) K =
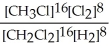
D) K =
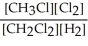
E) K =
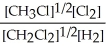

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is Δn for the following equation in relating Kc to Kp?
SO3(g)+ NO(g)⇌ SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
A) 0
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1
SO3(g)+ NO(g)⇌ SO2(g)+ NO2(g)
A) 0
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is Δn for the following equation in relating Kc to Kp?
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The equilibrium constant is given for one of the reactions below.Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. H2(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 HBr(g)Kc = 3.8 × 104
4 HBr(g)⇌ 2 H2(g)+ 2 Br2(g)Kc = ?
A) 1.9 × 104
B) 5.1 × 10-3
C) 2.6 × 10-5
D) 6.9 × 10-10
E) 1.6 × 103
4 HBr(g)⇌ 2 H2(g)+ 2 Br2(g)Kc = ?
A) 1.9 × 104
B) 5.1 × 10-3
C) 2.6 × 10-5
D) 6.9 × 10-10
E) 1.6 × 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Give the direction of the reaction,if K ≈ 1.
A) The forward reaction is favored.
B) The reverse reaction is favored.
C) Neither direction is favored.
D) If the temperature is raised, then the forward reaction is favored.
E) If the temperature is raised, then the reverse reaction is favored.
A) The forward reaction is favored.
B) The reverse reaction is favored.
C) Neither direction is favored.
D) If the temperature is raised, then the forward reaction is favored.
E) If the temperature is raised, then the reverse reaction is favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Give the direction of the reaction,if K >> 1.
A) The forward reaction is favored.
B) The reverse reaction is favored.
C) Neither direction is favored.
D) If the temperature is raised, then the forward reaction is favored.
E) If the temperature is raised, then the reverse reaction is favored.
A) The forward reaction is favored.
B) The reverse reaction is favored.
C) Neither direction is favored.
D) If the temperature is raised, then the forward reaction is favored.
E) If the temperature is raised, then the reverse reaction is favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The equilibrium constant is given for one of the reactions below.Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. H2(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 HBr(g)Kc = 3.8 × 104
2 HBr(g)⇌ H2(g)+ Br2(g)Kc = ?
A) 1.9 × 104
B) 5.3 × 10-5
C) 2.6 × 10-5
D) 6.4 × 10-4
E) 1.6 × 103
2 HBr(g)⇌ H2(g)+ Br2(g)Kc = ?
A) 1.9 × 104
B) 5.3 × 10-5
C) 2.6 × 10-5
D) 6.4 × 10-4
E) 1.6 × 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Give the direction of the reaction,if K << 1.
A) The forward reaction is favored.
B) The reverse reaction is favored.
C) Neither direction is favored.
D) If the temperature is raised, then the forward reaction is favored.
E) If the temperature is raised, then the reverse reaction is favored.
A) The forward reaction is favored.
B) The reverse reaction is favored.
C) Neither direction is favored.
D) If the temperature is raised, then the forward reaction is favored.
E) If the temperature is raised, then the reverse reaction is favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is Δn for the following equation in relating Kc to Kp?
4 NH3(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 N2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1
4 NH3(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 N2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -2
D) 2
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is Δn for the following equation in relating Kc to Kp?
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -3
D) 2
E) 1
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)
A) 3
B) -1
C) -3
D) 2
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The equilibrium constant is given for two of the reactions below.Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. A(g)+ B(g)⇌ AB(g)Kc = 0.24
AB(g)+ A(g)⇌ A2B(g)Kc = 3.8
2 A(g)+ B(g)⇌ A2B(g)Kc = ?
A) 4.0
B) 0.91
C) 3.6
D) 16
E) 0.063
AB(g)+ A(g)⇌ A2B(g)Kc = 3.8
2 A(g)+ B(g)⇌ A2B(g)Kc = ?
A) 4.0
B) 0.91
C) 3.6
D) 16
E) 0.063

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The equilibrium constant is given for two of the reactions below.Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. 2A(g)+ B(g)⇌ A2B(g)Kc = ?
A2B(g)+ B(g)⇌ A2B2(g)Kc = 16.4
2A(g)+ 2B(g)⇌ A2B2(g)Kc = 28.2
A) 11.8
B) 0.00216
C) 0.582
D) 462
E) 1.72
A2B(g)+ B(g)⇌ A2B2(g)Kc = 16.4
2A(g)+ 2B(g)⇌ A2B2(g)Kc = 28.2
A) 11.8
B) 0.00216
C) 0.582
D) 462
E) 1.72

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The reaction below has a Kp value of 3.3 × 10-5.What is the value of Kc for this reaction at 700 K?
2 SO3(g)⇌ 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)
A) 5.7 × 10-7
B) 1.7 × 106
C) 3.3 × 10-5
D) 3.0 × 104
E) 1.9 × 10-3
2 SO3(g)⇌ 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)
A) 5.7 × 10-7
B) 1.7 × 106
C) 3.3 × 10-5
D) 3.0 × 104
E) 1.9 × 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P4(s)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ P4O10(s)
A) K =![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c956_80d0_d558bd28957a_TB6105_11.jpg)
B) K =![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c957_80d0_fba435eaed14_TB6105_11.jpg)
C) K = [O2]-5
D) K = [O2]5
E) K =![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c958_80d0_2117921d8fb8_TB6105_11.jpg)
A) K =
![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c956_80d0_d558bd28957a_TB6105_11.jpg)
B) K =
![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c957_80d0_fba435eaed14_TB6105_11.jpg)
C) K = [O2]-5
D) K = [O2]5
E) K =
![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c958_80d0_2117921d8fb8_TB6105_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The reaction below has a Kc value of 3.64 × 10-3.What is the value of Kp for this reaction at 25°C?
2 NaN3(s)⇌ 2 Na(s)+ 3 N2(g)
A) 131
B) 0.613
C) 8.90 × 10-2
D) 29.9
E) 53.2
2 NaN3(s)⇌ 2 Na(s)+ 3 N2(g)
A) 131
B) 0.613
C) 8.90 × 10-2
D) 29.9
E) 53.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) If Q < K, it means the forward reaction will proceed to form more products.
B) If Q > K, it means the forward reaction will proceed to form more products.
C) If Q = K, it means the reaction is not at equilibrium.
D) All of the above are true.
E) None of the above are true.
A) If Q < K, it means the forward reaction will proceed to form more products.
B) If Q > K, it means the forward reaction will proceed to form more products.
C) If Q = K, it means the reaction is not at equilibrium.
D) All of the above are true.
E) None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Determine the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [P4O10]eq = 2.000 moles,[P4]eq = 3.000 moles,[O2]eq = 4.000 M P4O10(s)⇌ P4(s)+ 5 O2(g)
A) 20.00
B) 4.000
C) 1.320
D) 1536
E) 1024
A) 20.00
B) 4.000
C) 1.320
D) 1536
E) 1024

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a reaction mixture containing only products,what is the value of Q?
A) -1
B) 1
C) ∞
D) 0
E) It cannot be determined without concentrations.
A) -1
B) 1
C) ∞
D) 0
E) It cannot be determined without concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a reaction mixture containing reactants and products,each at a concentration of 1M,what is the value of Q?
A) -1
B) 1
C) ∞
D) 0
E) It cannot be determined without concentrations.
A) -1
B) 1
C) ∞
D) 0
E) It cannot be determined without concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Determine the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [N2]eq = 1.5 M,[H2]eq = 1.1 M,[NH3]eq = 0.47 M. N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)⇌ 2 NH3(g)
A) 3.5
B) 0.28
C) 9.1
D) 0.11
E) 0.78
A) 3.5
B) 0.28
C) 9.1
D) 0.11
E) 0.78

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Dynamic equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
B) The equilibrium constant for the forward reaction is equal to the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction.
C) A reaction quotient (Q) larger than the equilibrium constant (K) means that the reaction will favor the production of more products.
D) Dynamic equilibrium indicates that the amount of reactants and products are equal.
E) All of the above are true.
A) Dynamic equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.
B) The equilibrium constant for the forward reaction is equal to the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction.
C) A reaction quotient (Q) larger than the equilibrium constant (K) means that the reaction will favor the production of more products.
D) Dynamic equilibrium indicates that the amount of reactants and products are equal.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Determine the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [HCl]eq = 0.13 M,[HI]eq = 5.6 × 10-16 M,[Cl2]eq = 0.0019 M. 2 HI(g)+ Cl2(g)⇌ 2 HCl(g)+ I2(s)
A) 8.2 × 10-18
B) 2.8 × 1031
C) 1.2 × 1017
D) 1.4 × 10-19
E) 3.5 × 10-32
A) 8.2 × 10-18
B) 2.8 × 1031
C) 1.2 × 1017
D) 1.4 × 10-19
E) 3.5 × 10-32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Determine the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [HCl]eq = 0.13 M,[HI]eq = 5.6 × 10-16 M,[Cl2]eq = 0.0019 M. 2 HCl(g)+ I2(s)⇌ 2 HI(g)+ Cl2(g)
A) 8.2 × 10-18
B) 2.8 × 1031
C) 1.2 × 1017
D) 1.4 × 10-19
E) 3.5 × 10-32
A) 8.2 × 10-18
B) 2.8 × 1031
C) 1.2 × 1017
D) 1.4 × 10-19
E) 3.5 × 10-32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the following reaction,equilibrium concentrations,and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature.Determine the equilibrium concentration of H2O(g). C2H4(g)+ H2O(g)⇌ C2H5OH(g)Kc = 9.0 × 103
[C2H4]eq = 0.015 M [C2H5OH]eq = 1.69 M
A) 9.9 × 10-7 M
B) 80. M
C) 1.0 M
D) 1.68 M
E) 0.013 M
[C2H4]eq = 0.015 M [C2H5OH]eq = 1.69 M
A) 9.9 × 10-7 M
B) 80. M
C) 1.0 M
D) 1.68 M
E) 0.013 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Calculate the value of [N2]eq if [H2]eq = 2.0 M,[NH3]eq = 0.5 M,and Kc = 2. N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)⇌ 2 NH3(g)
A) 0.016 M
B) 0.031 M
C) 0.062 M
D) 0.40 M
E) 62.5 M
A) 0.016 M
B) 0.031 M
C) 0.062 M
D) 0.40 M
E) 62.5 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P4O10(s)⇌ P4(s)+ 5 O2(g)
A) K =![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c959_80d0_0d77752c2b3b_TB6105_11.jpg)
B) K =![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_f06a_80d0_c15063611890_TB6105_11.jpg)
C) K = [O2]-5
D) K = [O2]5
E) K =![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_f06b_80d0_7f80535046dc_TB6105_11.jpg)
A) K =
![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_c959_80d0_0d77752c2b3b_TB6105_11.jpg)
B) K =
![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_f06a_80d0_c15063611890_TB6105_11.jpg)
C) K = [O2]-5
D) K = [O2]5
E) K =
![<strong>Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub>(s)⇌ P<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 5 O<sub>2</sub>(g)</strong> A) K = B) K = C) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>-5</sup> D) K = [O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) K =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6105/11ea6923_183c_f06b_80d0_7f80535046dc_TB6105_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Calculate P [NO]eq,if P [NOCl]eq = 0.33 atm,P [Cl2]eq = 0.50 atm,and Kp = 1.9 × 10-2. 2 NOCl(g)⇌ 2 NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
A) 1.7 atm
B) 0.0042 atm
C) 0.30 atm
D) 0.064 atm
E) 0.087 atm
A) 1.7 atm
B) 0.0042 atm
C) 0.30 atm
D) 0.064 atm
E) 0.087 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following reaction: CH4(g)+ 2 H2S(g)⇌ CS2(g)+ 4 H2(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.50 M CH4 and 0.75 M H2S.If the equilibrium concentration of H2 is 0.44 M,find the equilibrium constant (Kc)for the reaction.
A) 0.23
B) 0.038
C) 2.9
D) 10.
E) 0.34
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.50 M CH4 and 0.75 M H2S.If the equilibrium concentration of H2 is 0.44 M,find the equilibrium constant (Kc)for the reaction.
A) 0.23
B) 0.038
C) 2.9
D) 10.
E) 0.34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Determine the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [N2]eq = 3.6 M,[O2]eq = 4.1 M,[N2O]eq = 3.3 × 10-18 M. 2 N2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 N2O(g)
A) 2.2 × 10-19
B) 4.5 × 1018
C) 2.0 × 10-37
D) 5.0 × 1036
E) 4.9 × 10-17
A) 2.2 × 10-19
B) 4.5 × 1018
C) 2.0 × 10-37
D) 5.0 × 1036
E) 4.9 × 10-17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a reaction mixture containing only reactants,what is the value of Q?
A) -1
B) 1
C) ∞
D) 0
E) It cannot be determined without concentrations.
A) -1
B) 1
C) ∞
D) 0
E) It cannot be determined without concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Determine the value of Kp for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: P(CO)eq = 6.8 × 10-11 atm,P(O2)eq = 1.3 × 10-3 atm,P(CO2)eq = 0.041 atm. 2 CO(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 CO2(g)
A) 3.6 × 10-21
B) 2.8 × 1020
C) 4.6 × 1011
D) 2.2 × 10-12
E) 3.6 × 10-15
A) 3.6 × 10-21
B) 2.8 × 1020
C) 4.6 × 1011
D) 2.2 × 10-12
E) 3.6 × 10-15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) If Q < K, it means the reverse reaction will proceed to form more reactants.
B) If Q > K, it means the forward reaction will proceed to form more products.
C) If Q = K, it means the reaction is at equilibrium.
D) All of the above are true.
E) None of the above are true.
A) If Q < K, it means the reverse reaction will proceed to form more reactants.
B) If Q > K, it means the forward reaction will proceed to form more products.
C) If Q = K, it means the reaction is at equilibrium.
D) All of the above are true.
E) None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) If Q < K, it means the reverse reaction will proceed to form more reactants.
B) If Q > K, it means the reverse reaction will proceed to form more reactants.
C) If Q = K, it means the reaction is not at equilibrium.
D) All of the above are true.
E) None of the above are true.
A) If Q < K, it means the reverse reaction will proceed to form more reactants.
B) If Q > K, it means the reverse reaction will proceed to form more reactants.
C) If Q = K, it means the reaction is not at equilibrium.
D) All of the above are true.
E) None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the following reaction: 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)⇌ 2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 2.8 M H2O and 2.6 M SO2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of H2S if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 1.3 × 10-6.
A) 0.045 M
B) 0.058 M
C) 0.028 M
D) 3.1 × 10-3 M
E) 0.12 M
A reaction mixture initially contains 2.8 M H2O and 2.6 M SO2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of H2S if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 1.3 × 10-6.
A) 0.045 M
B) 0.058 M
C) 0.028 M
D) 3.1 × 10-3 M
E) 0.12 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following reaction,equilibrium concentrations,and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature.Determine the equilibrium pressure of CO. CO(g)+ 2 H2(g)⇌ CH3OH(l)Kp = 2.25 × 104
P(H2)eq = 0.52 atm
A) 8.3 × 104 atm
B) 1.2 × 10-5 atm
C) 6.25 × 10-3 atm
D) 8.5 × 10-5 atm
E) 1.6 × 10-4 atm
P(H2)eq = 0.52 atm
A) 8.3 × 104 atm
B) 1.2 × 10-5 atm
C) 6.25 × 10-3 atm
D) 8.5 × 10-5 atm
E) 1.6 × 10-4 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will raising the pressure of the system from 5 atm to 8 atm?
2 NH3(g)⇌ N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)
A) It will shift to the right
B) It will shift to the left
C) It will have no effect
D) It will speed up the reaction
E) It will slow down the reaction
2 NH3(g)⇌ N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)
A) It will shift to the right
B) It will shift to the left
C) It will have no effect
D) It will speed up the reaction
E) It will slow down the reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will increasing the volume of the reaction mixture have on the system?
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider the following reaction: Xe(g)+ 2 F2(g)→ XeF4(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 2.24 atm Xe and 4.27 atm F2.If the equilibrium pressure of Xe is 0.34 atm,find the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the reaction.
A) 25
B) 0.12
C) 0.99
D) 8.3
E) 0.040
A reaction mixture initially contains 2.24 atm Xe and 4.27 atm F2.If the equilibrium pressure of Xe is 0.34 atm,find the equilibrium constant (Kp)for the reaction.
A) 25
B) 0.12
C) 0.99
D) 8.3
E) 0.040

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following reaction is exothermic.What set of conditions will always lead to the equilibrium shifting to the left?
2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g)
A) decrease the volume, decrease the temperature
B) increase the volume, decrease the temperature
C) increase the volume, increase the temperature
D) decrease the volume, increase the temperature
E) none of the above
2 NO(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 NOBr(g)
A) decrease the volume, decrease the temperature
B) increase the volume, decrease the temperature
C) increase the volume, increase the temperature
D) decrease the volume, increase the temperature
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following reaction: CuS(s)+ O2(g)⇌ Cu(s)+ SO2(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 2.9 M O2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of O2 if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 1.5.
A) 1.9 M
B) 1.7 M
C) 2.2 M
D) 1.2 M
E) 0.59 M
A reaction mixture initially contains 2.9 M O2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of O2 if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 1.5.
A) 1.9 M
B) 1.7 M
C) 2.2 M
D) 1.2 M
E) 0.59 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The following reaction is exothermic.Which change will shift the equilibrium to the left?
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)
A) raising the temperature
B) adding SO3
C) removing O2
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)
A) raising the temperature
B) adding SO3
C) removing O2
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the following reaction: COCl2(g)⇌ CO(g)+ Cl2(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 1.6 M COCl2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of CO if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 8.33 × 10-4.Calculate this based on the assumption that the answer is negligible compared to 1.6.
A) 4.2 × 10-4 M
B) 1.5 × 10-3 M
C) 3.7 × 10-2 M
D) 2.1 × 10-2 M
E) 1.3 × 10-3 M
A reaction mixture initially contains 1.6 M COCl2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of CO if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 8.33 × 10-4.Calculate this based on the assumption that the answer is negligible compared to 1.6.
A) 4.2 × 10-4 M
B) 1.5 × 10-3 M
C) 3.7 × 10-2 M
D) 2.1 × 10-2 M
E) 1.3 × 10-3 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will adding more H2S have on the system?
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left.
B) No change will be observed.
C) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left.
B) No change will be observed.
C) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consider the following reaction: CO2(g)+ C(graphite)⇌ 2 CO(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.56 atm CO2 and 0.32 atm CO.Determine the equilibrium pressure of CO if Kp for the reaction at this temperature is 2.25.
A) 0.83 atm
B) 0.31 atm
C) 0.26 atm
D) 0.58 atm
E) 0.42 atm
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.56 atm CO2 and 0.32 atm CO.Determine the equilibrium pressure of CO if Kp for the reaction at this temperature is 2.25.
A) 0.83 atm
B) 0.31 atm
C) 0.26 atm
D) 0.58 atm
E) 0.42 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the following reaction,equilibrium concentrations,and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature.Determine the equilibrium pressure of H2. D2(g)+ H2(g)⇌ 2 HD(g)Kp = 1.80
P(D2)eq = 1.1 × 10-3 atm P(HD)eq = 2.7 × 10-3 atm
A) 2.7 atm
B) 1.4 atm
C) 0.73 atm
D) 3.7 × 10-3 atm
E) 8.1 × 10-4 atm
P(D2)eq = 1.1 × 10-3 atm P(HD)eq = 2.7 × 10-3 atm
A) 2.7 atm
B) 1.4 atm
C) 0.73 atm
D) 3.7 × 10-3 atm
E) 8.1 × 10-4 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider the following reaction: NO(g)+ SO3(g)⇌ NO2(g)+ SO2(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.86 atm NO and 0.86 atm SO3.Determine the equilibrium pressure of NO2 if Kp for the reaction at this temperature is 0.0118.
A) 0.78 atm
B) 0.084 atm
C) 0.012 atm
D) 0.85 atm
E) 0.048 atm
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.86 atm NO and 0.86 atm SO3.Determine the equilibrium pressure of NO2 if Kp for the reaction at this temperature is 0.0118.
A) 0.78 atm
B) 0.084 atm
C) 0.012 atm
D) 0.85 atm
E) 0.048 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the following reaction,equilibrium concentrations,and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature.Determine the equilibrium concentration of SO3(g). 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)Kc = 1.7 × 108
[SO2]eq = 0.0034 M [O2]eq = 0.0018 M
A) 1.9 M
B) 1.0 × 103 M
C) 0.53 M
D) 9.6 × 10-4 M
E) 0.73 M
[SO2]eq = 0.0034 M [O2]eq = 0.0018 M
A) 1.9 M
B) 1.0 × 103 M
C) 0.53 M
D) 9.6 × 10-4 M
E) 0.73 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will adding more SO3 have on the system?
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)⇌ SO3(g)+ NO(g)
A) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to decrease the pressure.
C) No change will occur since SO3 is not included in the equilibrium expression.
D) The reaction will shift in the direction of reactants.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)⇌ SO3(g)+ NO(g)
A) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to decrease the pressure.
C) No change will occur since SO3 is not included in the equilibrium expression.
D) The reaction will shift in the direction of reactants.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The following reaction is exothermic.Which change will shift the equilibrium to the left?
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)
A) raising the temperature
B) decrease pressure
C) increase volume
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)
A) raising the temperature
B) decrease pressure
C) increase volume
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The following reaction is endothermic.What effect will decreasing the temperature have on the system?
I2(g)+ Cl2(g)⇌ 2 ICl(g)
A) The equilibrium constant will change and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction
B) The equilibrium constant will change and the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction
C) The equilibrium constant will remain constant and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction
D) The equilibrium constant will remain constant and the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction
I2(g)+ Cl2(g)⇌ 2 ICl(g)
A) The equilibrium constant will change and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction
B) The equilibrium constant will change and the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction
C) The equilibrium constant will remain constant and the reaction will proceed in the forward direction
D) The equilibrium constant will remain constant and the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following reaction,equilibrium concentrations,and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature.Determine the equilibrium concentration of SO3(g). 2 SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 SO3(g)Kc = 1.7 × 108
[SO3]eq = 0.0034 M [O2]eq = 0.0018 M
A) 2.8 × 1013 M
B) 1.88 M
C) 6.1 × 10-6 M
D) 1.0 × 103 M
E) 1.4 M
[SO3]eq = 0.0034 M [O2]eq = 0.0018 M
A) 2.8 × 1013 M
B) 1.88 M
C) 6.1 × 10-6 M
D) 1.0 × 103 M
E) 1.4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will removing NO2 have on the system?
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)⇌ SO3(g)+ NO(g)
A) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to decrease the pressure.
C) No change will occur since SO3 is not included in the equilibrium expression.
D) The reaction will shift in the direction of reactants.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
SO2(g)+ NO2(g)⇌ SO3(g)+ NO(g)
A) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to decrease the pressure.
C) No change will occur since SO3 is not included in the equilibrium expression.
D) The reaction will shift in the direction of reactants.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will removing H2O have on the system?
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left.
B) No change will be observed.
C) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left.
B) No change will be observed.
C) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift in the direction of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Determine the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [C3H8]= 0.15 M,[O2] = 0.35 M,[CO2] = 1.3 M,[H2O] = 2.8 M C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A) 1.7 × 105
B) 3.2 × 10-6
C) 6.7 × 103
D) 7.4 × 102
E) 6.1.9 × 10-4
A) 1.7 × 105
B) 3.2 × 10-6
C) 6.7 × 103
D) 7.4 × 102
E) 6.1.9 × 10-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will adding some C have on the system?
CO2(g)+ C(graphite)⇌ 2 CO(g)
A) No effect will be observed since C is not included in the equilibrium expression.
B) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
CO2(g)+ C(graphite)⇌ 2 CO(g)
A) No effect will be observed since C is not included in the equilibrium expression.
B) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will increasing the pressure of the reaction mixture have on the system?
CuS(s)+ O2(g)⇌ Cu(s)+ SO2(g)
A) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
CuS(s)+ O2(g)⇌ Cu(s)+ SO2(g)
A) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will reducing the volume have on the system?
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2220 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) No effect will be observed.
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2220 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) No effect will be observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Consider the following reaction,equilibrium concentrations,and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature.Determine the equilibrium concentration of H2O(g). 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)Kc = 5.50 × 102
[H2] = 0.480 M [O2] = 0.310 M
A) 4.23 × 10-3 M
B) 0.426 M
C) 6.27 M
D) 39.3 M
E) 5.52 × 106 M
[H2] = 0.480 M [O2] = 0.310 M
A) 4.23 × 10-3 M
B) 0.426 M
C) 6.27 M
D) 39.3 M
E) 5.52 × 106 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The following reaction is allowed to come to equilibrium with a measured partial pressure of 0.68 atm for O2,0.72 atm for N2,and 2.83 atm for NO.What is Kp for the reaction at this temperature?
N2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 NO(g)
A) 32.7
B) 16.4
C) 5.78
D) 2.29
E) 0.0611
N2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2 NO(g)
A) 32.7
B) 16.4
C) 5.78
D) 2.29
E) 0.0611

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will reducing the volume of the reaction mixture have on the system?
CuS(s)+ O2(g)⇌ Cu(s)+ SO2(g)
A) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
CuS(s)+ O2(g)⇌ Cu(s)+ SO2(g)
A) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
For the following reaction: I2(g)+ Br2(g)⇌ 2 IBr(g)
A vessel initially contains 2.50 M I2 and 2.50 M Br2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of IBr if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 3.27.
A) 1.19 M
B) 1.84 M
C) 2.18 M
D) 0.854 M
E) 0.642 M
A vessel initially contains 2.50 M I2 and 2.50 M Br2.Determine the equilibrium concentration of IBr if Kc for the reaction at this temperature is 3.27.
A) 1.19 M
B) 1.84 M
C) 2.18 M
D) 0.854 M
E) 0.642 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will decreasing the temperature have on the system?
CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)⇌ CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)ΔH° = +890 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
E) No effect will be observed.
CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(l)⇌ CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)ΔH° = +890 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
E) No effect will be observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will adding CO2 have on the system?
CO2(g)+ C(graphite)⇌ 2 CO(g)
A) No effect will be observed since CO2 is not included in the equilibrium expression.
B) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
CO2(g)+ C(graphite)⇌ 2 CO(g)
A) No effect will be observed since CO2 is not included in the equilibrium expression.
B) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will increase.
E) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. 2 N2(g)+ 6 H2(g)⇔ 4 NH3(g)
A) K =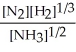
B) K =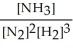
C) K =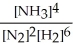
D) K =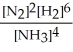
E) K =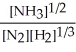
A) K =
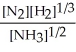
B) K =
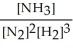
C) K =
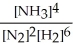
D) K =
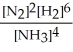
E) K =
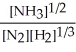

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
For the following reaction of N2O4,the equilibrium constant is 0.593 at a particular temperature. N2O4(g)⇌ 2 NO2(g)
If the initial concentration of N2O4 is 0.880M,what are the equilibrium concentrations?
A) [N2O4] = 0.705M, [NO2] = 0.350M
B) [N2O4] = 0.678M, [NO2] = 0.404M
C) [N2O4] = 0.332M, [NO2] = 1.094M
D) [N2O4] = 0.586M, [NO2] = 0.588M
E) [N2O4] = 0.000M, [NO2] = 1.760M
If the initial concentration of N2O4 is 0.880M,what are the equilibrium concentrations?
A) [N2O4] = 0.705M, [NO2] = 0.350M
B) [N2O4] = 0.678M, [NO2] = 0.404M
C) [N2O4] = 0.332M, [NO2] = 1.094M
D) [N2O4] = 0.586M, [NO2] = 0.588M
E) [N2O4] = 0.000M, [NO2] = 1.760M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will reducing the pressure have on the system?
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2220 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) No effect will be observed.
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2220 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) No effect will be observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will increasing the temperature have on the system?
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2220 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) No effect will be observed.
C3H8(g)+ 5 O2(g)⇌ 3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(l)ΔH° = -2220 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
C) The equilibrium constant will increase.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) No effect will be observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will increasing the temperature have on the system?
Fe3O4(s)+ CO(g)⇌ 3 FeO(s)+ CO2(g)ΔH°= +35.9 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will increase.
C) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
D) No effect will be observed.
E) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
Fe3O4(s)+ CO(g)⇌ 3 FeO(s)+ CO2(g)ΔH°= +35.9 kJ
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will increase.
C) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
D) No effect will be observed.
E) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will reducing the volume of the reaction mixture have on the system?
Xe(g)+ 2 F2(g)→ XeF4(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will increase.
C) No effect will be observed.
D) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
Xe(g)+ 2 F2(g)→ XeF4(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will increase.
C) No effect will be observed.
D) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will adding 1 mole of Ar to the reaction mixture have on the system?
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will increasing the pressure of the reaction mixture have on the system?
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.
2 H2S(g)+ 3 O2(g)⇌ 2 H2O(g)+ 2 SO2(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
B) No effect will be observed.
C) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
D) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Express the equilibrium constant for the following reaction. 3 CH3Cl(g)+ 3/2 Cl2(g)⇔ 3 CH2Cl2(g)+ 3/2 H2(g)
A) K =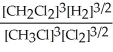
B) K =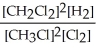
C) K =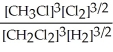
D) K =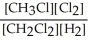
E) K =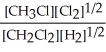
A) K =
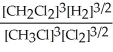
B) K =
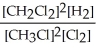
C) K =
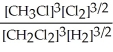
D) K =
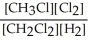
E) K =
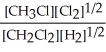

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium.What effect will reducing the pressure of the reaction mixture have on the system?
Xe(g)+ 2 F2(g)→ XeF4(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will increase.
C) No effect will be observed.
D) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.
Xe(g)+ 2 F2(g)→ XeF4(g)
A) The reaction will shift to the left in the direction of reactants.
B) The equilibrium constant will increase.
C) No effect will be observed.
D) The reaction will shift to the right in the direction of products.
E) The equilibrium constant will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



